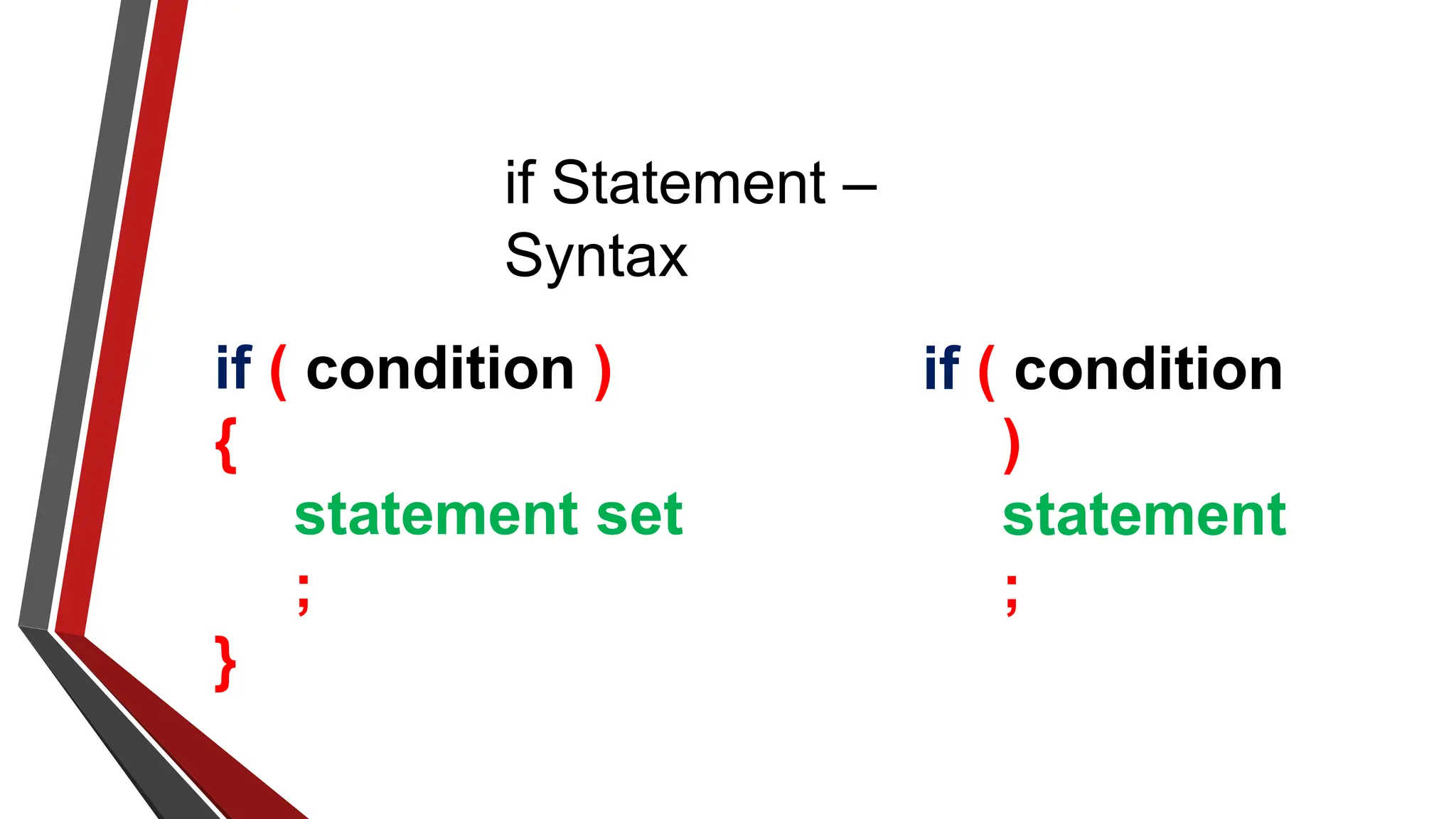
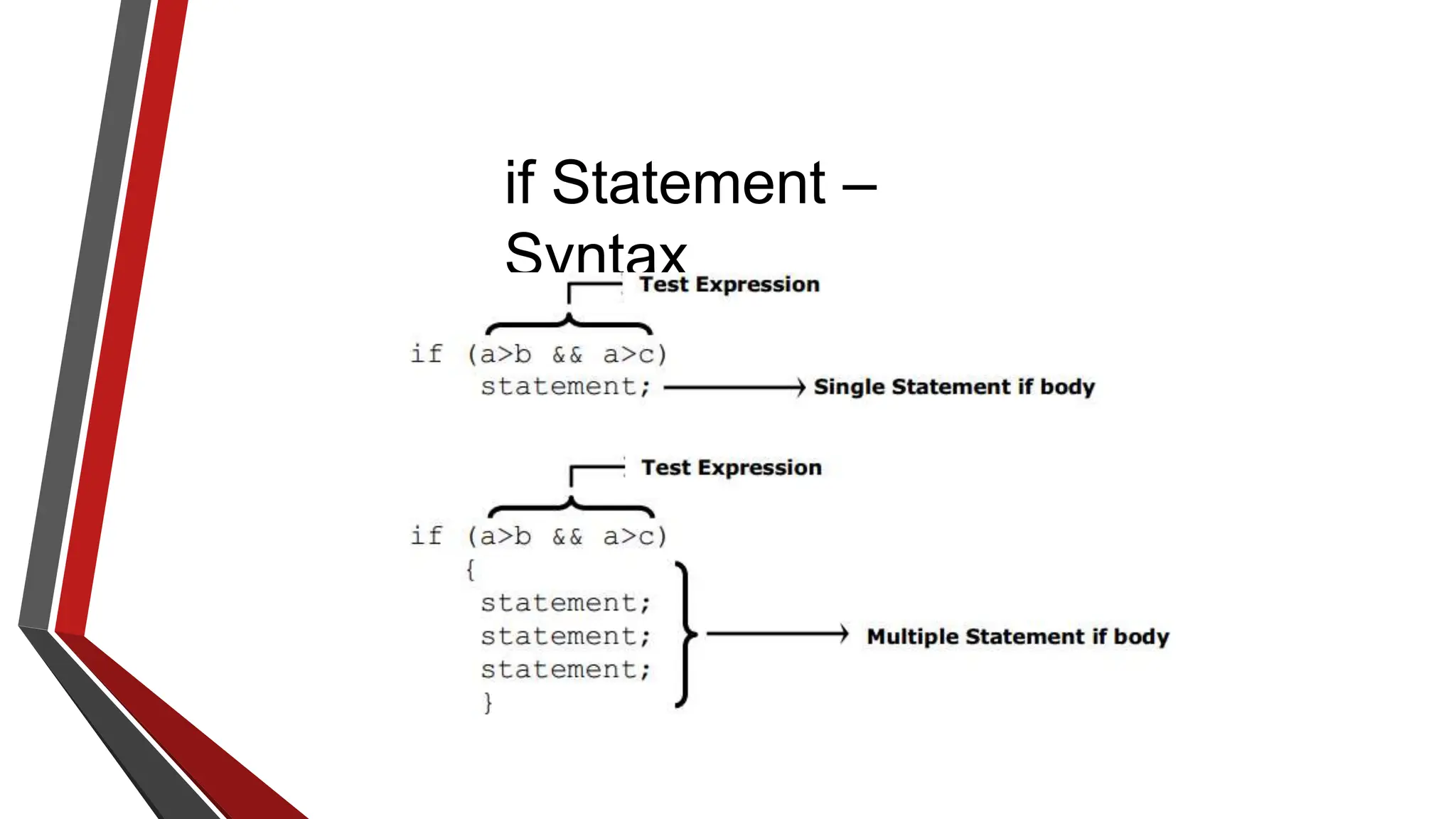
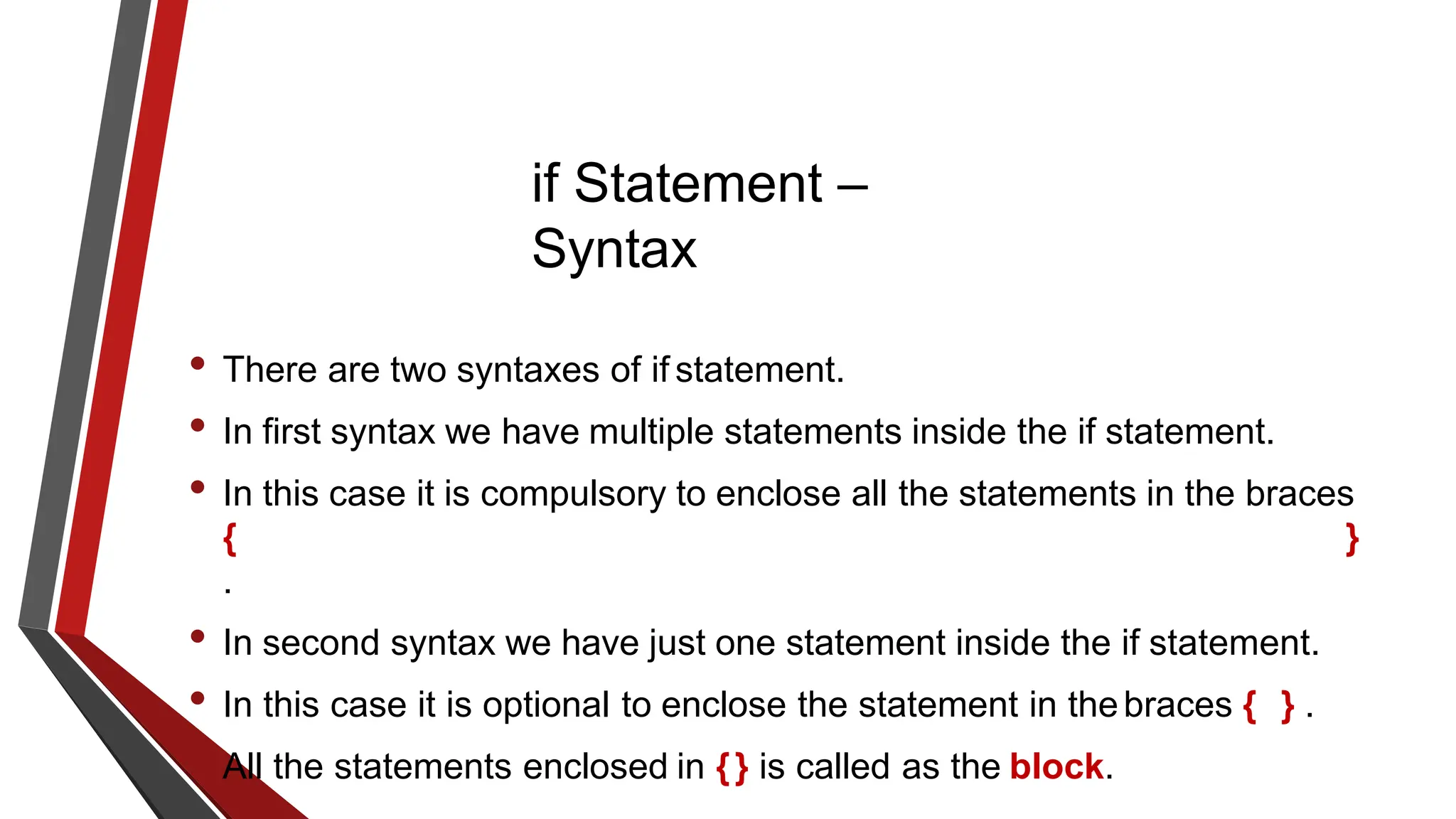
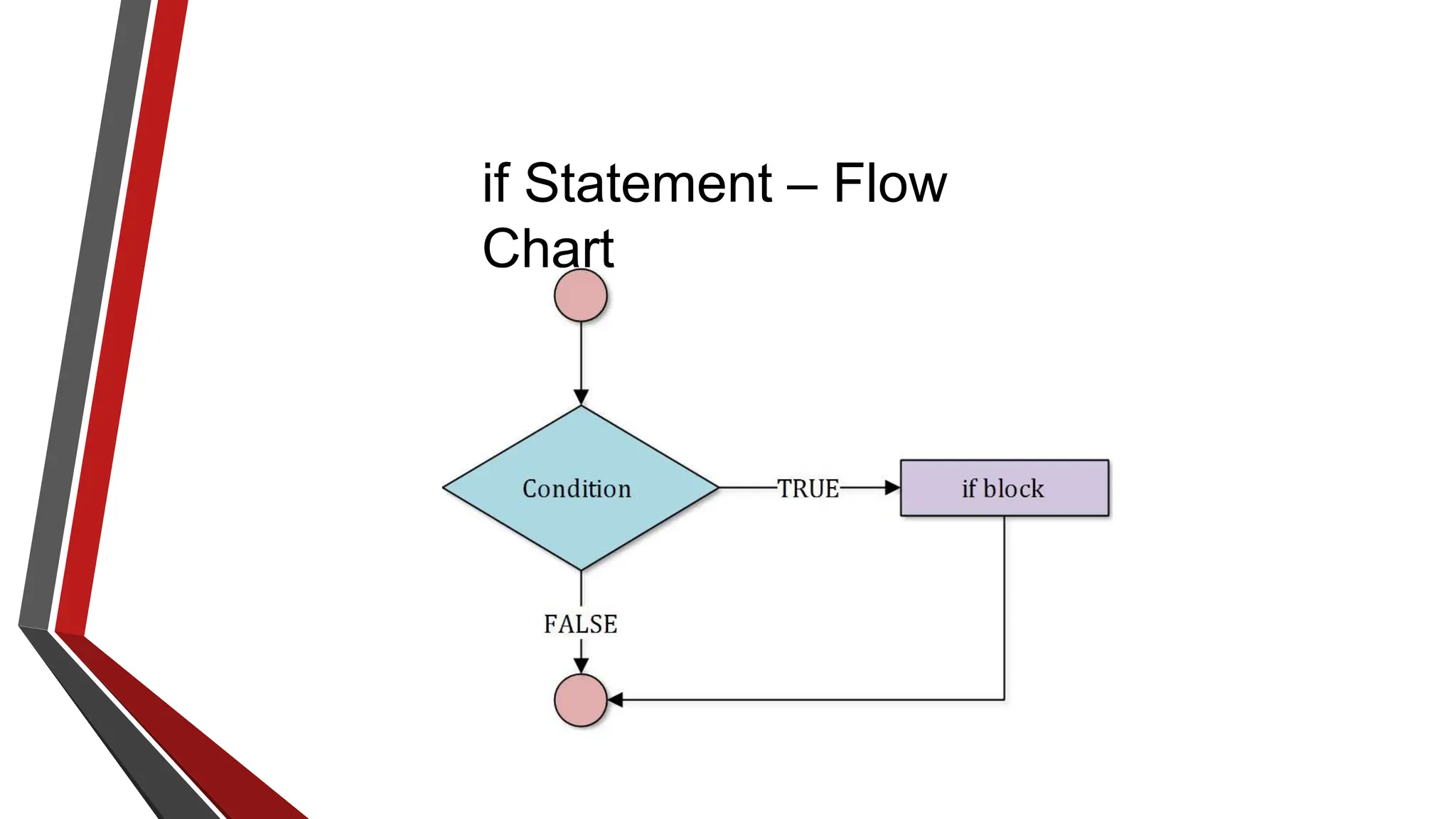
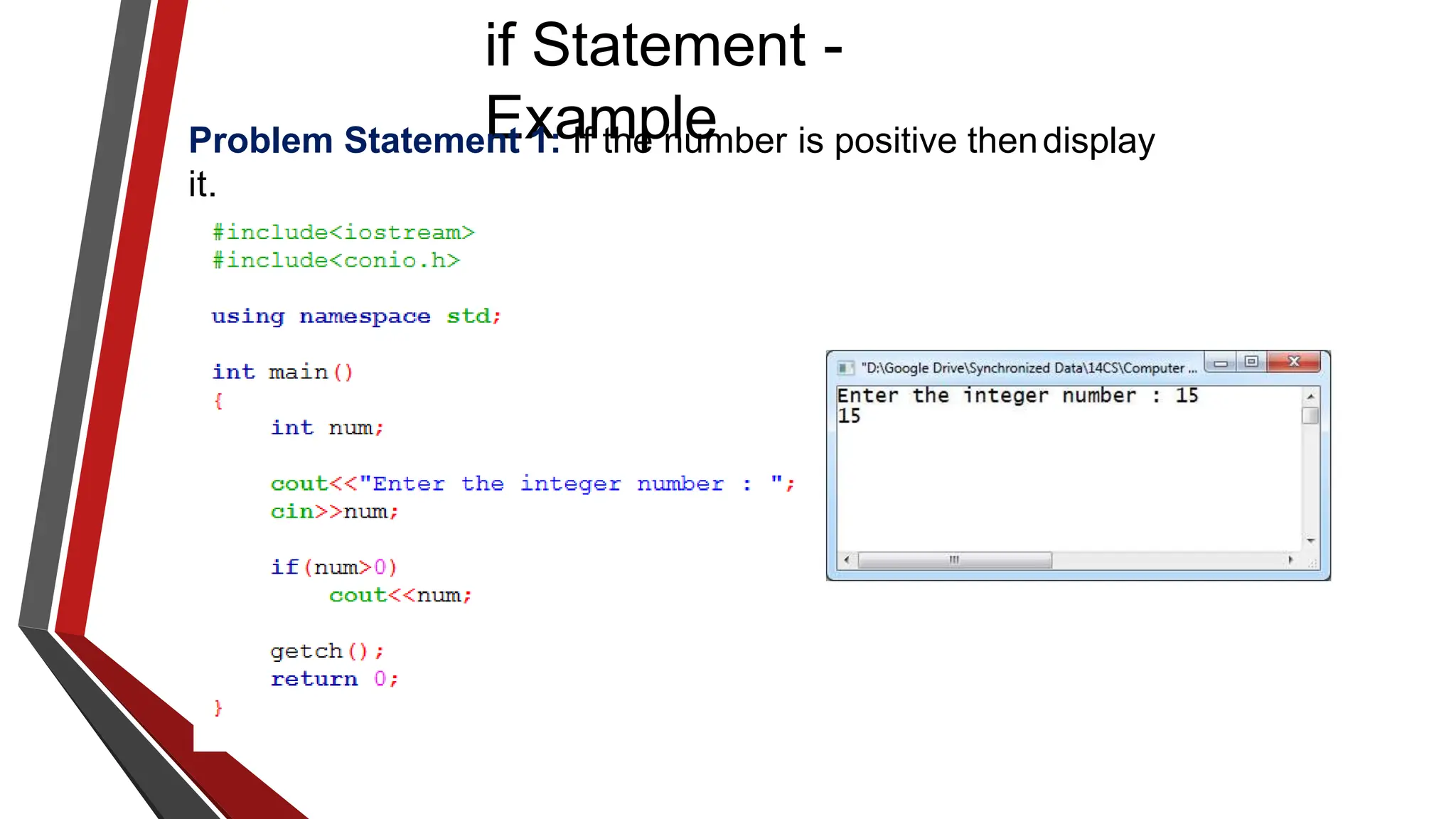
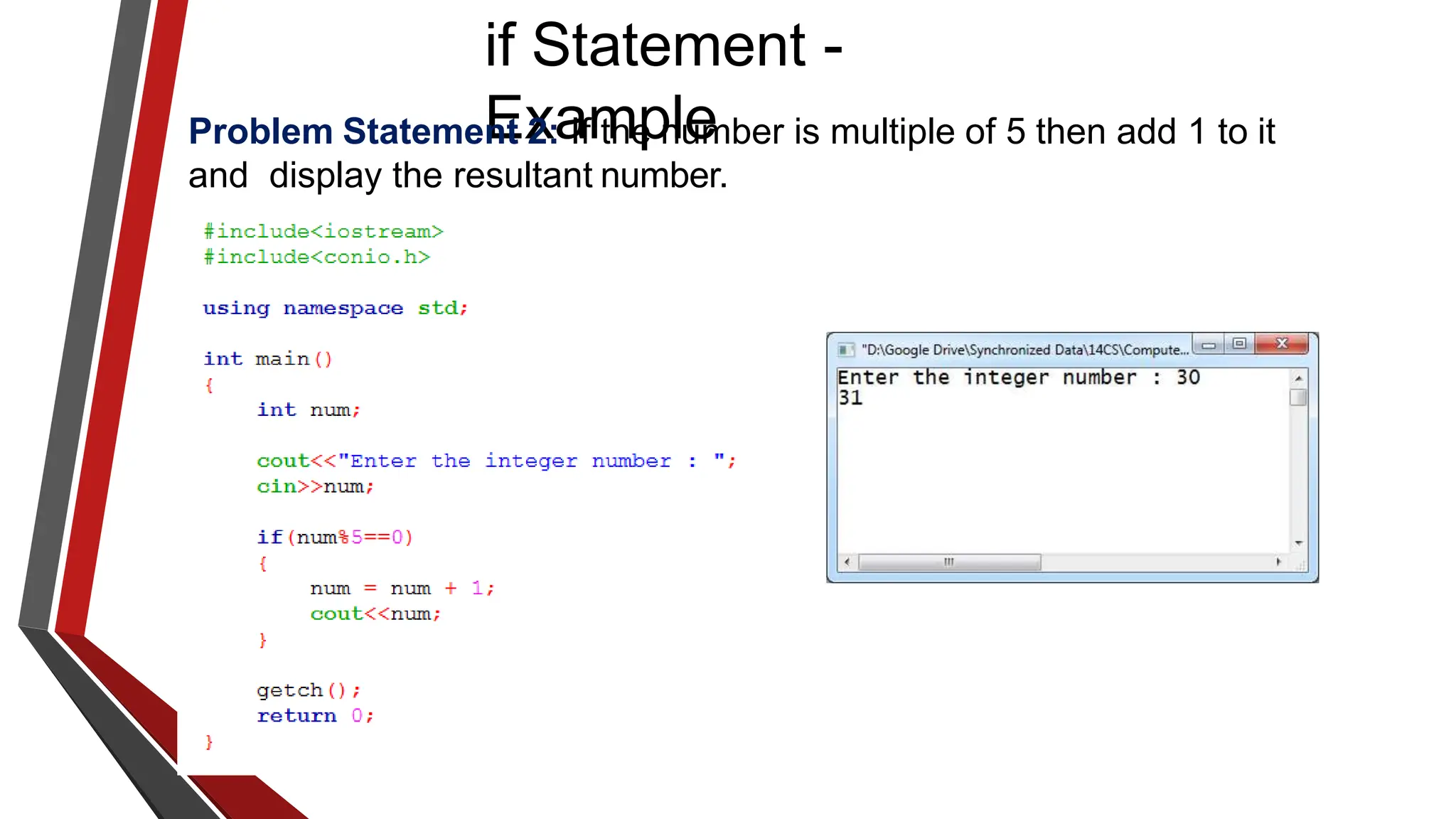
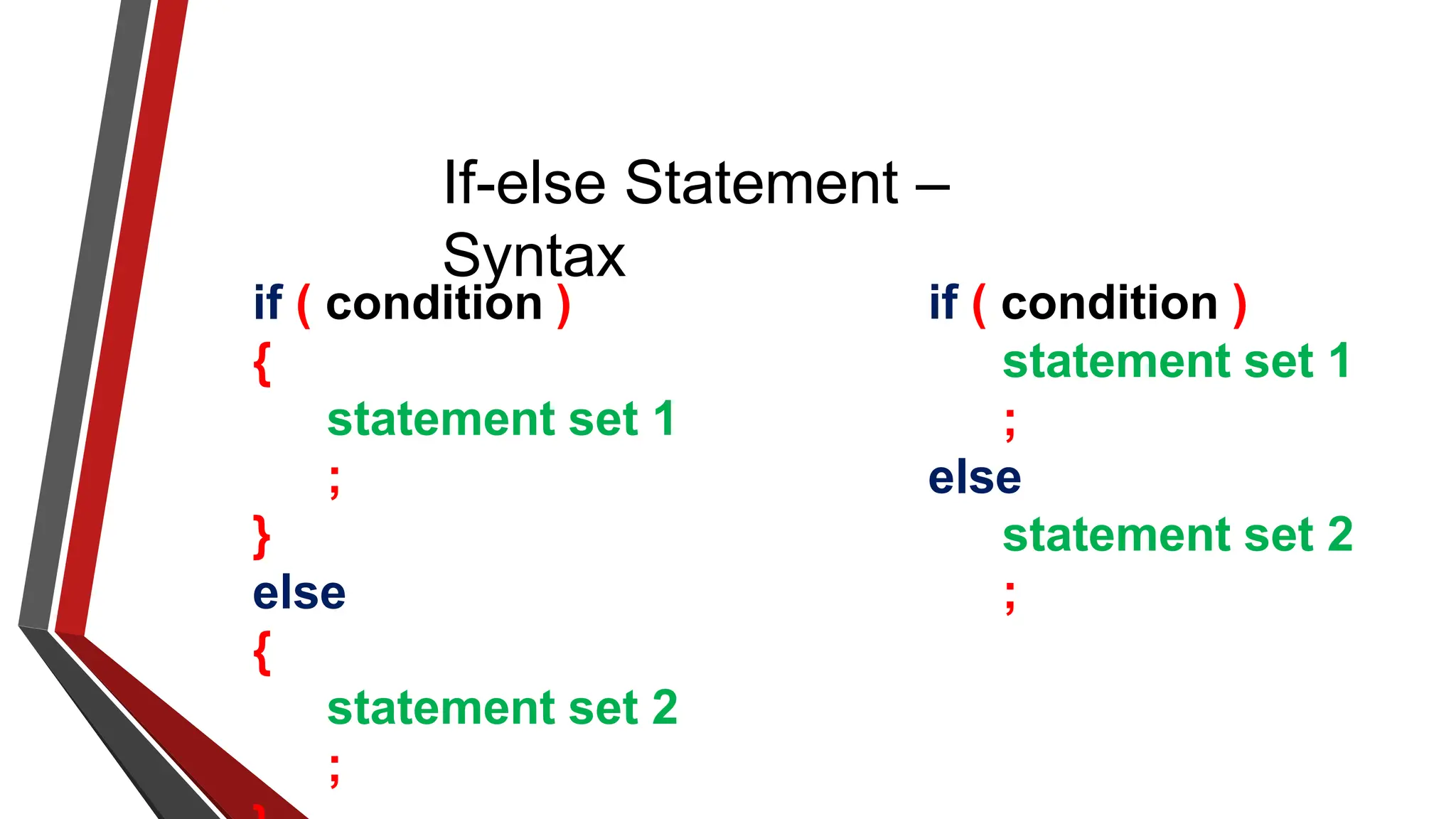
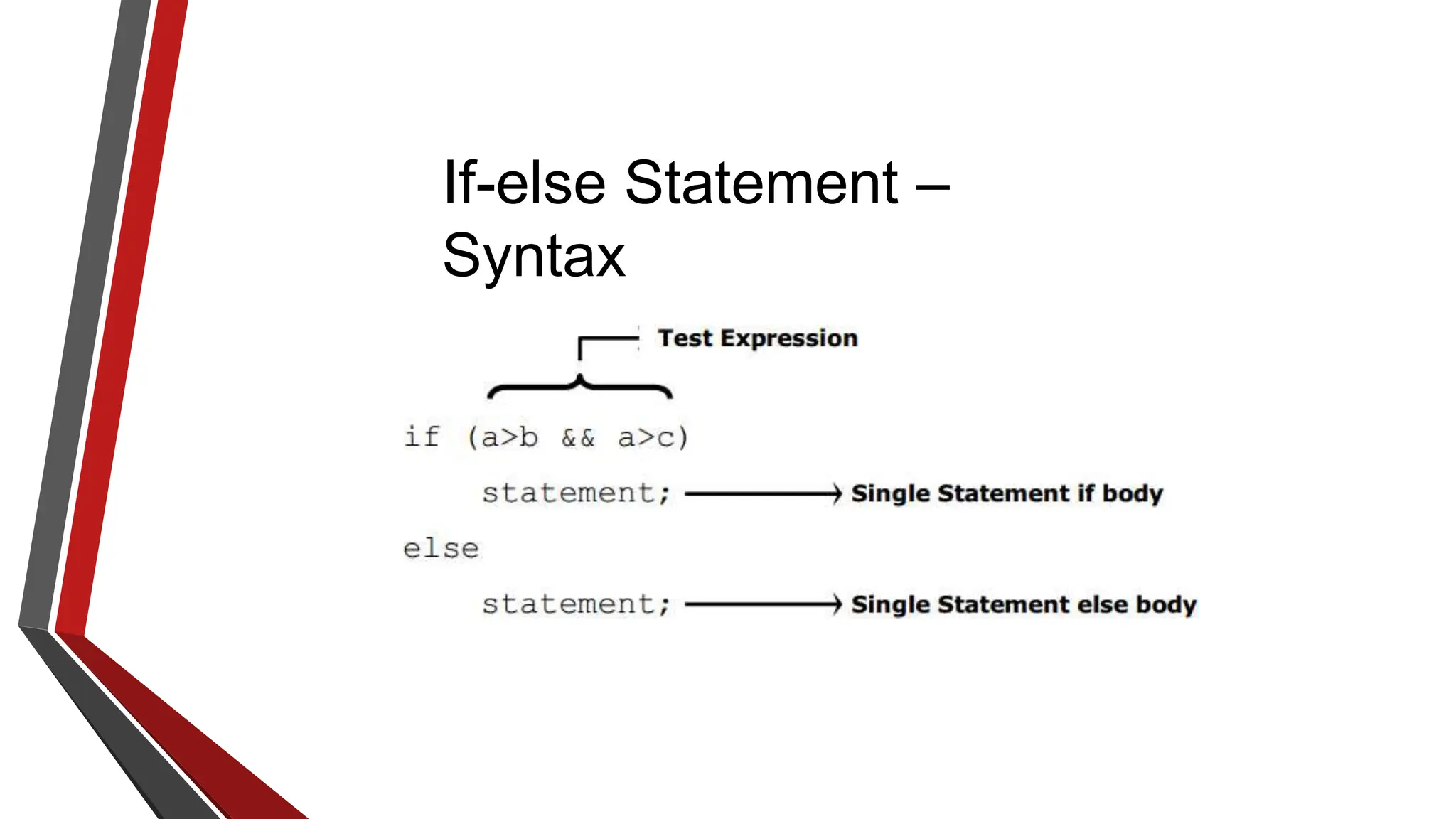
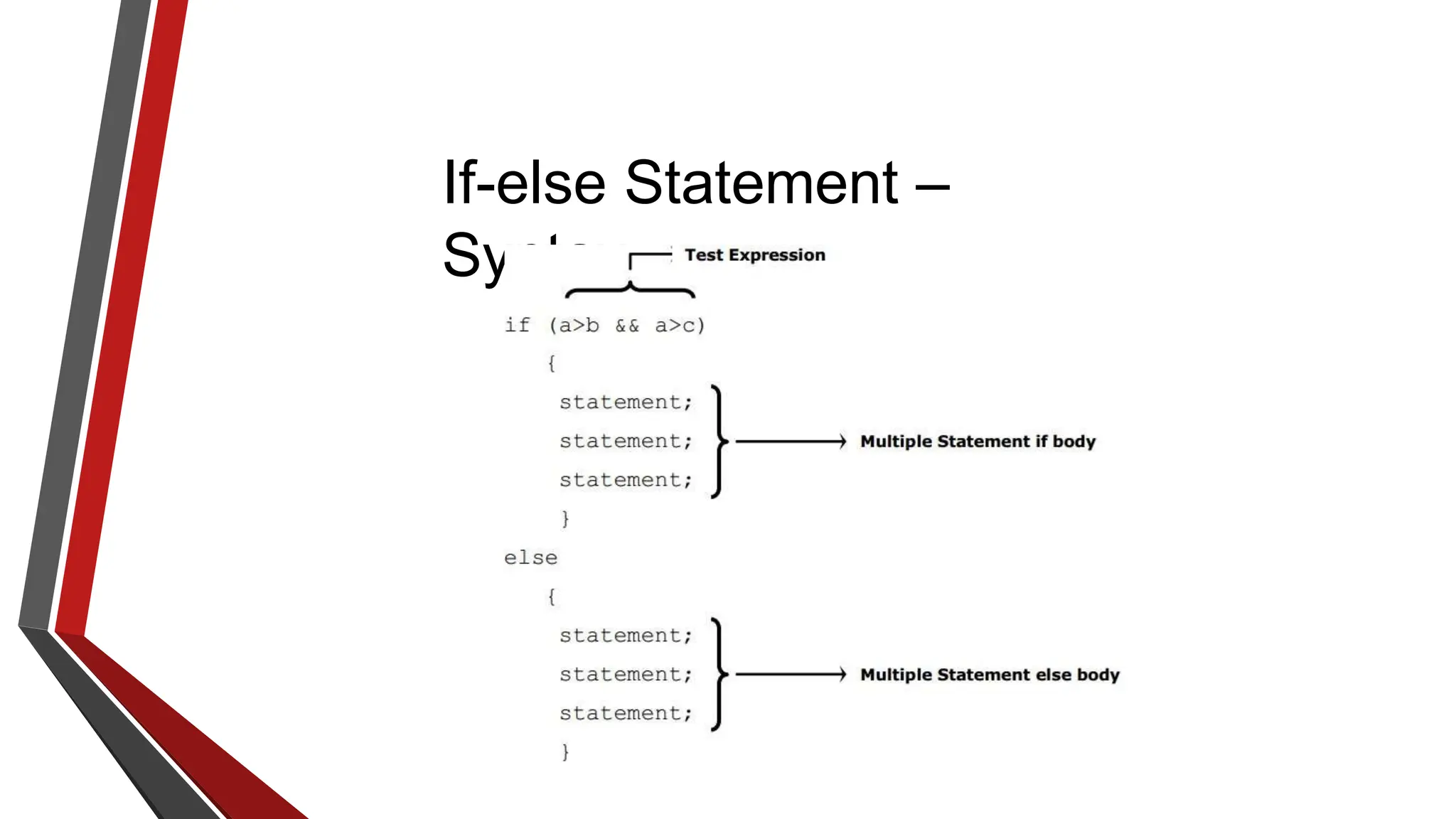
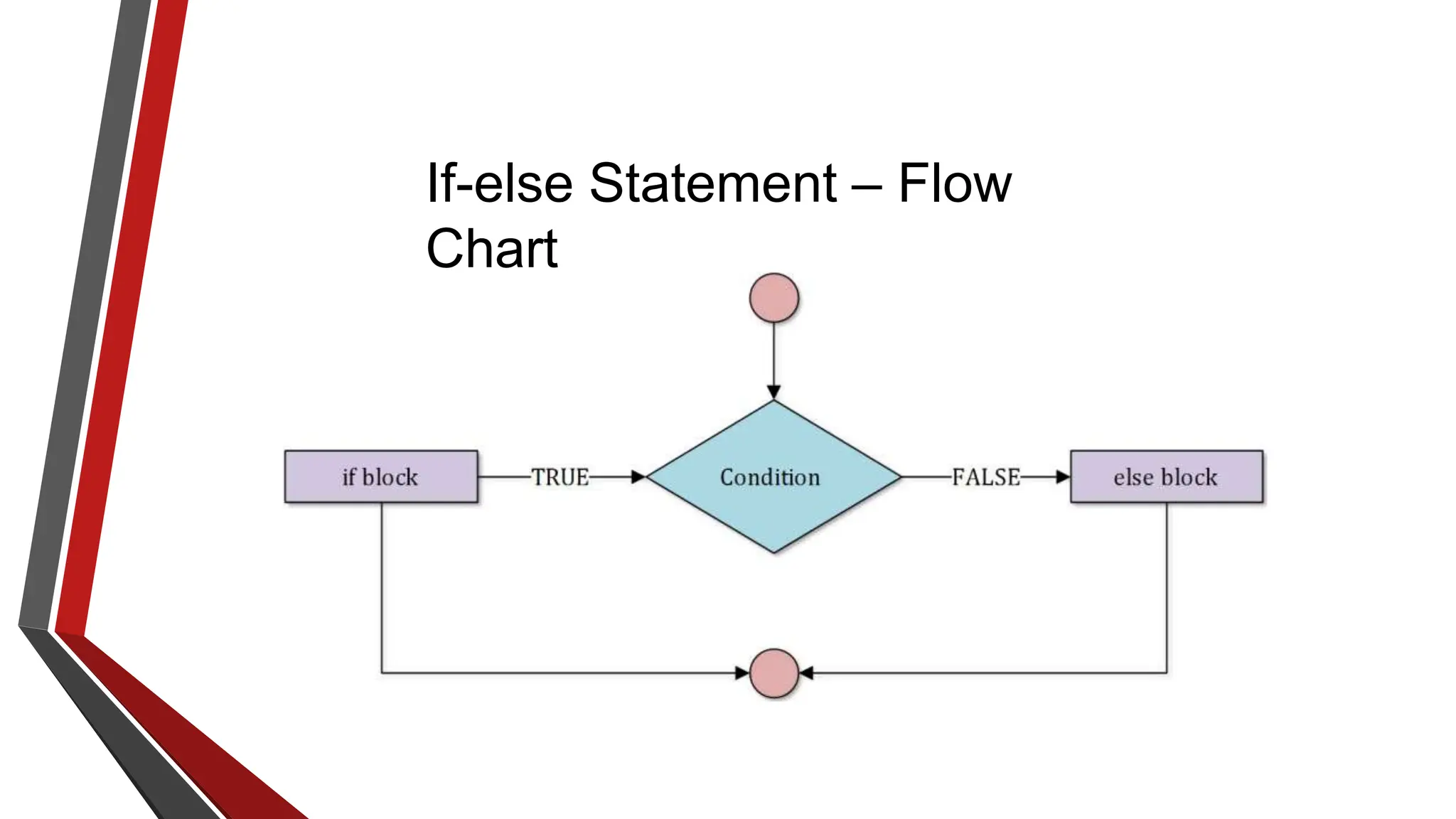
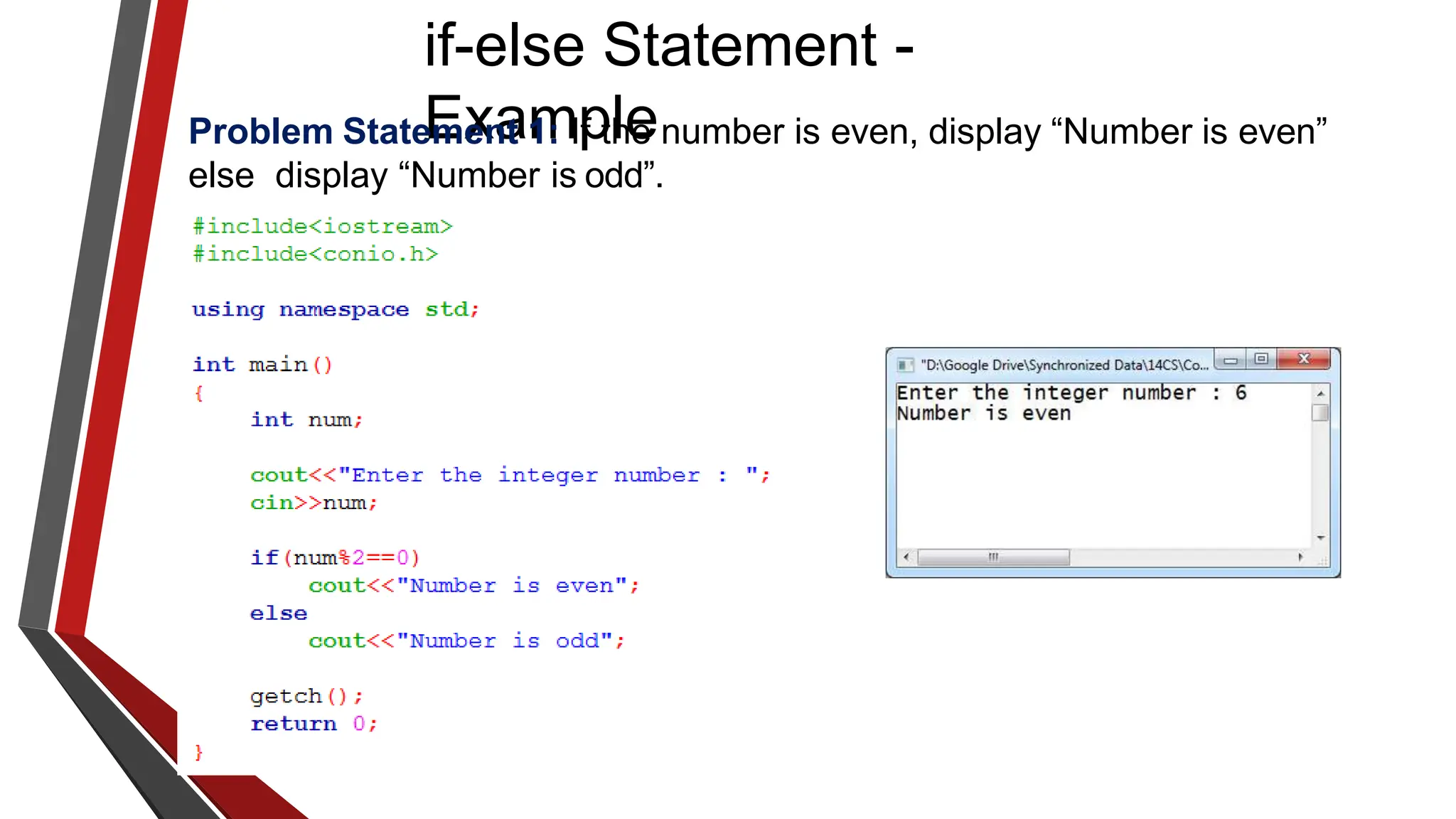
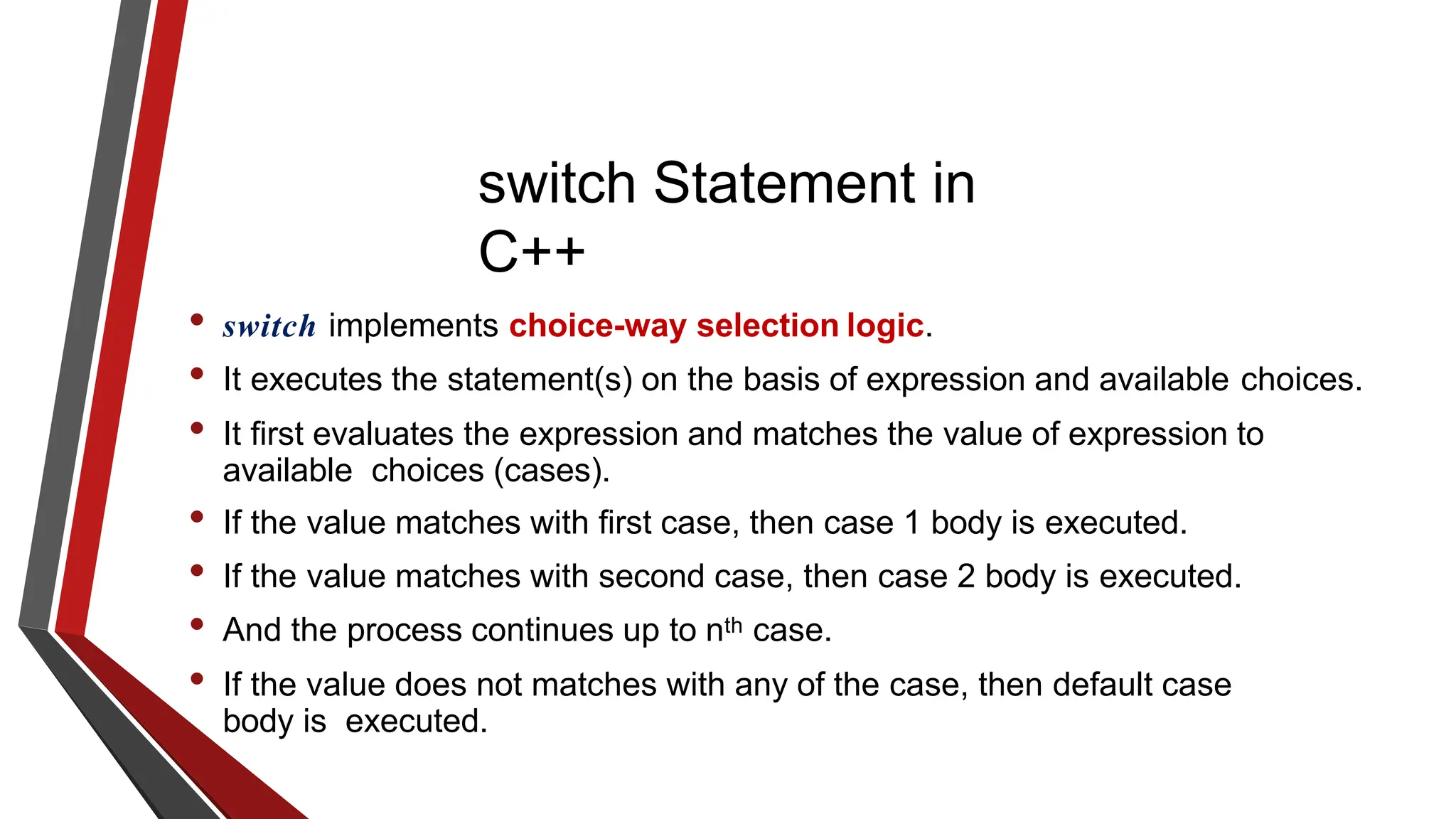
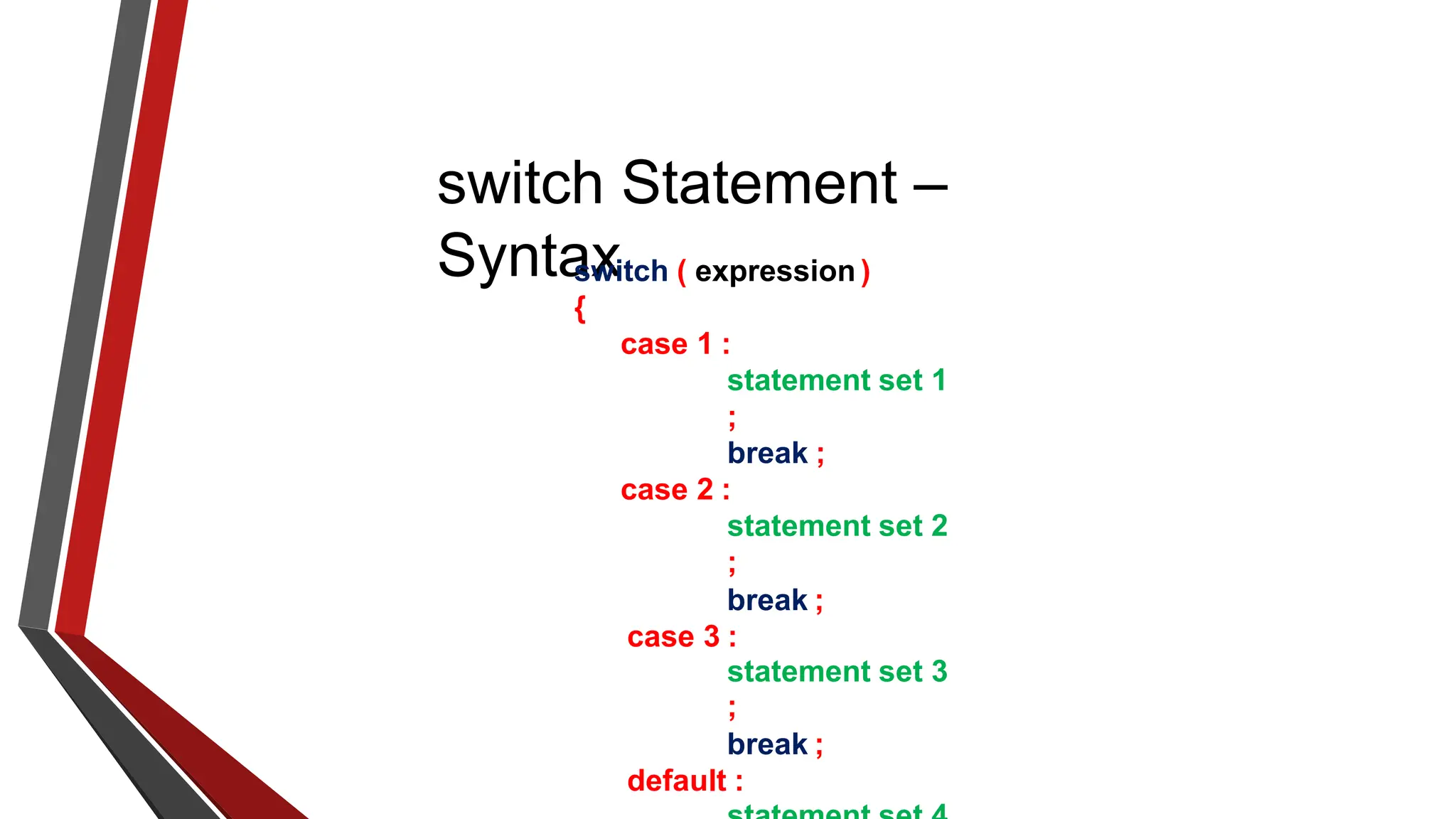
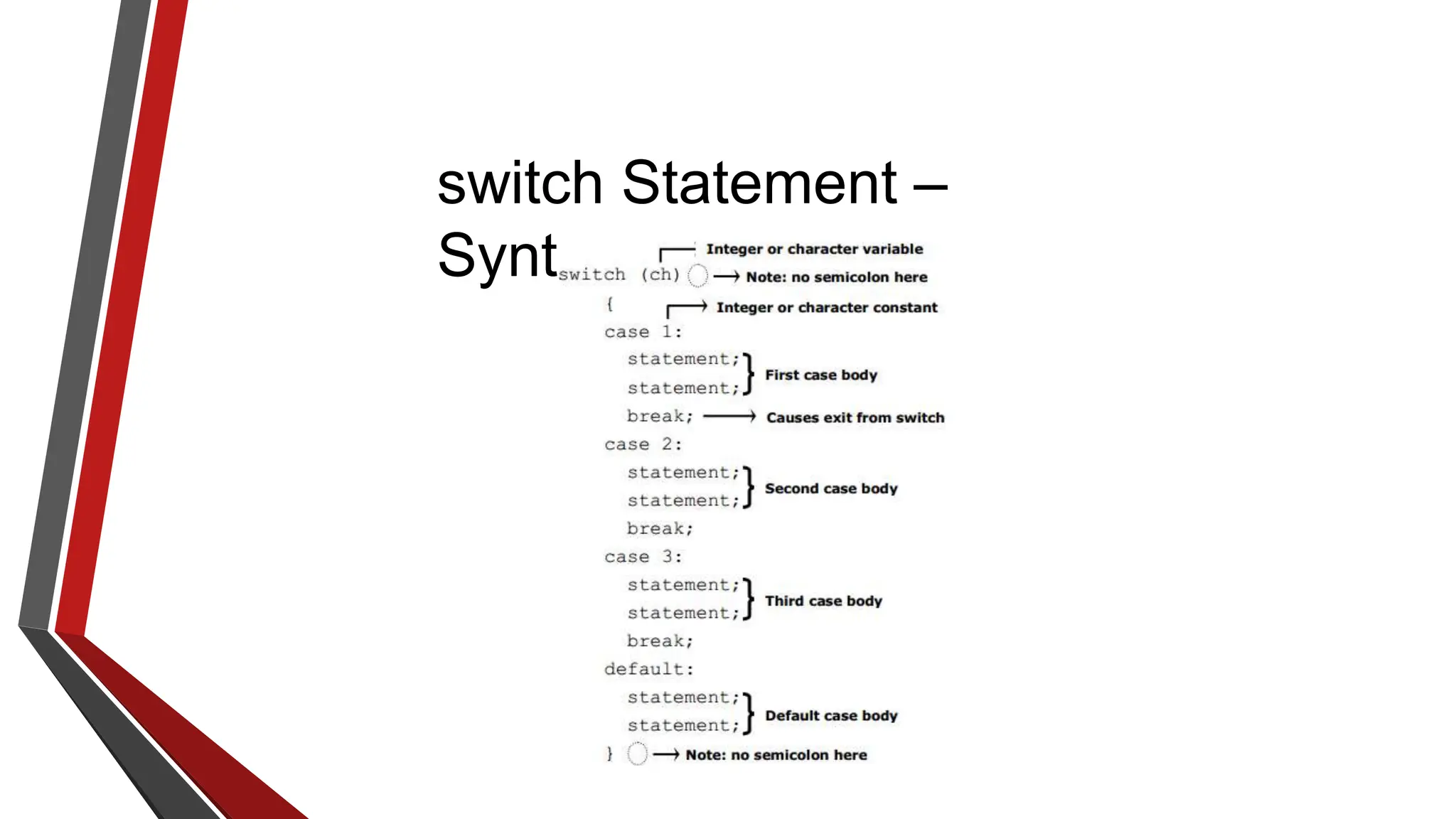
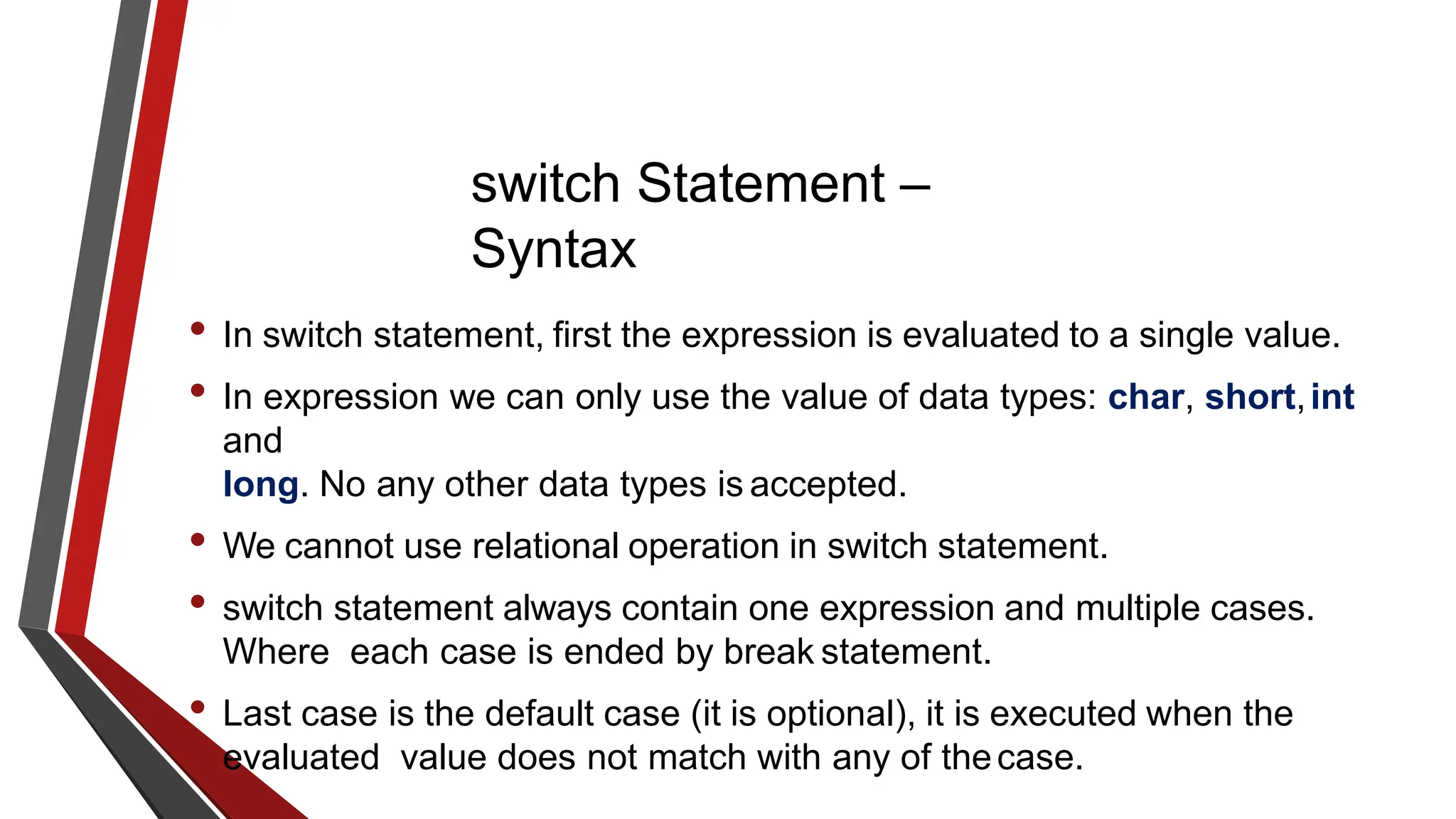
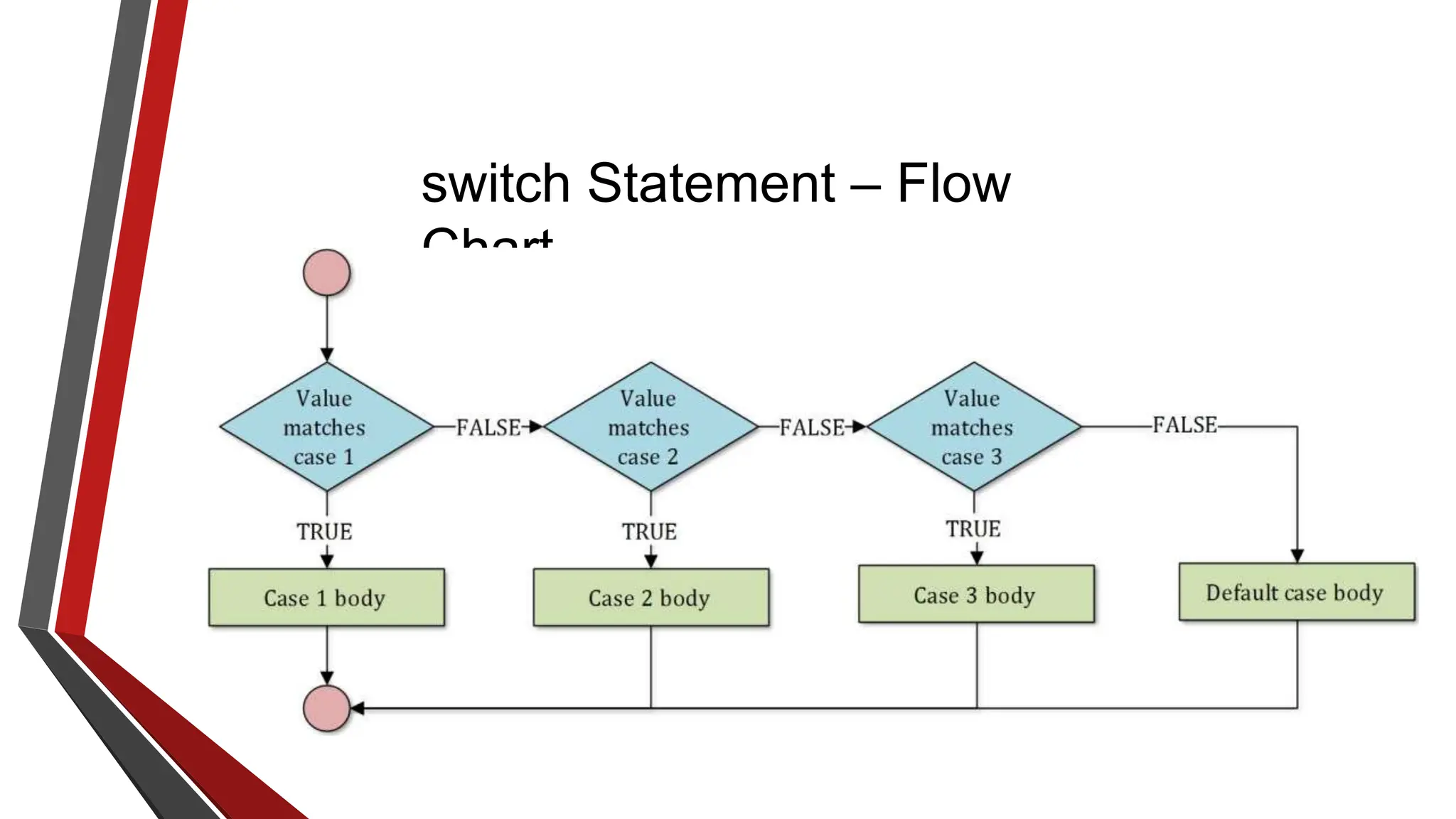
The document provides an overview of conditional control flow and its structures in C++, including if statements, if-else statements, and switch statements. It explains how these constructs execute statements based on specified conditions, detailing their syntax and flow with examples. Additionally, it outlines the rules regarding the use of braces and data types in switch statements.