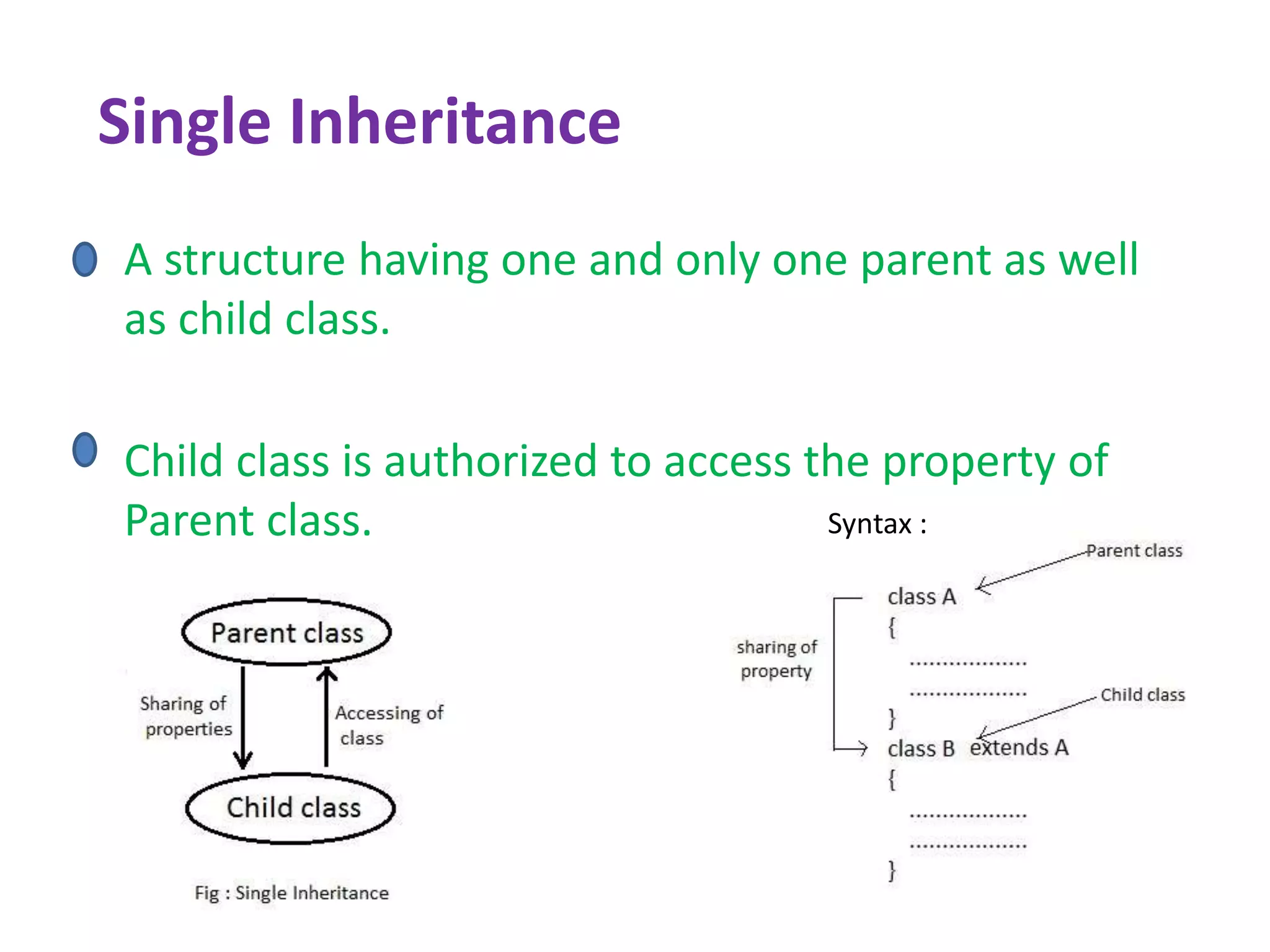
This document discusses inheritance in object-oriented programming. It defines inheritance as establishing a link between classes that allows sharing and accessing properties. There are three types of inheritance: single, multilevel, and hierarchical. Single inheritance involves one parent and one child class, multilevel inheritance adds intermediate classes, and hierarchical inheritance has one parent and multiple child classes. The document provides examples of inheritance code in Java and demonstrates a program using inheritance with interfaces. It notes some limitations of inheritance in Java.












![A Program demonstrating Inheritance in
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
interface Prn1{
void Bits(int x);}
interface Prn2{
void Bytes();}
class Prn3{
void Mega(){
int x=5,y,i=1;
long z=1;
while(i<=10){
y=x*i;
i++;
//System.out.println(y);
z=z*y; }
System.out.println("Product of Table of 5 : "+z);}}
class RPT extends Prn3 implements Prn2{
int x,y,z;
void Bits(int a){
if(a%3==0)
System.out.println("nnn"+a+" is modulated by 3.nn");
else
System.out.println("nnn"+a+" is not modulated by 3.nn");}
public void Bytes(){
Scanner S=new Scanner(System.in);
x=10;
System.out.print("Enter a no. for a rectangle width : ");
y=S.nextInt();
z=x*y;
System.out.println("nnArea of rectangle : "+x+"x"+y+"="+z);
System.out.println();}}
class Intrfc{
public static void main(String[] Arg){
RPT obj=new RPT();
obj.Bits(16);
obj.Bytes();
obj.Mega();}}
Output :
16 is not modulated by 3.
Enter a no. for a rectangle width : 20
Area of rectangle : 10x20=200
Product of table of 5 : 35437500000000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritanceppt-copy-141124110120-conversion-gate01/75/Inheritance-in-JAVA-PPT-14-2048.jpg)

