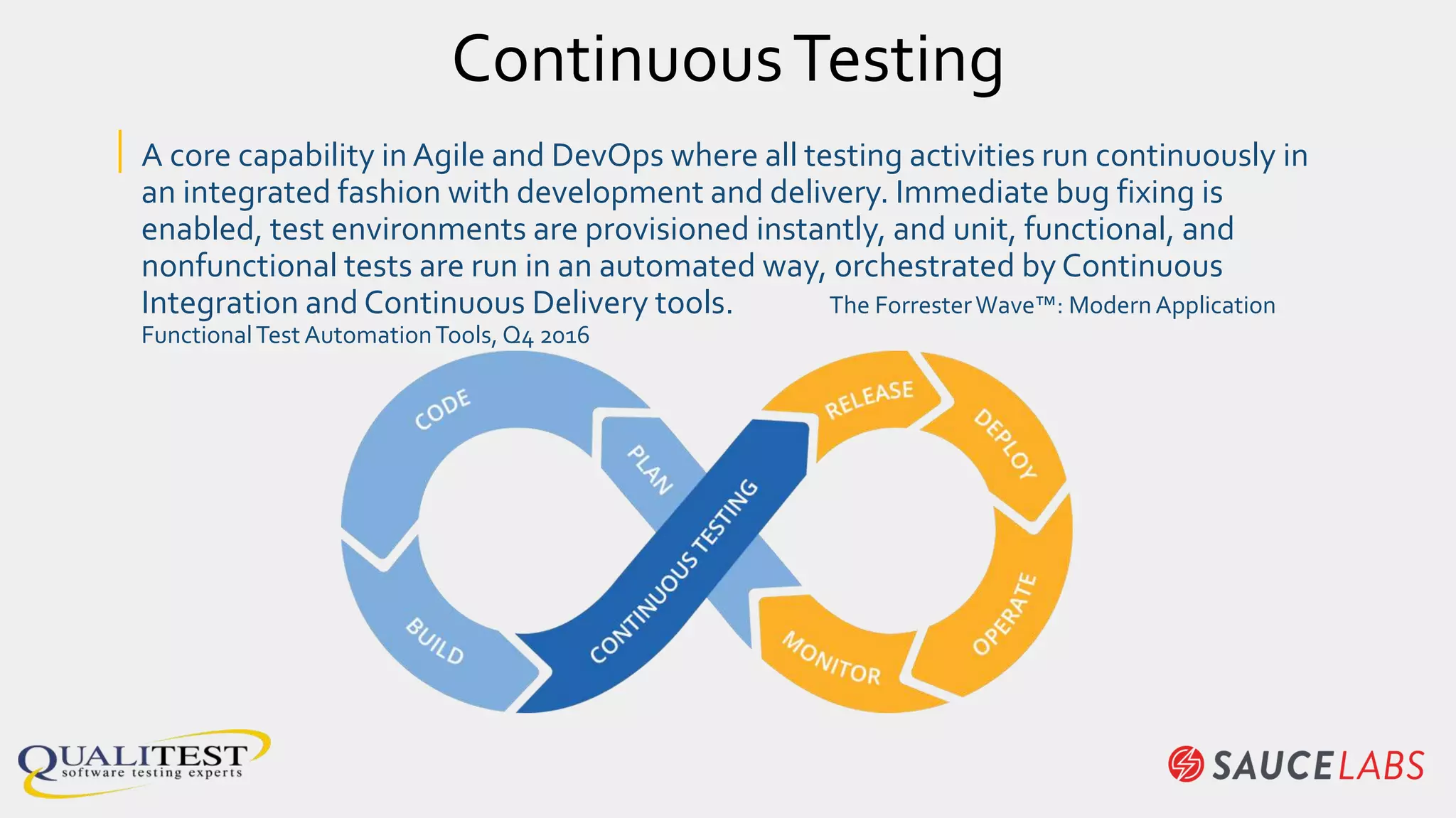
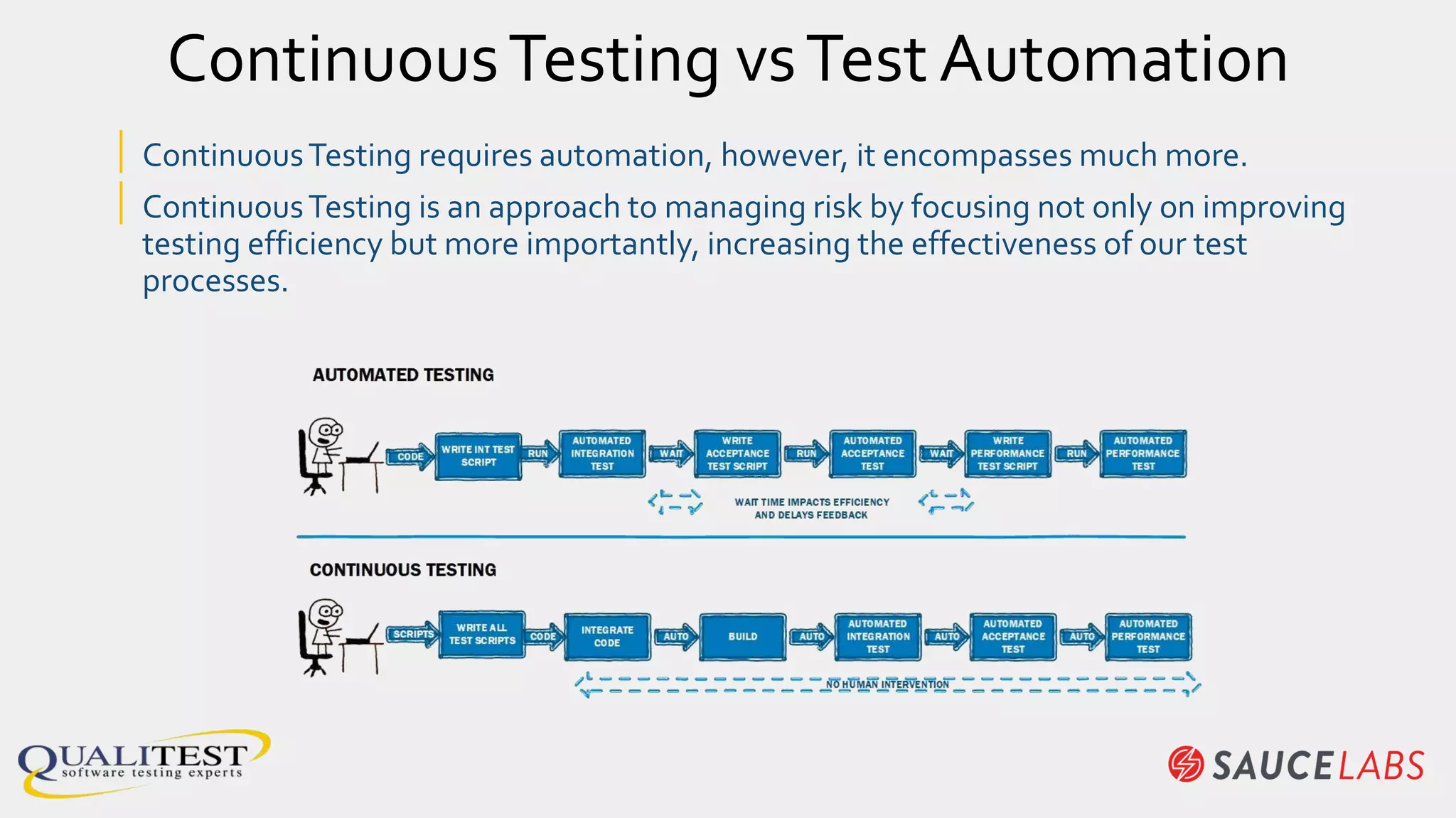
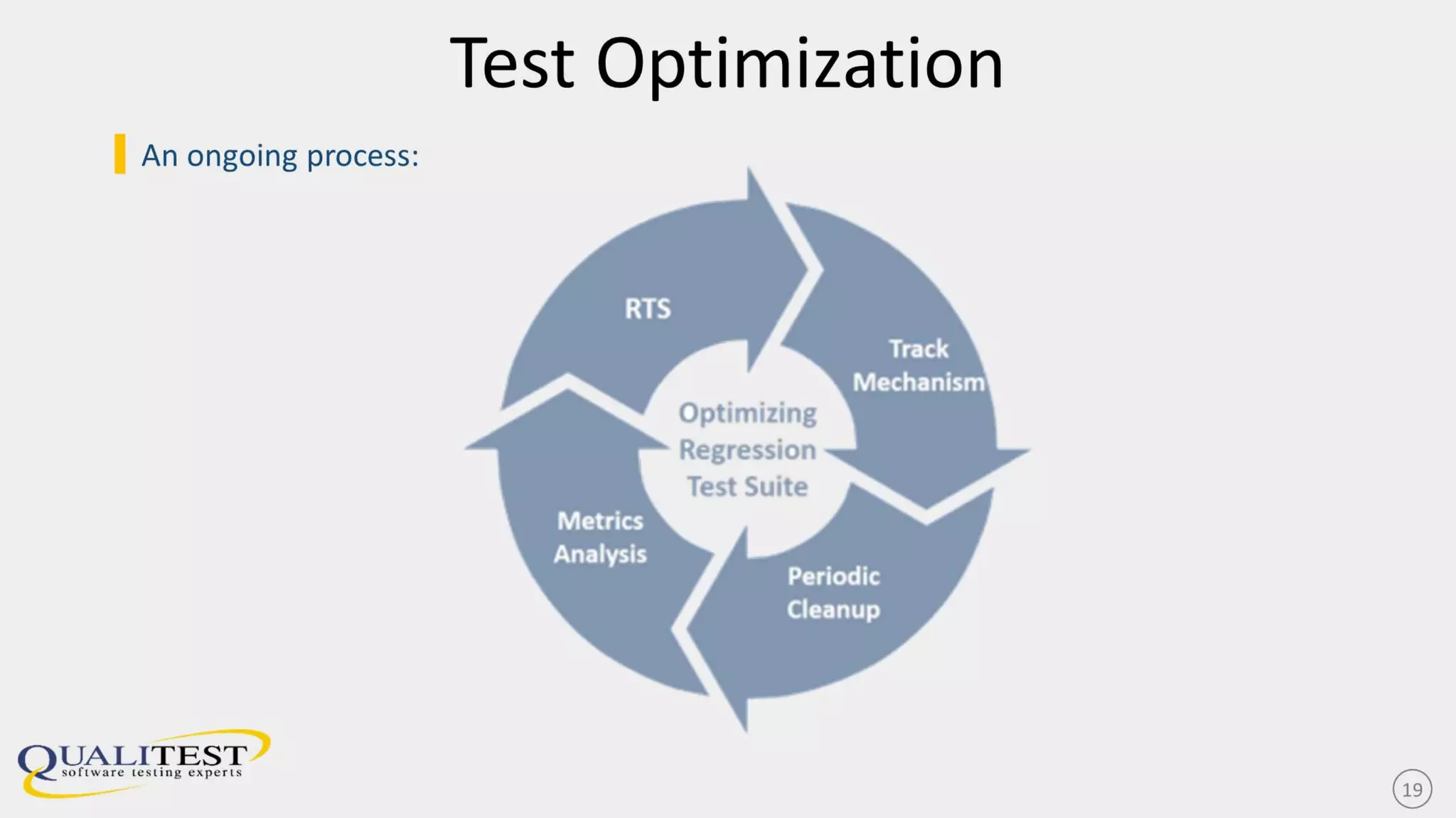
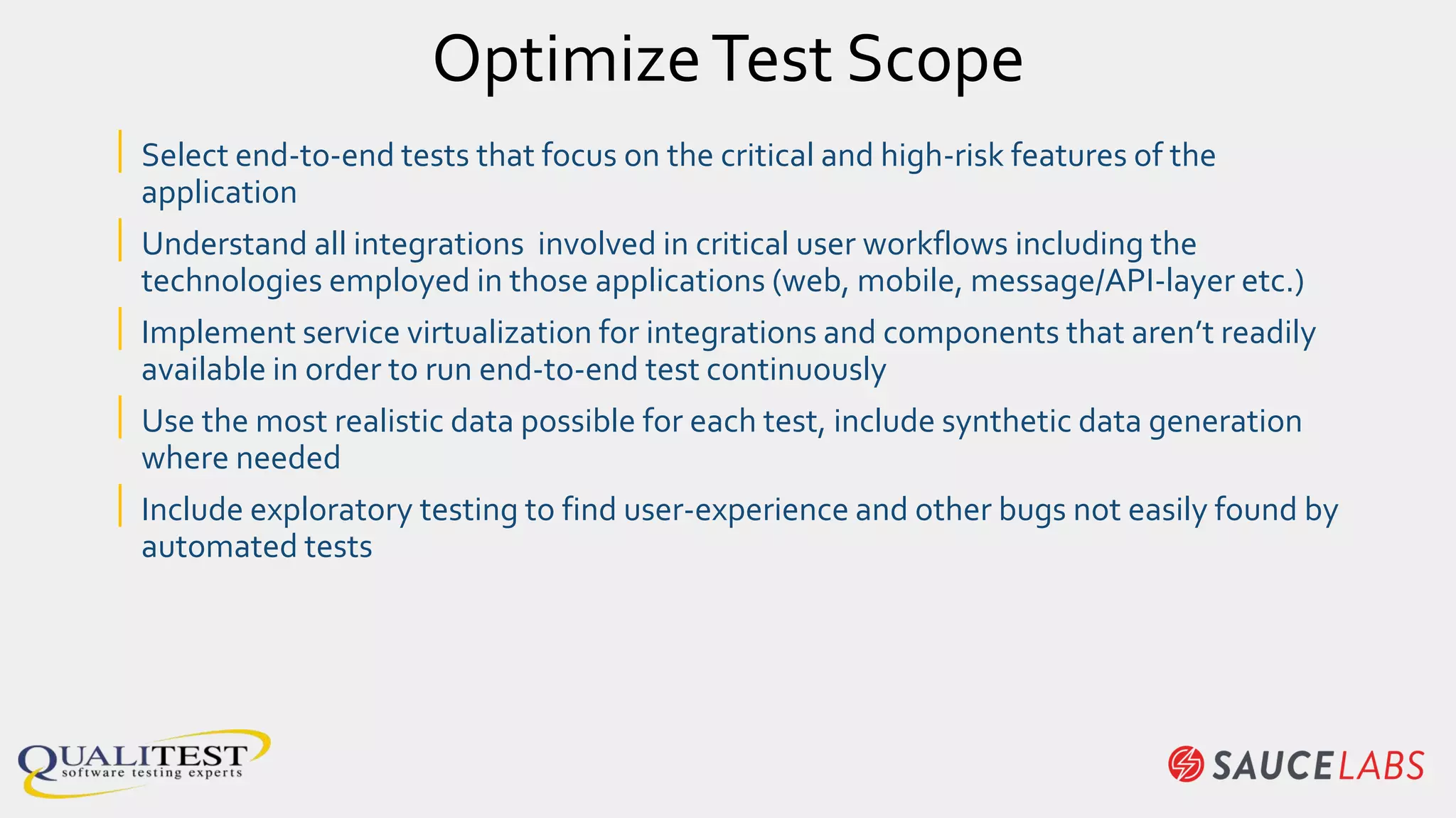
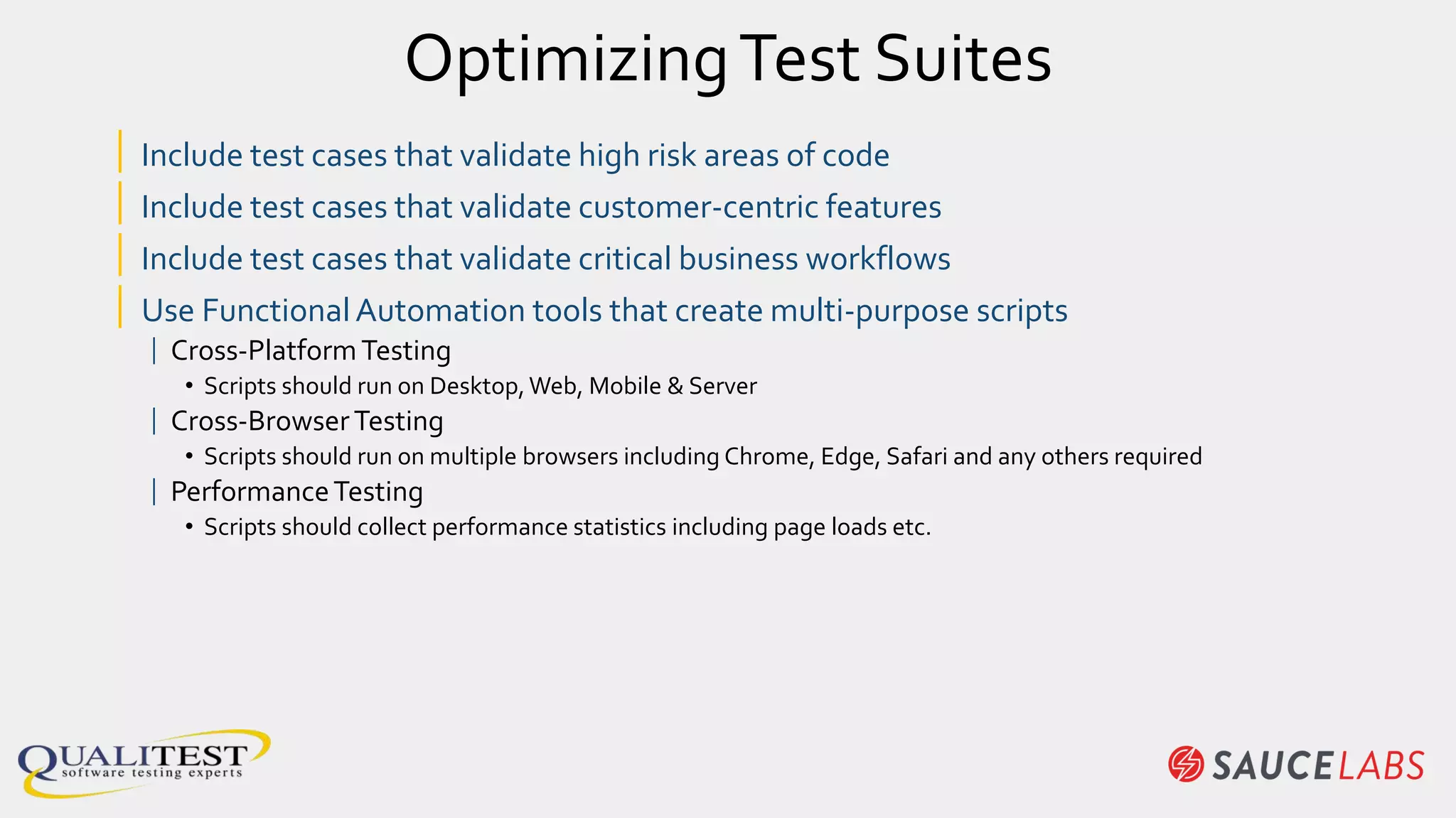
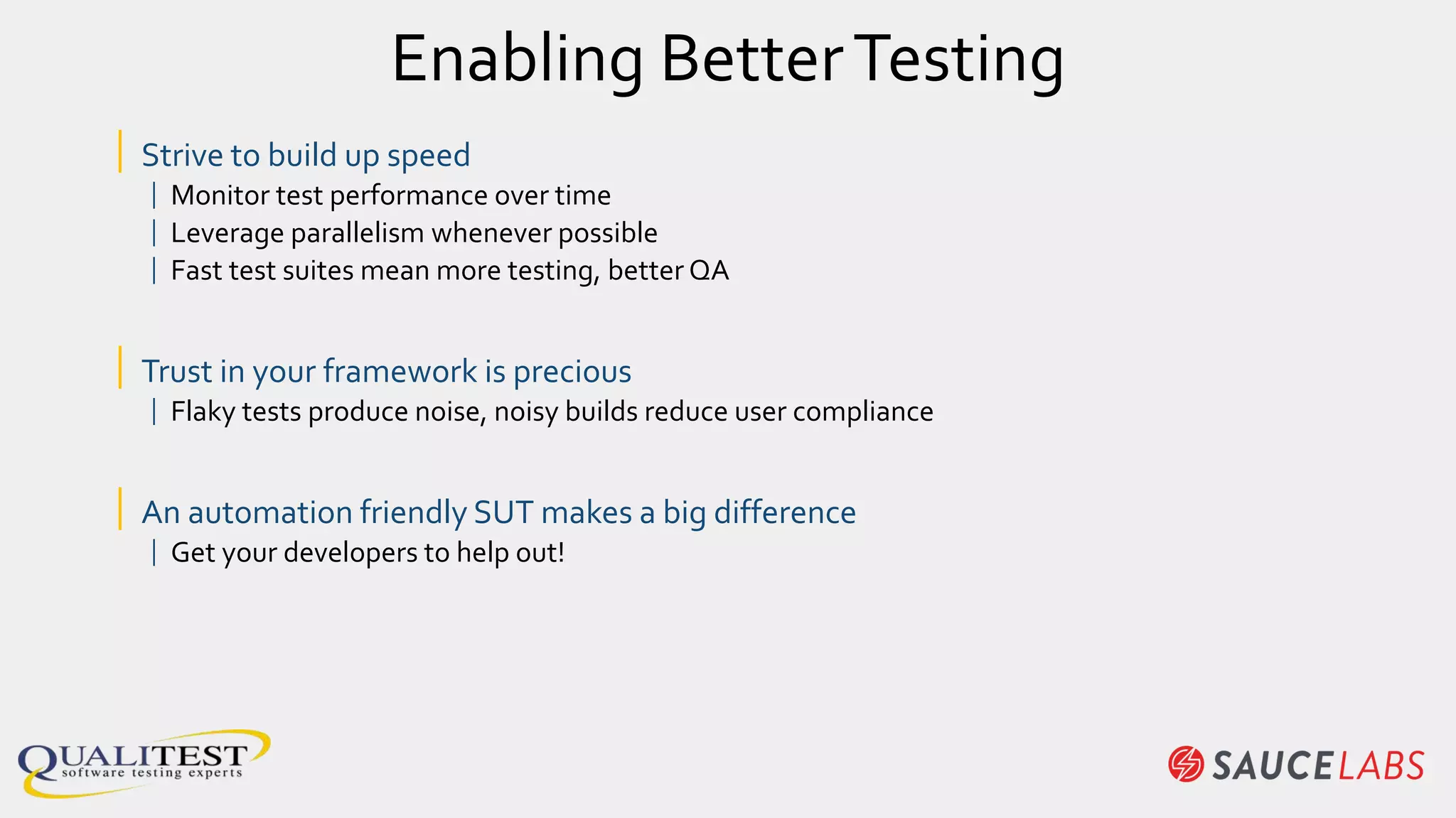
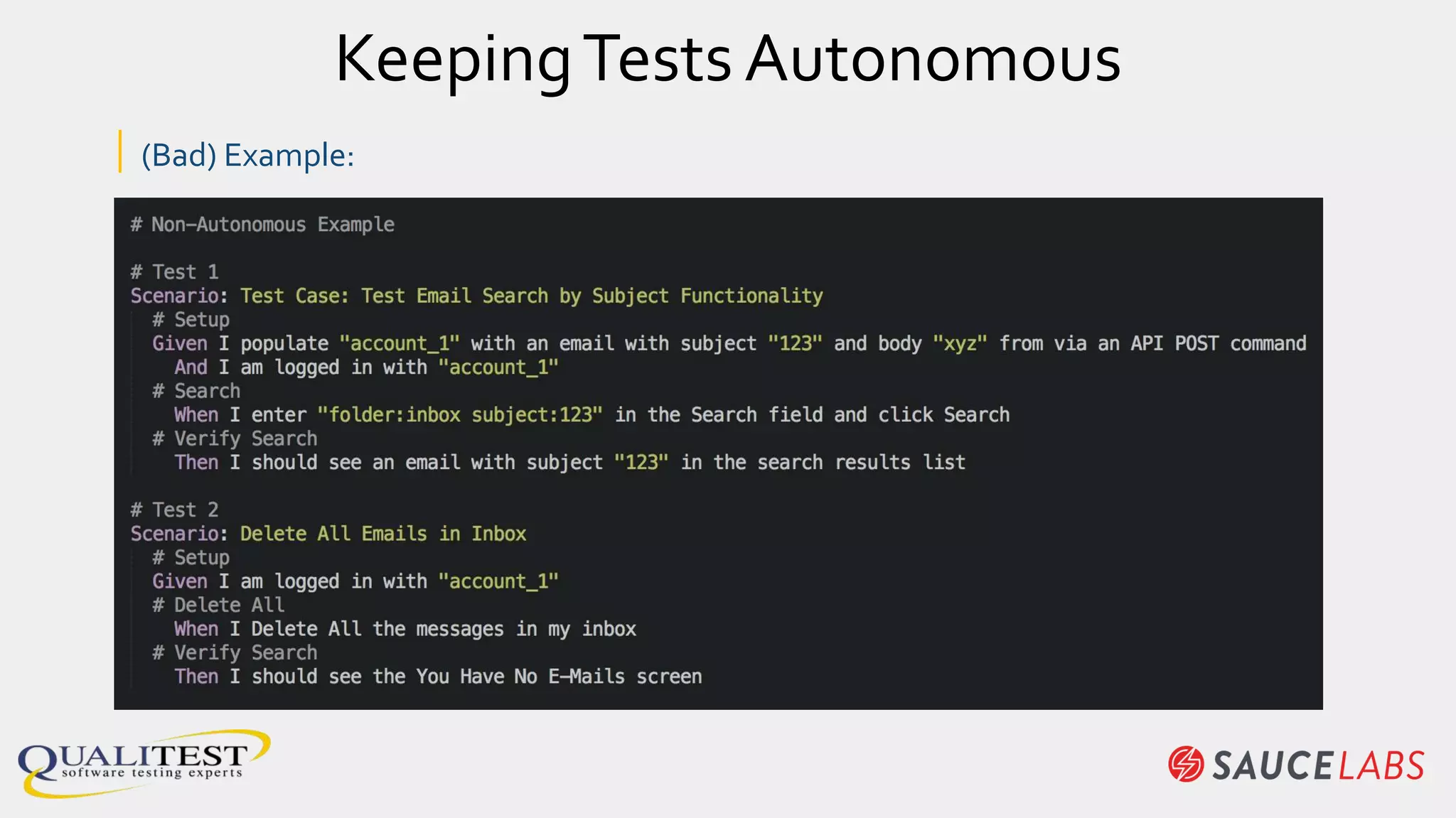
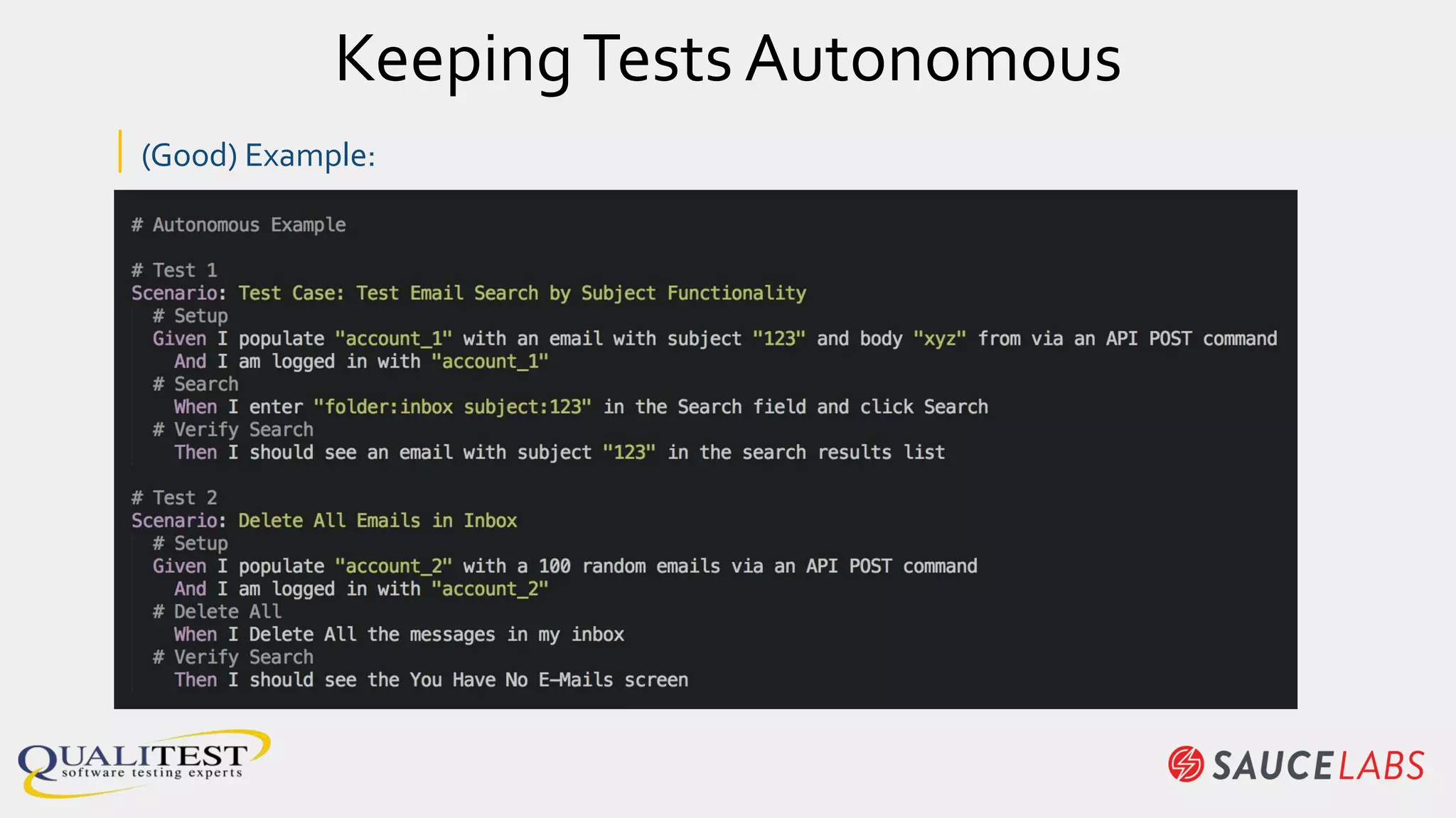
The document discusses the importance of continuous testing and test optimization within software development, emphasizing the need for increased quality and efficiency in testing processes. It highlights the critical role of automation in continuous integration and delivery, risk management, and the implementation of best practices to maintain effective testing environments. Ultimately, the focus is on minimizing business risk through comprehensive test coverage and agile methodologies in a rapidly evolving tech landscape.