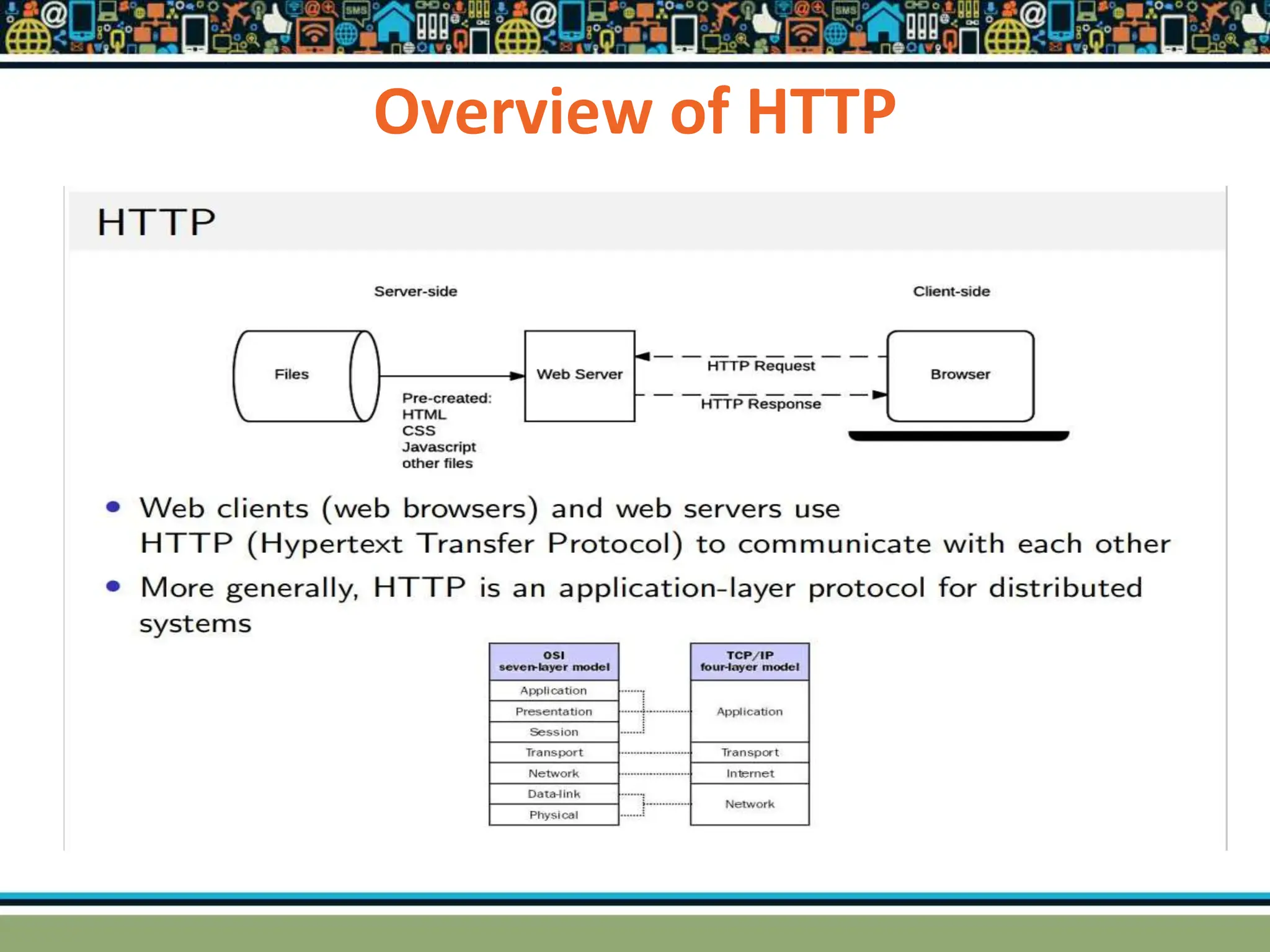
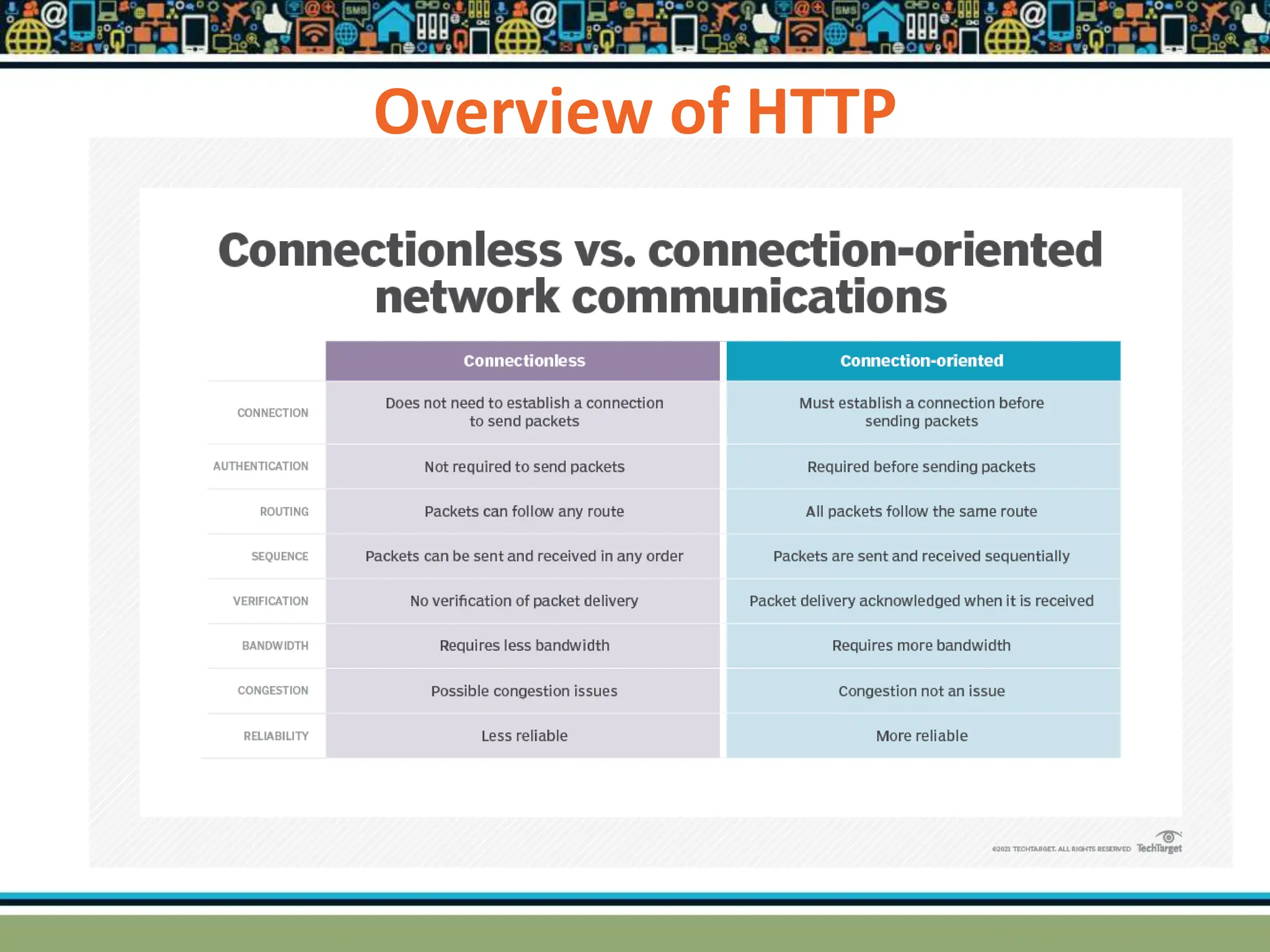
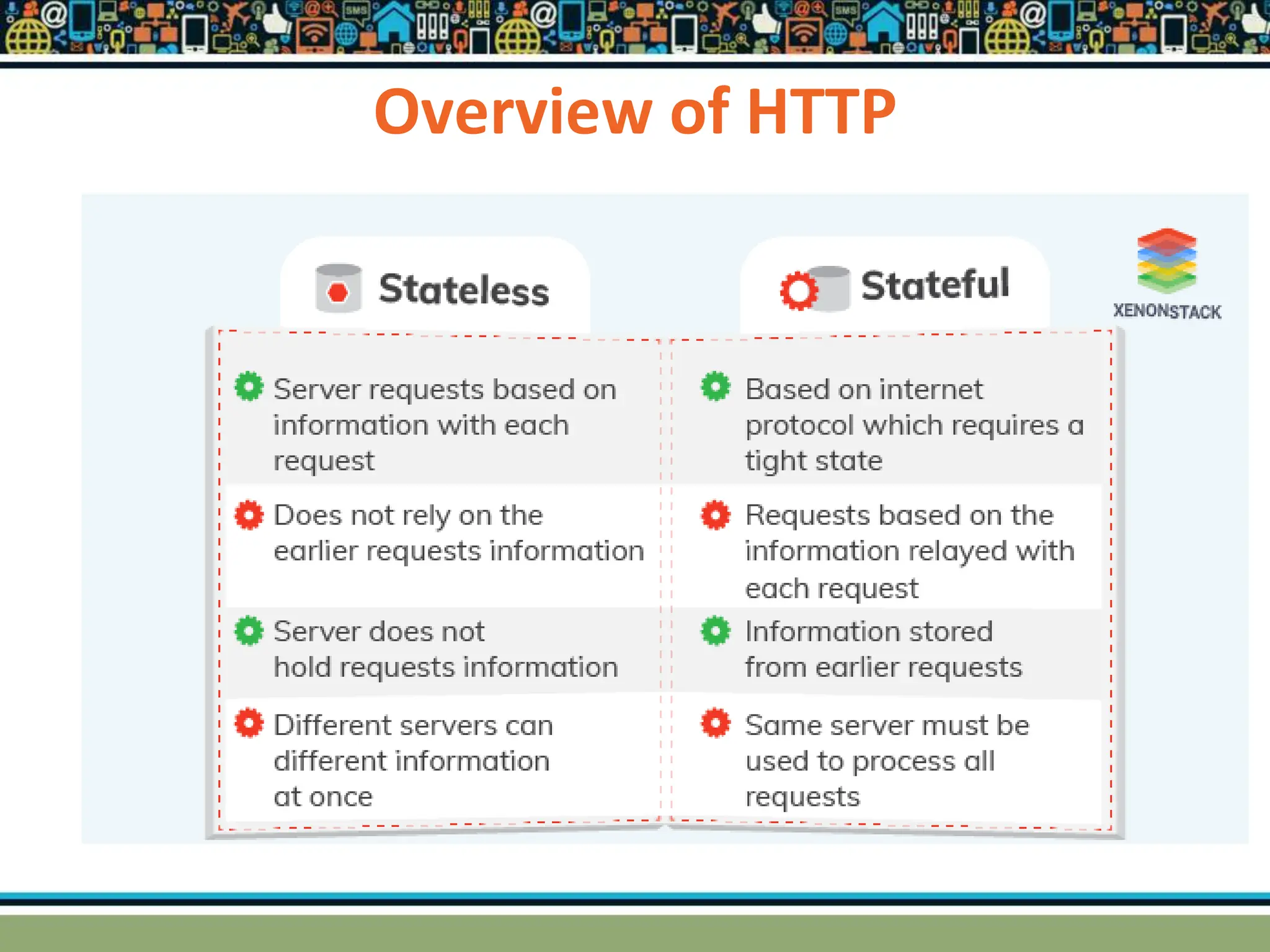
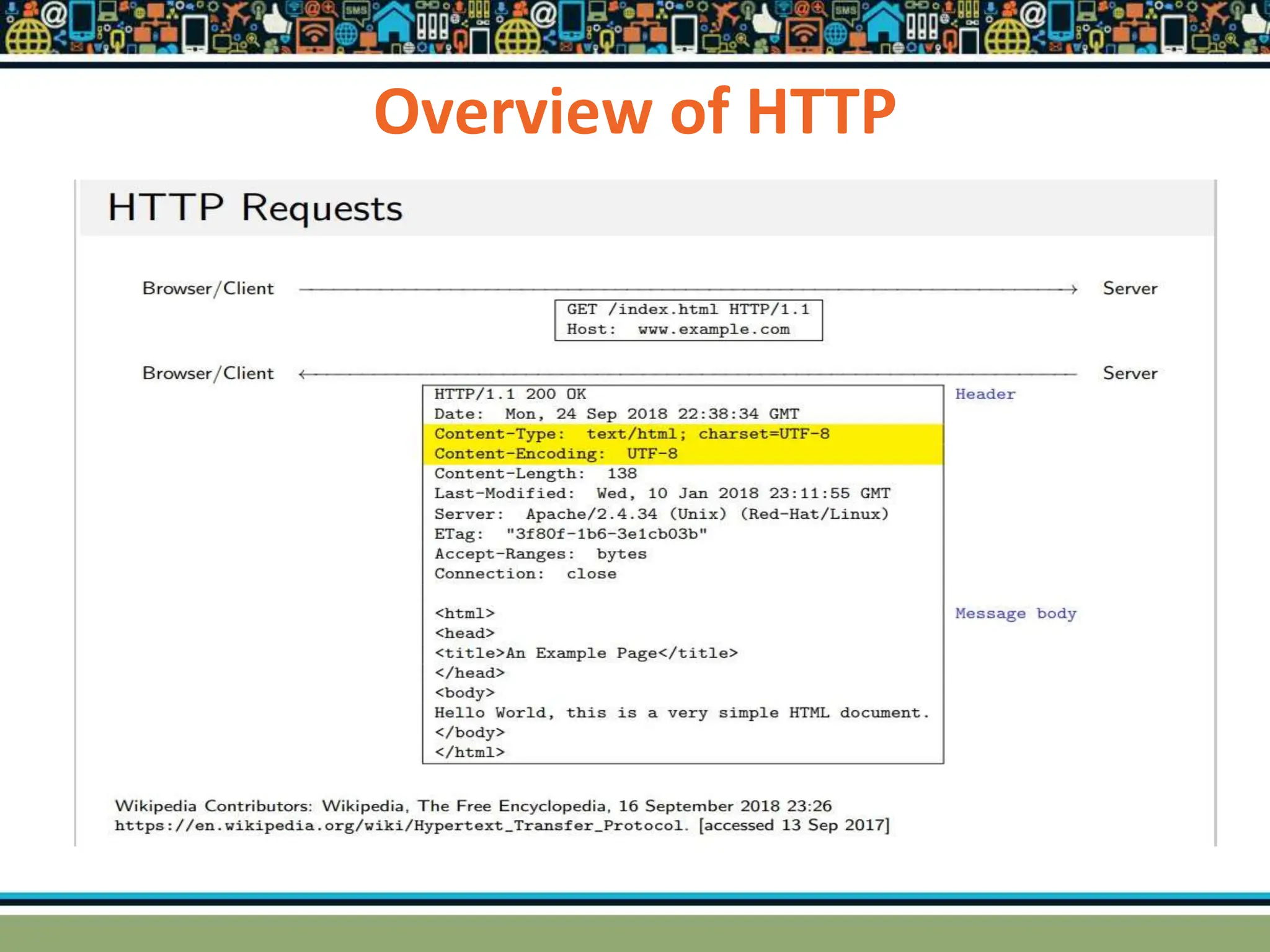
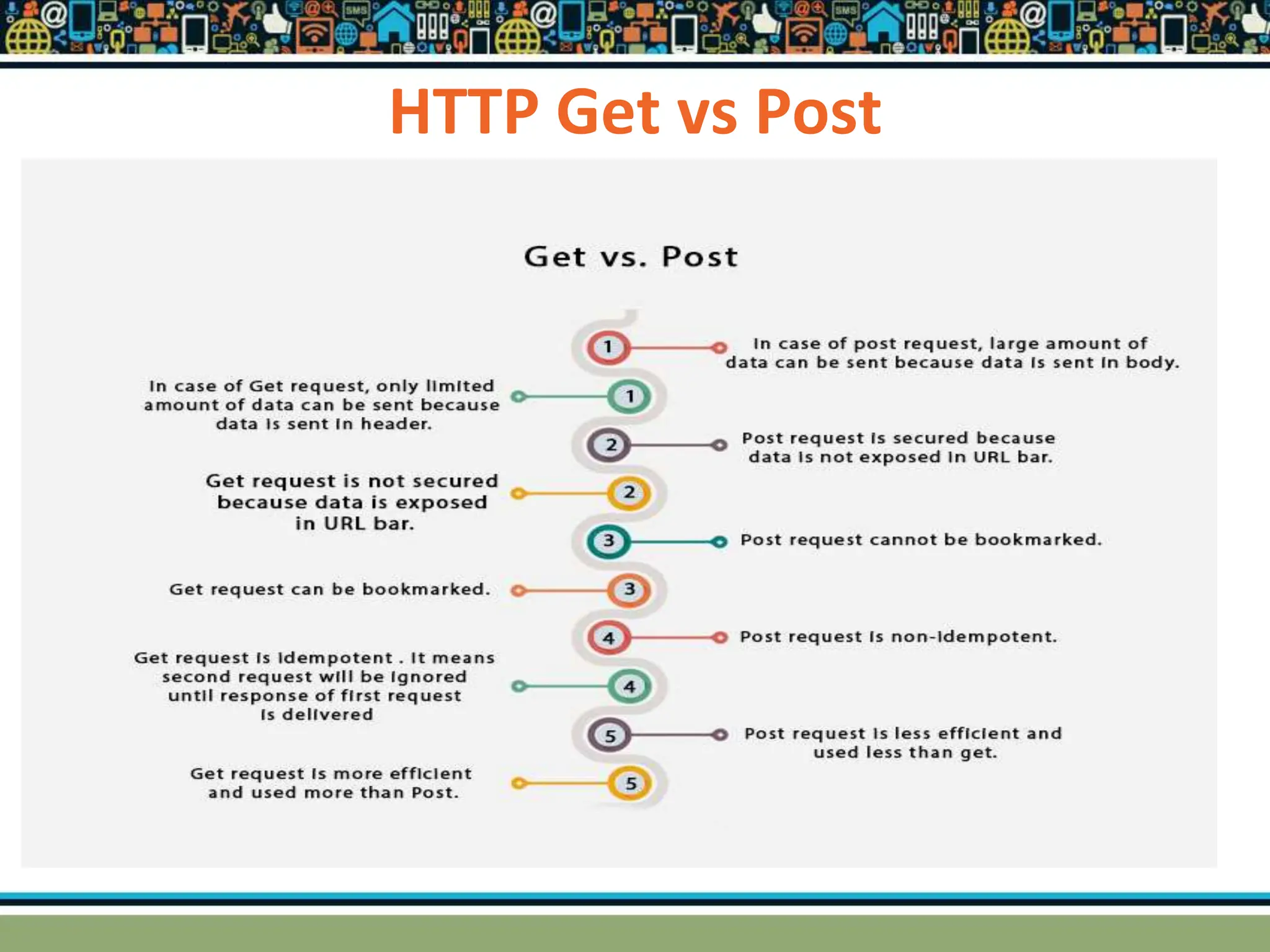
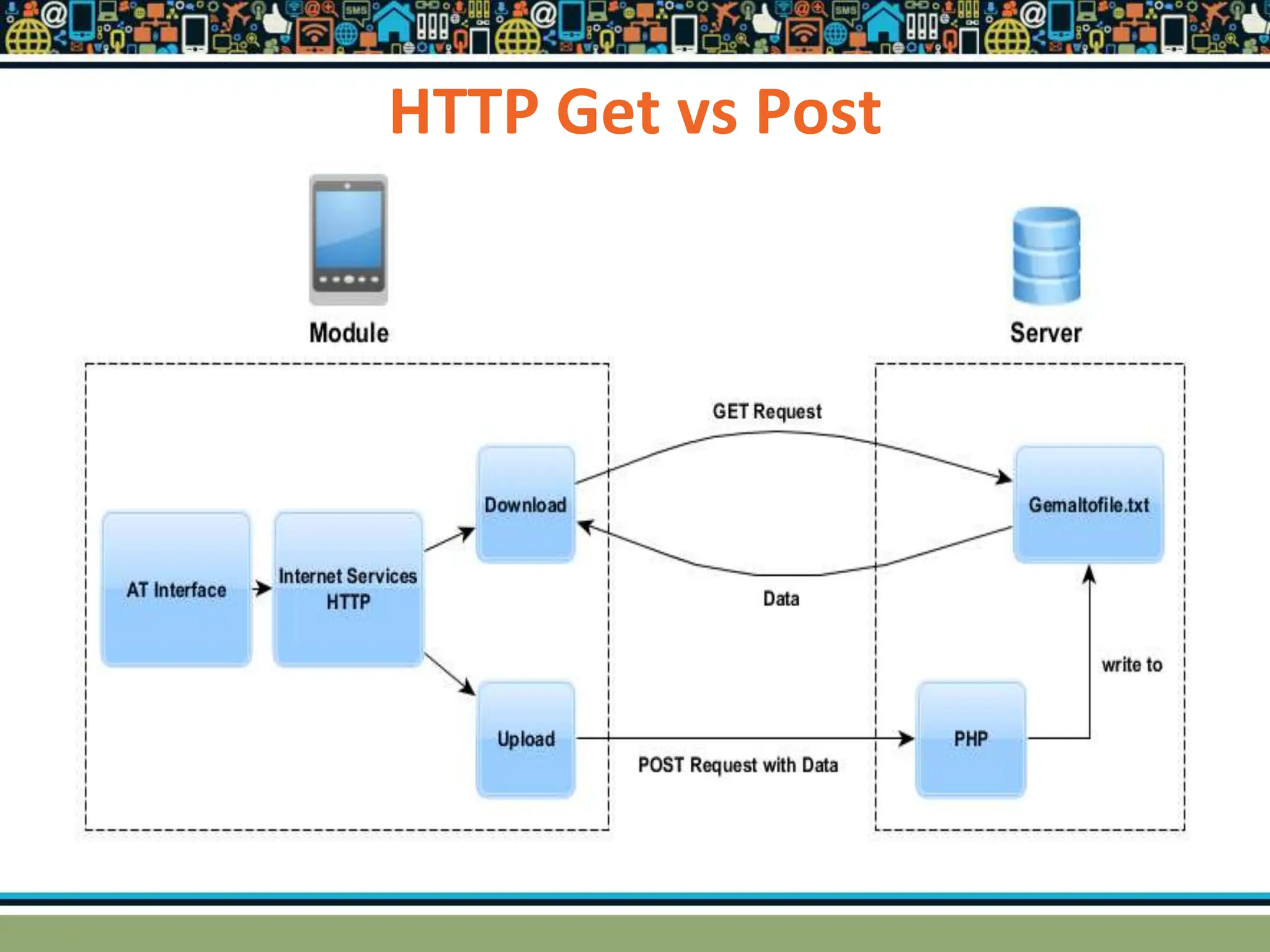
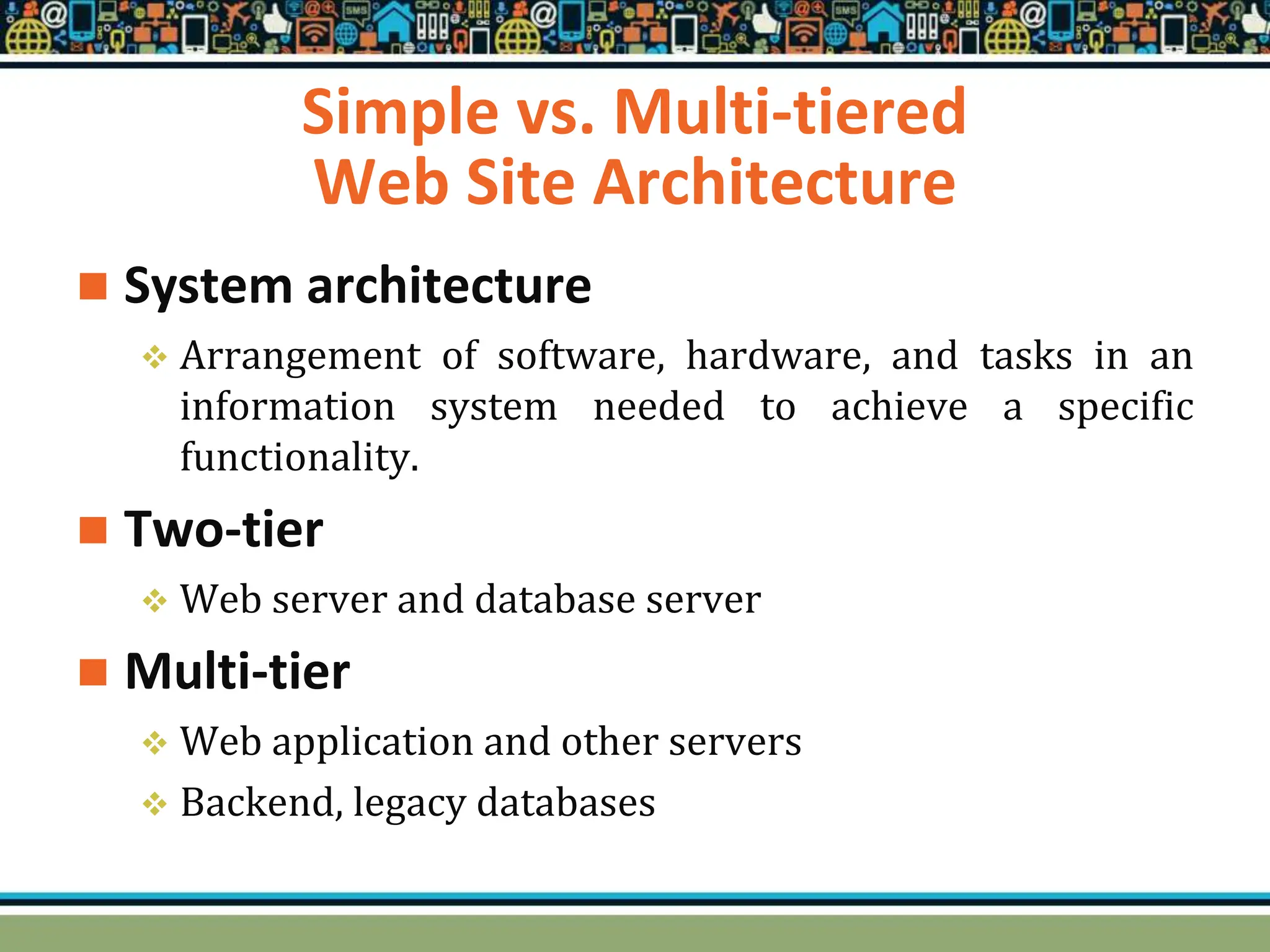
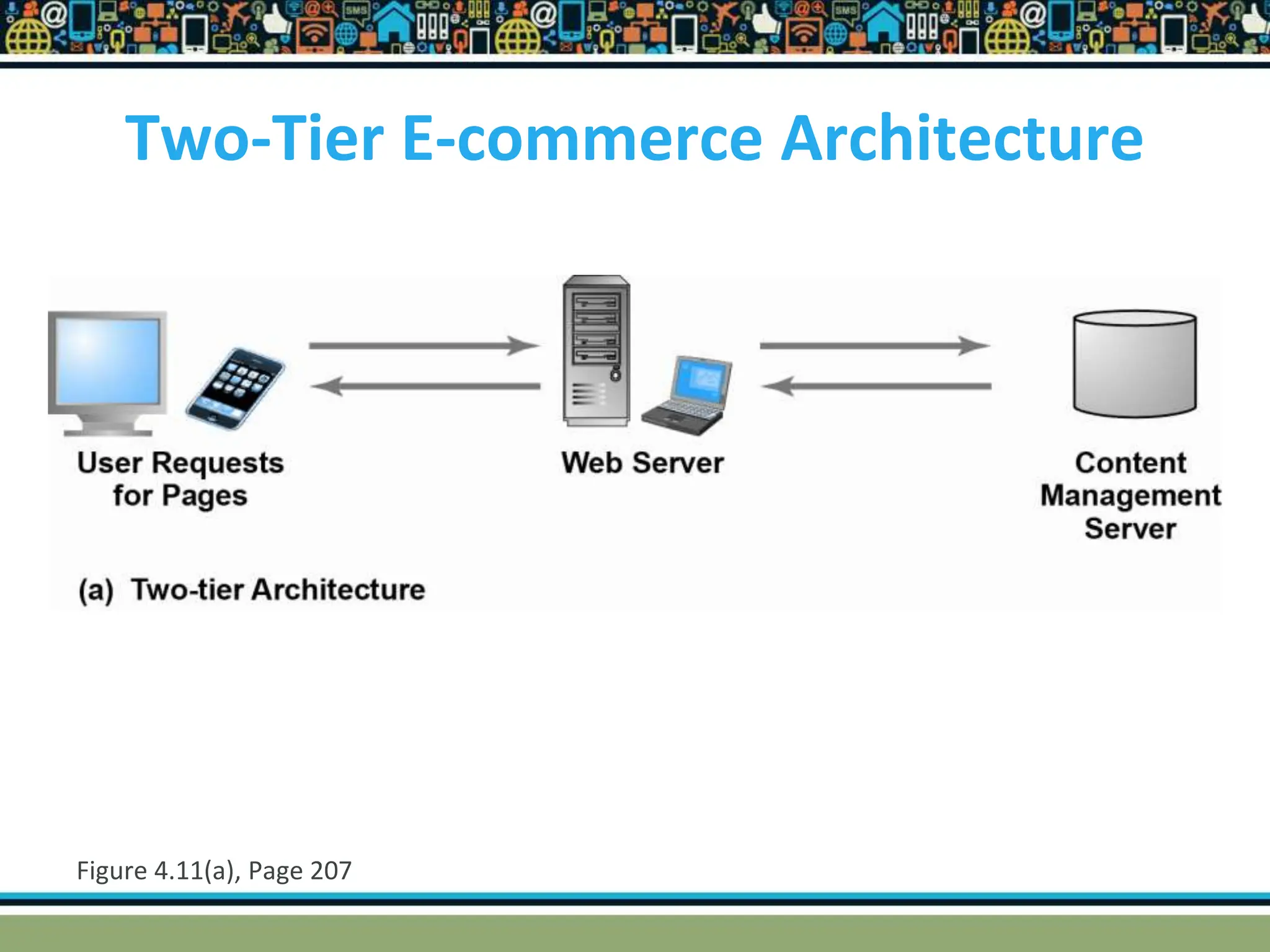
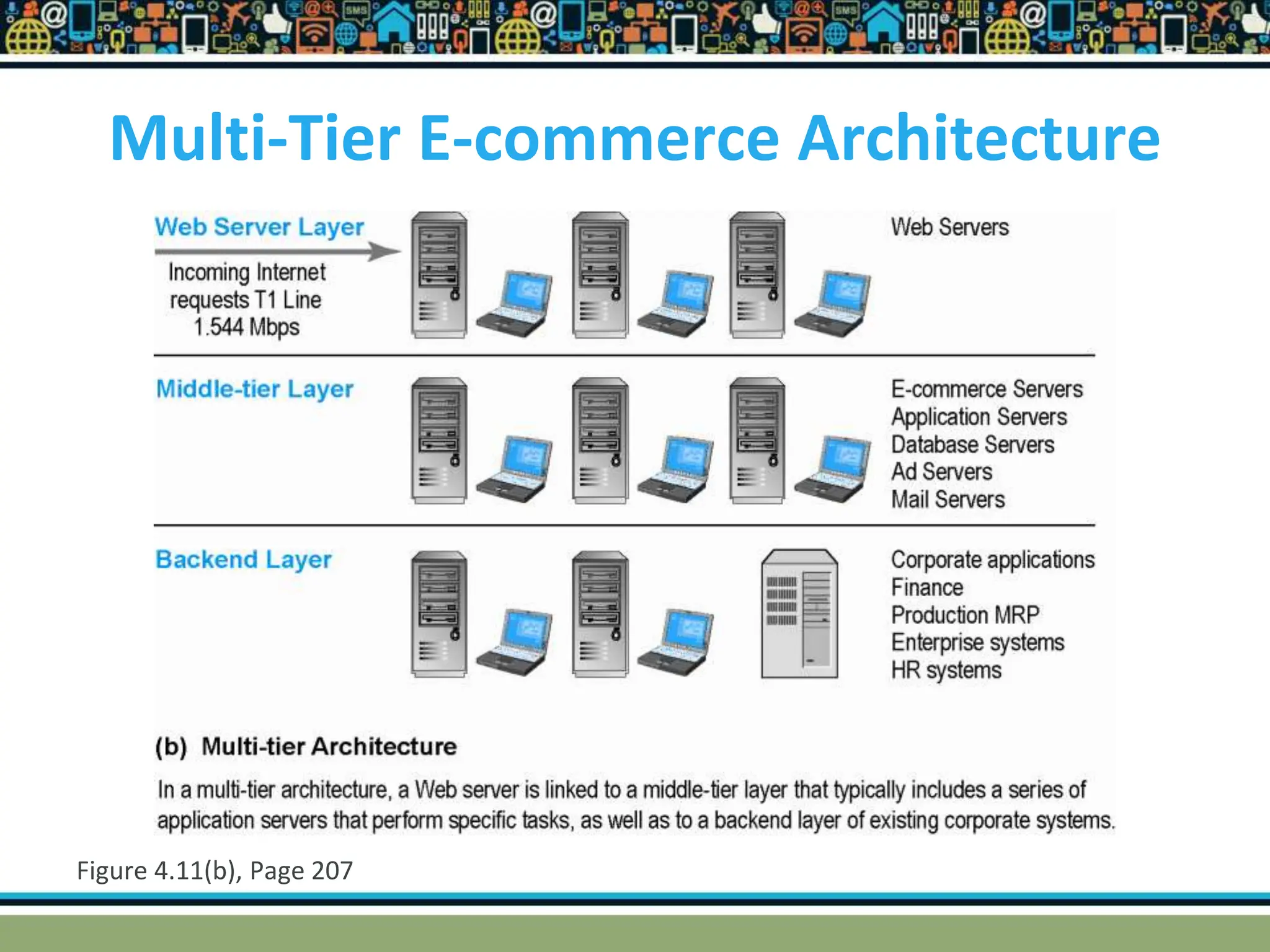
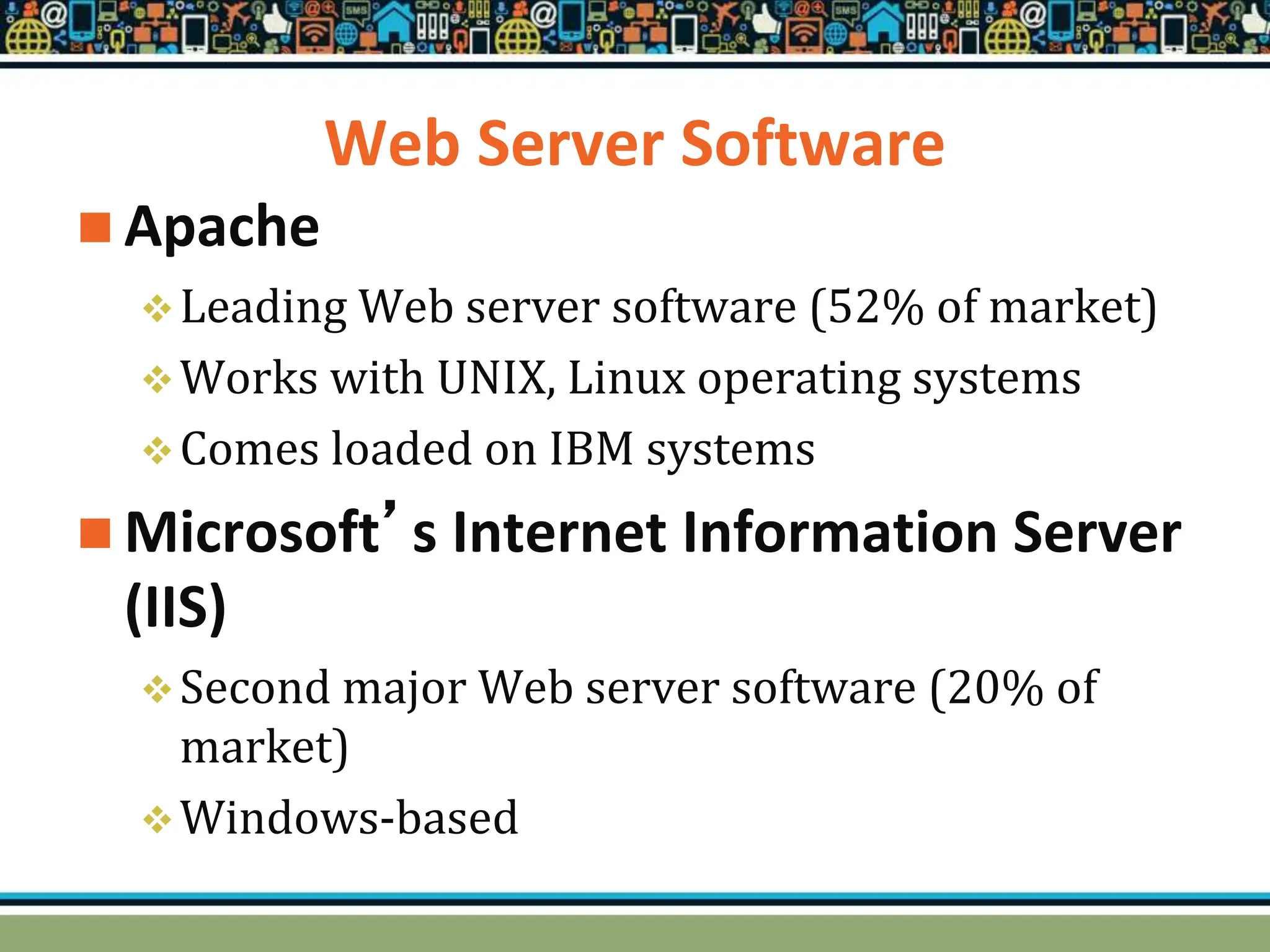
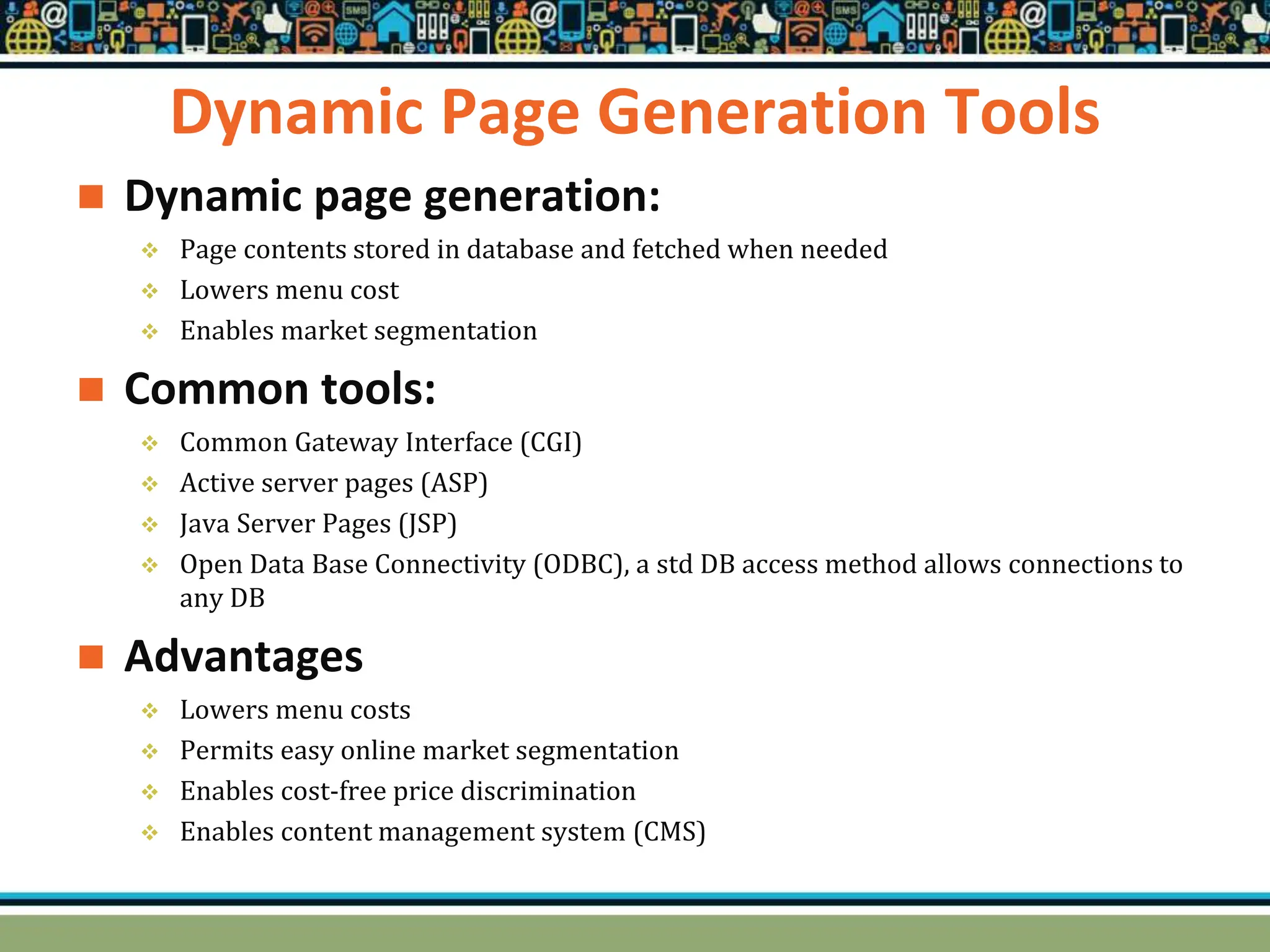
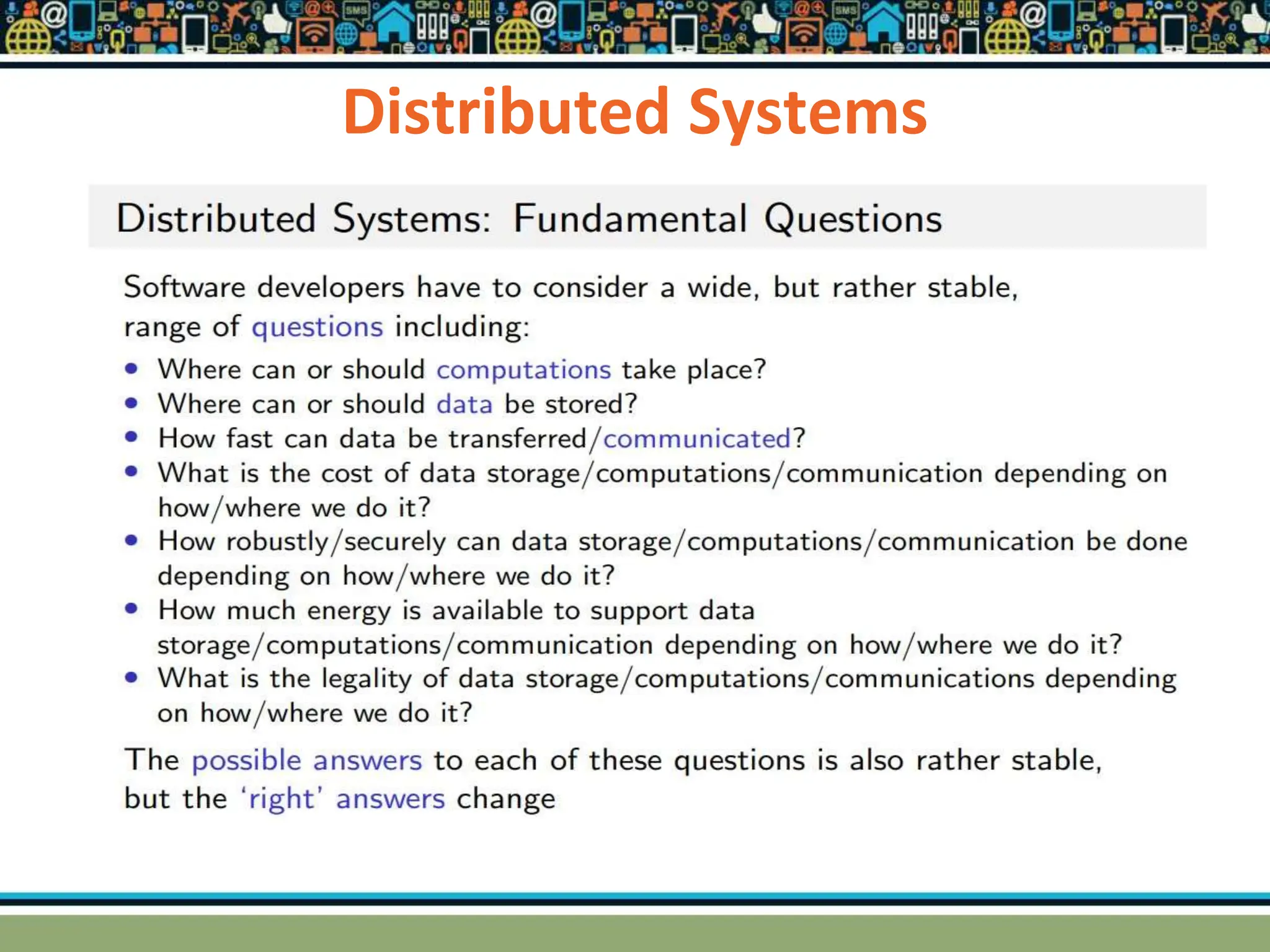
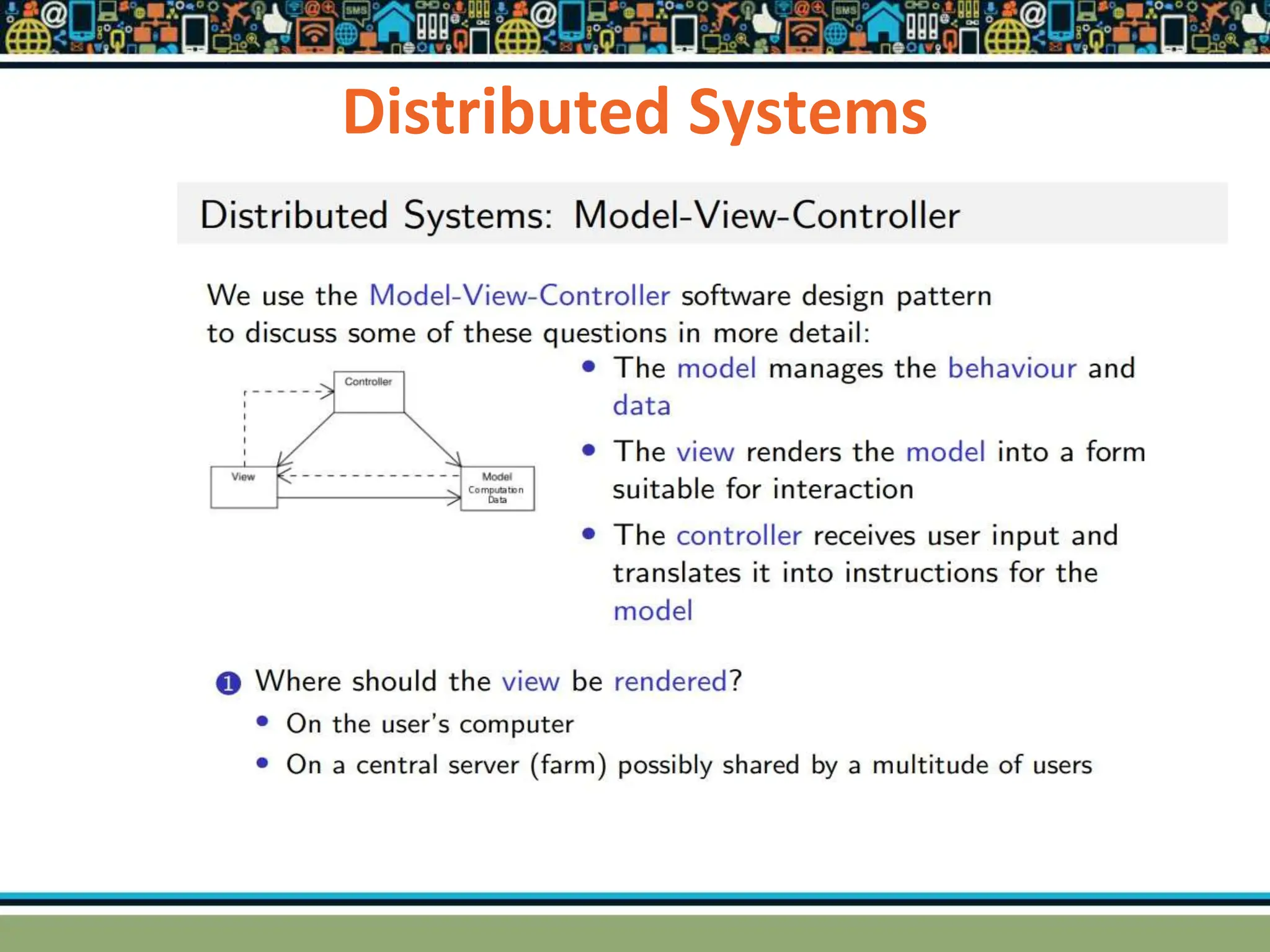
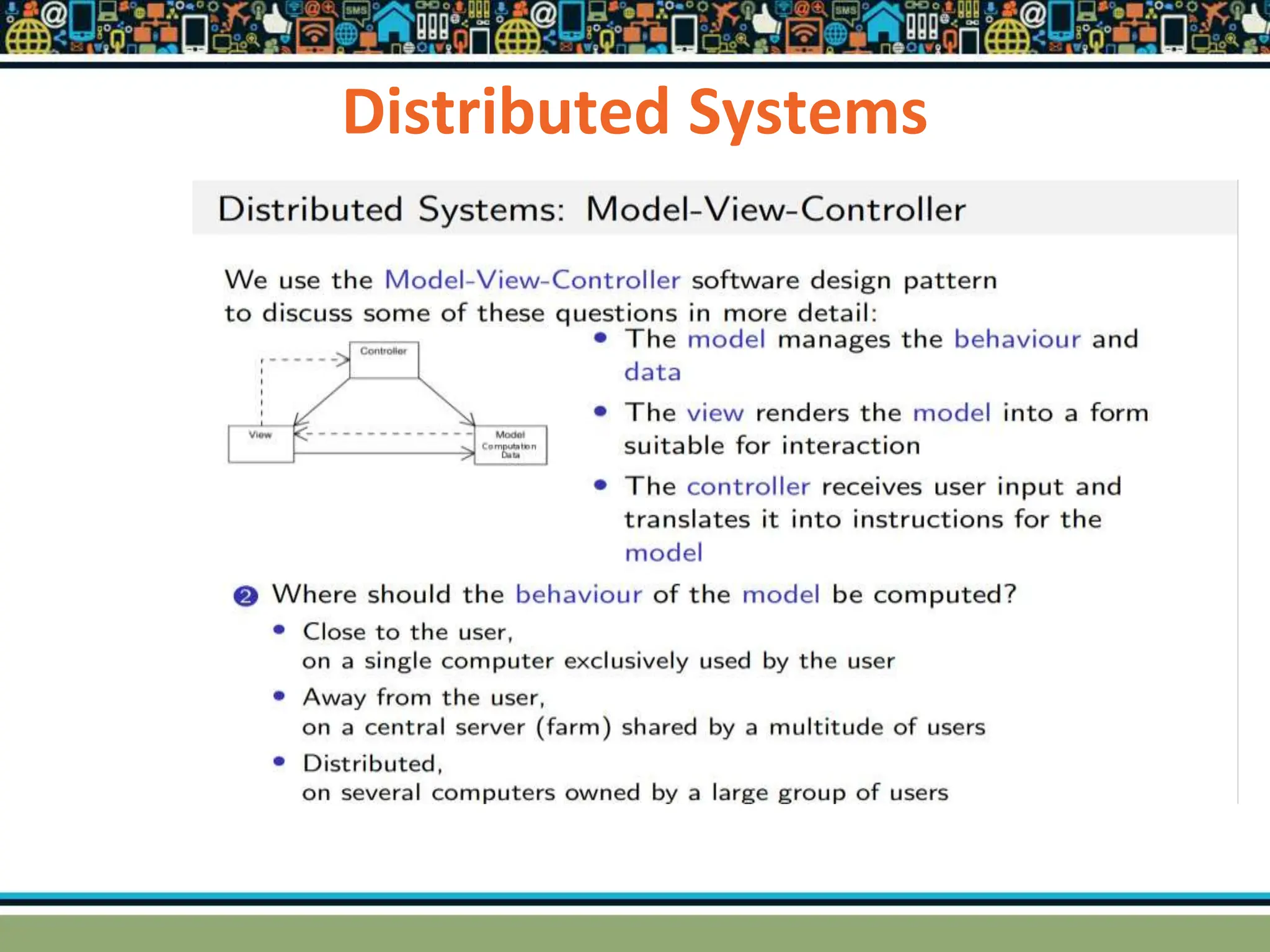
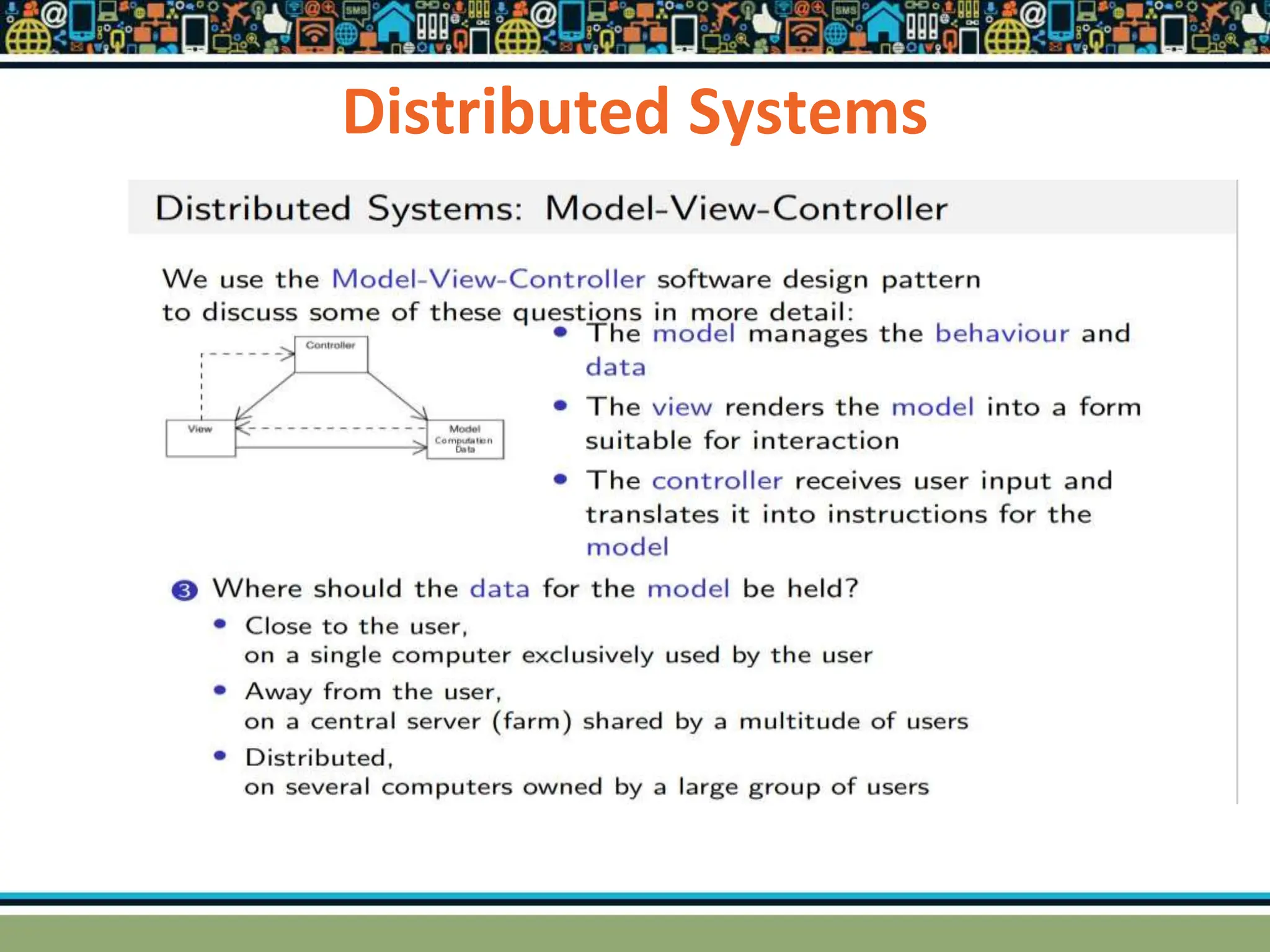
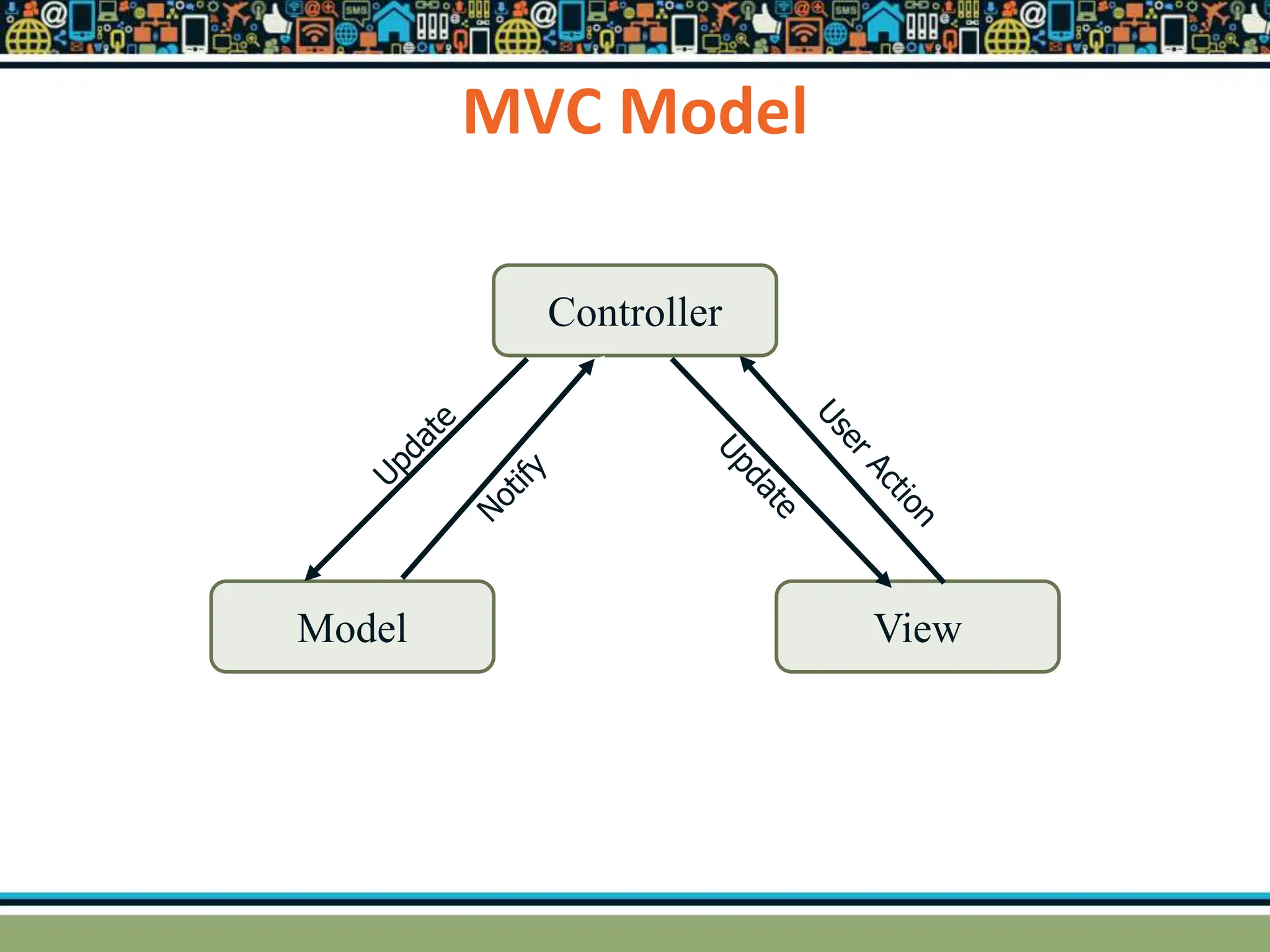
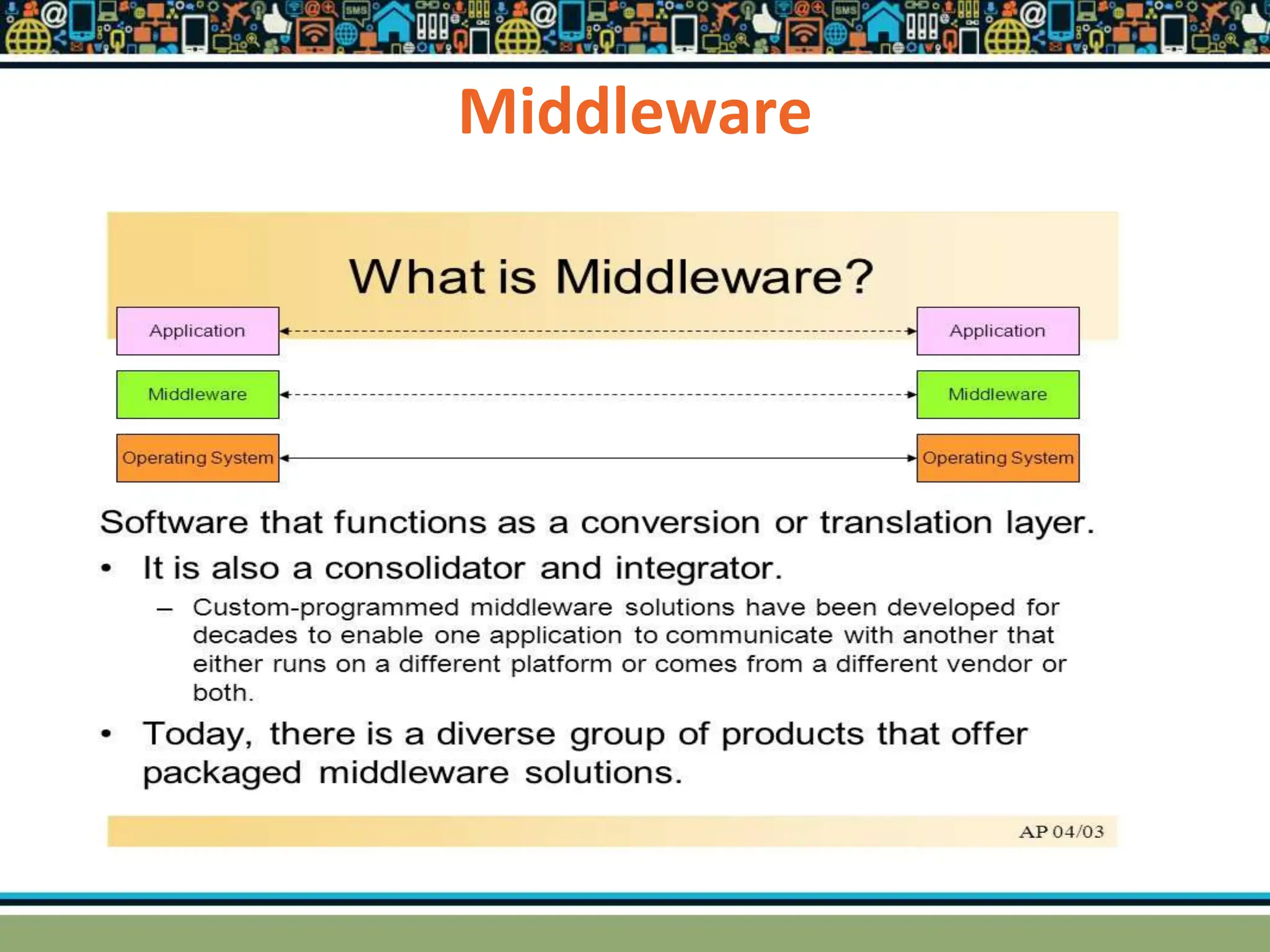
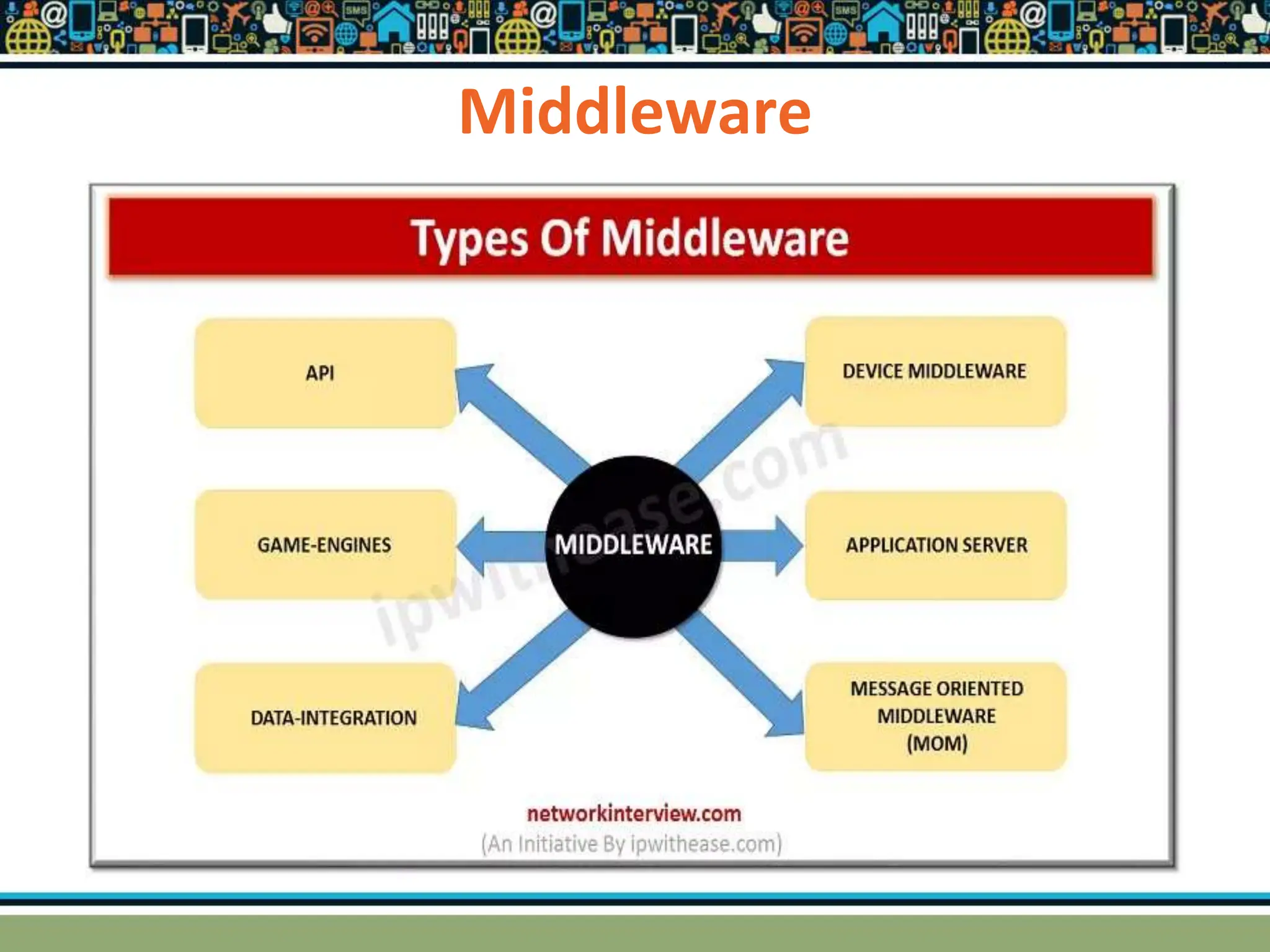
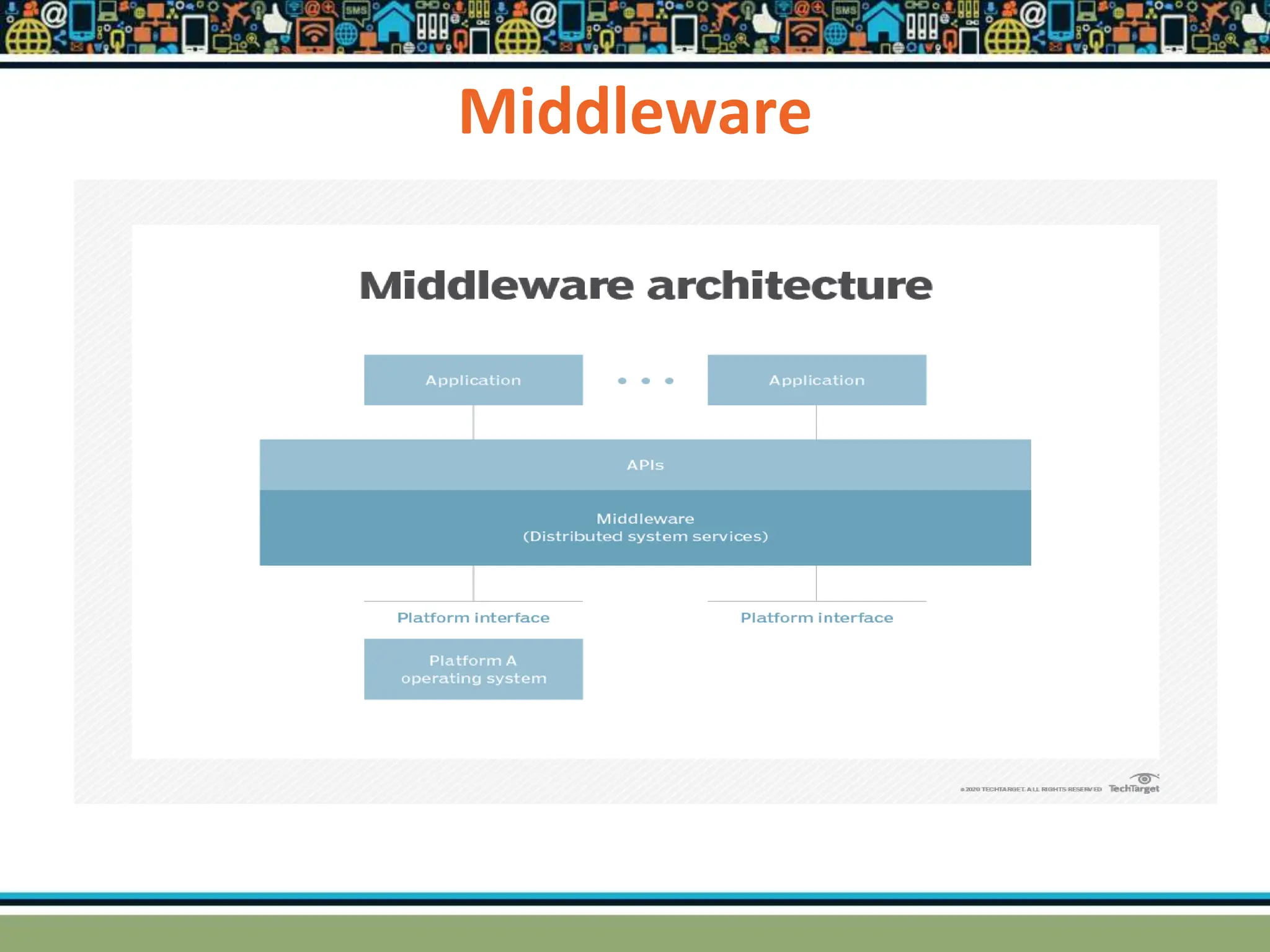
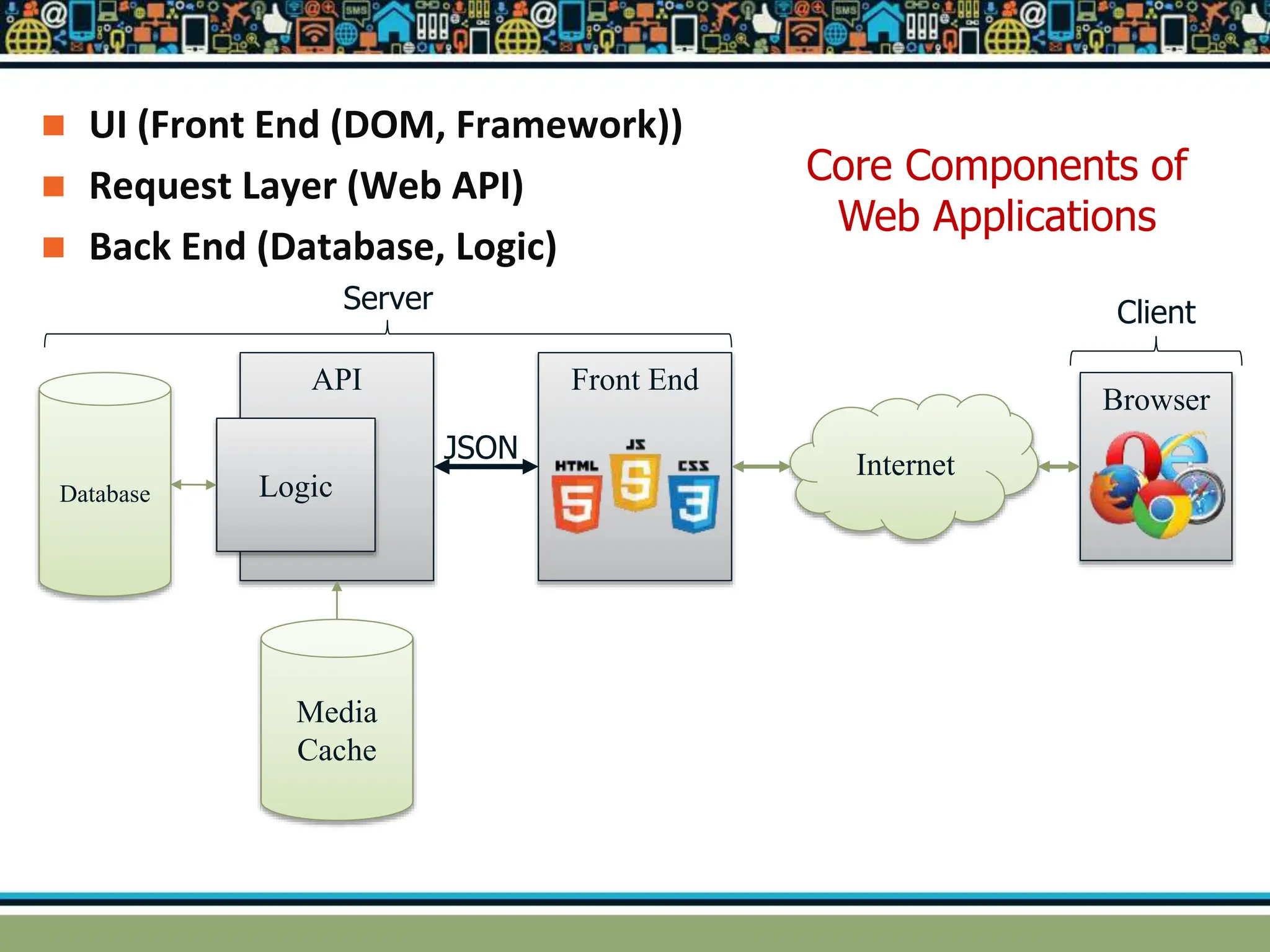
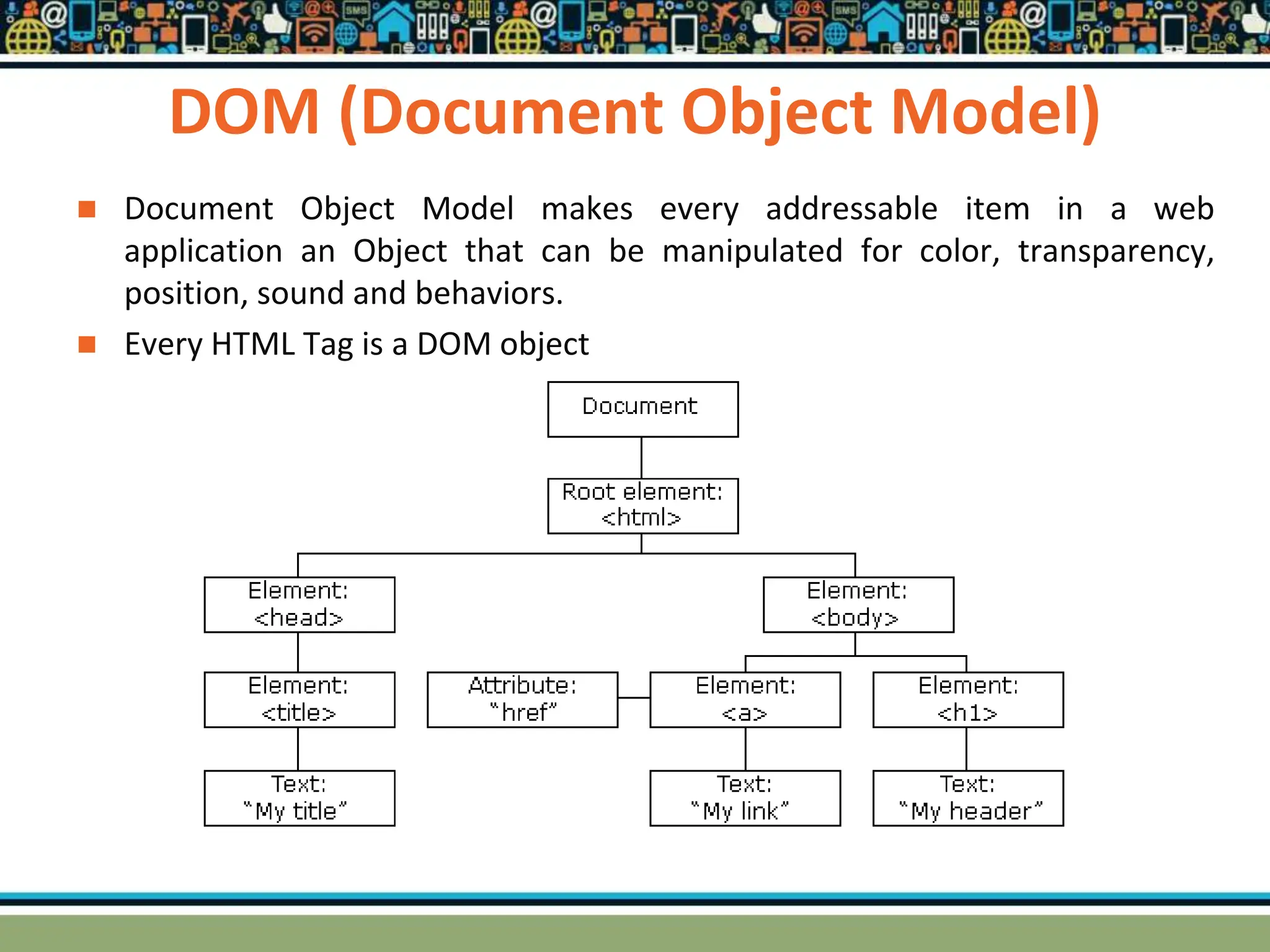
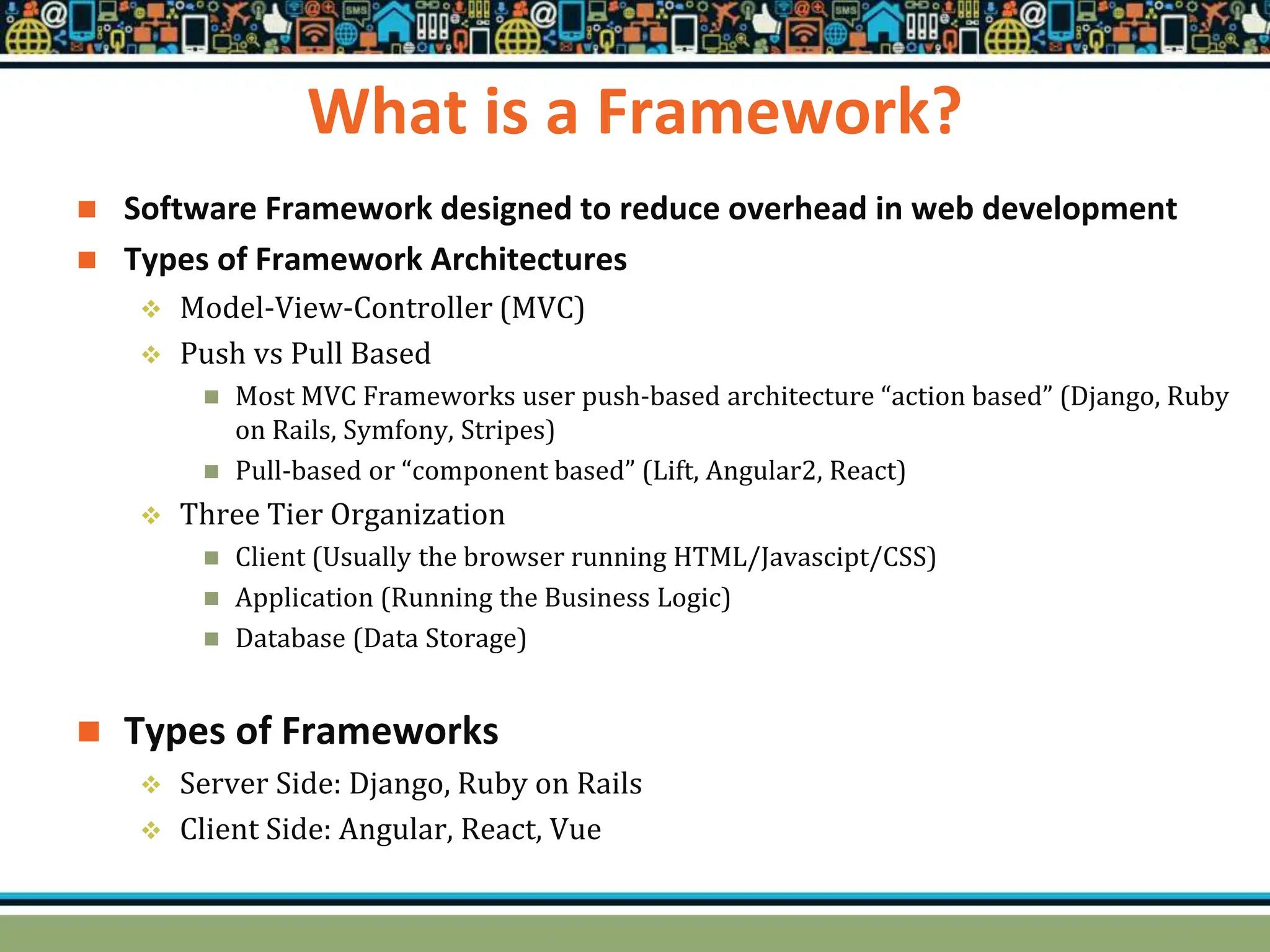
HTTP is a TCP/IP based communication protocol used to deliver web content. It provides a standardized way for computers to communicate requests and responses. HTTP is connectionless, media independent, and stateless. Server-side programming processes user input, compiles pages, structures applications, and interacts with storage. Common server-side languages include PHP, Python, and ASP.Net. Client-side programming makes webpages interactive and allows interaction with temporary storage. Common client-side languages are JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. Web architectures can be simple/two-tier with a web and database server, or multi-tier with additional servers and legacy databases. Popular web servers are Apache and IIS. Dynamic page generation lowers costs and