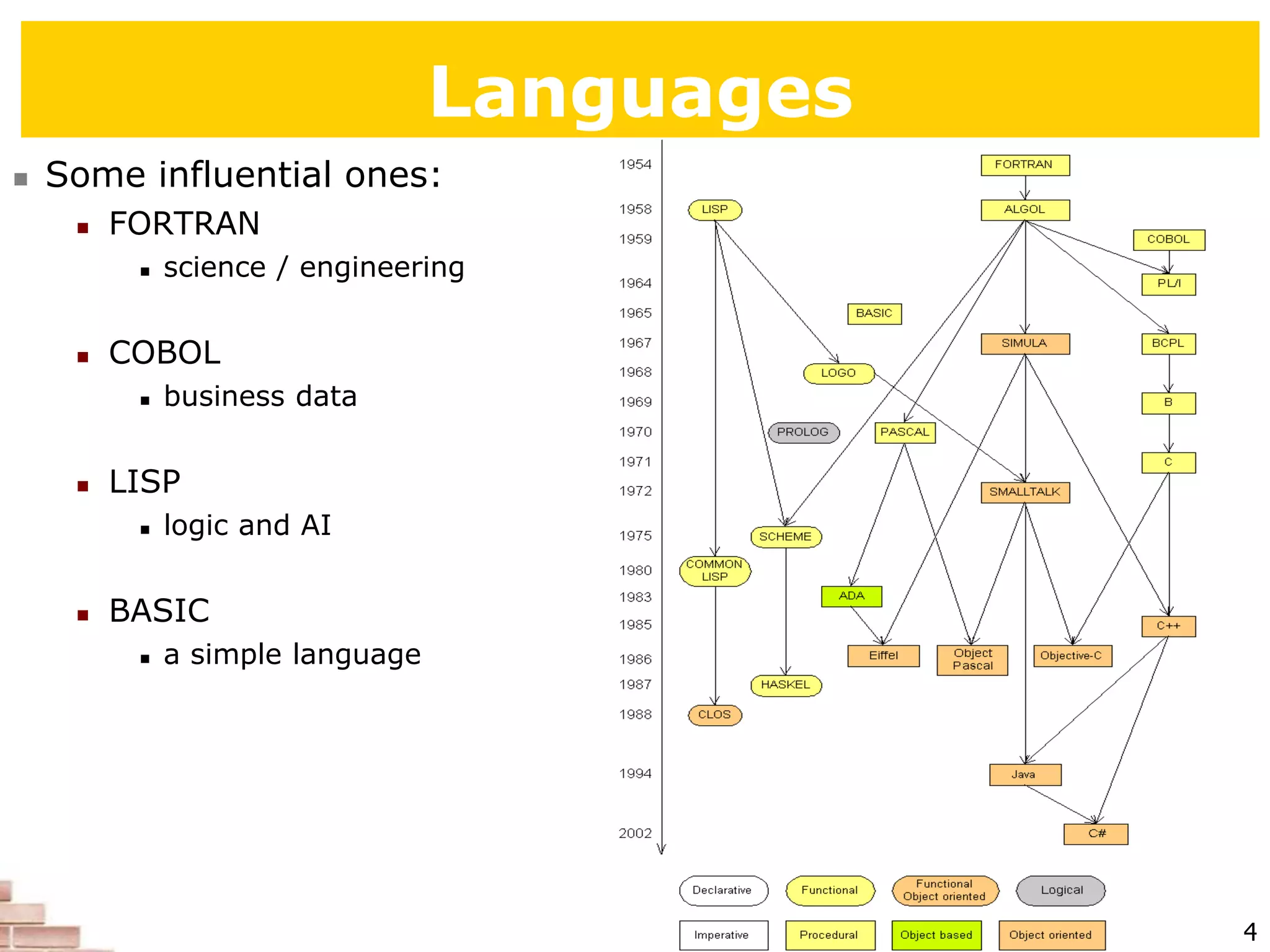
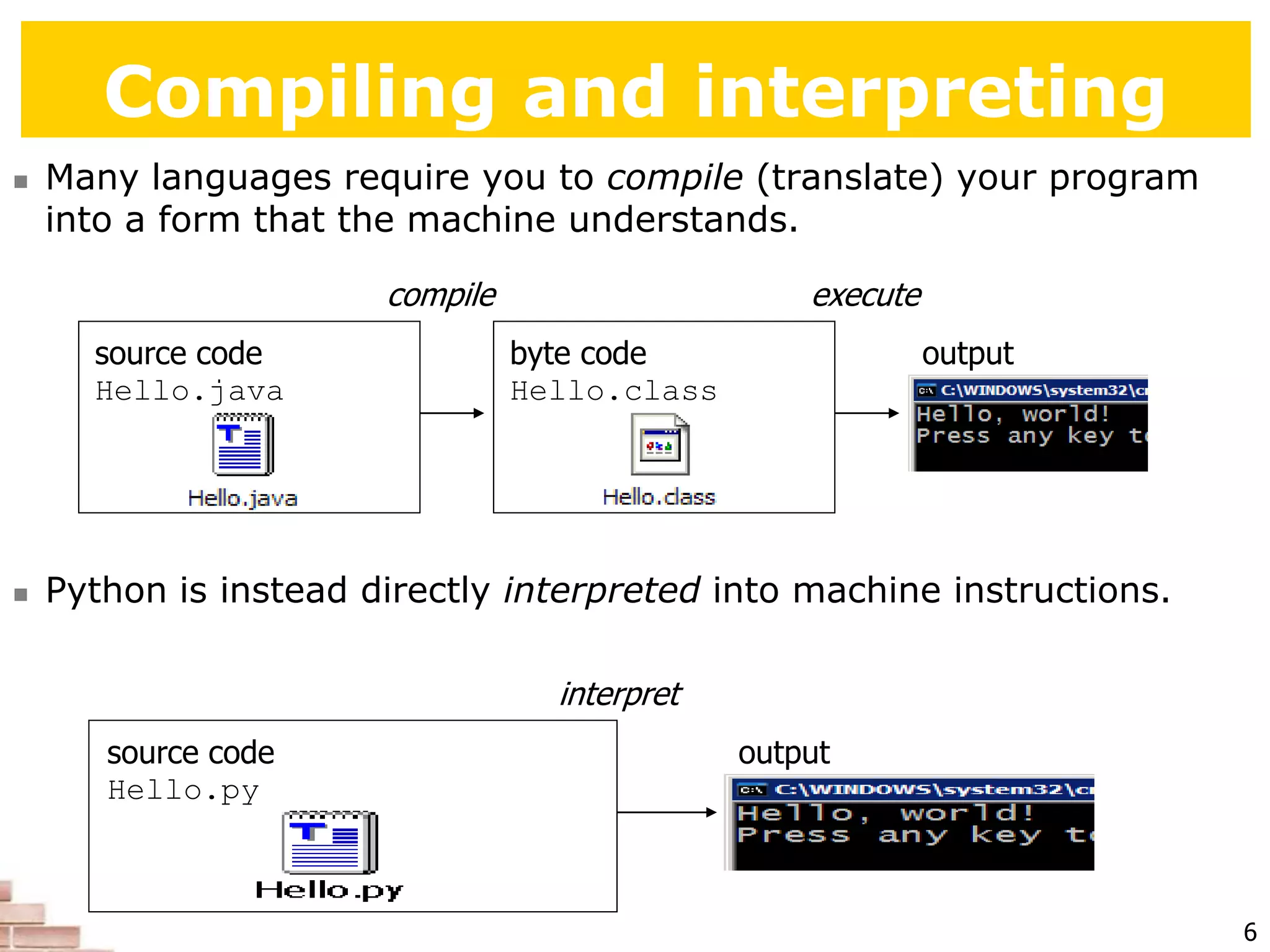
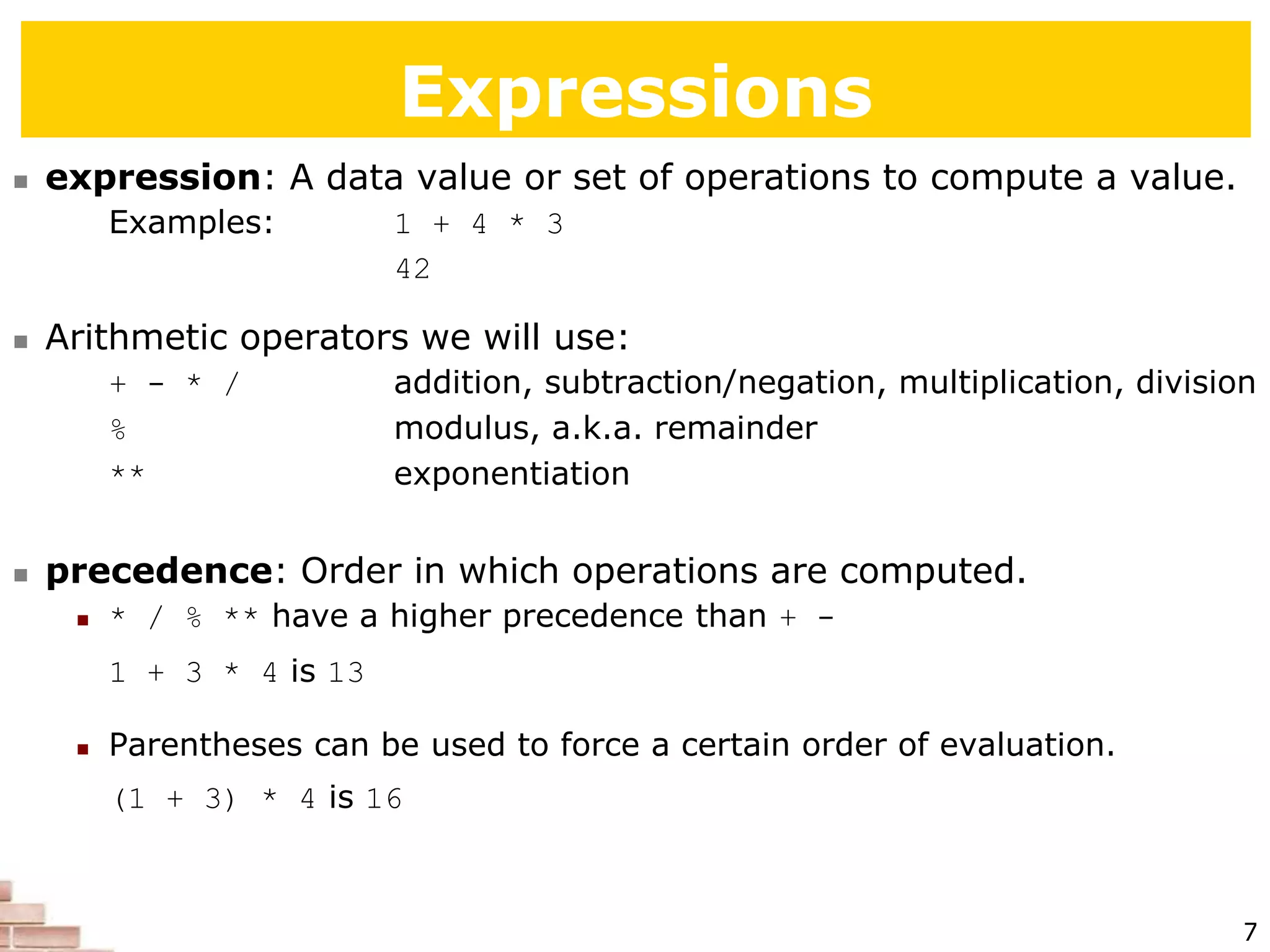
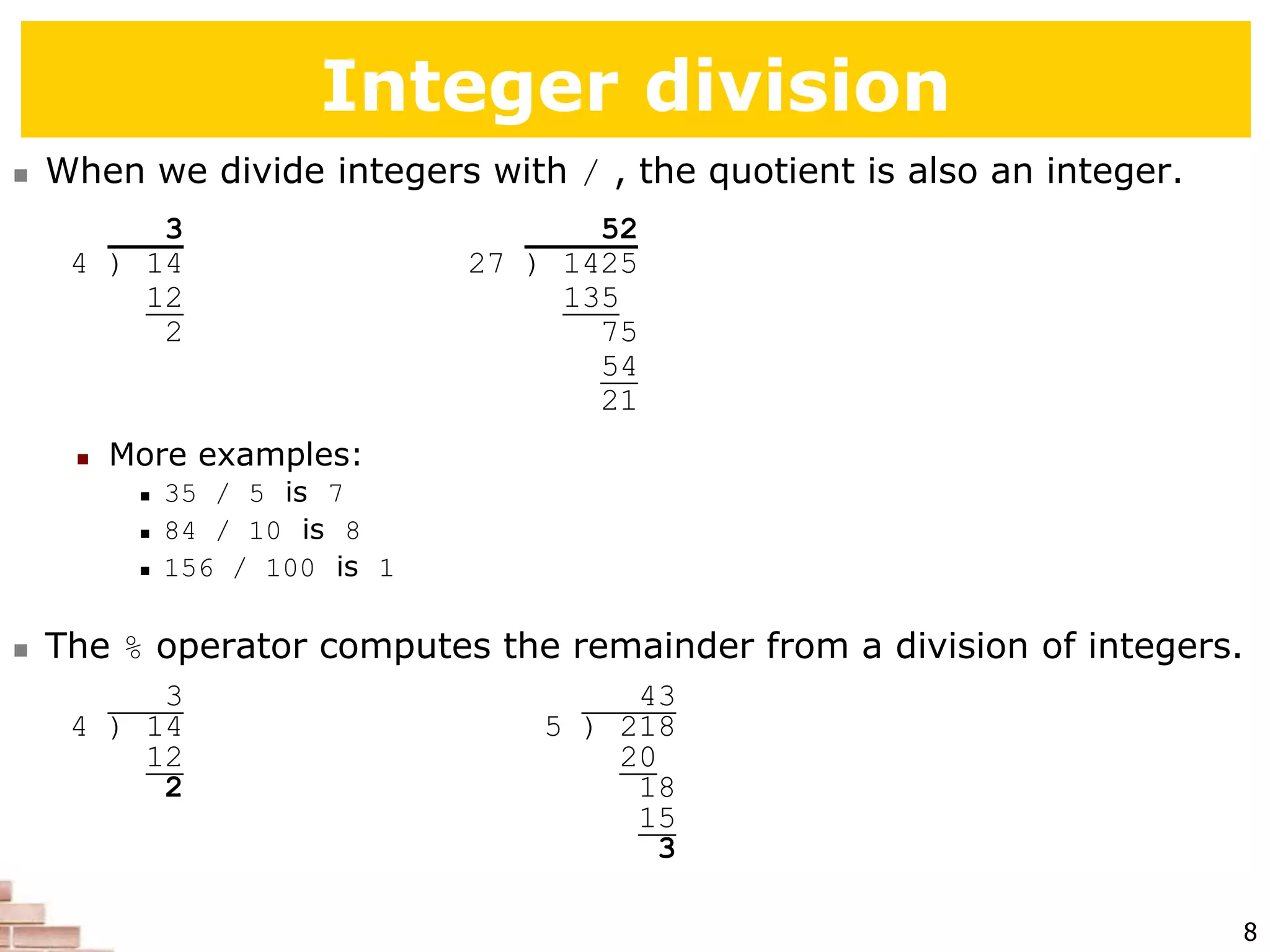
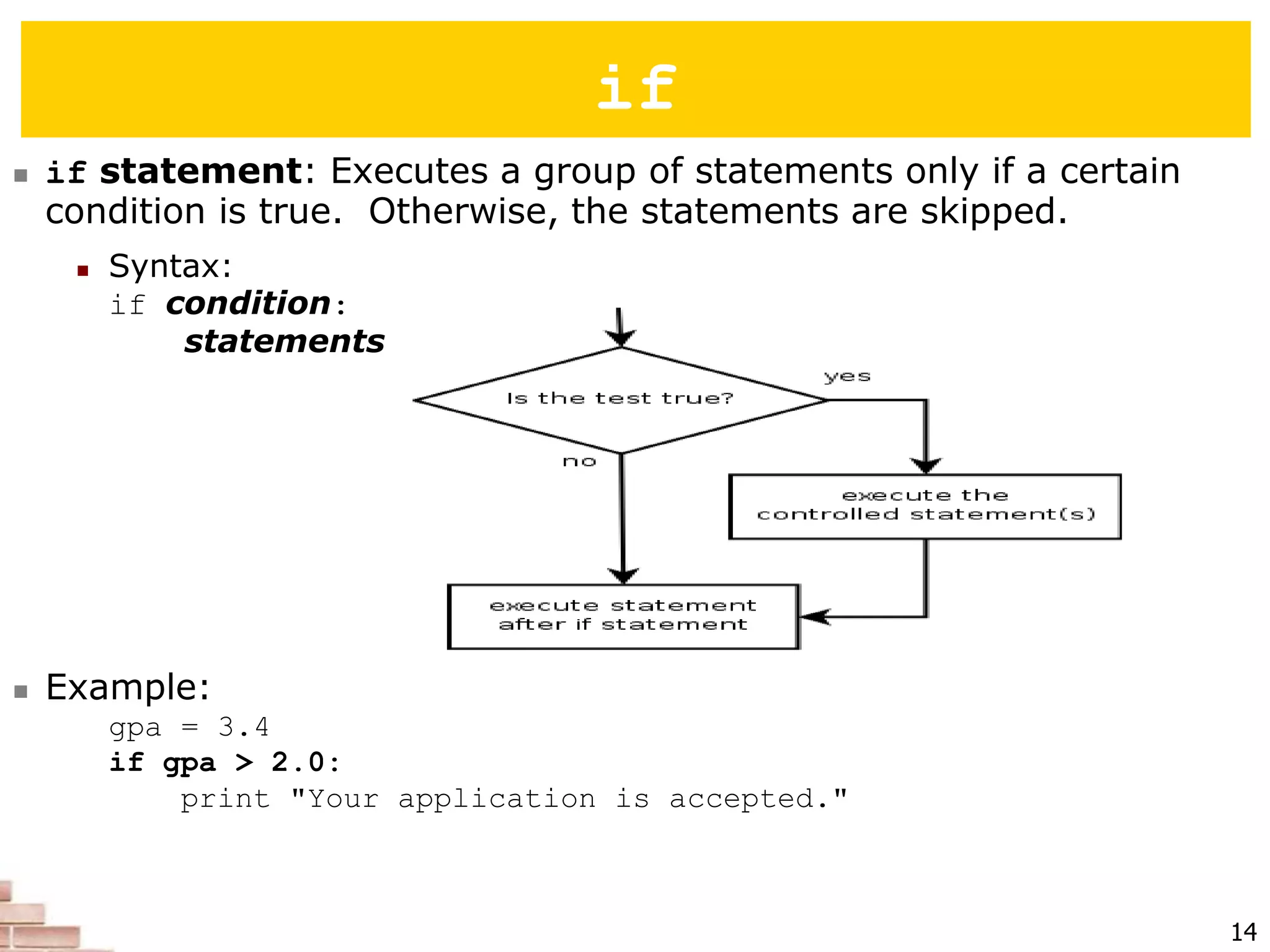
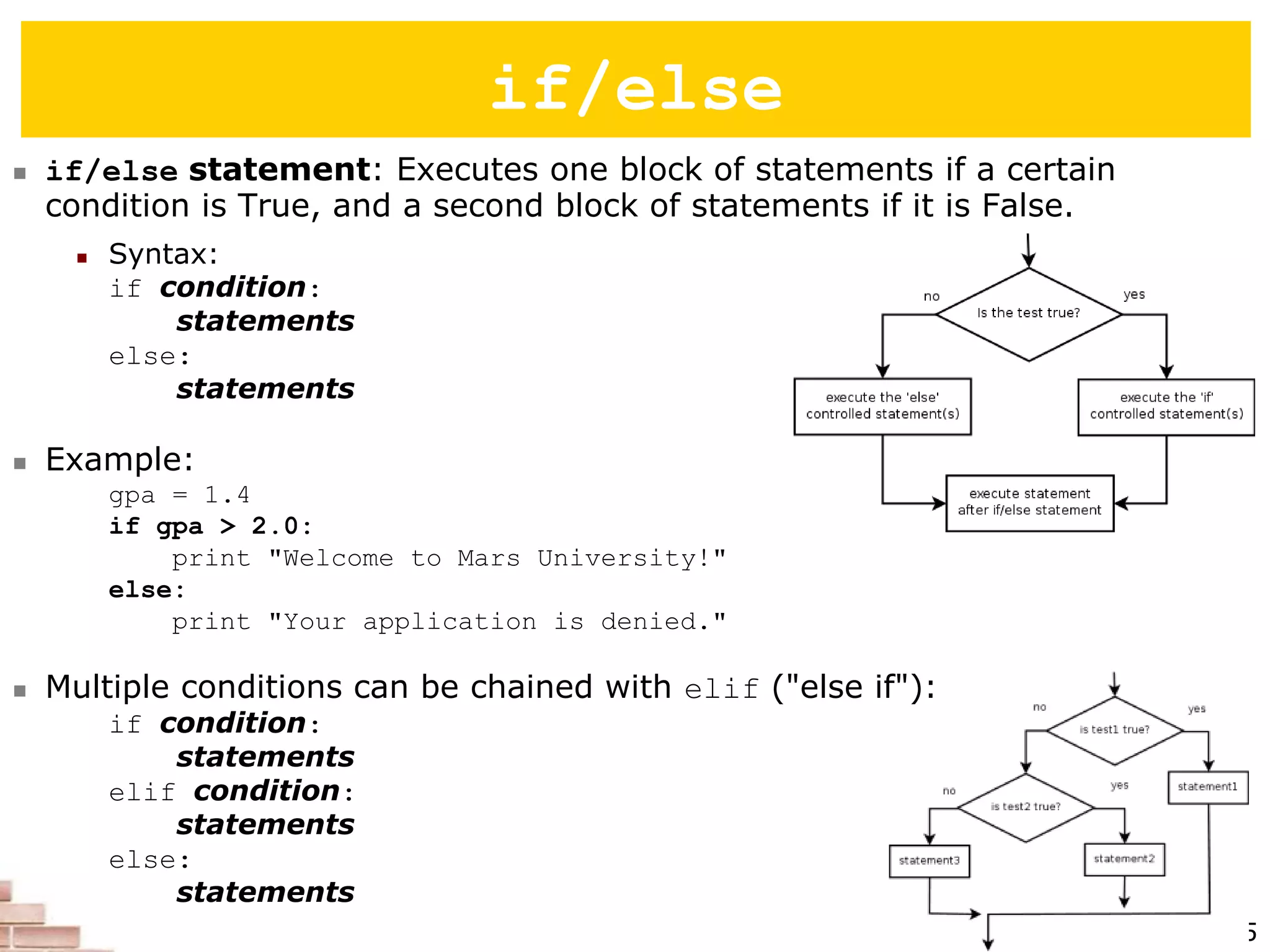
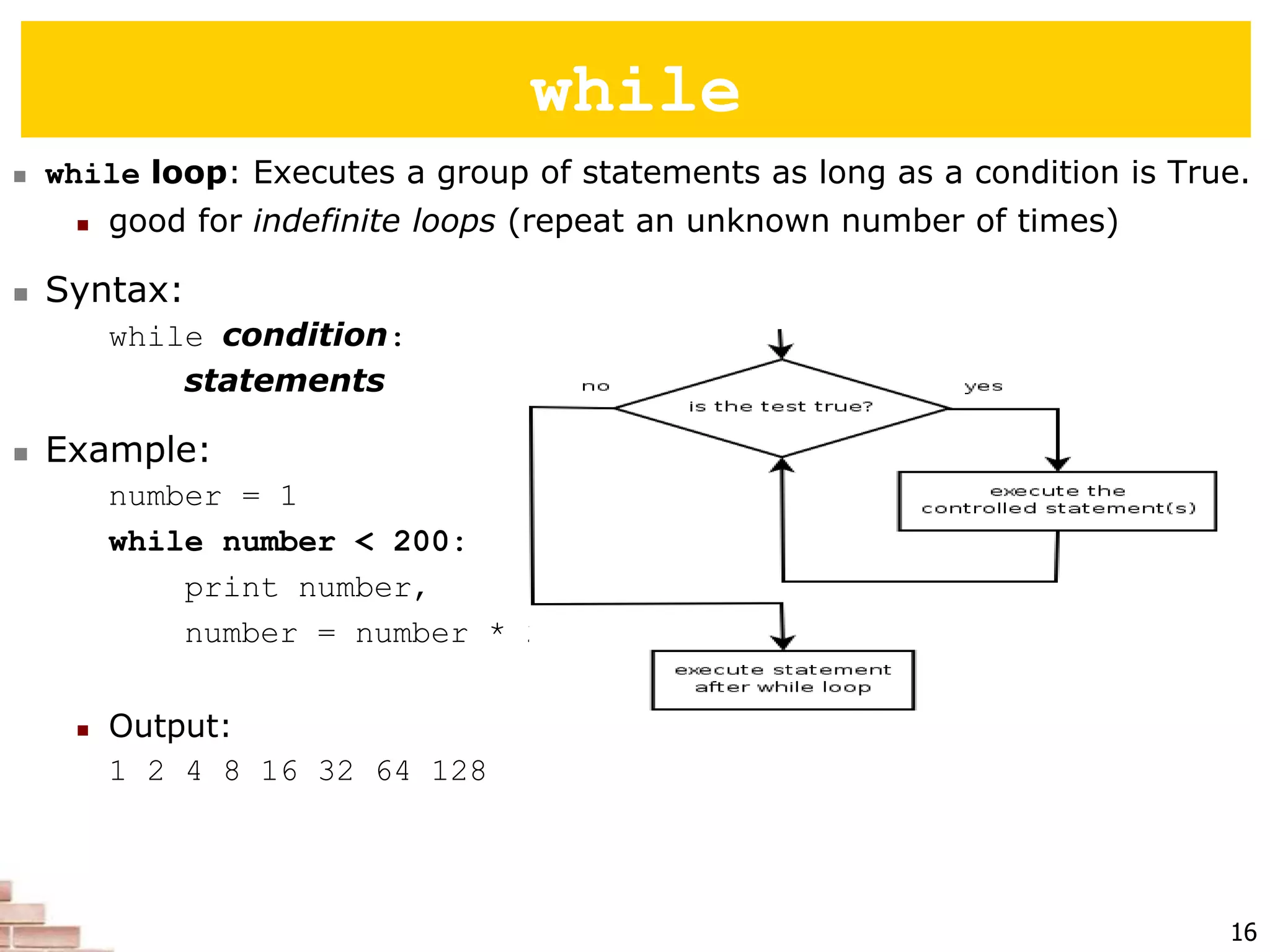
The document explains the concept of scripting languages, specifically focusing on Python as a high-level, interpreted, and object-oriented programming language suitable for beginners. It covers essential programming fundamentals such as syntax, expressions, loops, and conditional statements, as well as the importance of input and output in Python. Additionally, it highlights file processing and includes mentions of a tutor specializing in teaching Python and Java.