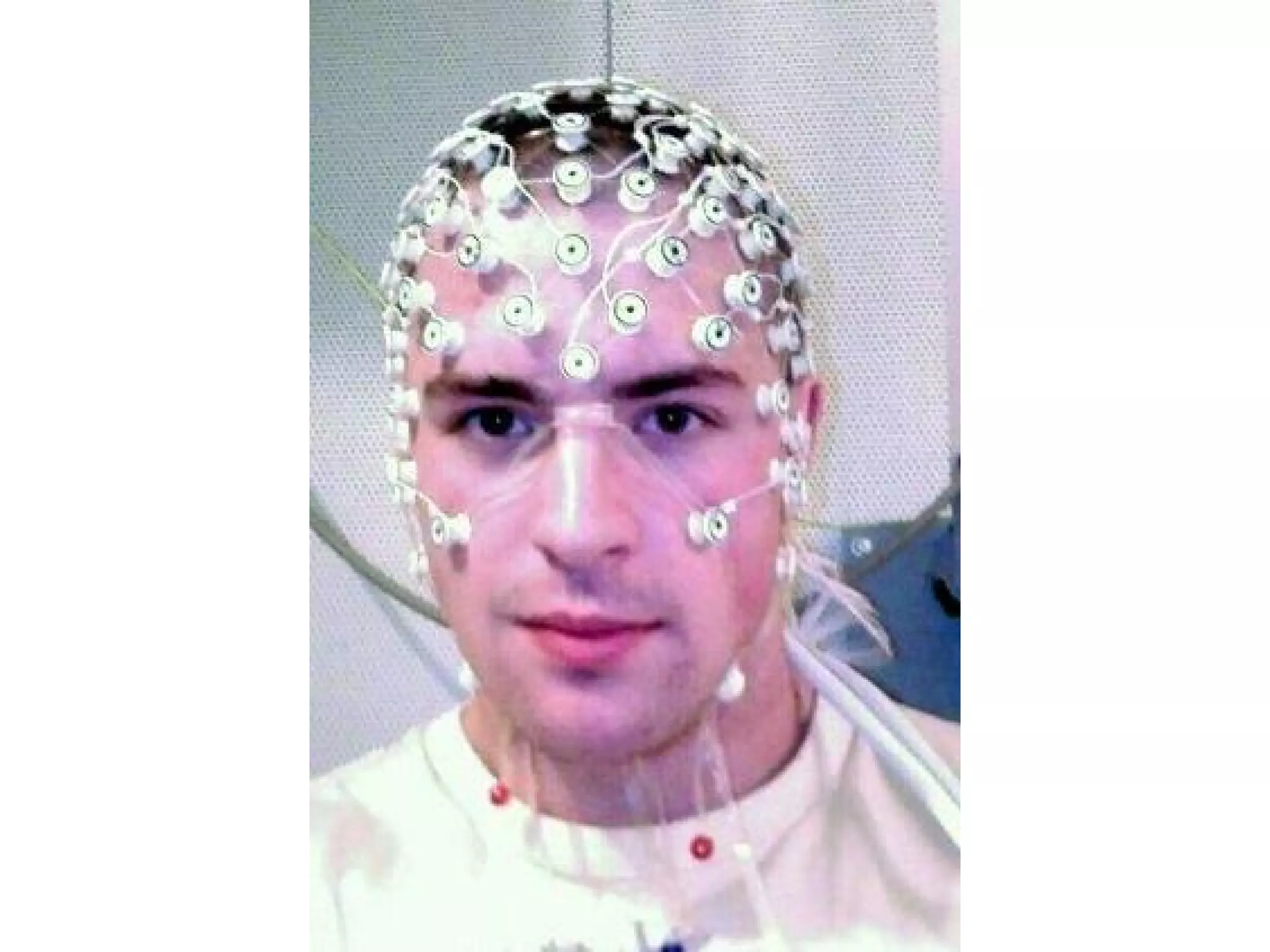
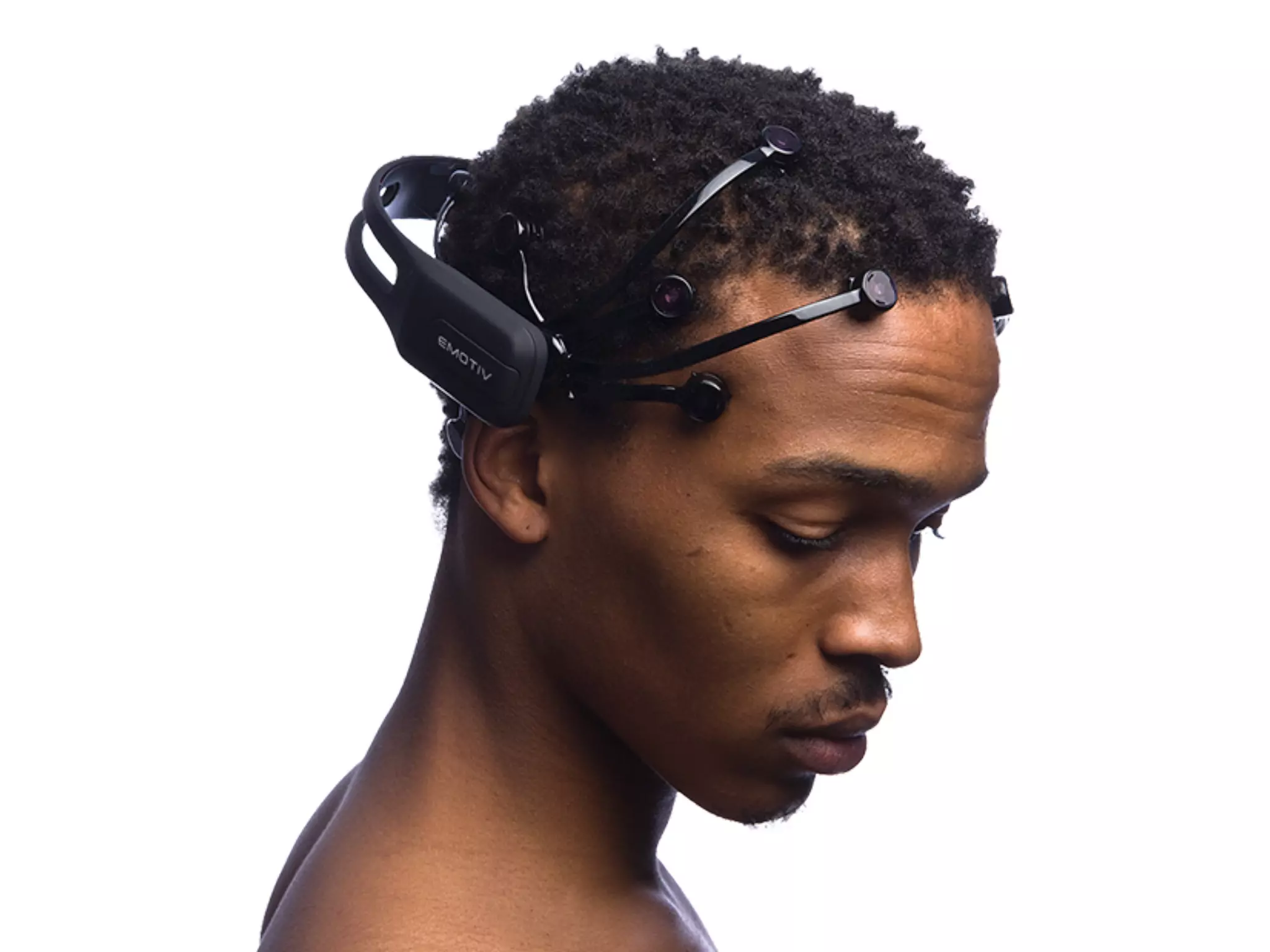
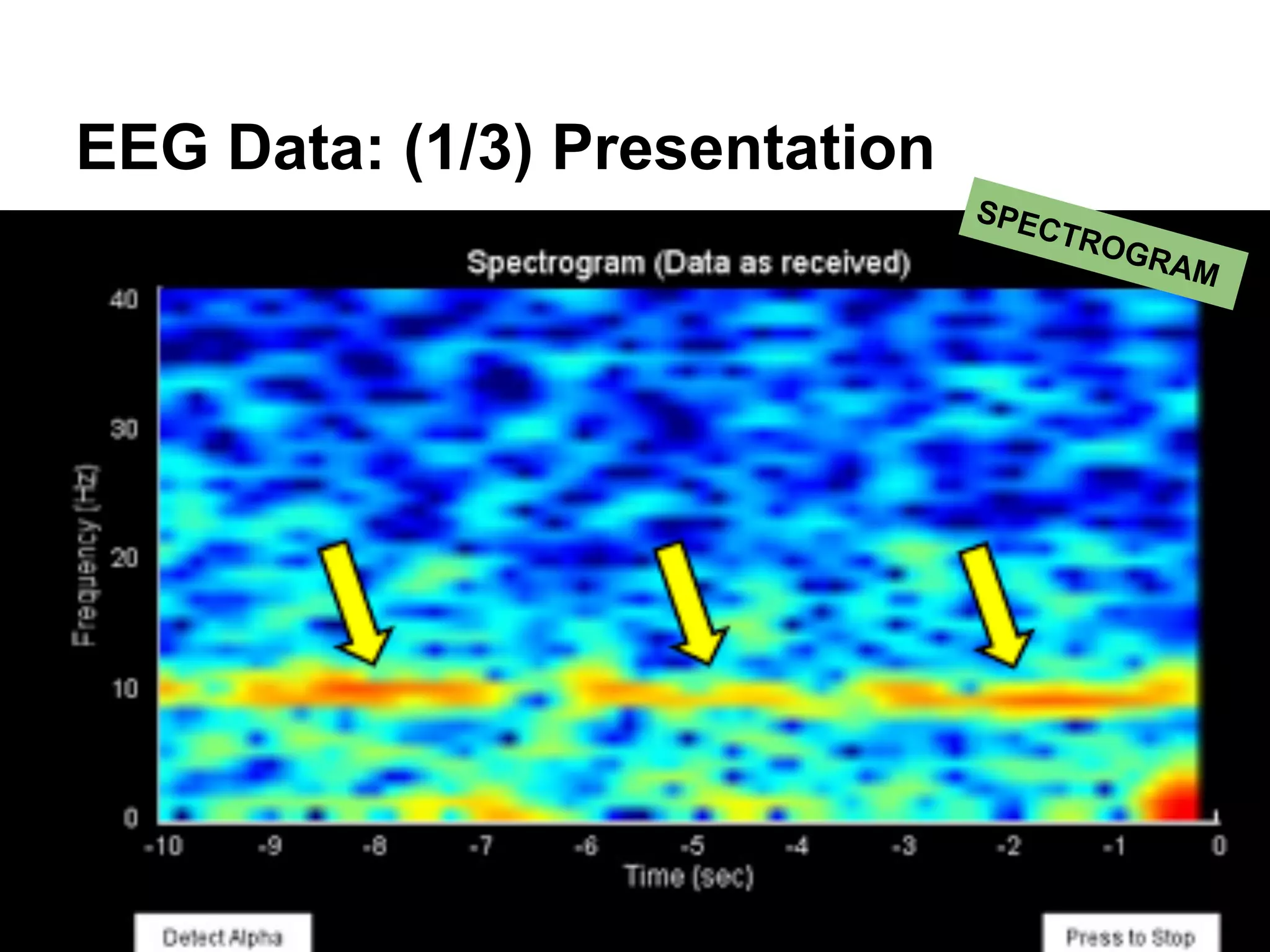
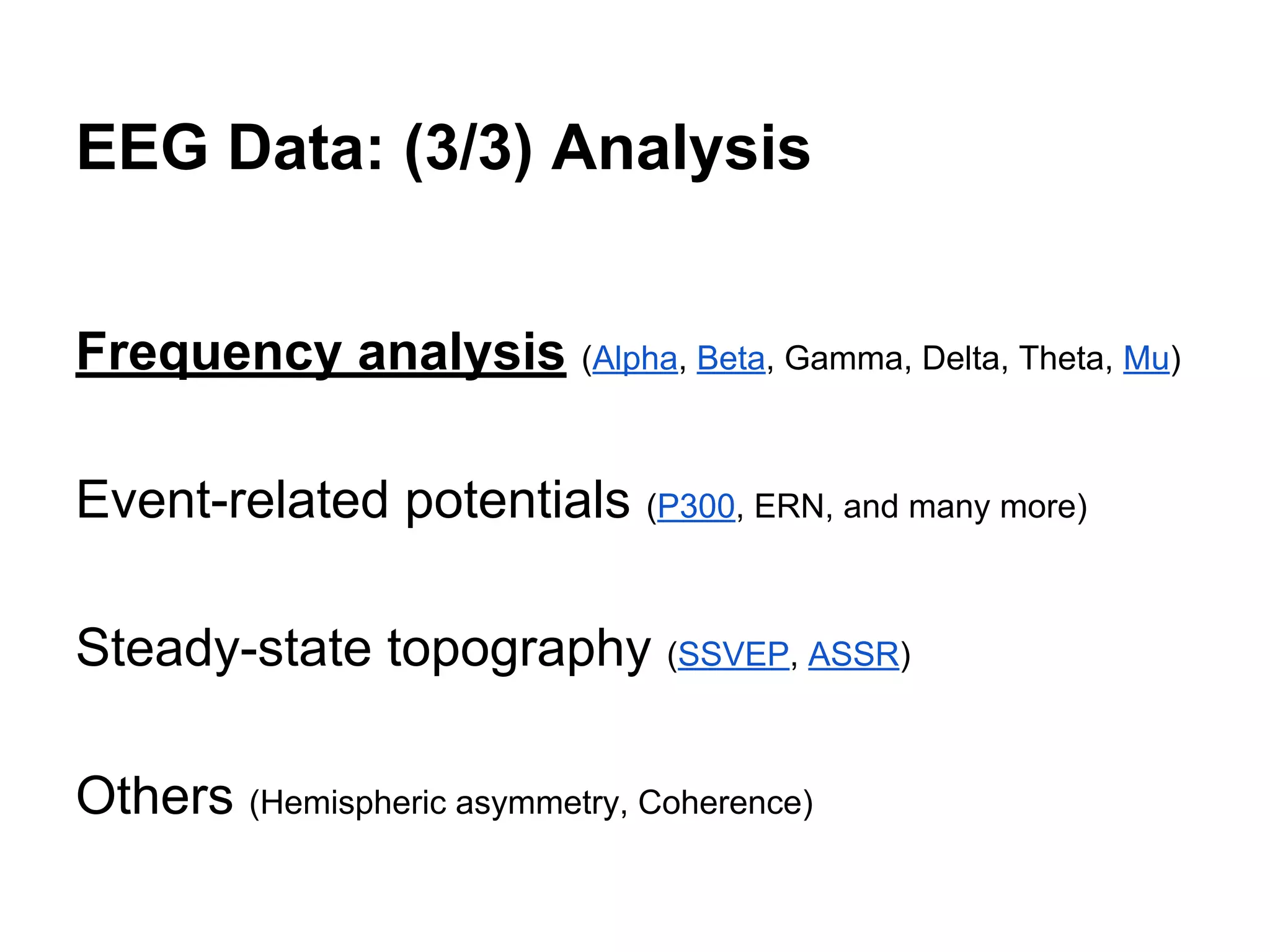
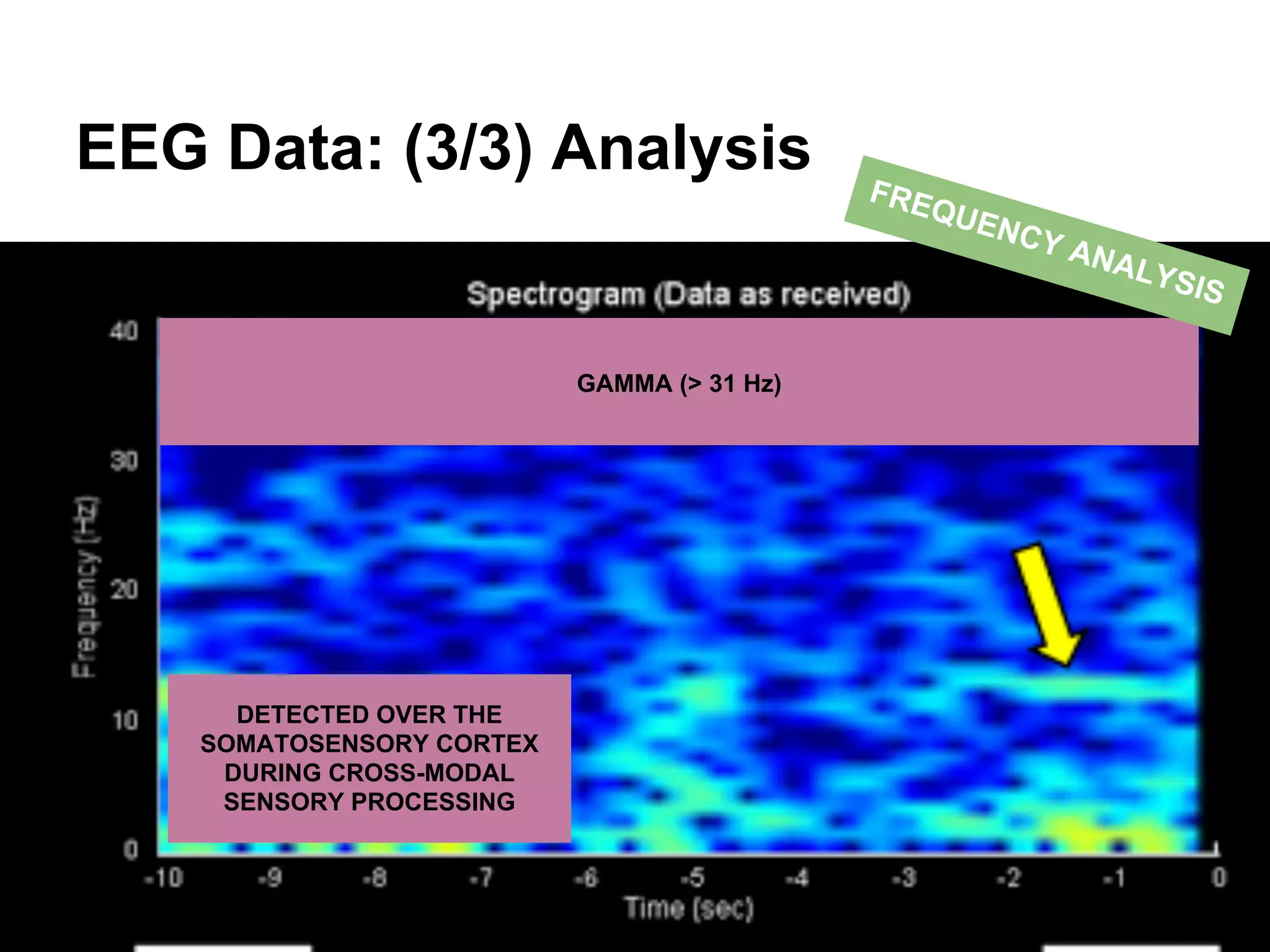
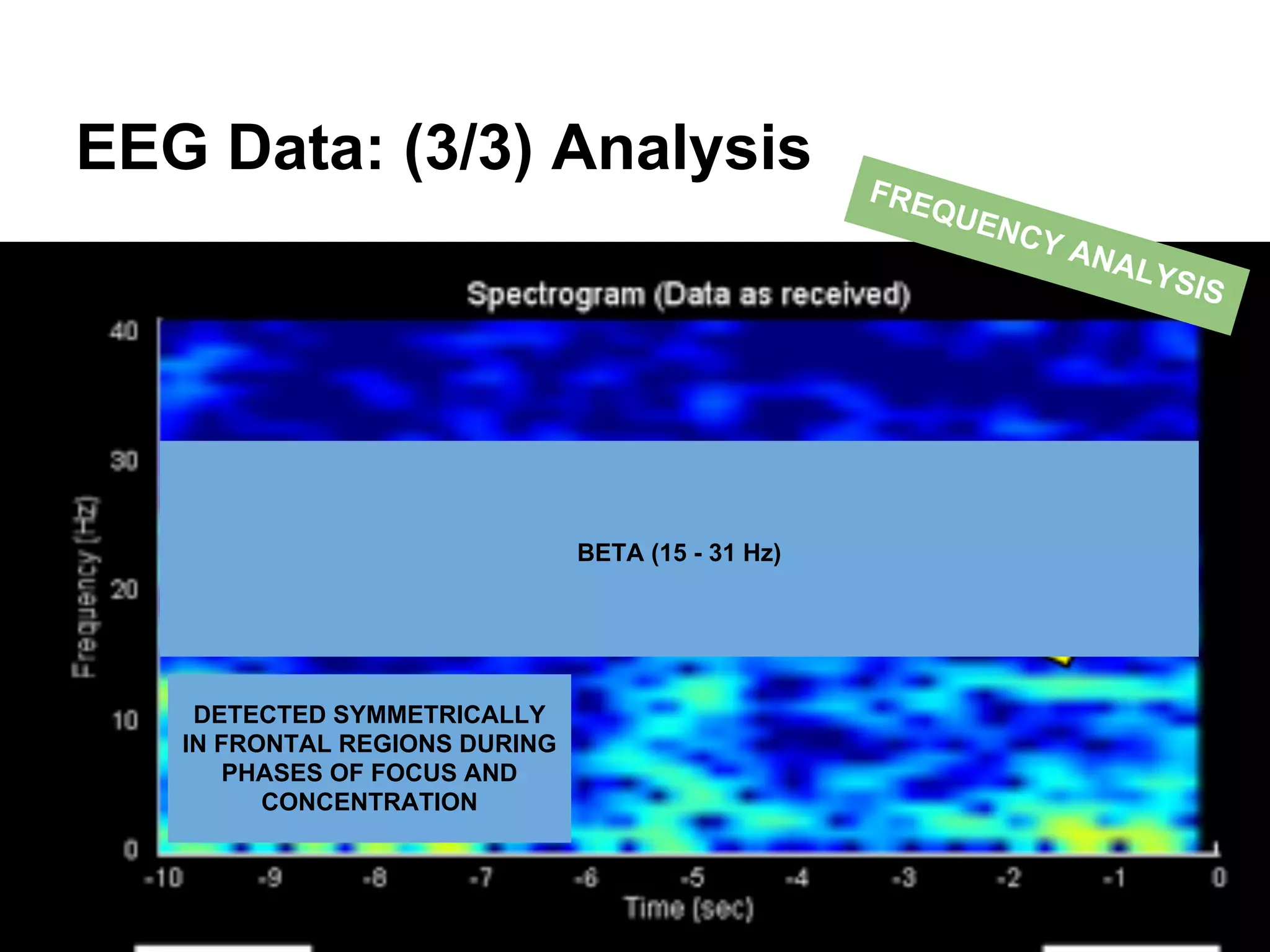
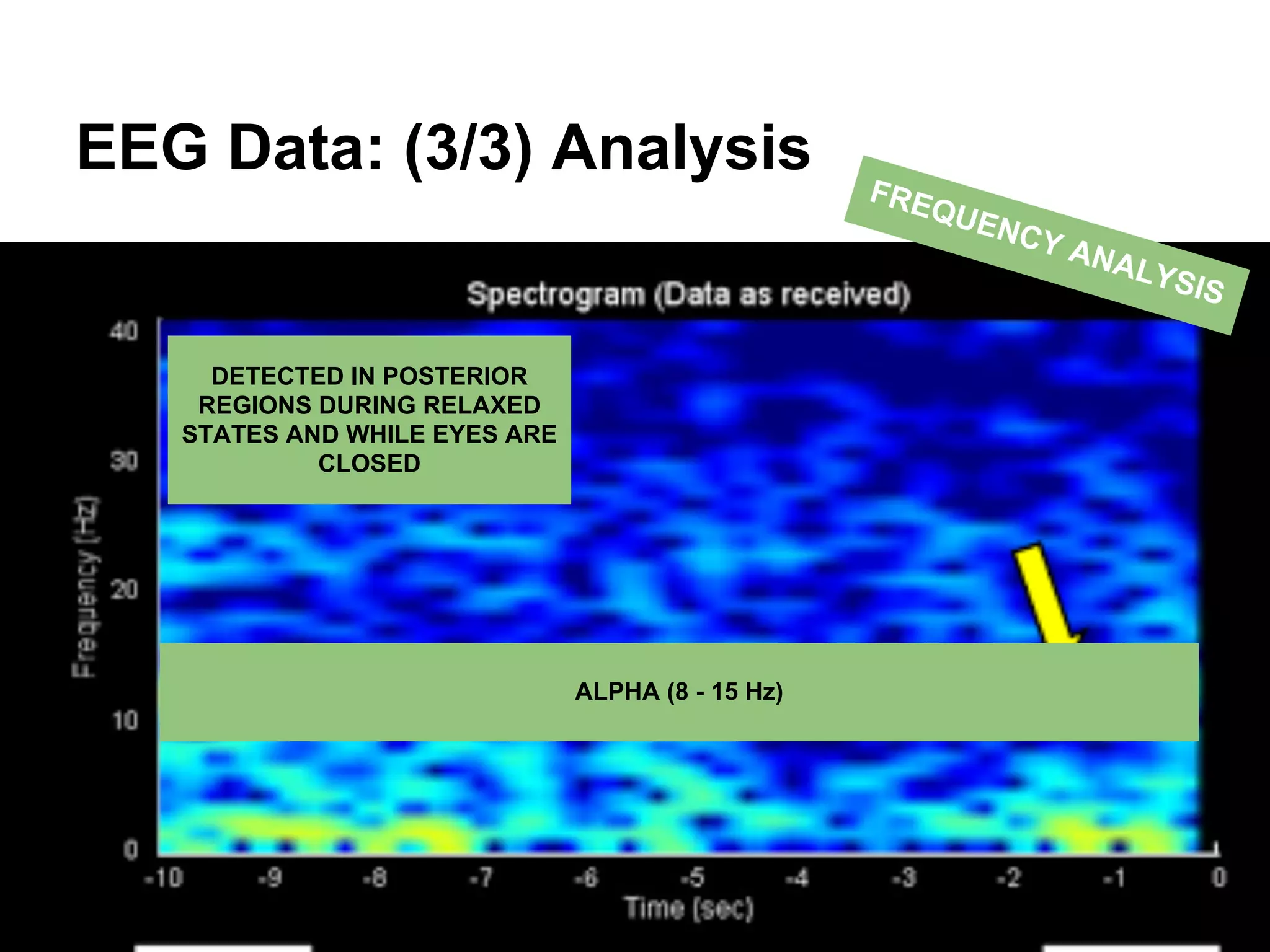
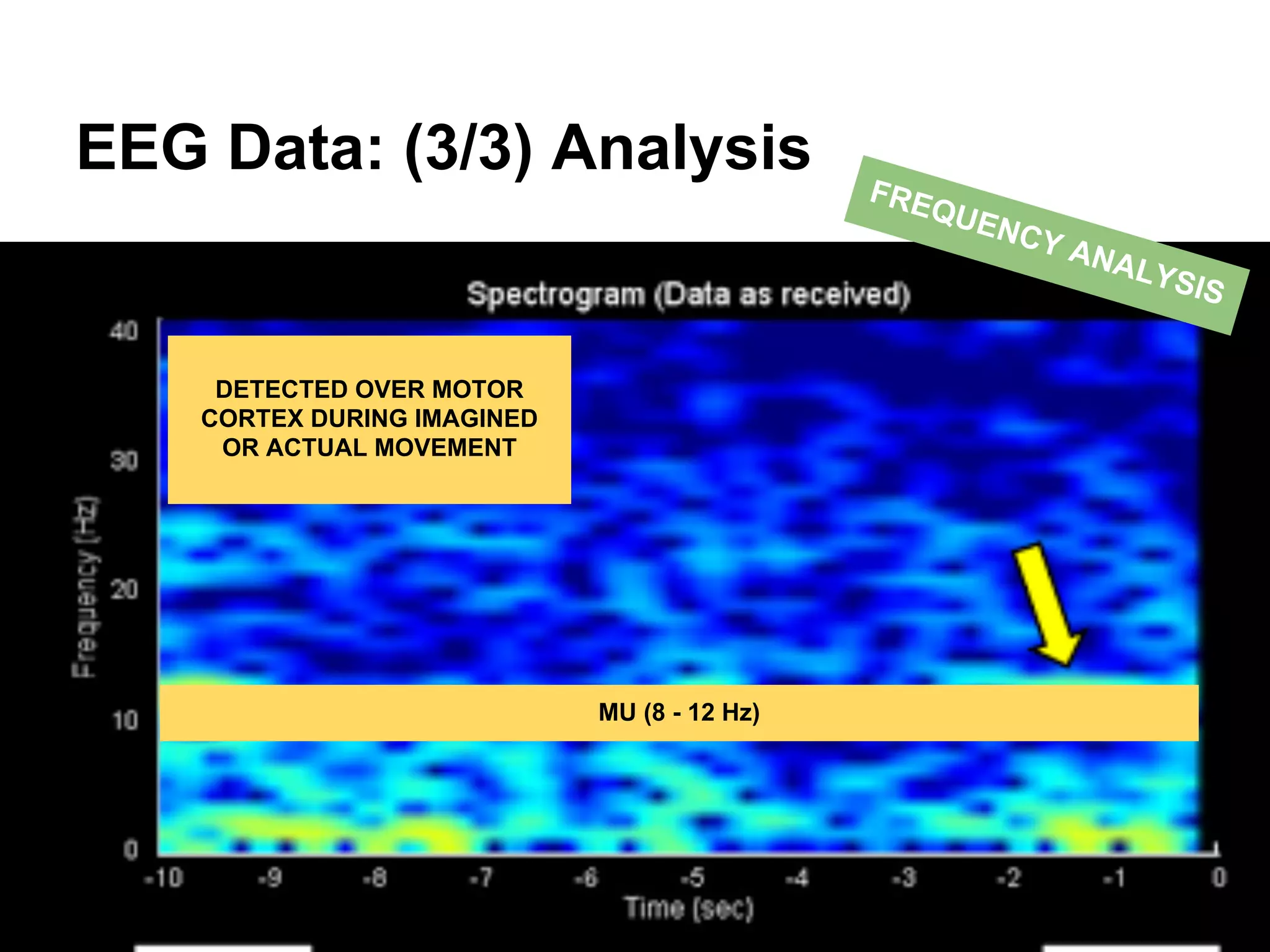
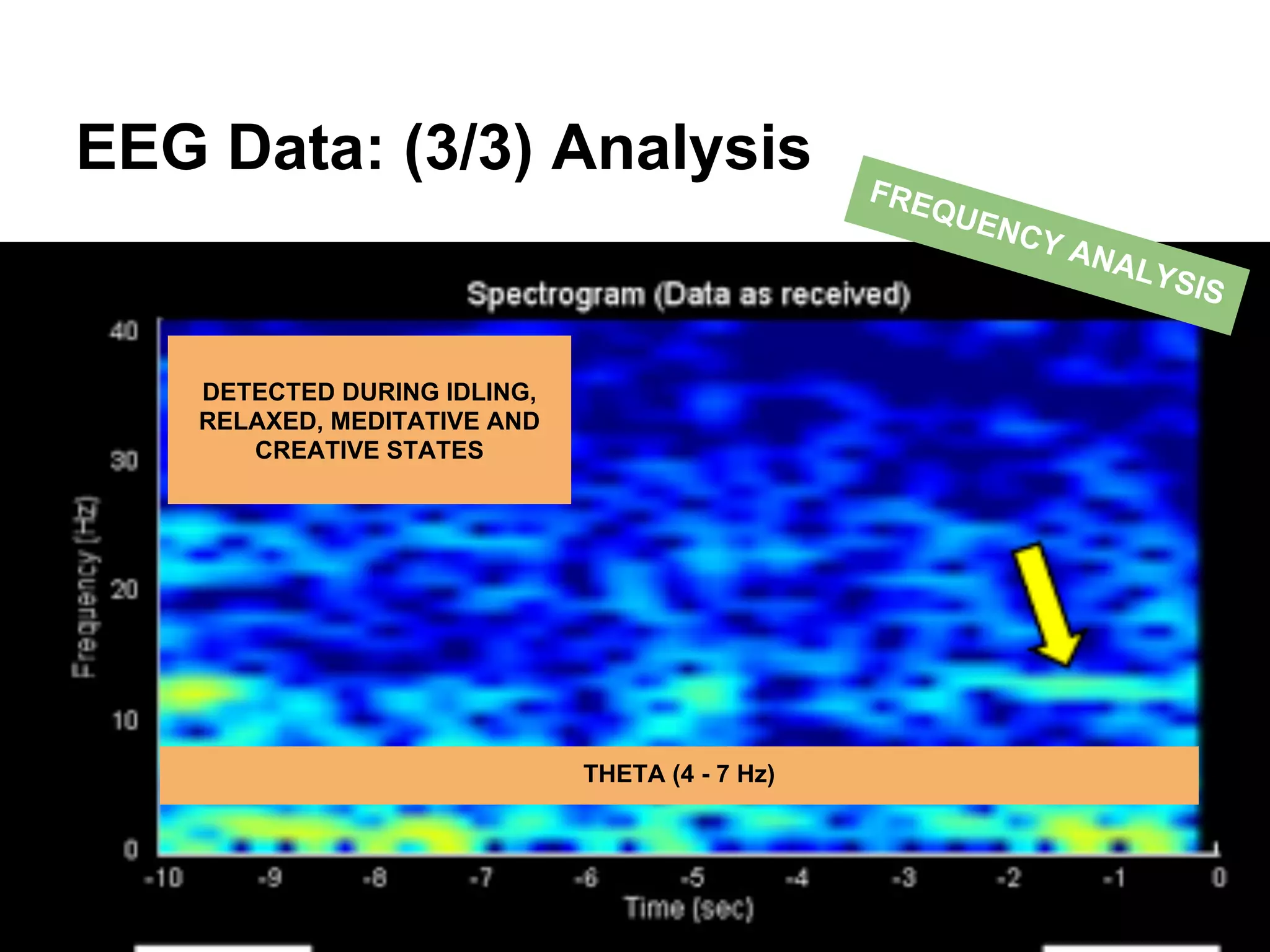
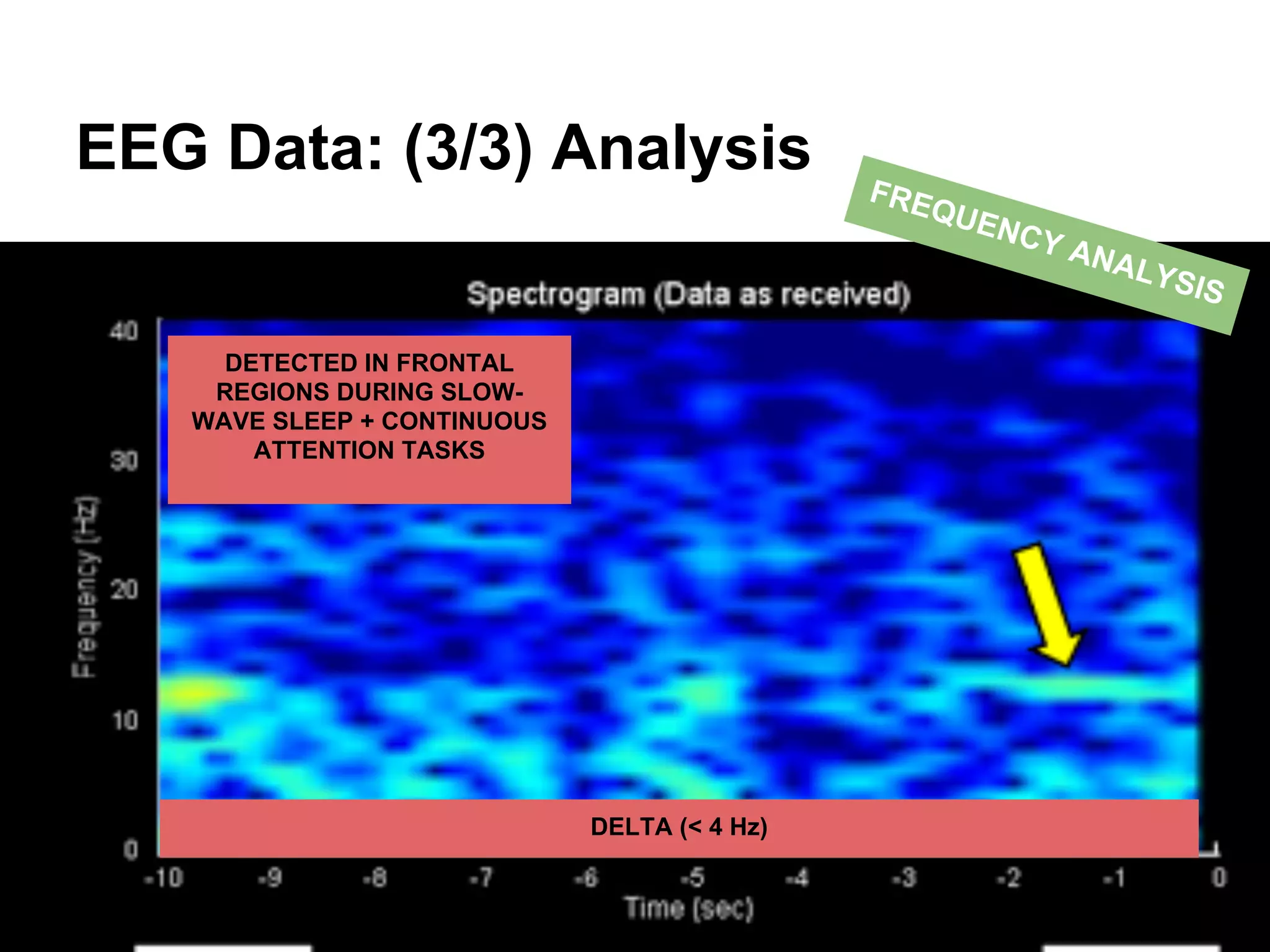
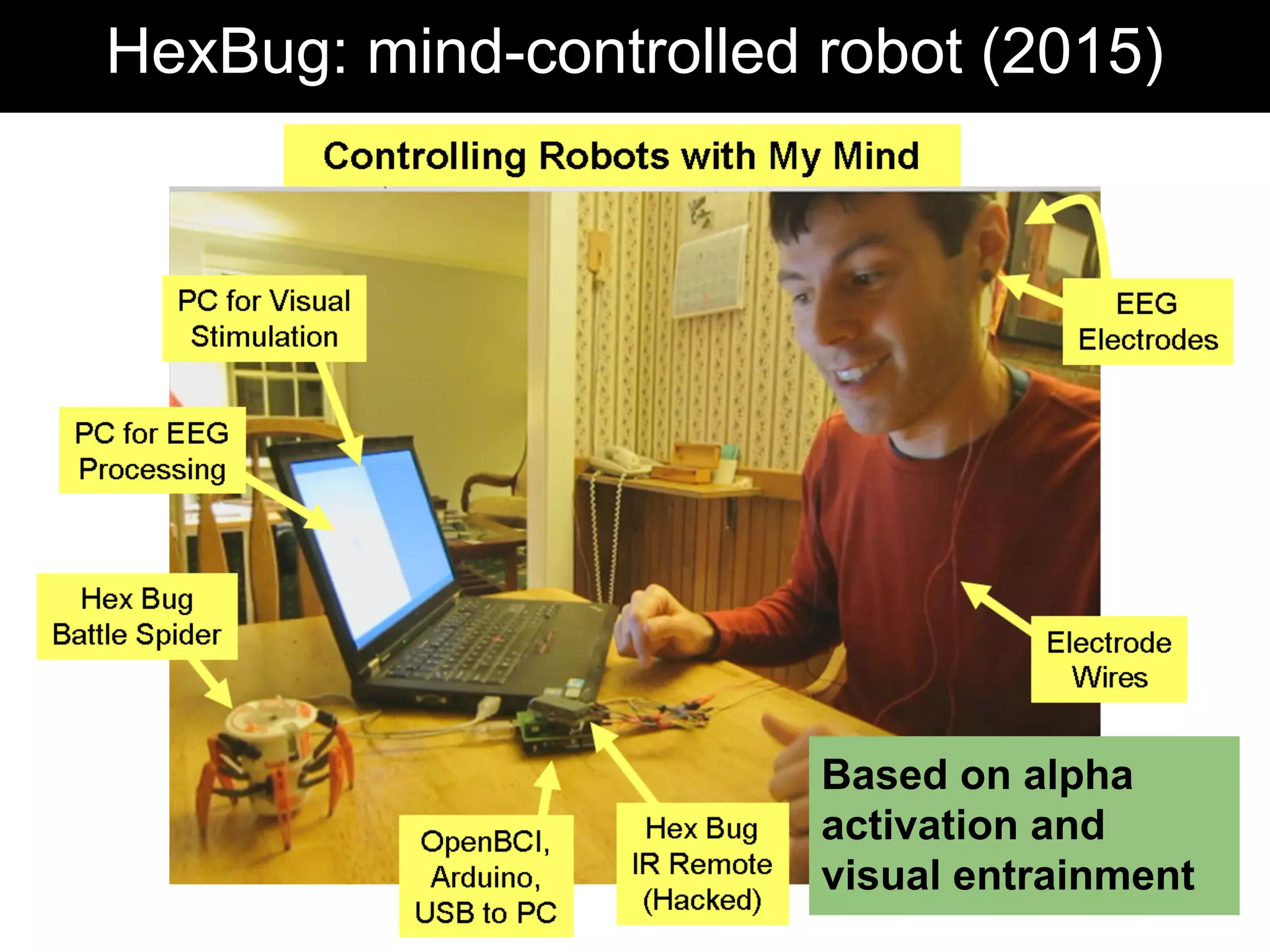
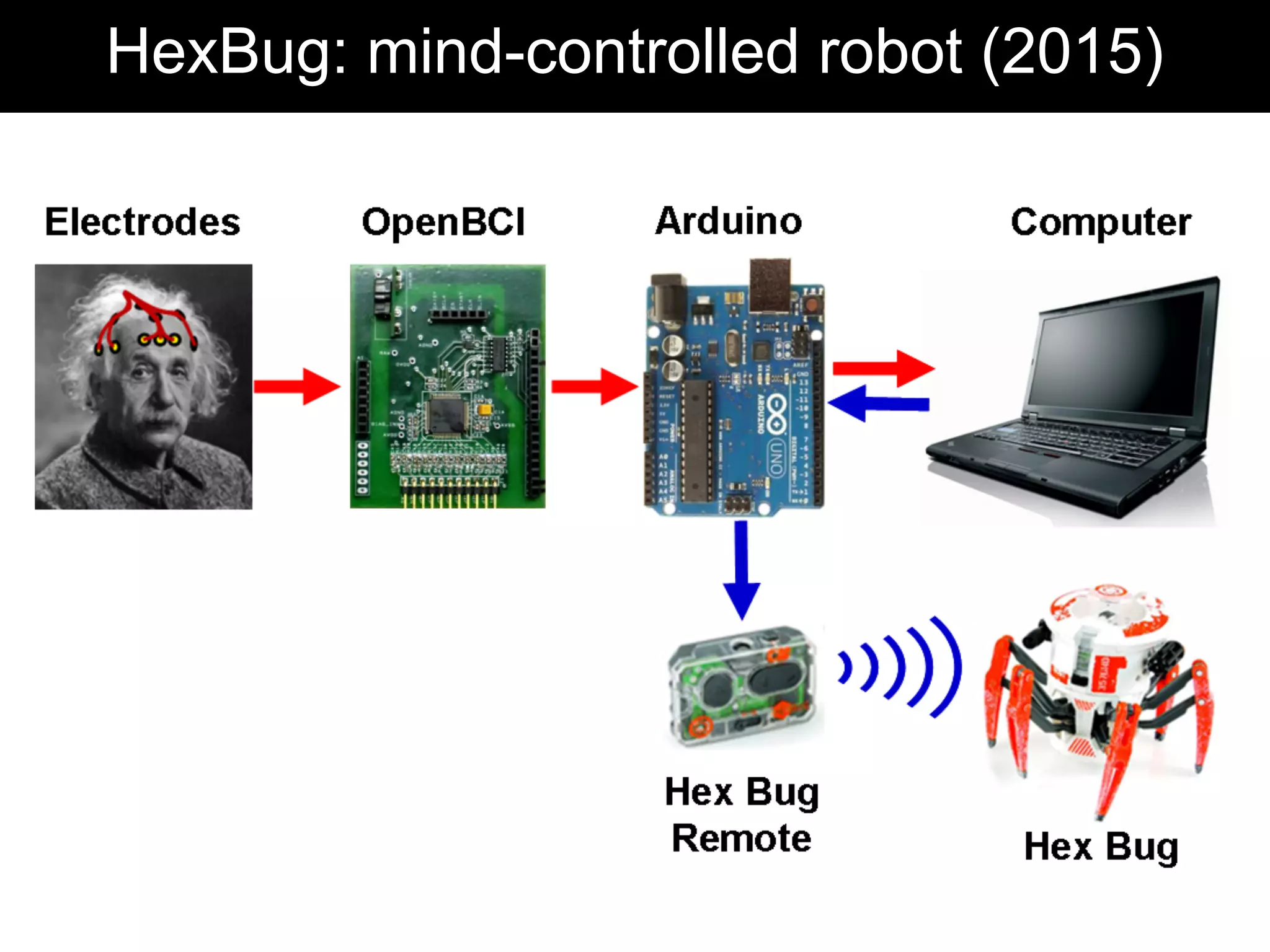
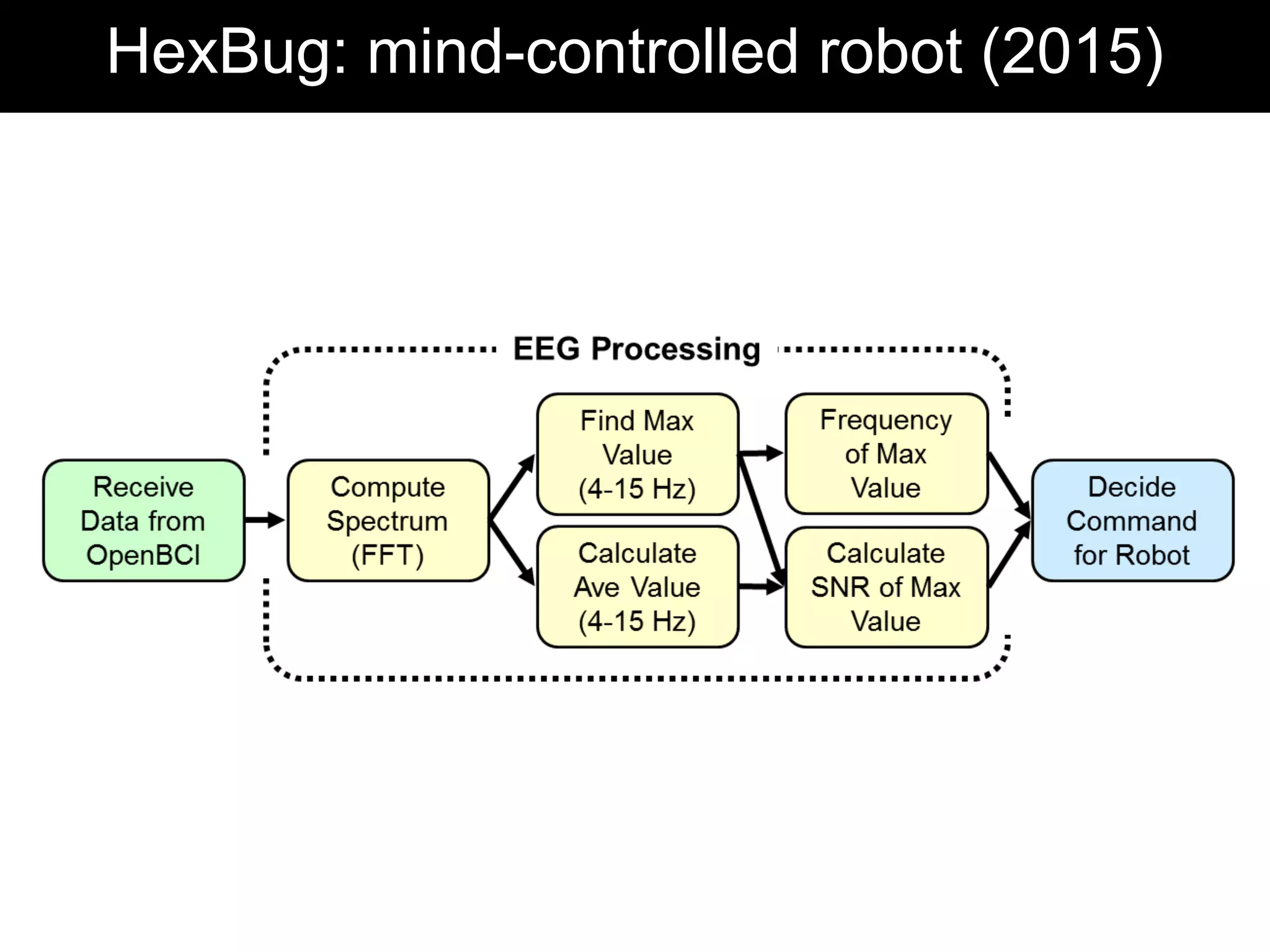
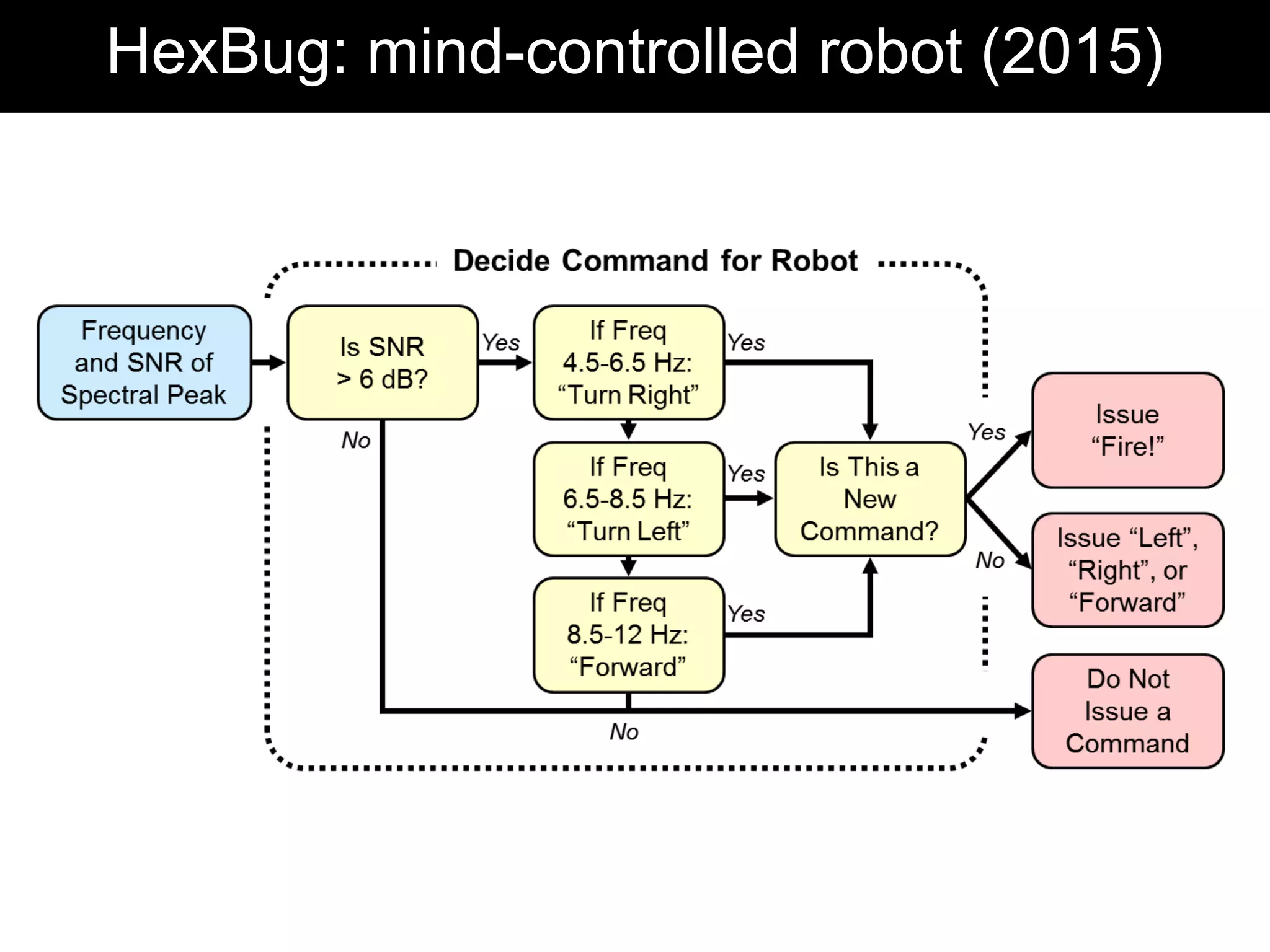
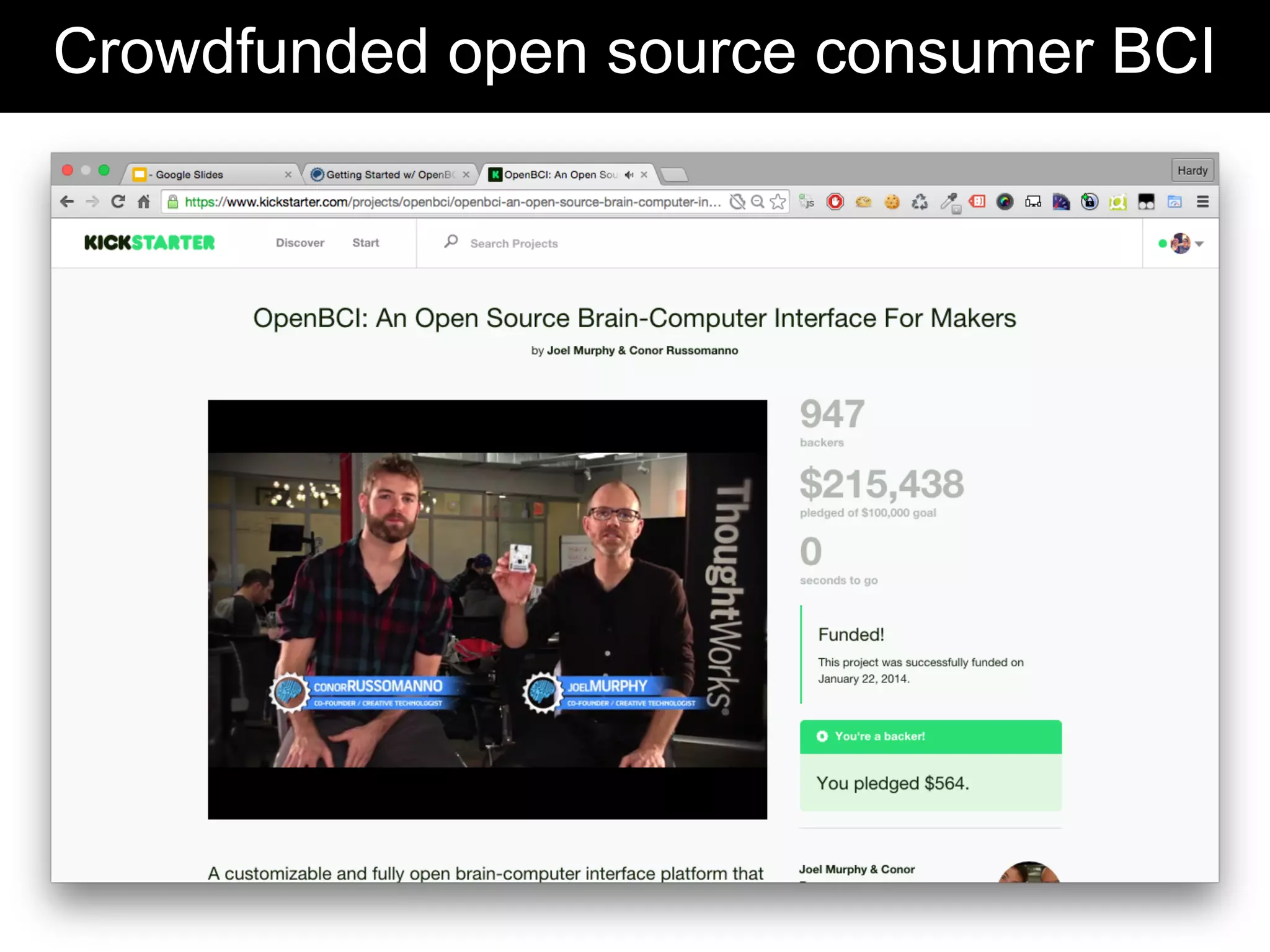
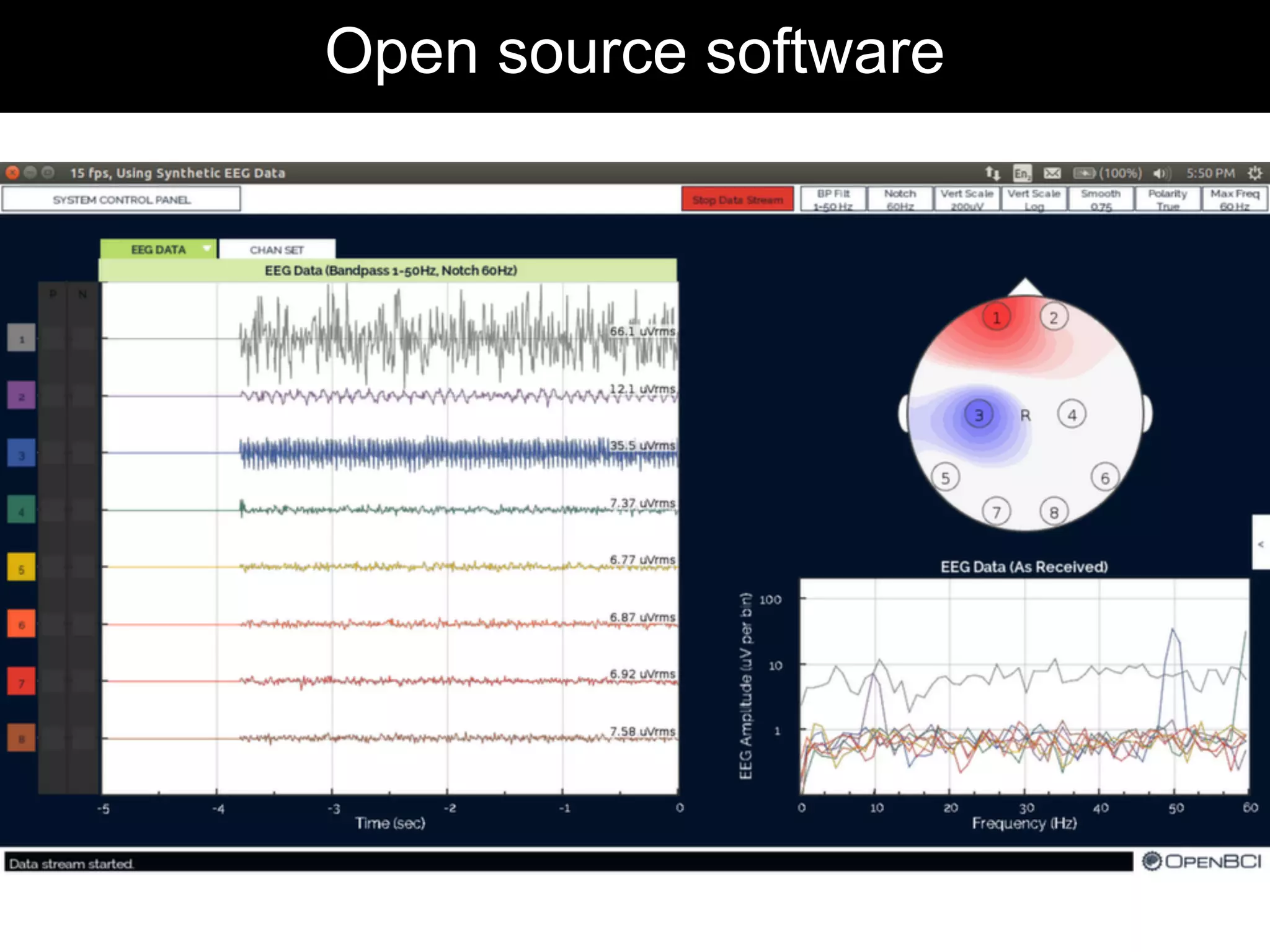
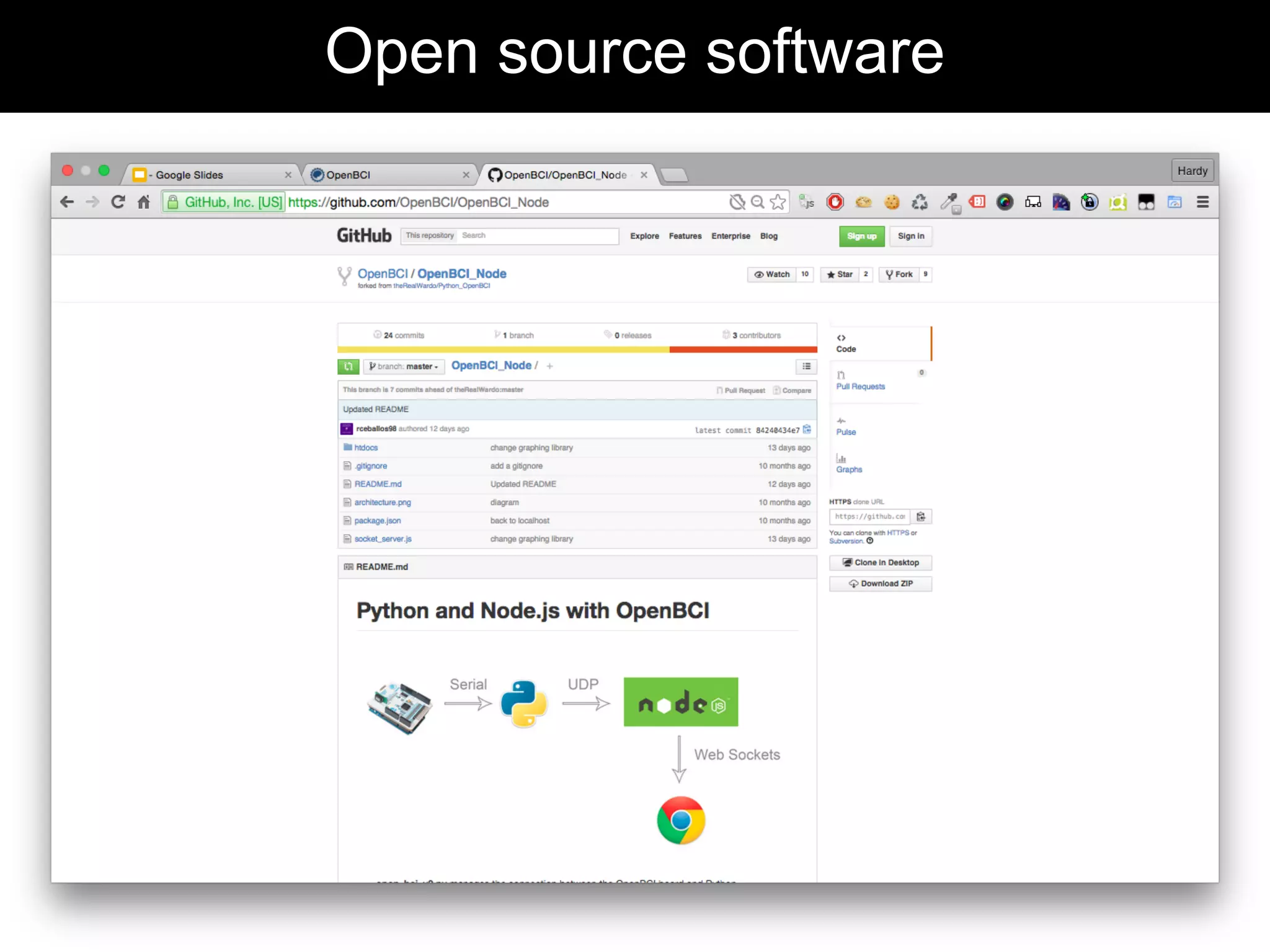
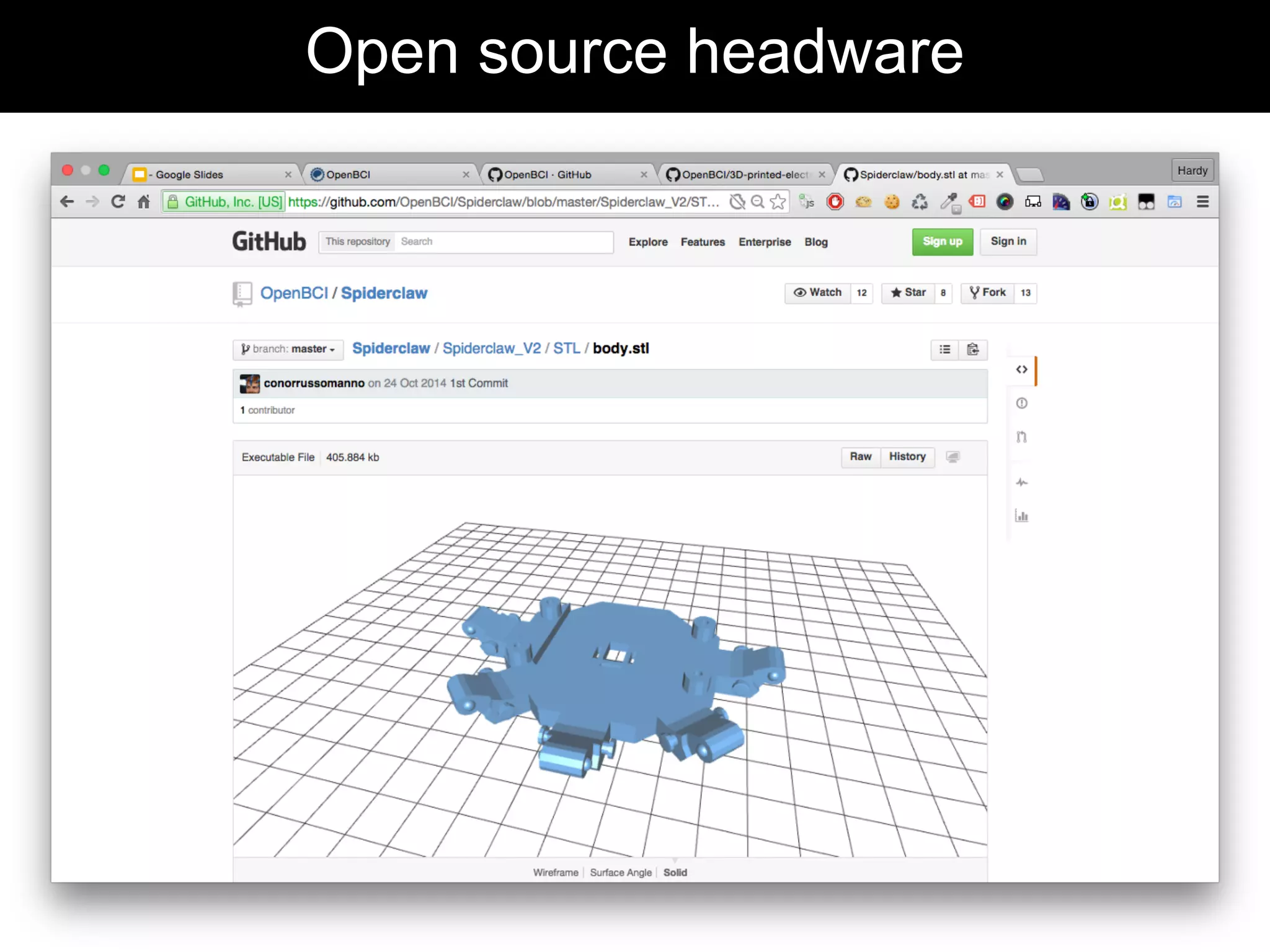
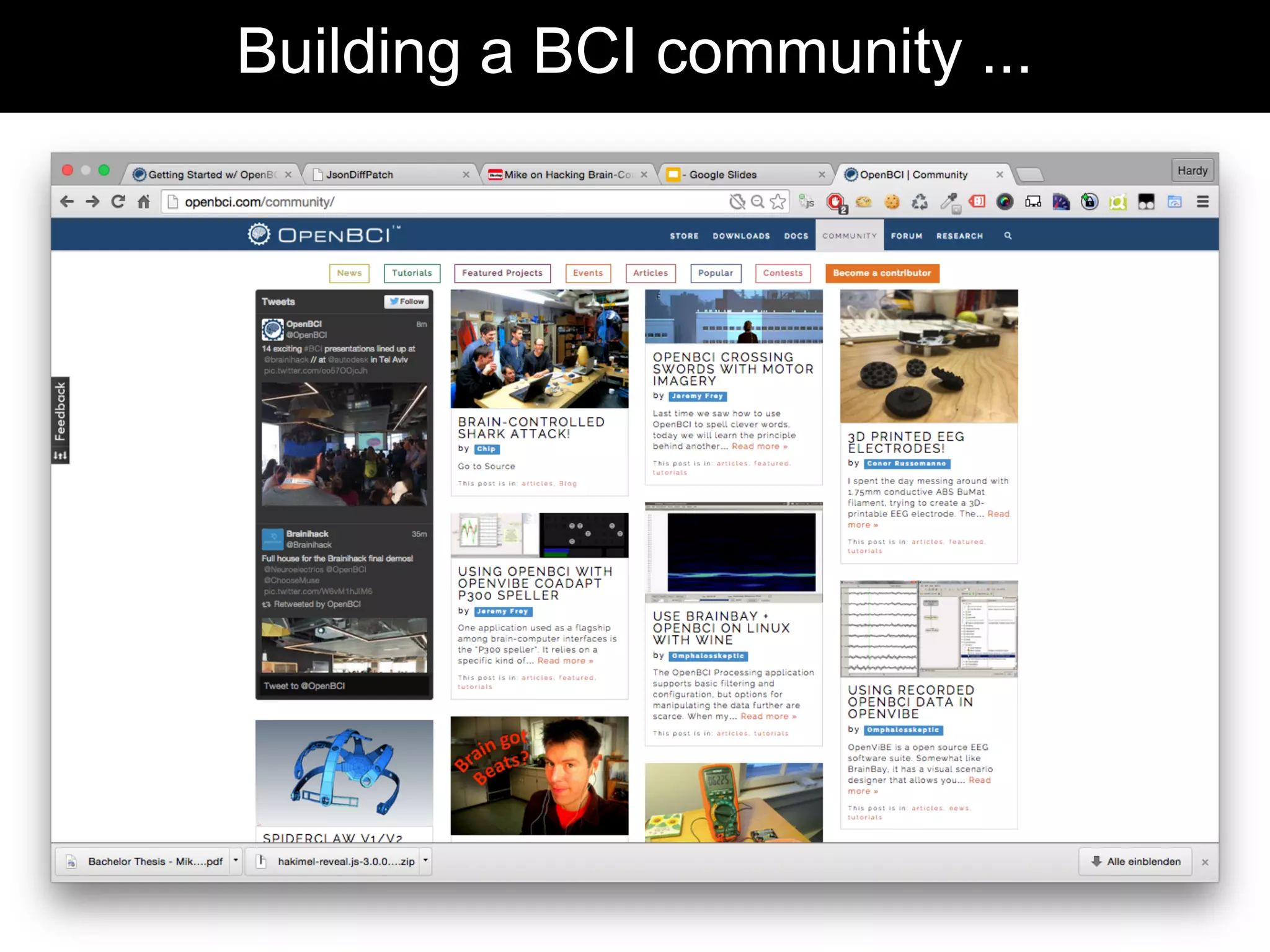
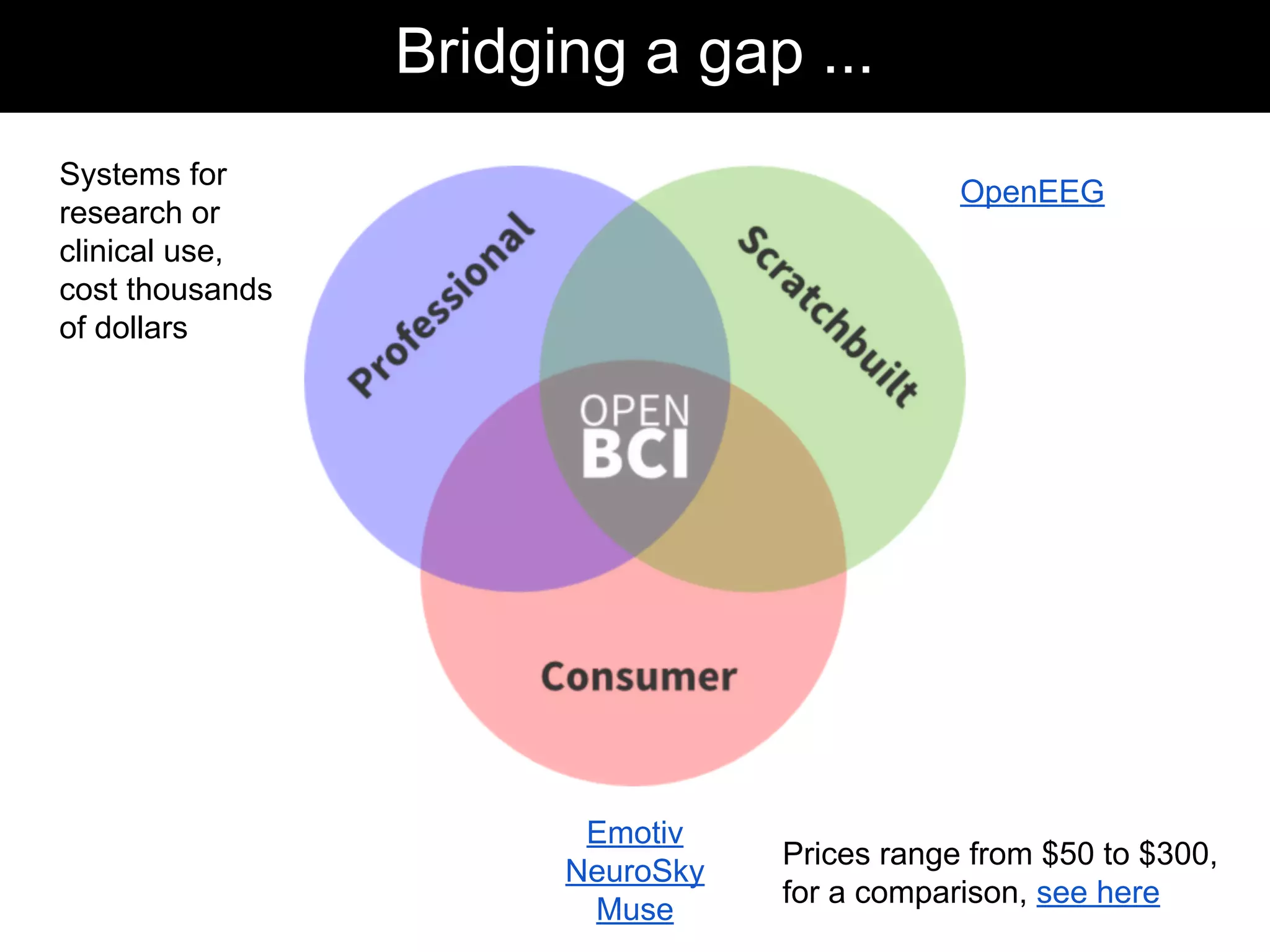
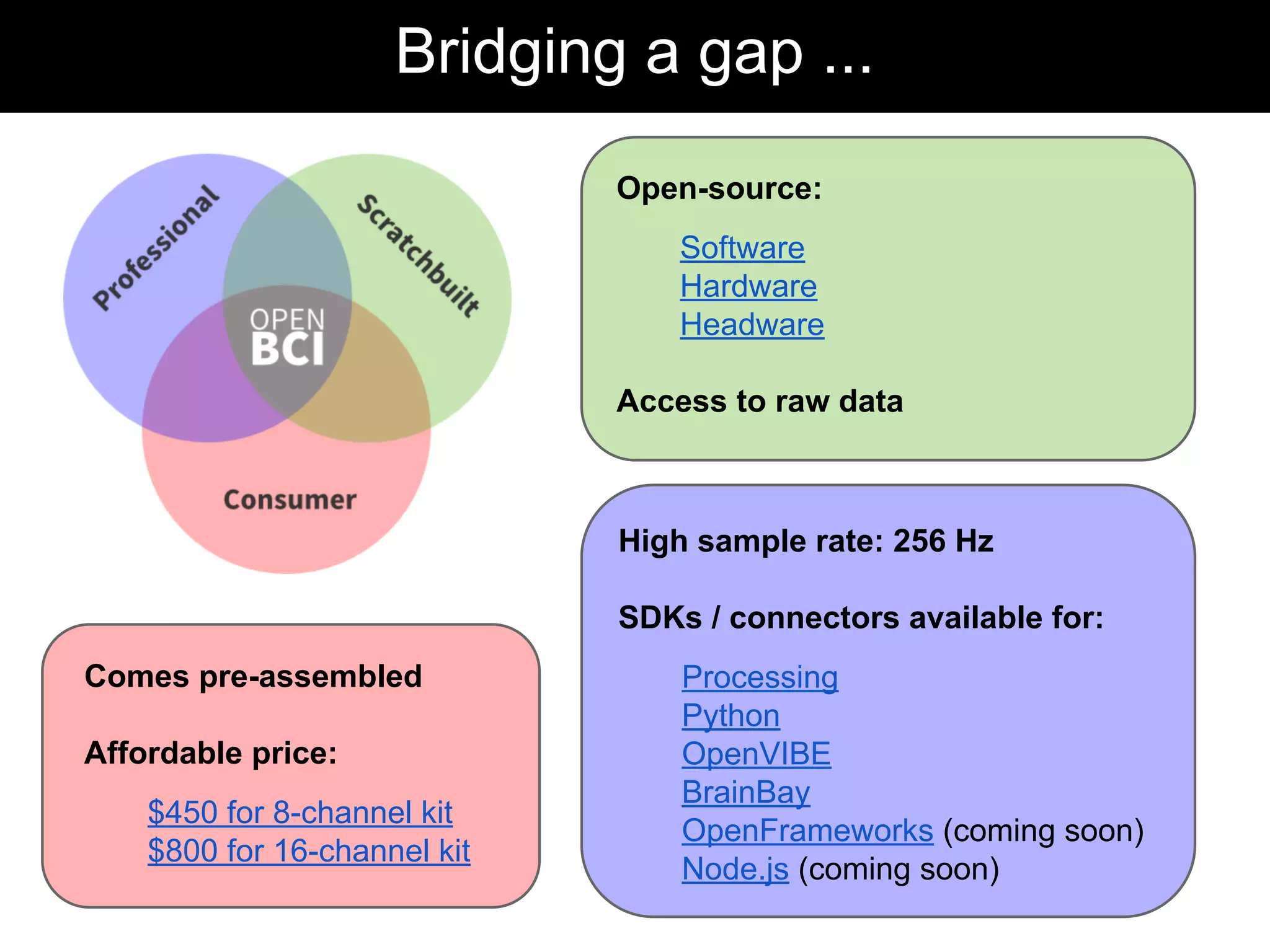
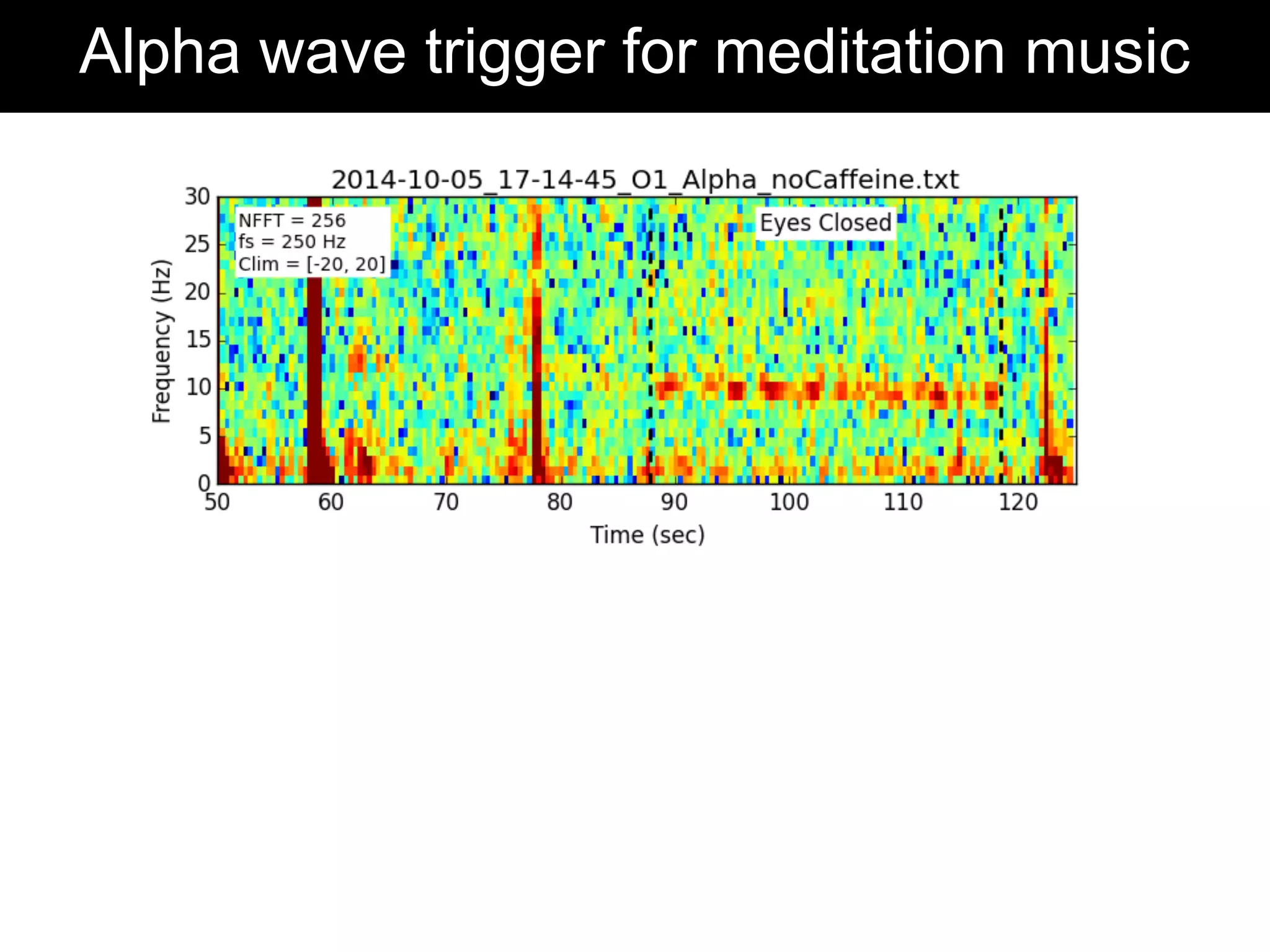
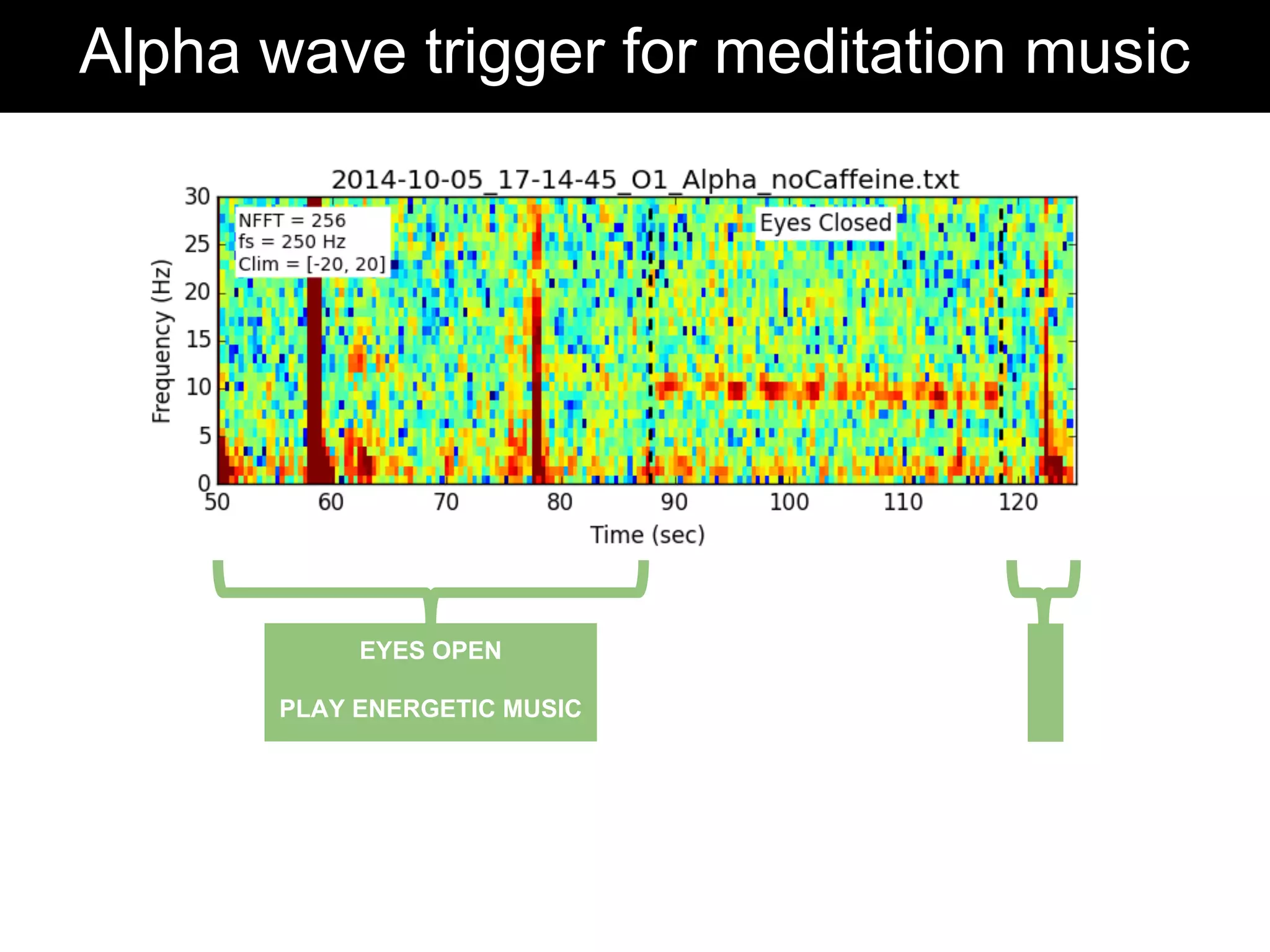
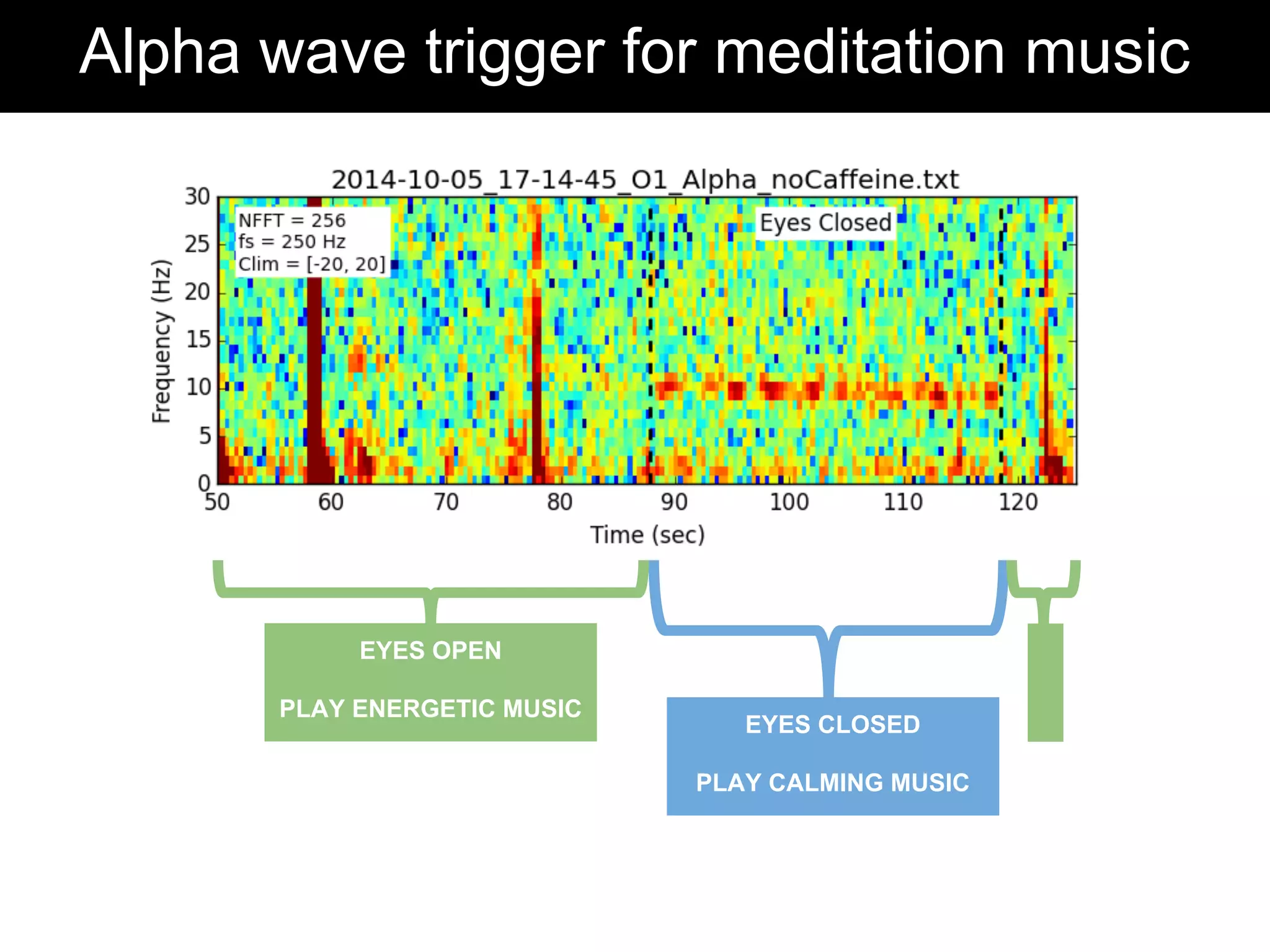
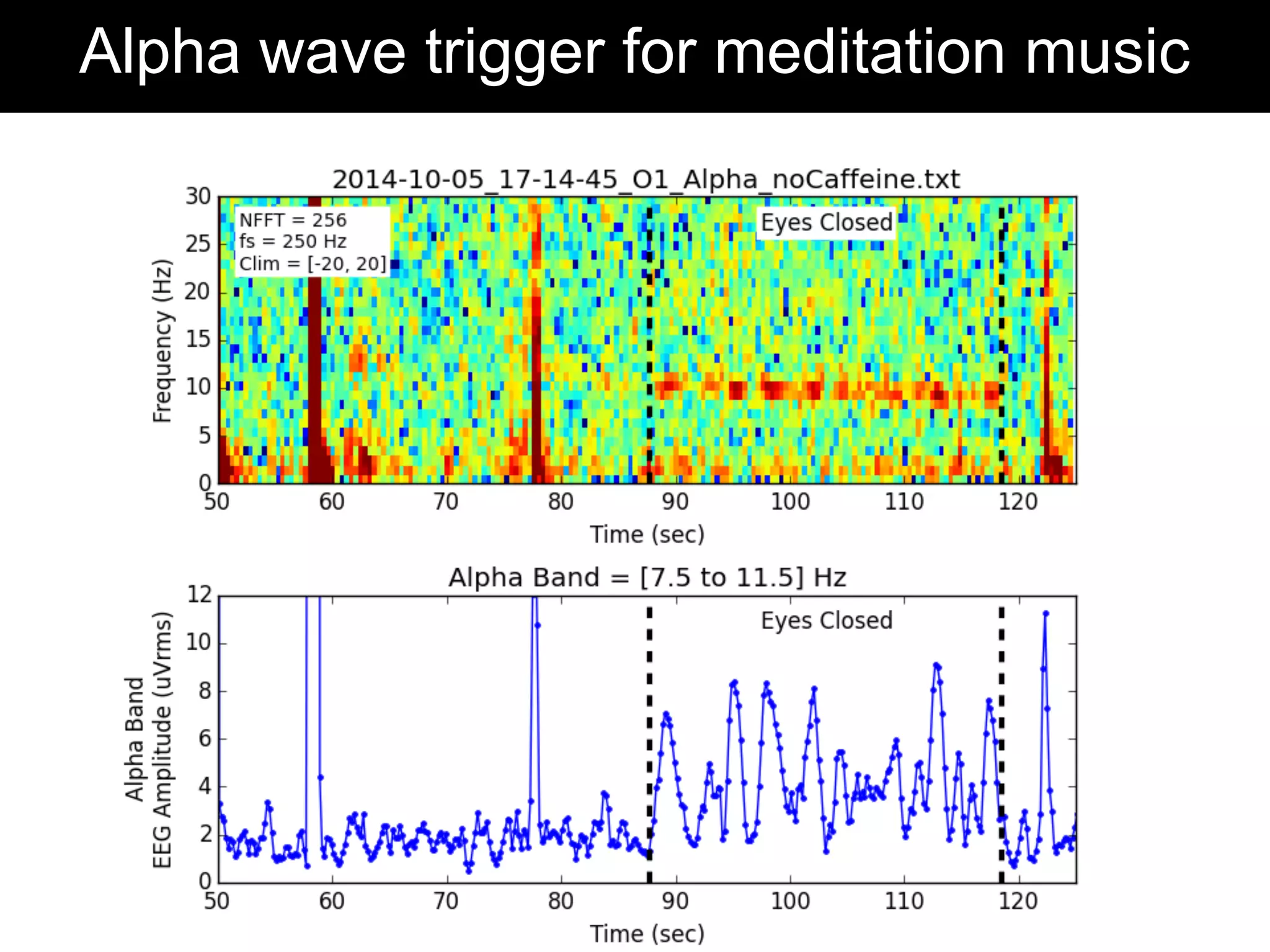
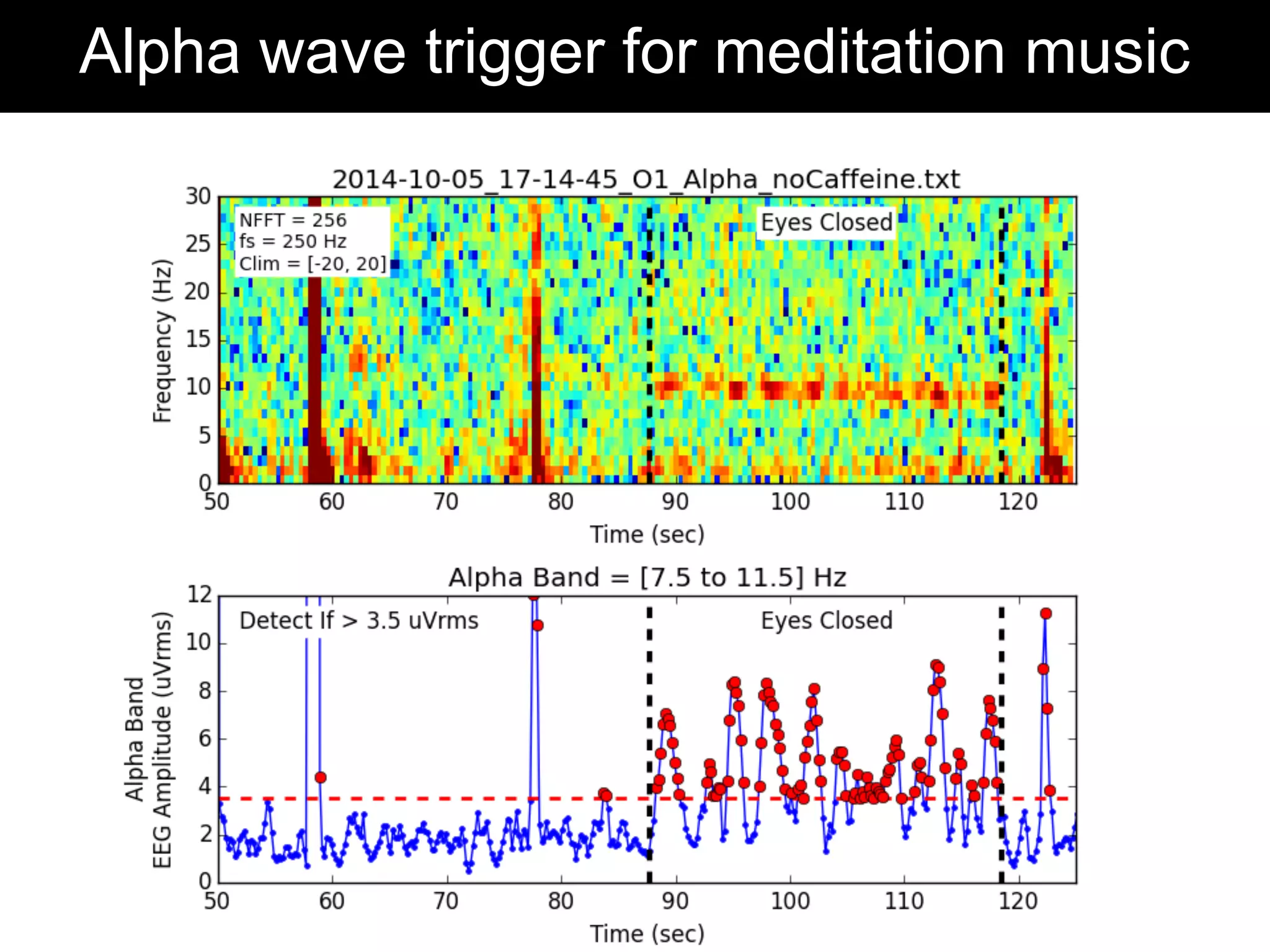
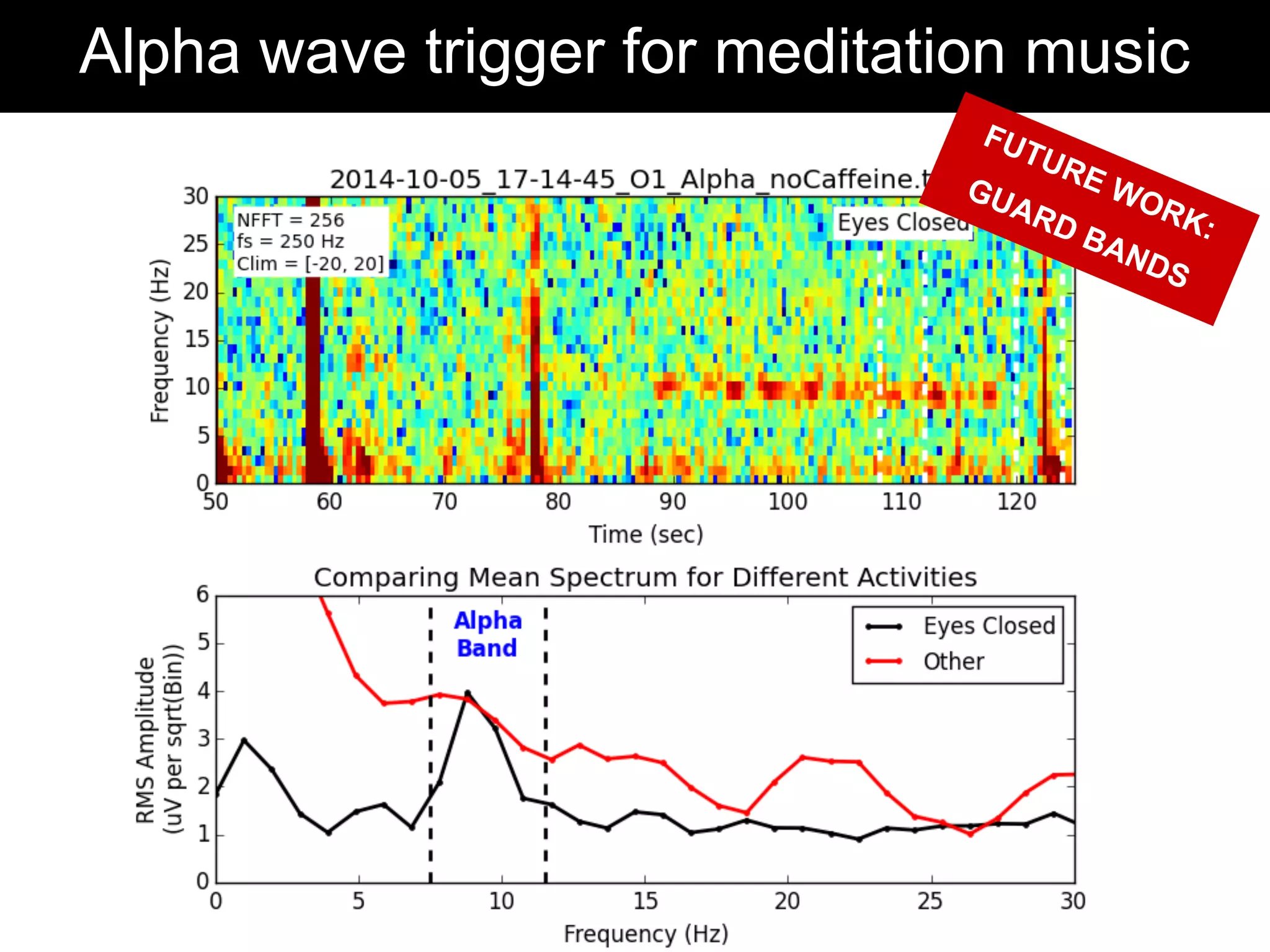
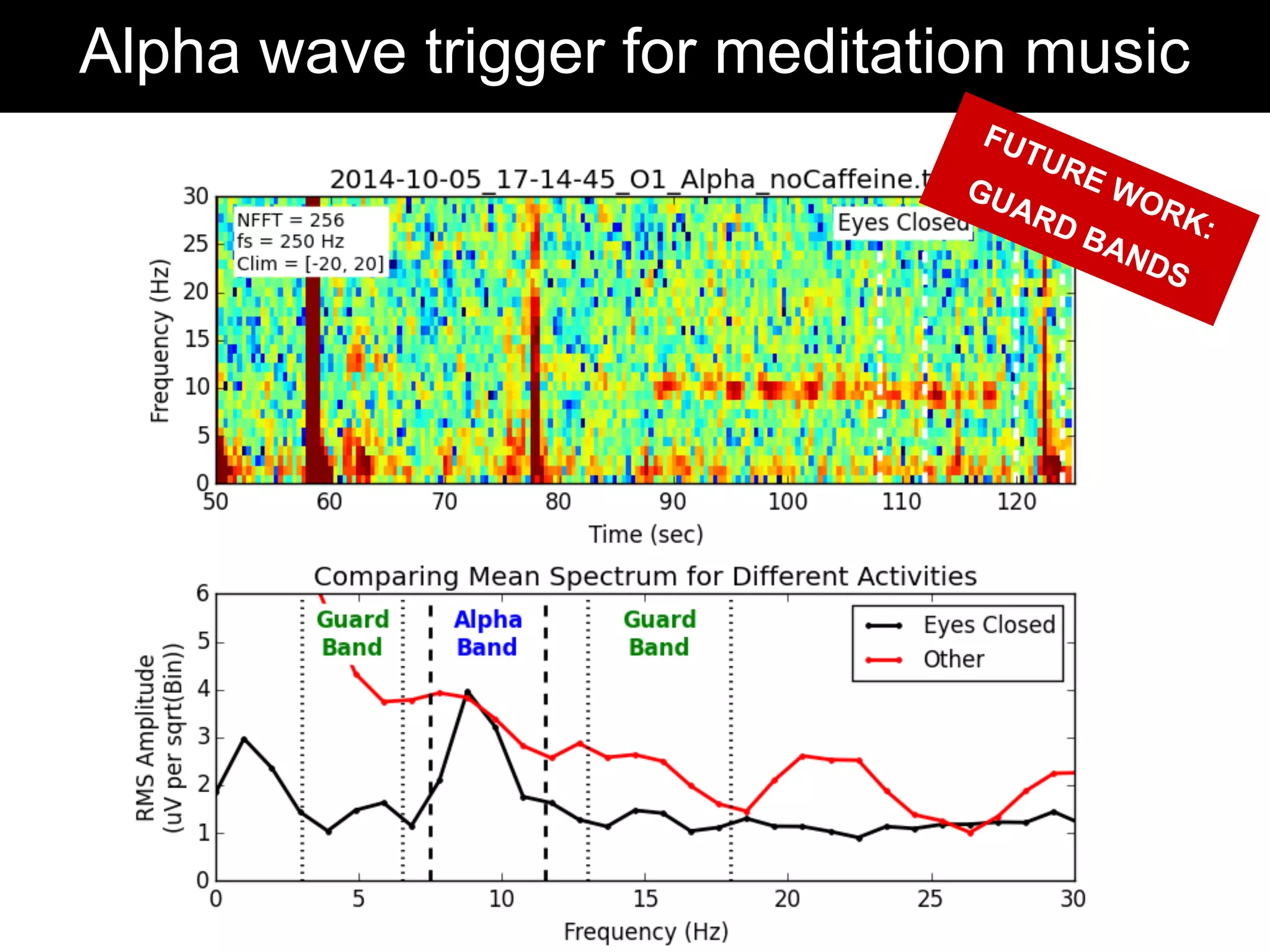
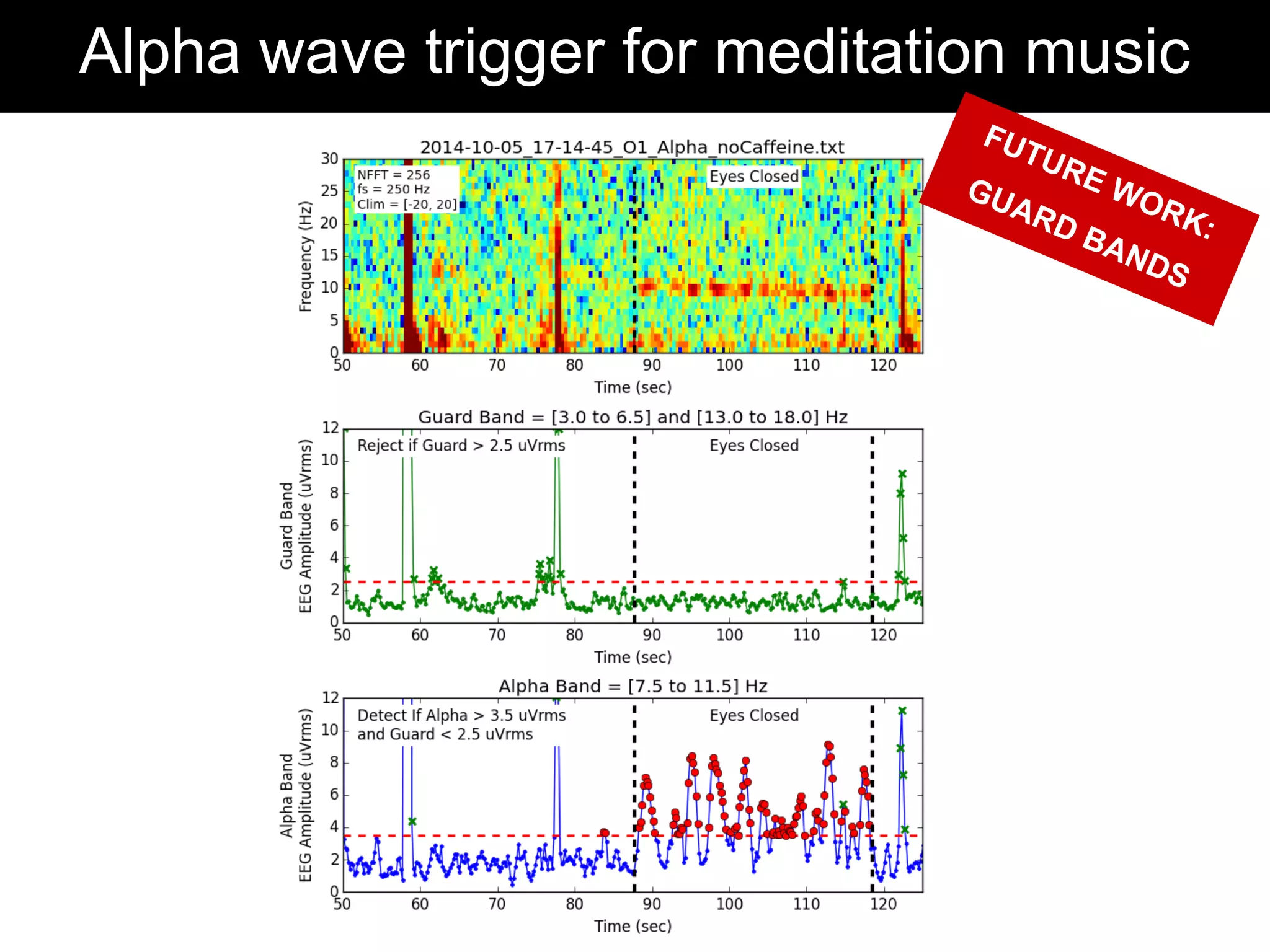
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), detailing their definition, types, and data analysis methods. It presents OpenBCI as an open-source platform that supports community engagement and offers affordable BCI solutions, along with examples of practical applications, including games that utilize EEG data for user interaction. The conclusion highlights the potential for further development and innovation within the BCI field.