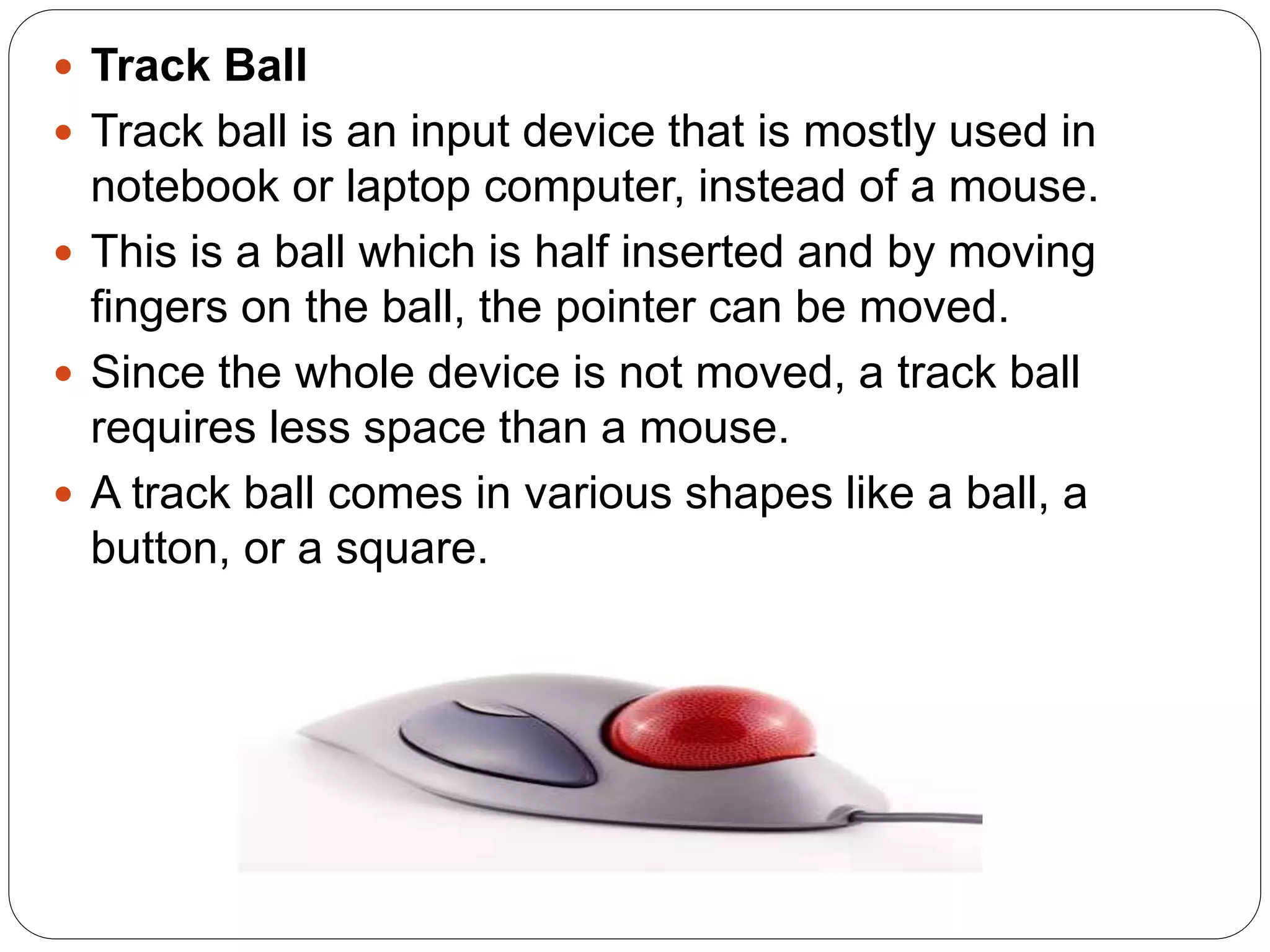
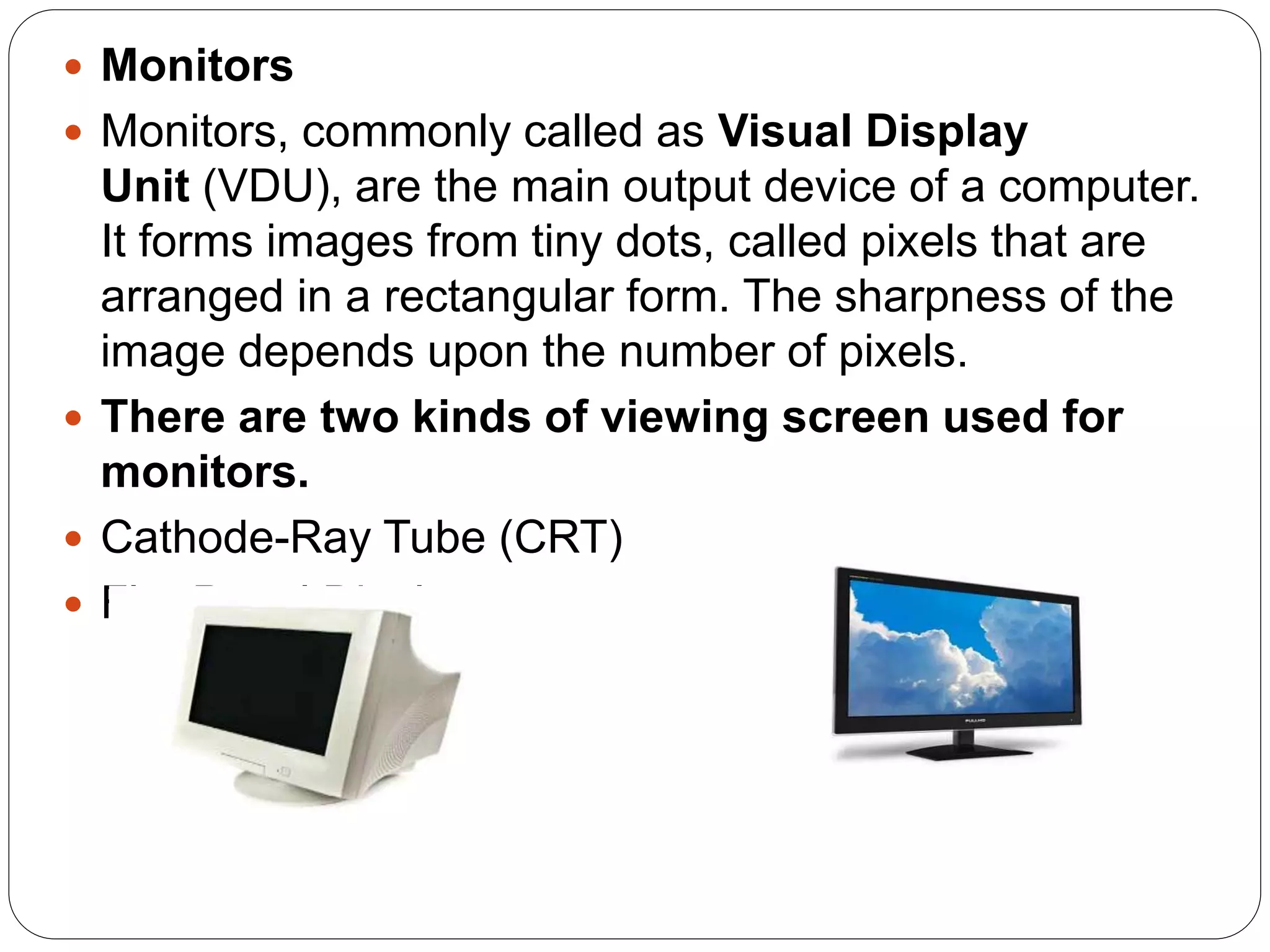
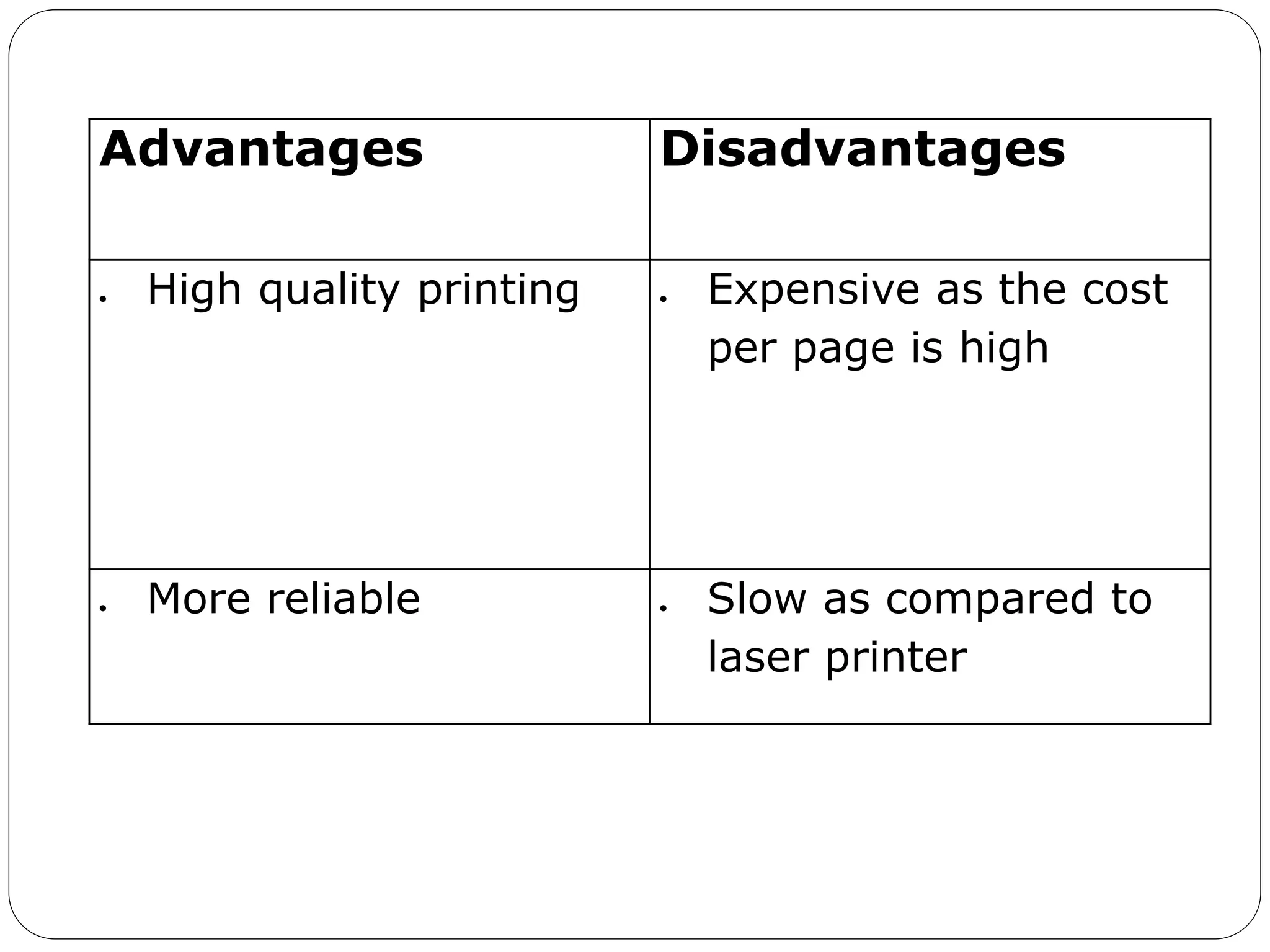
This document discusses computer input and output devices. It defines input devices as devices that accept data from the user and lists common input devices like the keyboard, mouse, scanner, and magnetic ink card reader. It then discusses important output devices like computer monitors, printers (impact and non-impact), and describes their functions. The document also provides an overview of computer memory, including cache memory, primary memory, secondary storage, RAM and ROM.