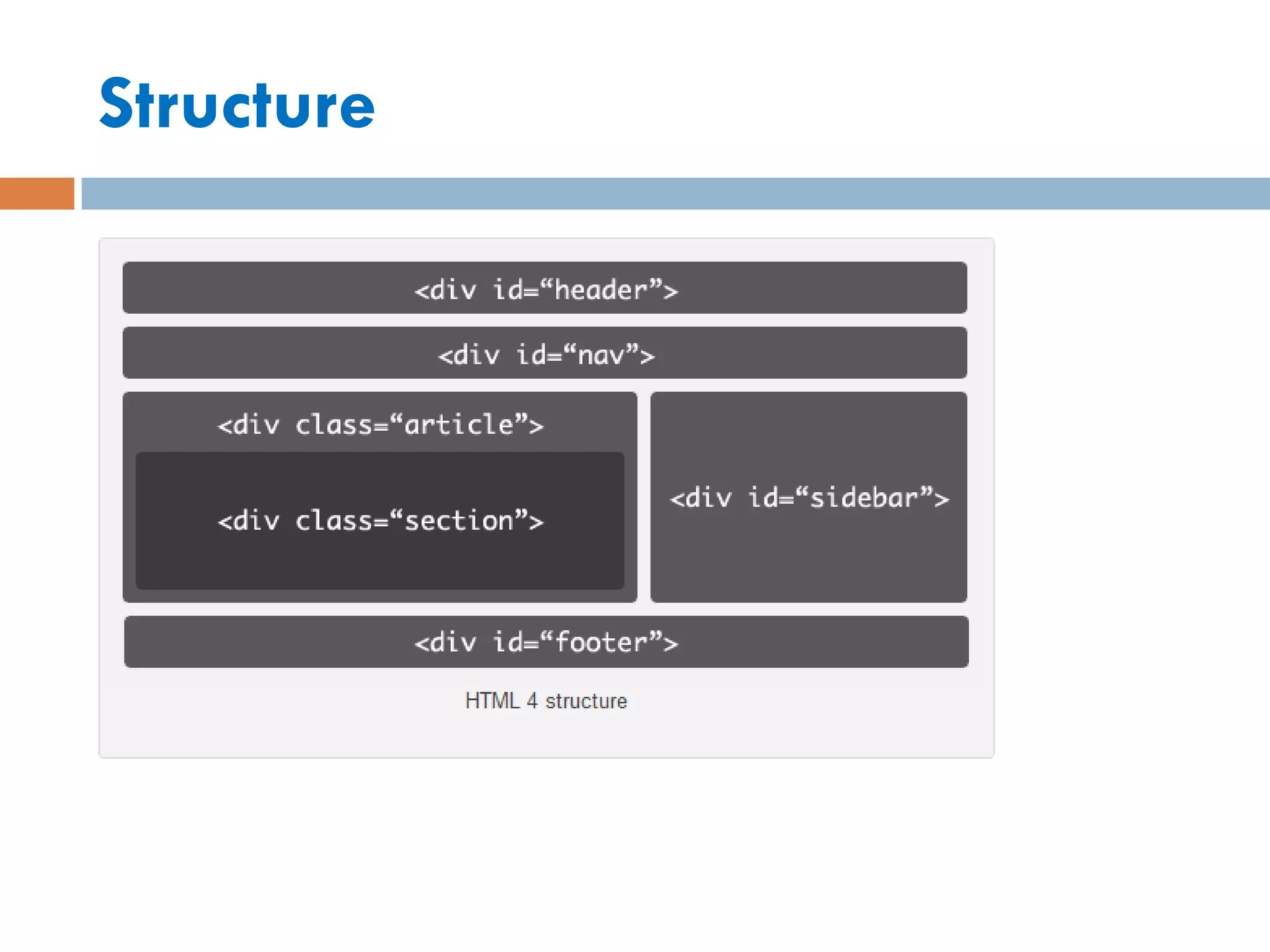
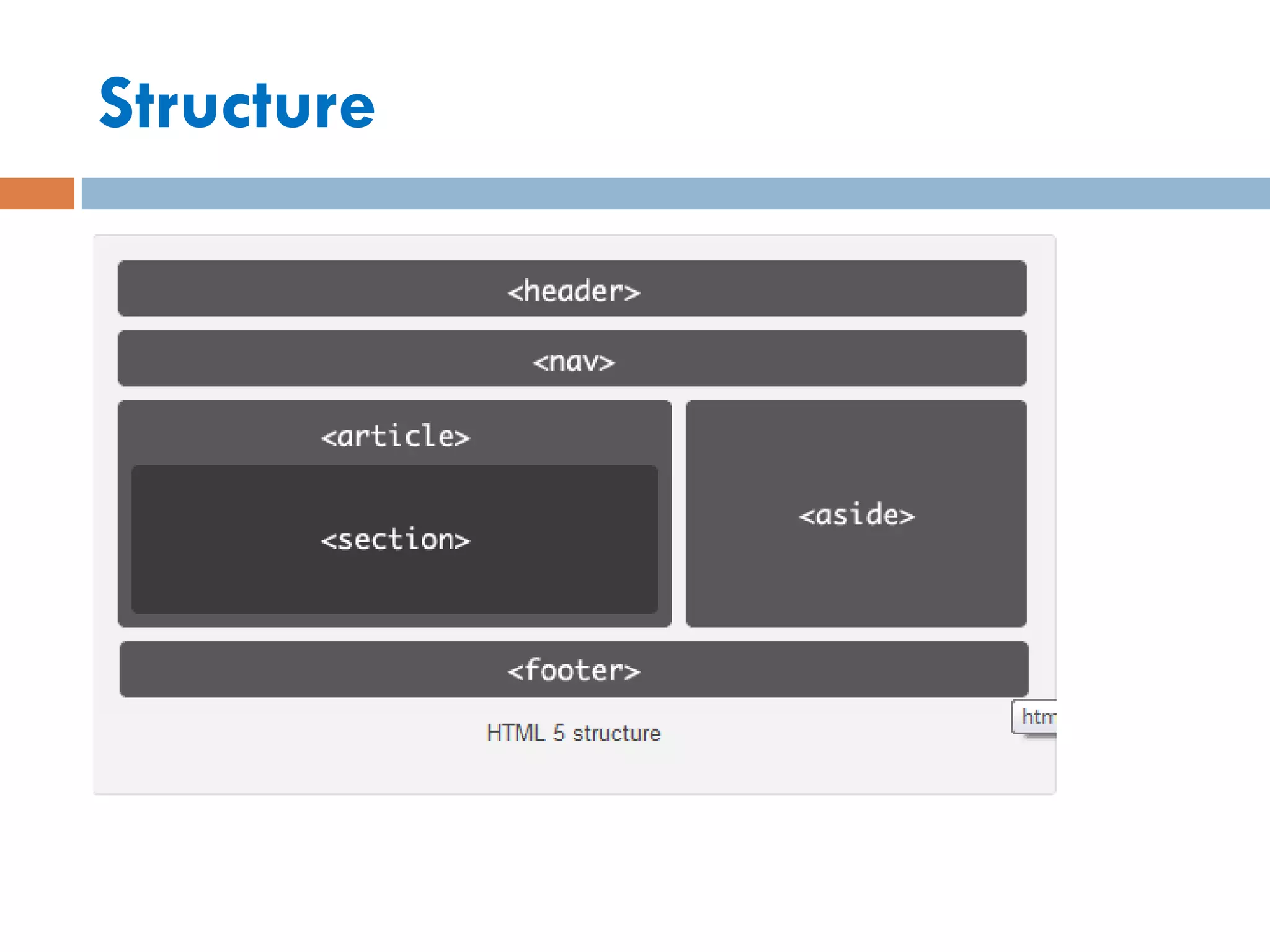
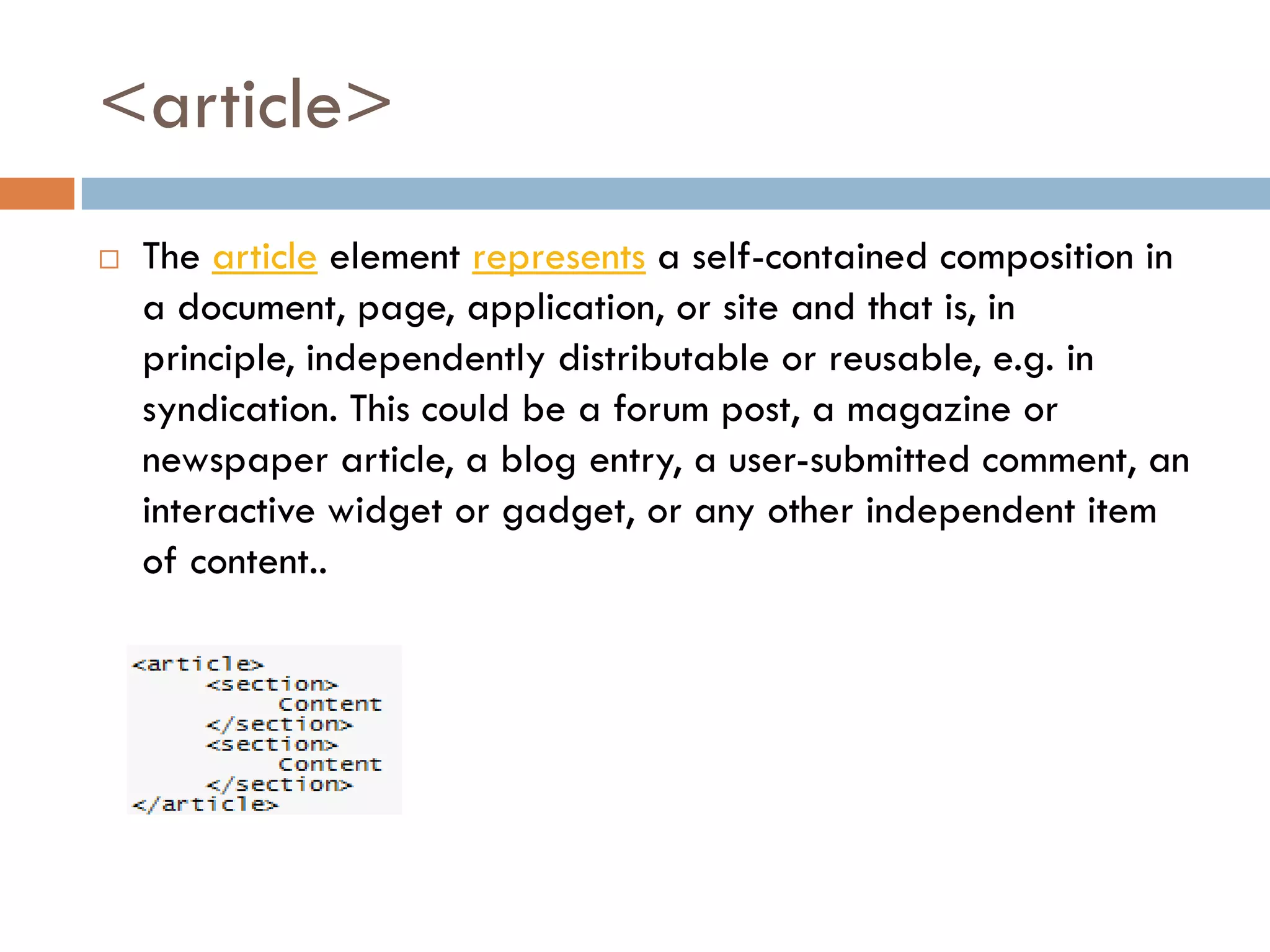
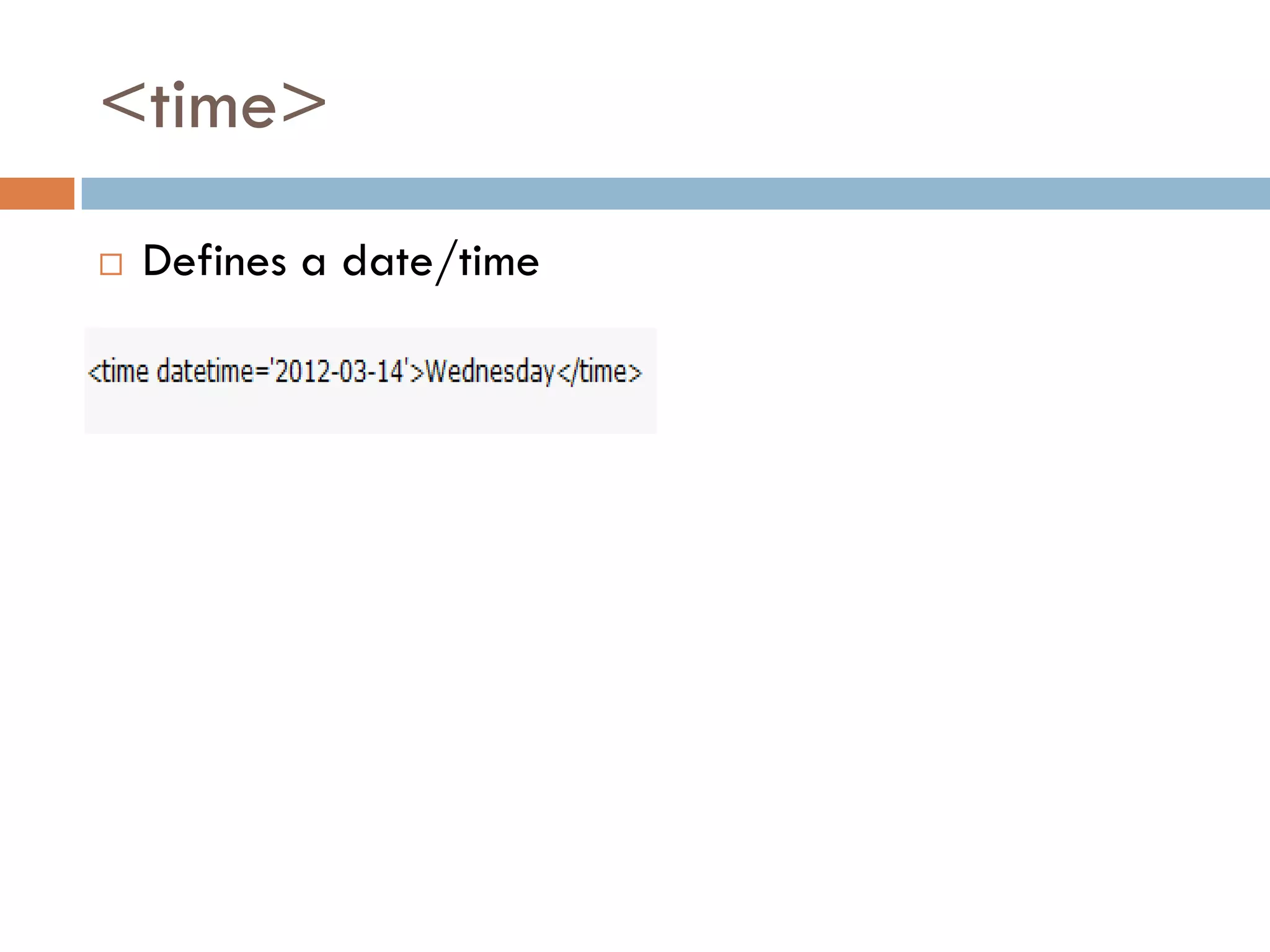
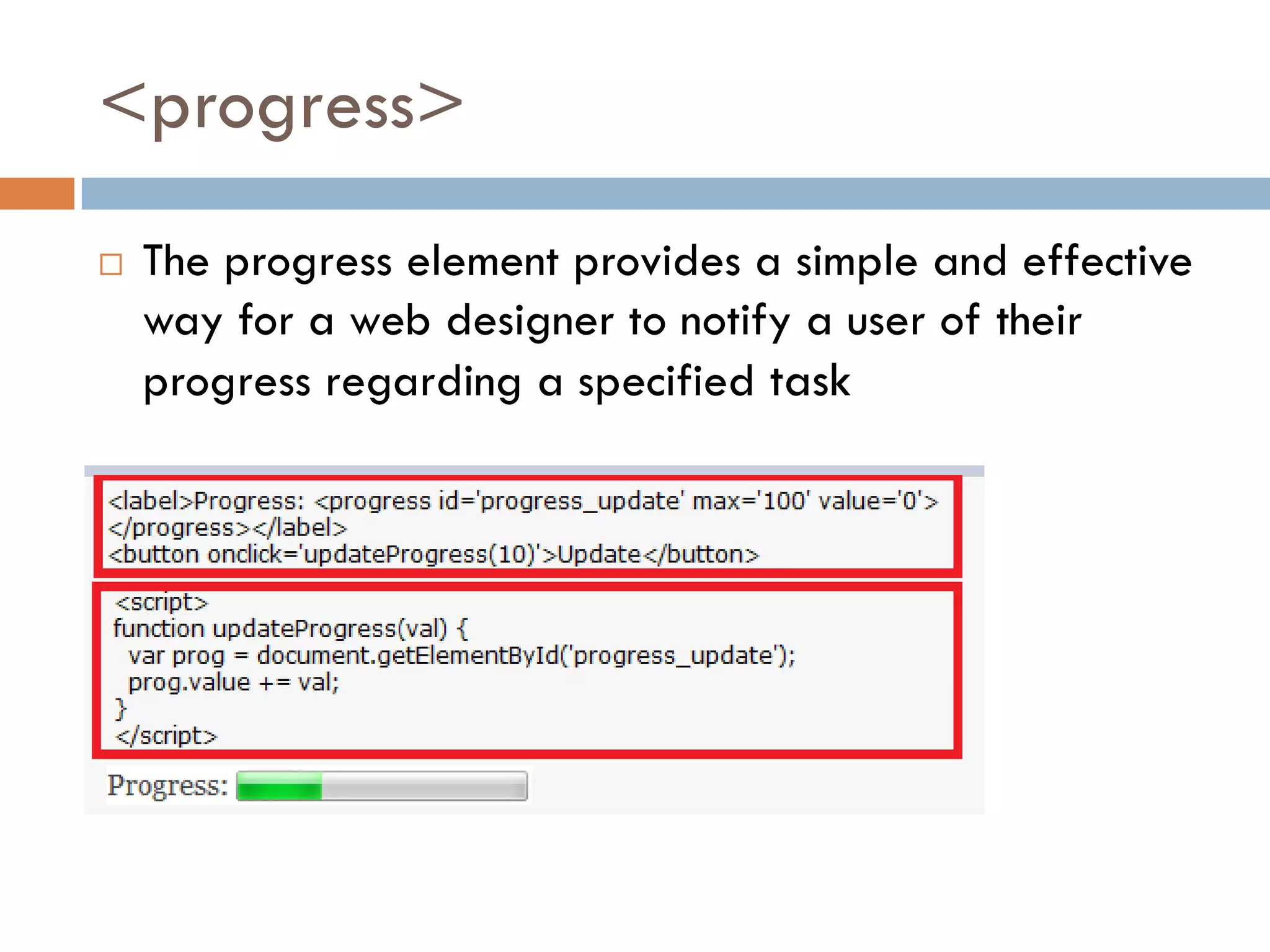
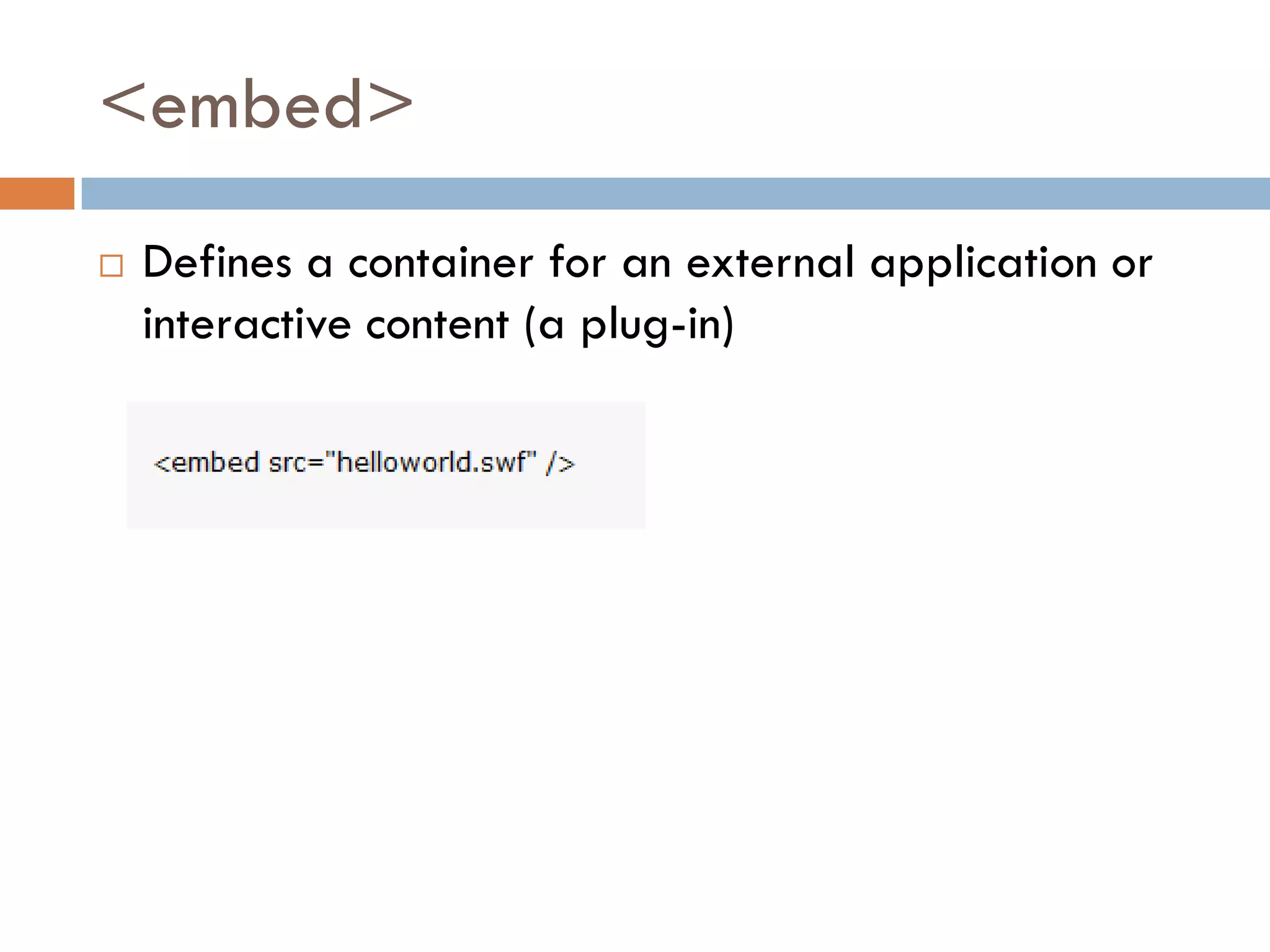
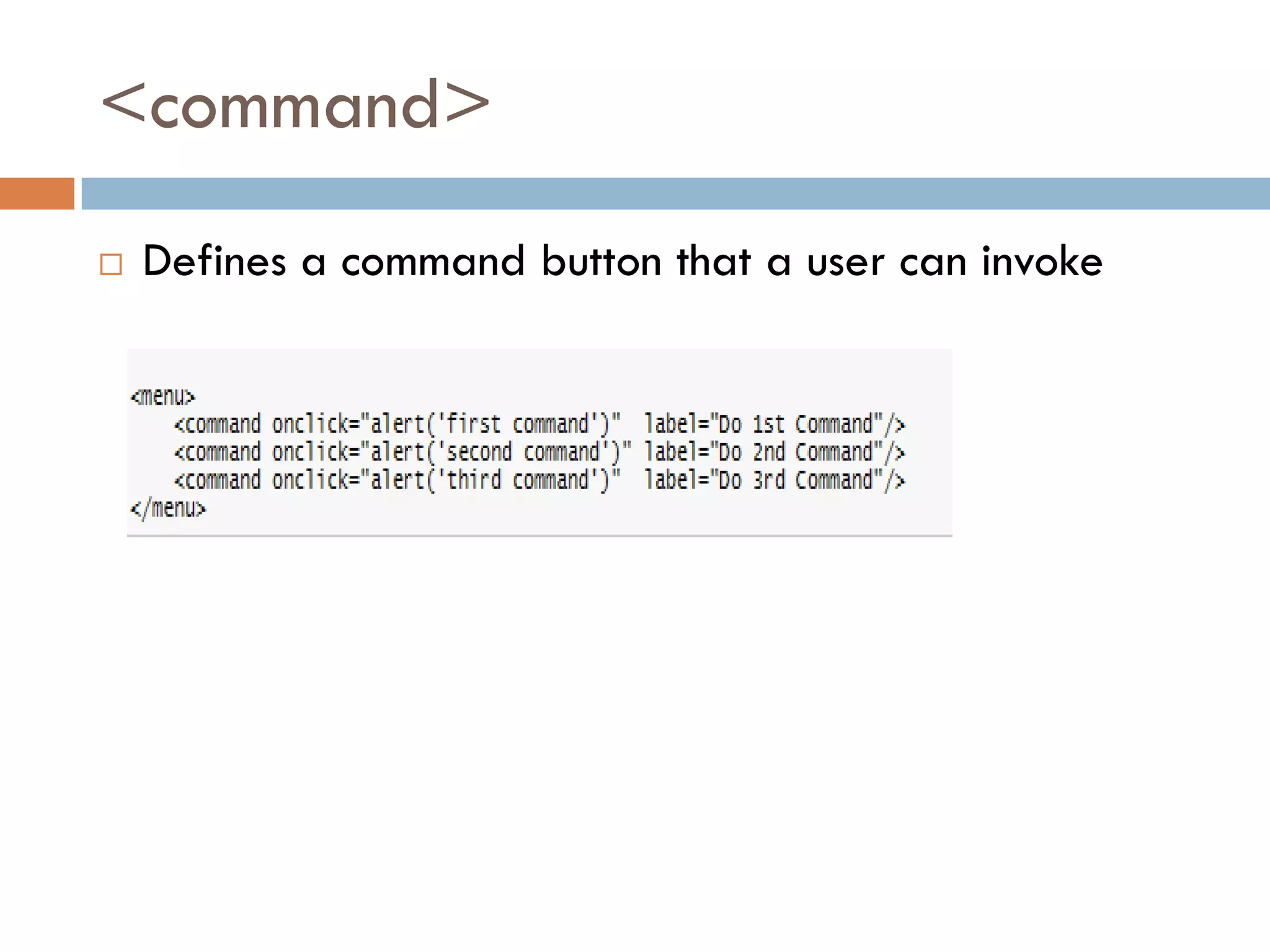
This document discusses the structure and semantic elements in HTML5. It describes elements such as <section>, <header>, <article>, and <nav> that define different sections of a web page. It also covers inline elements like <mark> and <time> as well as embedded media elements <audio> and <video>. Finally, it discusses interactive elements such as <details> and <menu> and concludes with a demonstration of HTML5 structure and semantics.