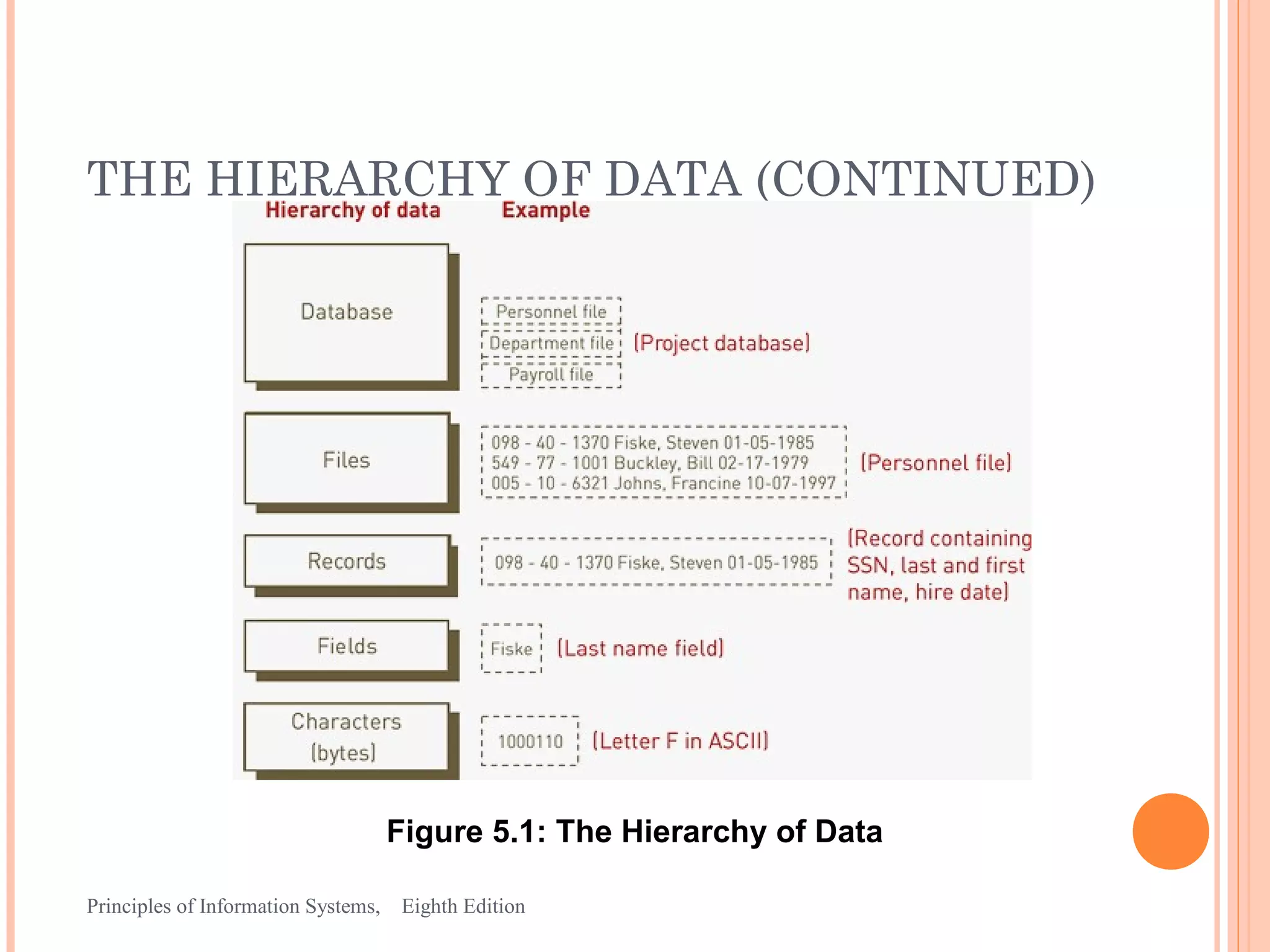
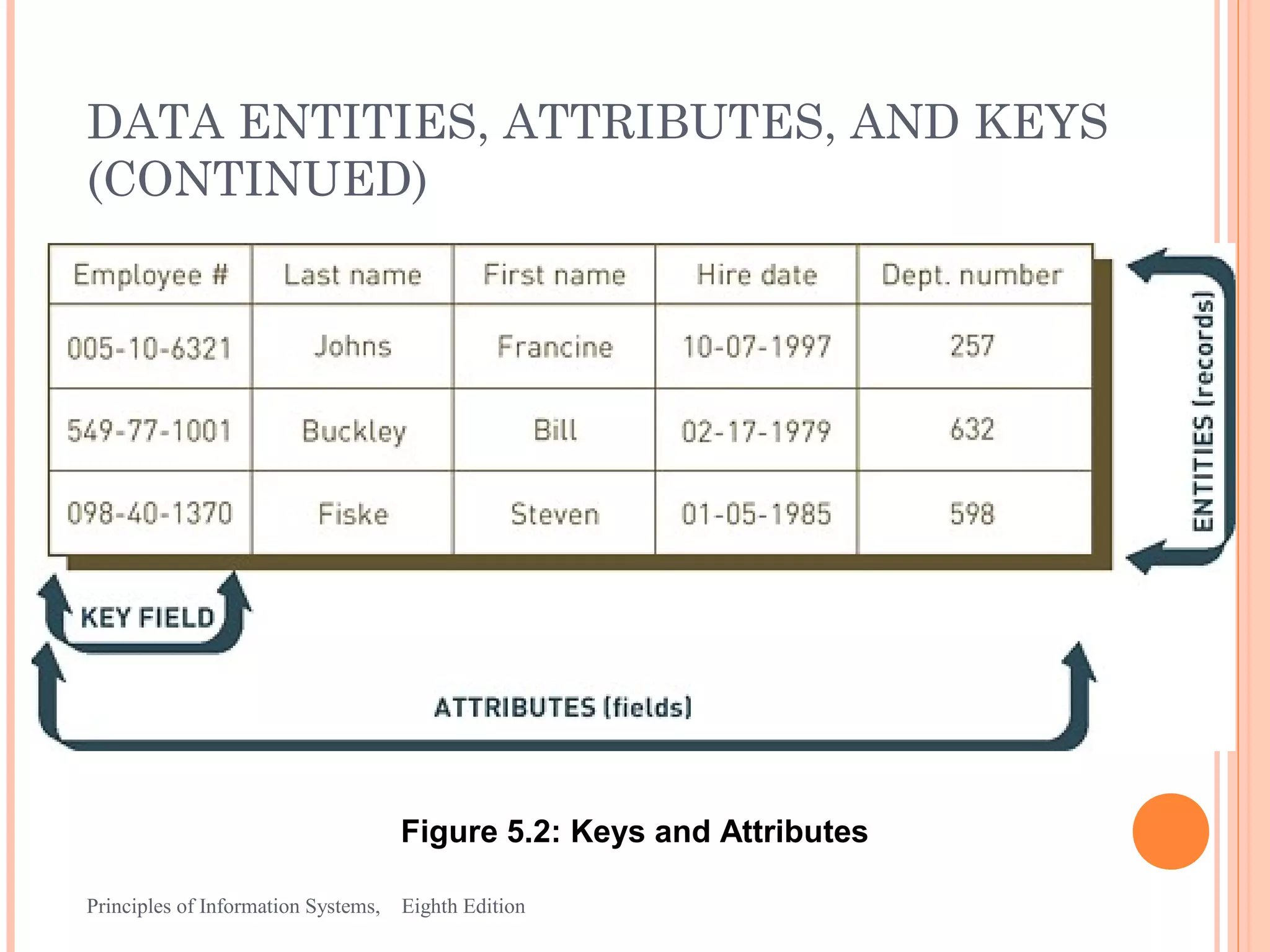
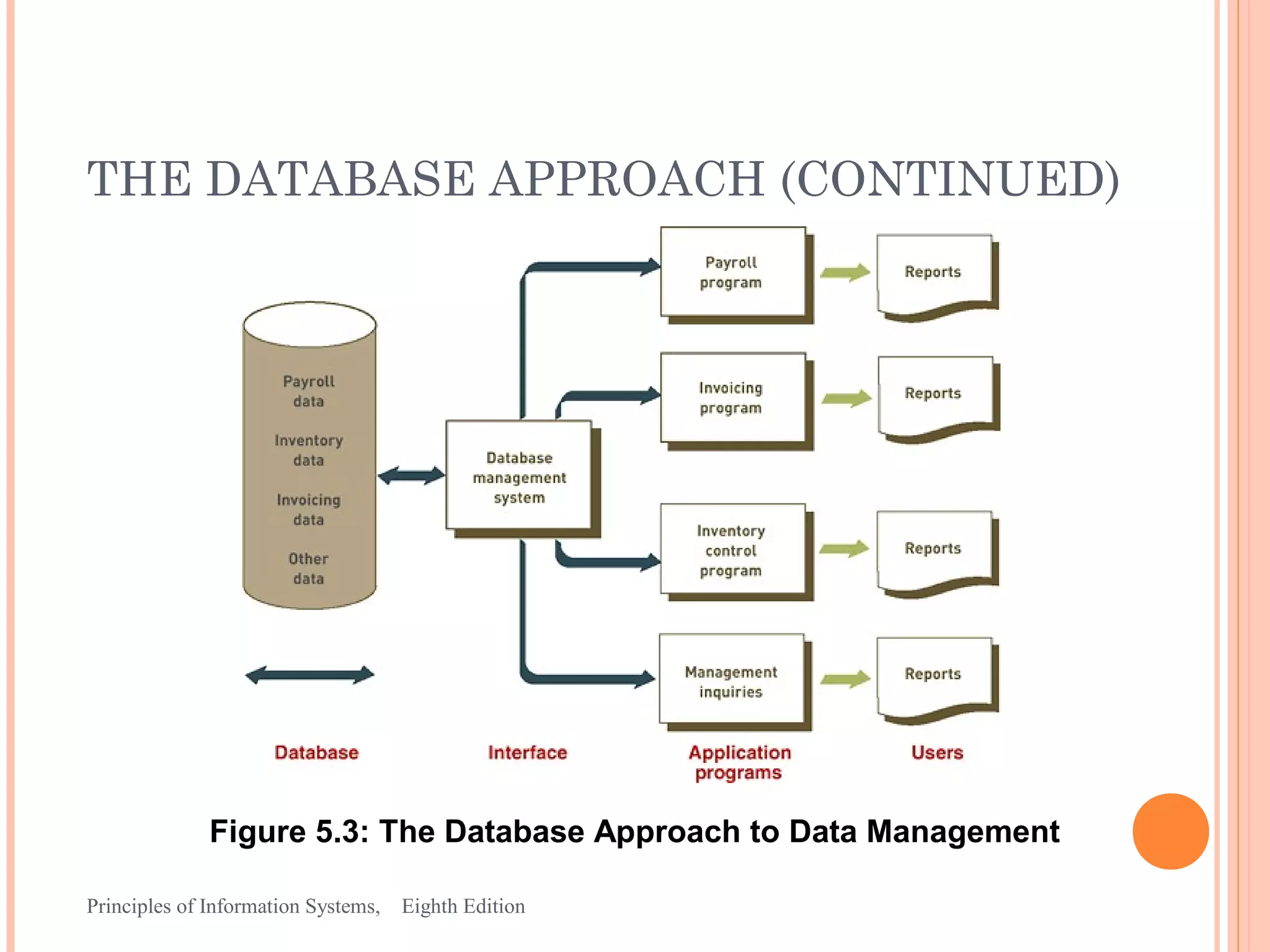
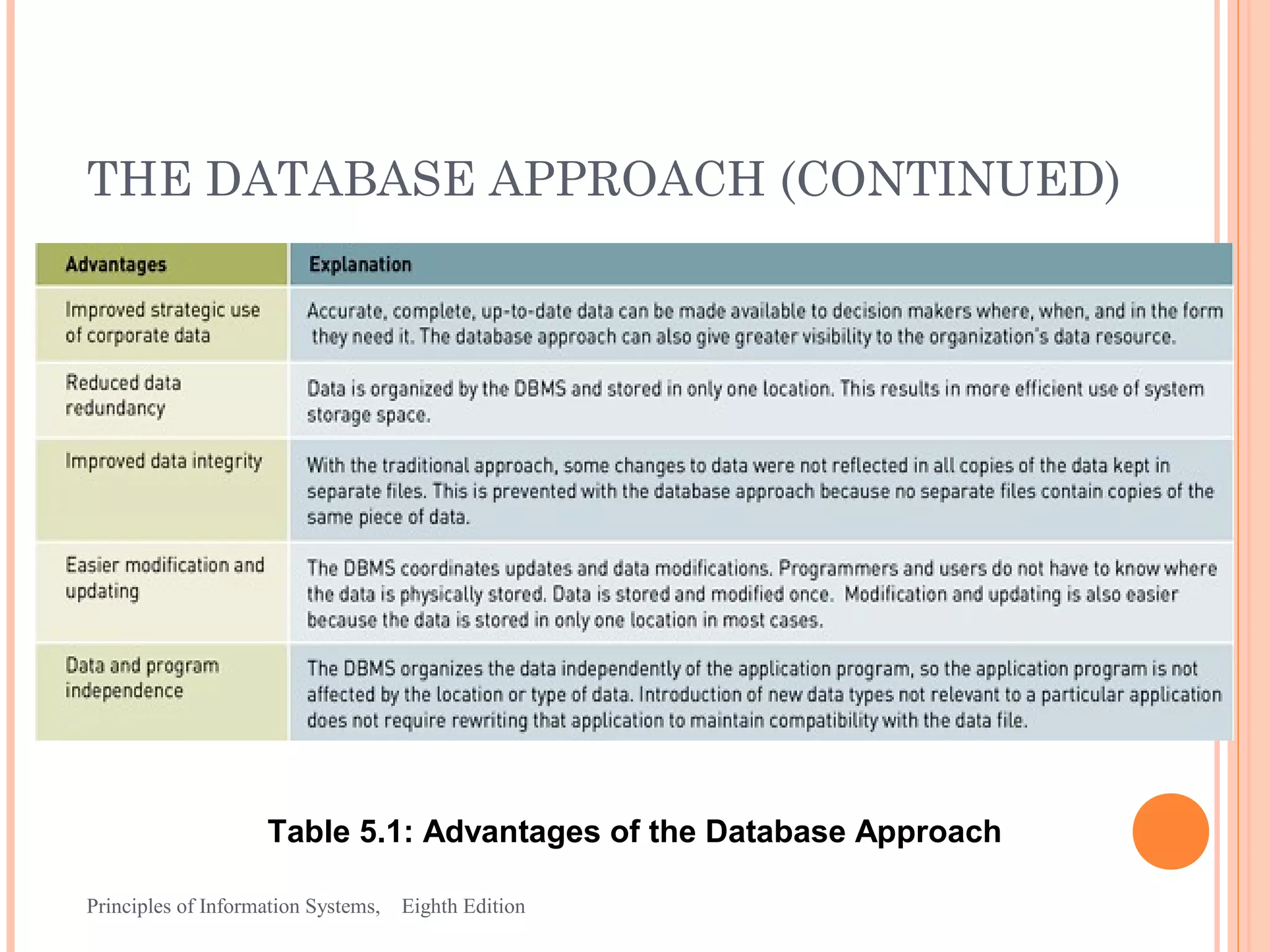
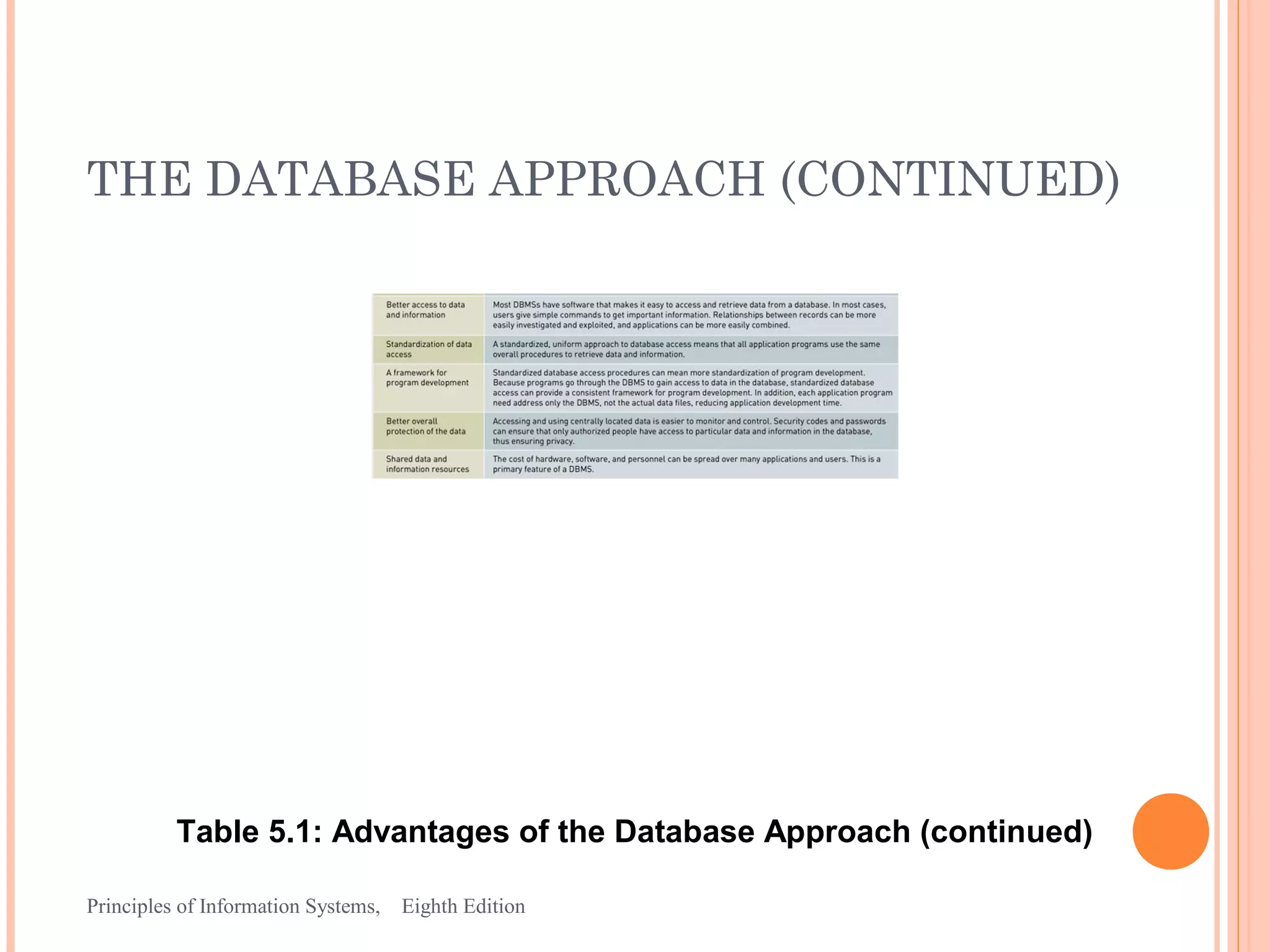
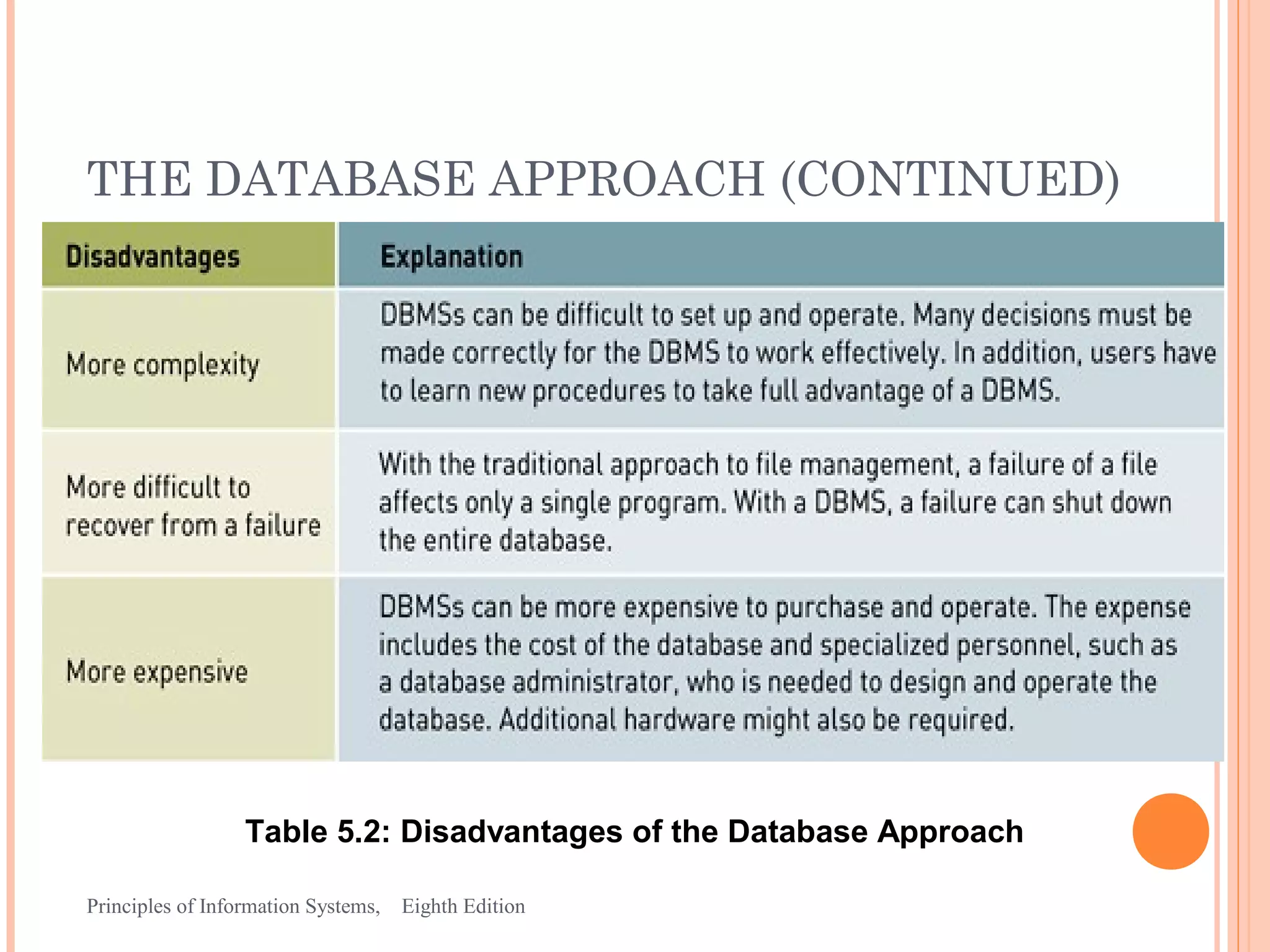
This document discusses organizing data and information in databases. It covers database concepts like data entities, attributes, keys and the hierarchy of data. The advantages of the database approach are outlined, which include consistent data definitions, centralized data administration, data independence and data sharing. Popular database management systems allow users to define, construct and maintain database for storage, retrieval and use of data.