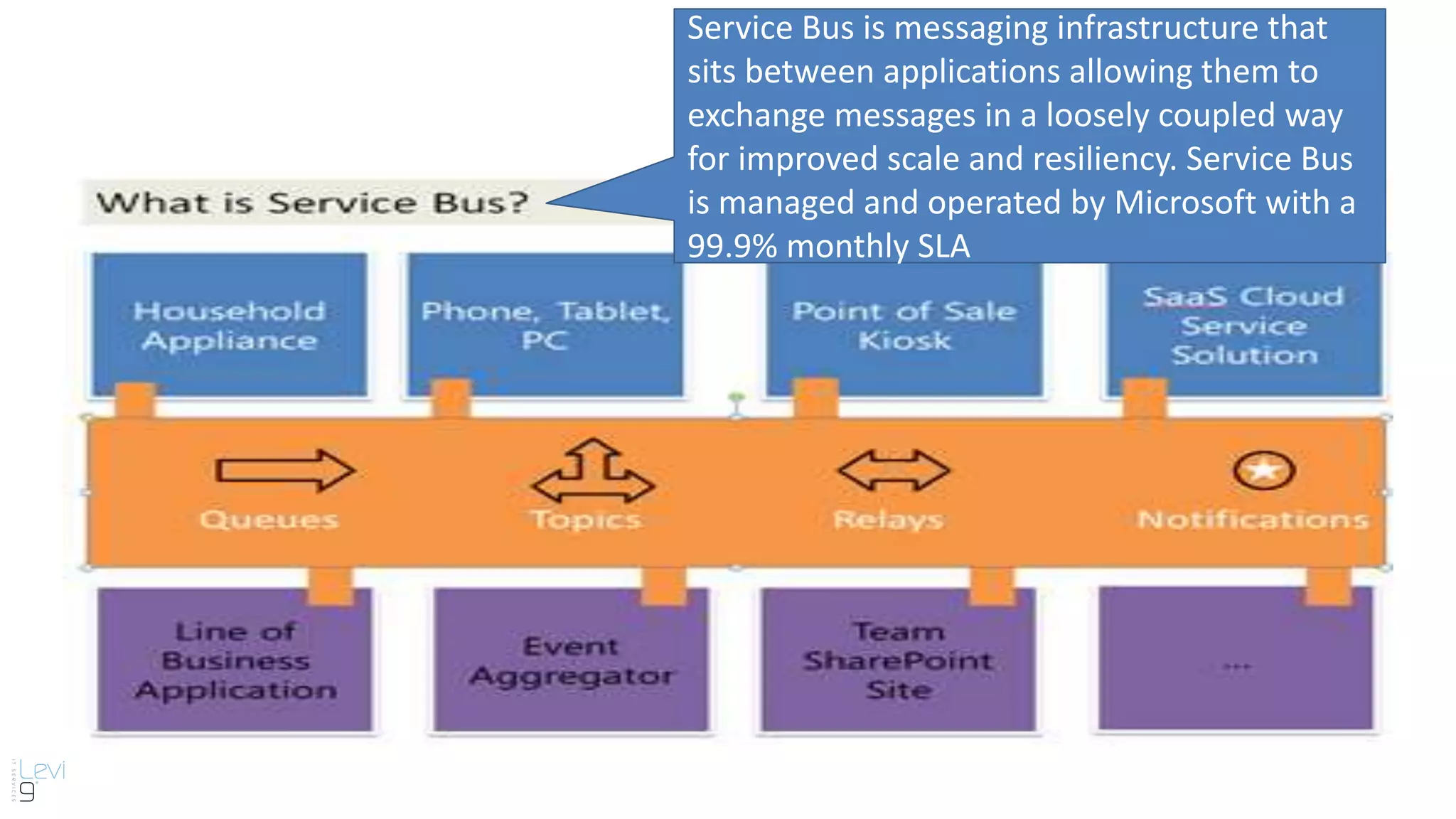
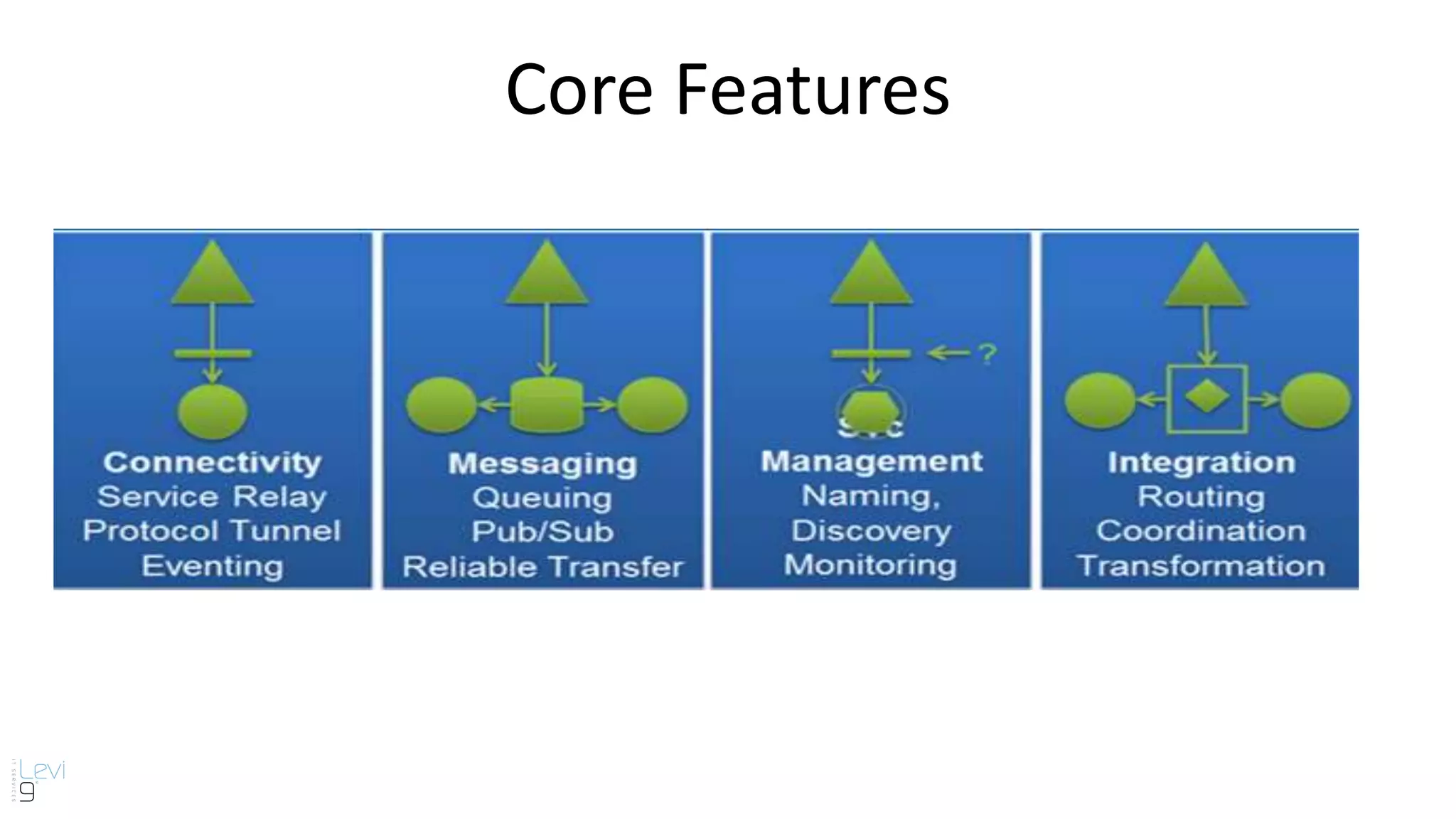
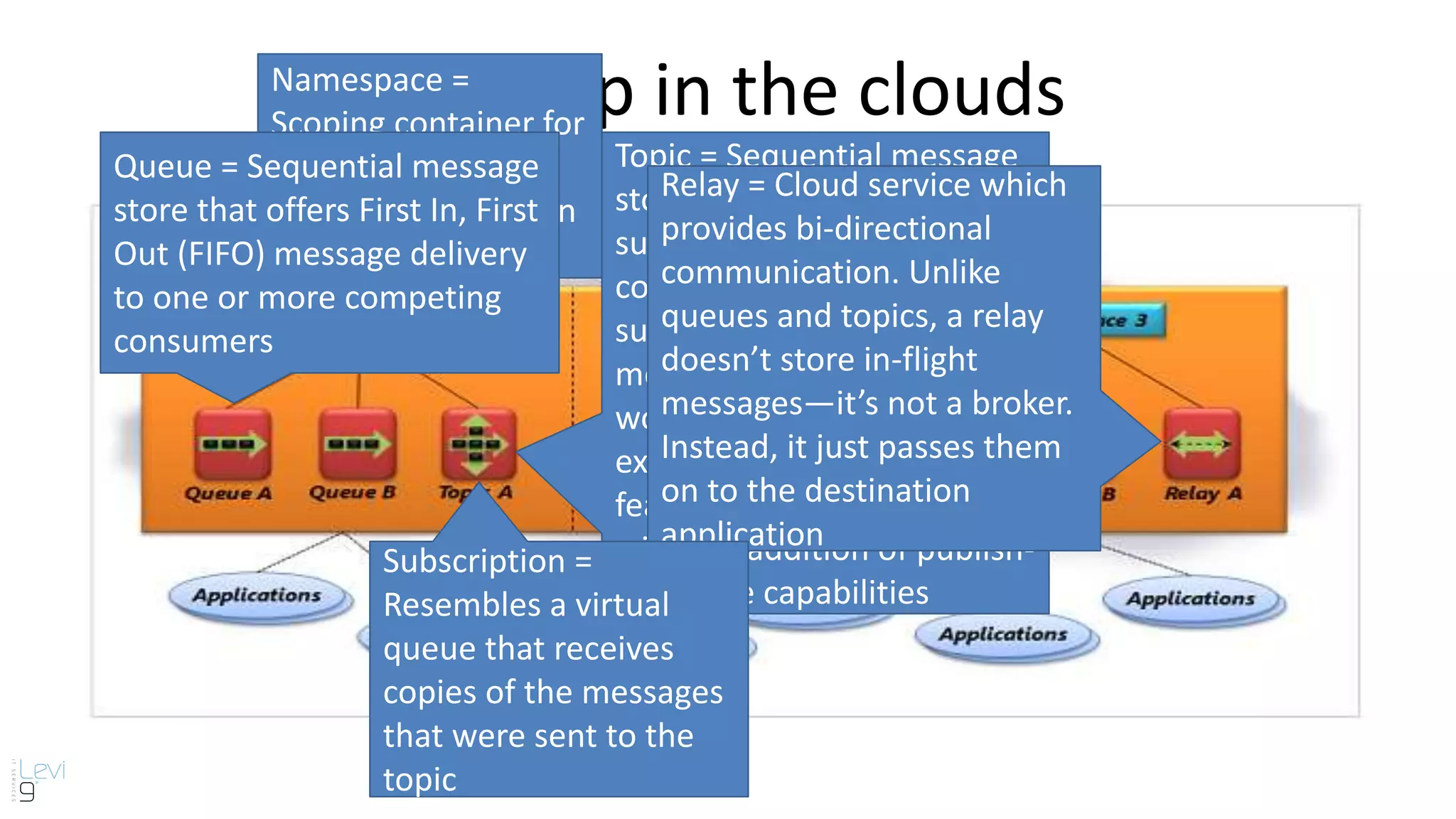
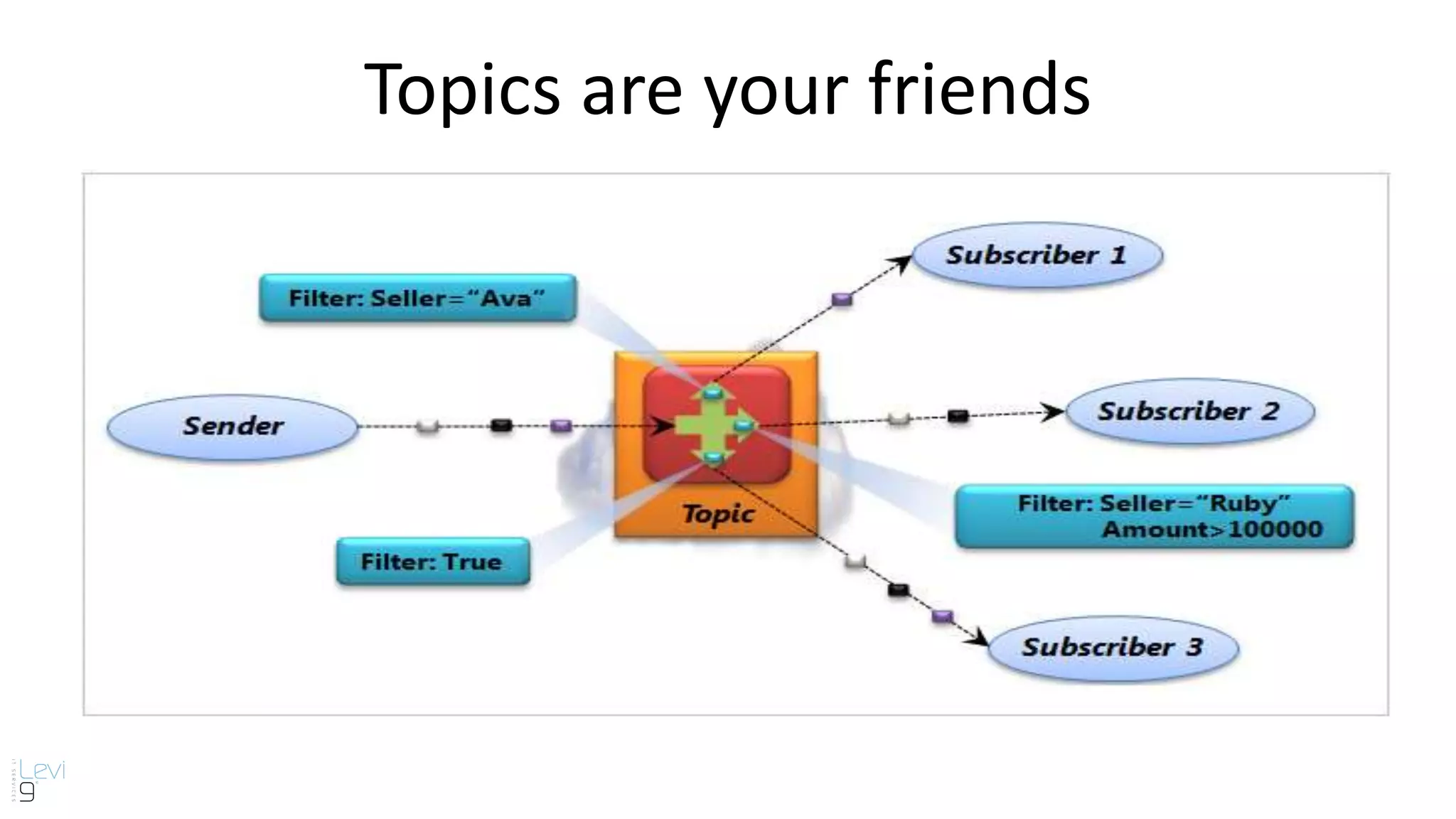
The document provides information about cloud computing and Windows Azure Service Bus. It defines cloud computing and its service models including Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. It then describes key benefits of cloud computing such as improved productivity, cost savings, scalability, speed, and mobility. The document proceeds to explain core features of Windows Azure Service Bus including namespaces, queues, topics, subscriptions, and relays. It discusses messaging scenarios such as temporal decoupling, load leveling, load balancing, and publish/subscribe. It encourages using Windows Azure Service Bus and provides a conclusion about messaging.