The document is a comprehensive guide on Python programming, covering its history, syntax, data types, control flow, and standard library functionalities. It addresses the language's high-level, object-oriented nature, its wide application in various industries, and its ease of use for rapid development. Additionally, it includes practical coding exercises and resources for further learning.







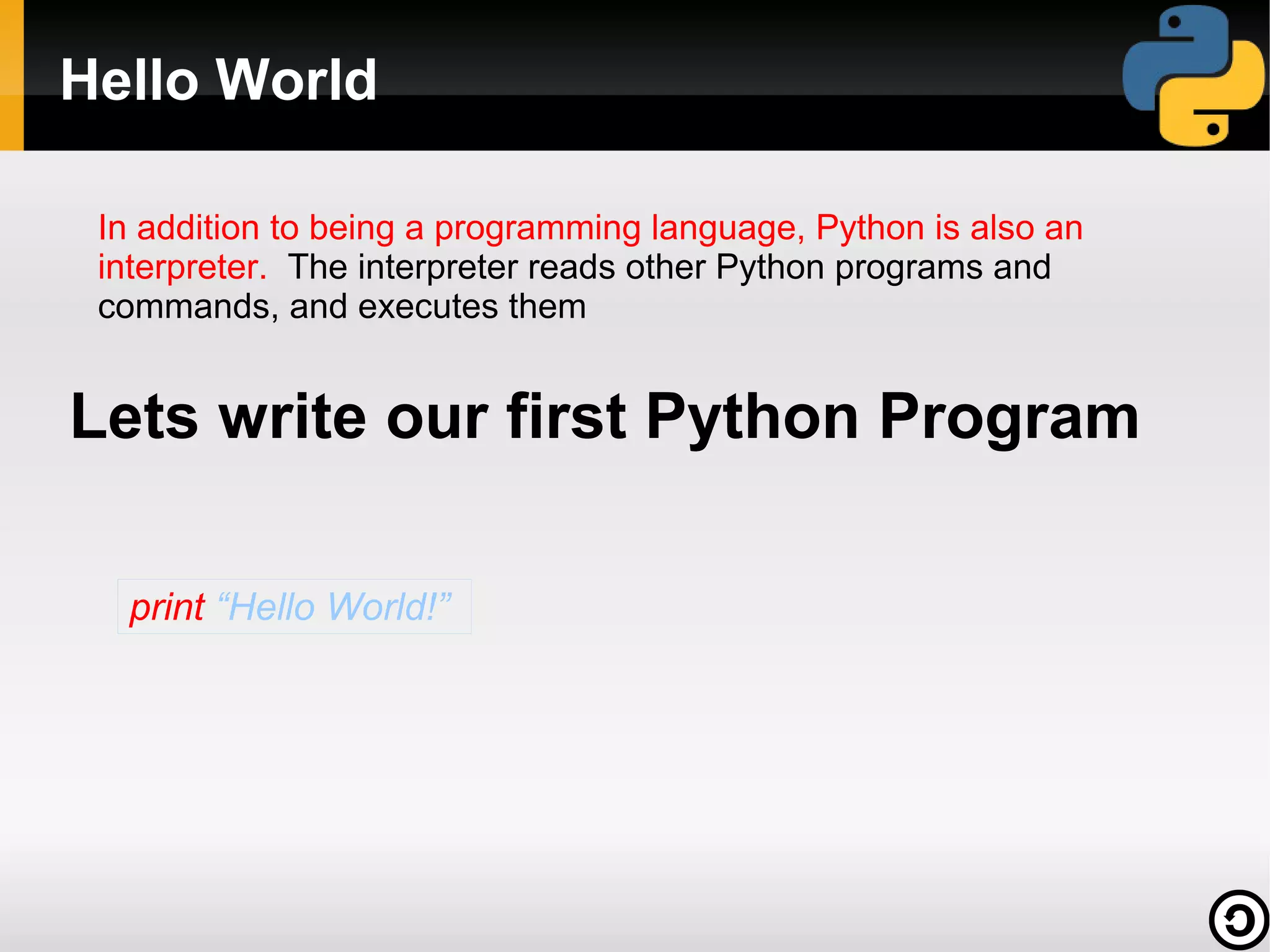
![Python is simple
print "Hello World!"
Python
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
cout << "Hello World!";
}
C++
public class helloWorld
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsonpython-140216042545-phpapp02/75/Hands-on-Session-on-Python-9-2048.jpg)


![Strings: format()
>>>age = 22
>>>name = 'Sumit'
>>>len(name)
>>>print “I am %s and I have owned %d cars” %(“sumit”, 3)
I am sumit I have owned 3 cars
>>> name = name + ”Raj”
>>> 3*name
>>>name[:]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsonpython-140216042545-phpapp02/75/Hands-on-Session-on-Python-12-2048.jpg)

![Strings...
>>> string.lower()
>>> string.upper()
>>> string[start:end:stride]
>>> S = ‘hello world’
>>> S[0] = ‘h’
>>> S[1] = ‘e’
>>> S[-1] = ‘d’
>>> S[1:3] = ‘el’
>>> S[:-2] = ‘hello wor’
>>> S[2:] = ‘llo world’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsonpython-140216042545-phpapp02/75/Hands-on-Session-on-Python-14-2048.jpg)



![Data Structures
●
List
●
●
[1, 2, 4, “Hello”, False]
●
●
Mutable data type, array-like
list.sort() ,list.append() ,len(list), list[i]
Tuple
●
●
●
Immutable data type, faster than lists
(1, 2, 3, “Hello”, False)
Dictionary
●
{42: “The answer”, “key”: “value”}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsonpython-140216042545-phpapp02/75/Hands-on-Session-on-Python-18-2048.jpg)


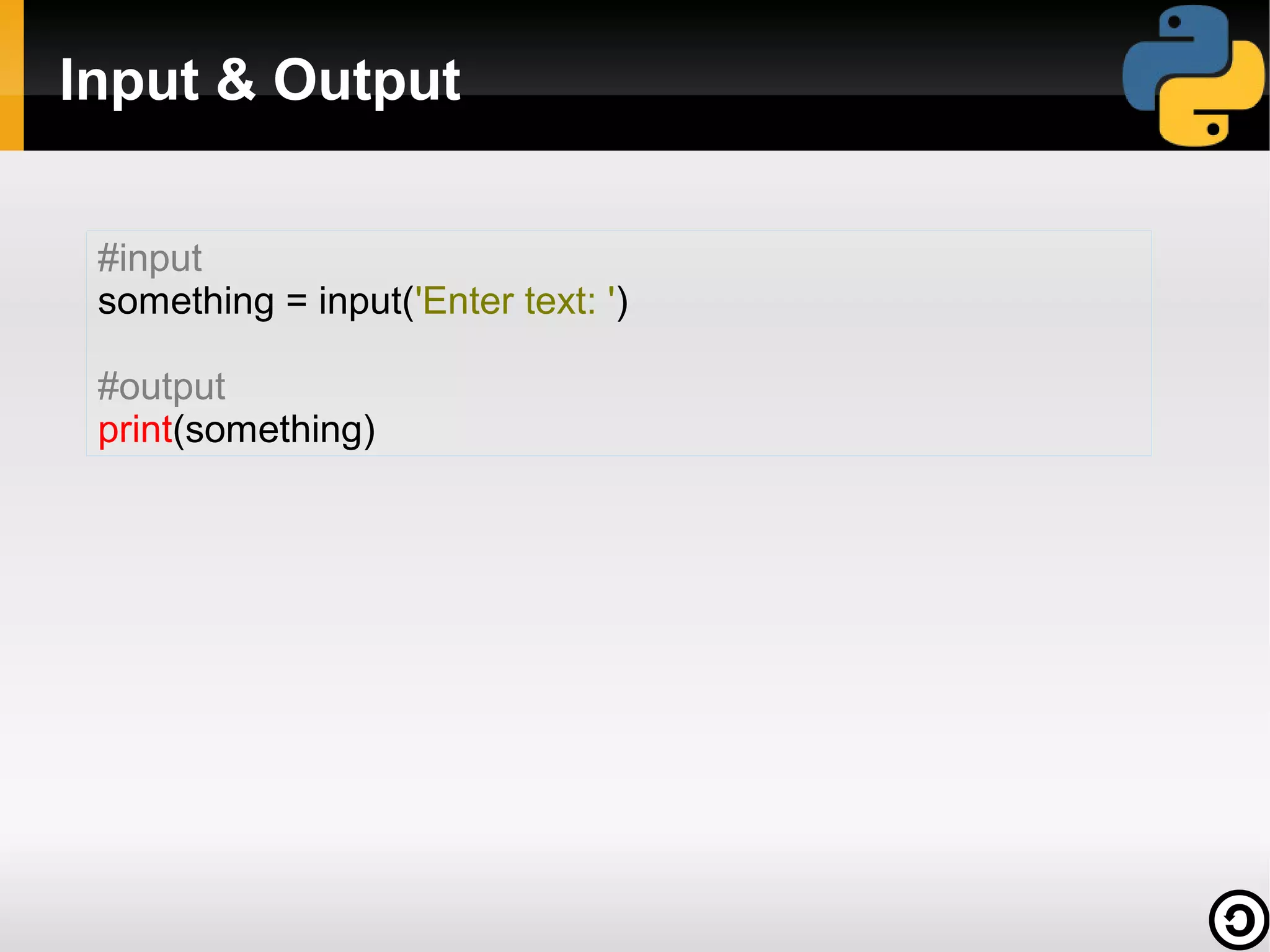
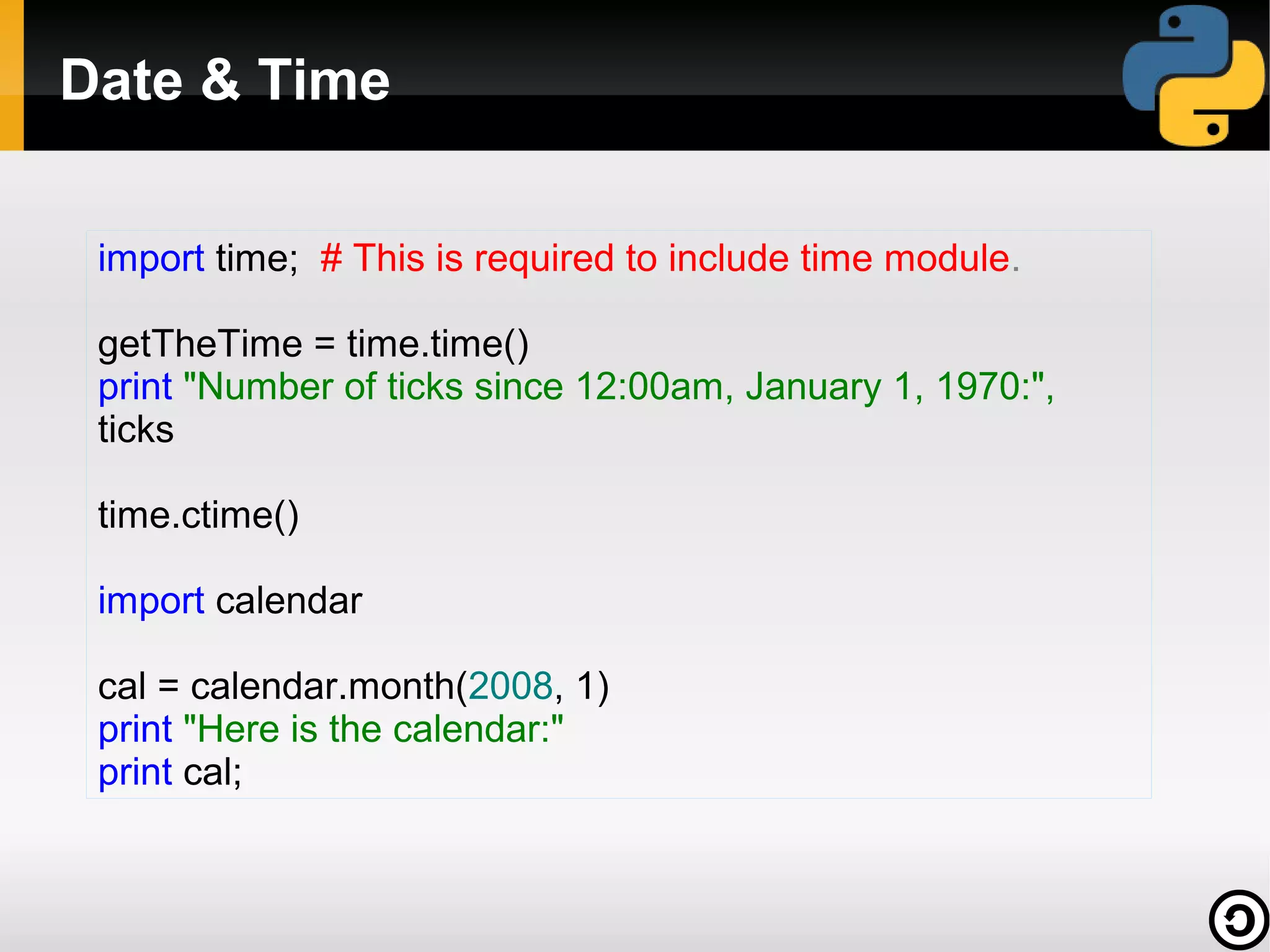



![A simple Python code to send a mail
try:
msg = MIMEText(content, text_subtype)
msg['Subject']= subject
msg['From'] = sender # some SMTP servers will do this
automatically, not all
conn = SMTP(SMTPserver)
conn.set_debuglevel(False)
conn.login(USERNAME, PASSWORD)
try:
conn.sendmail(sender, destination, msg.as_string())
finally:
conn.close()
except Exception, exc:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsonpython-140216042545-phpapp02/75/Hands-on-Session-on-Python-26-2048.jpg)



