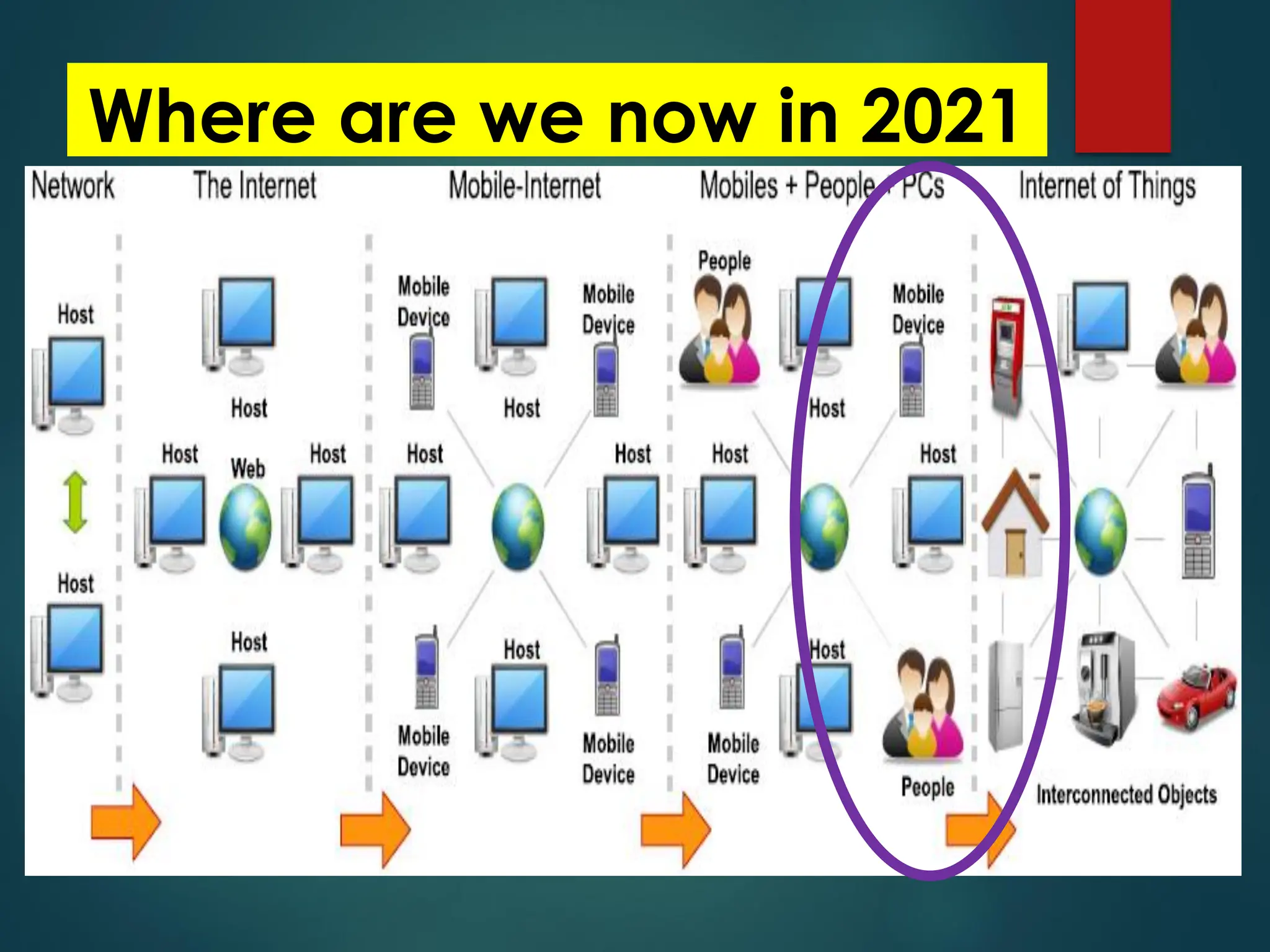
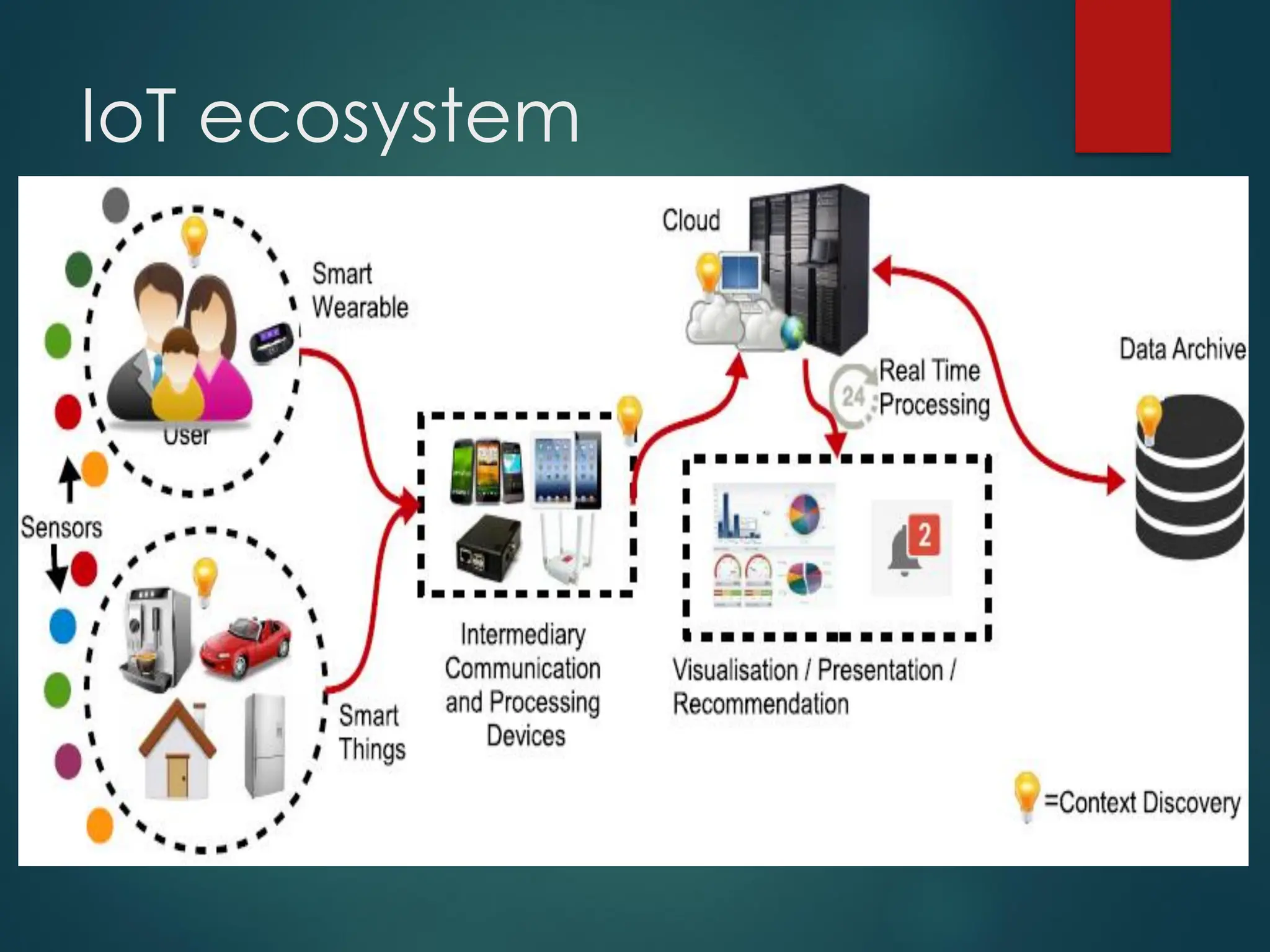
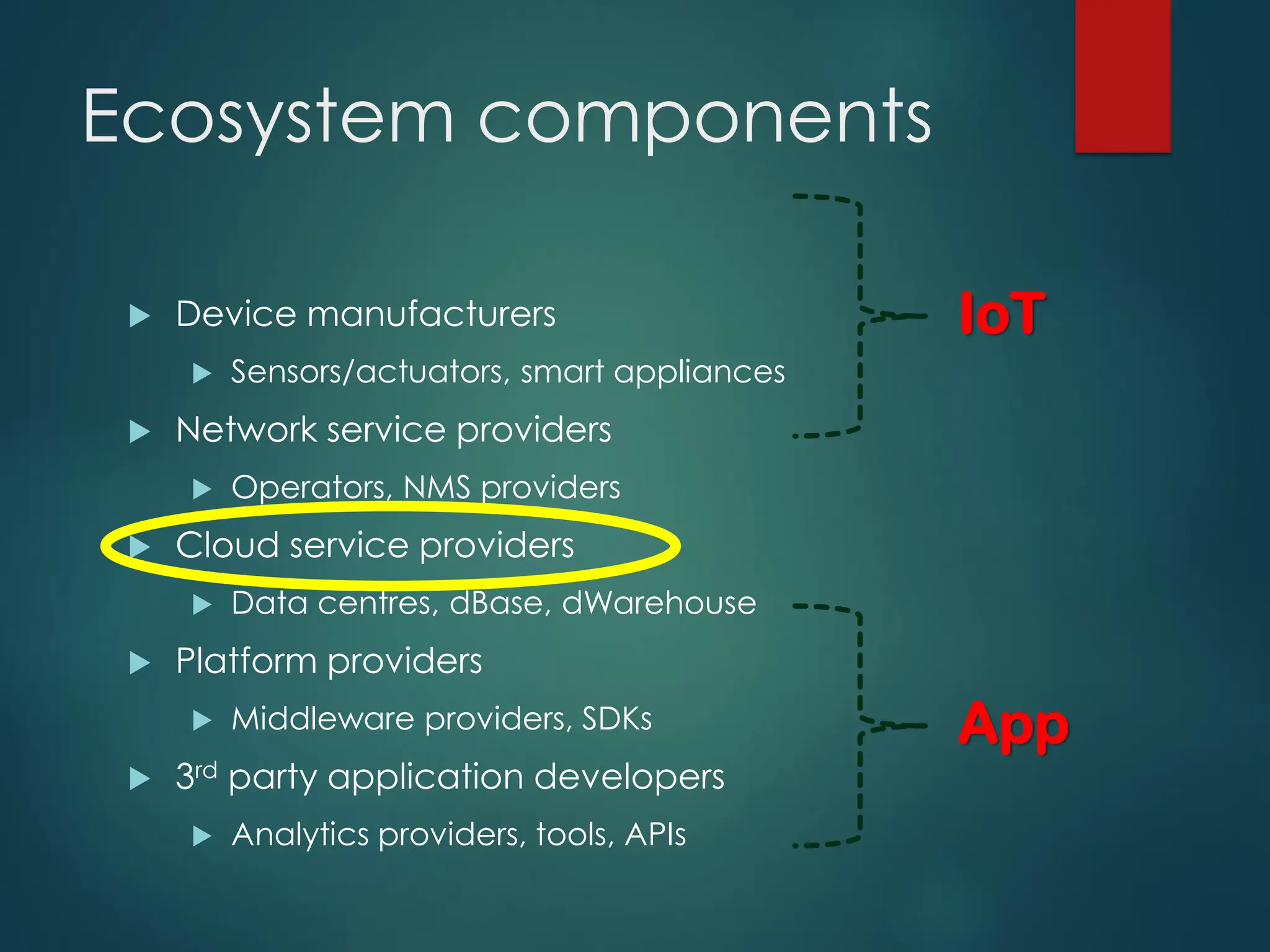
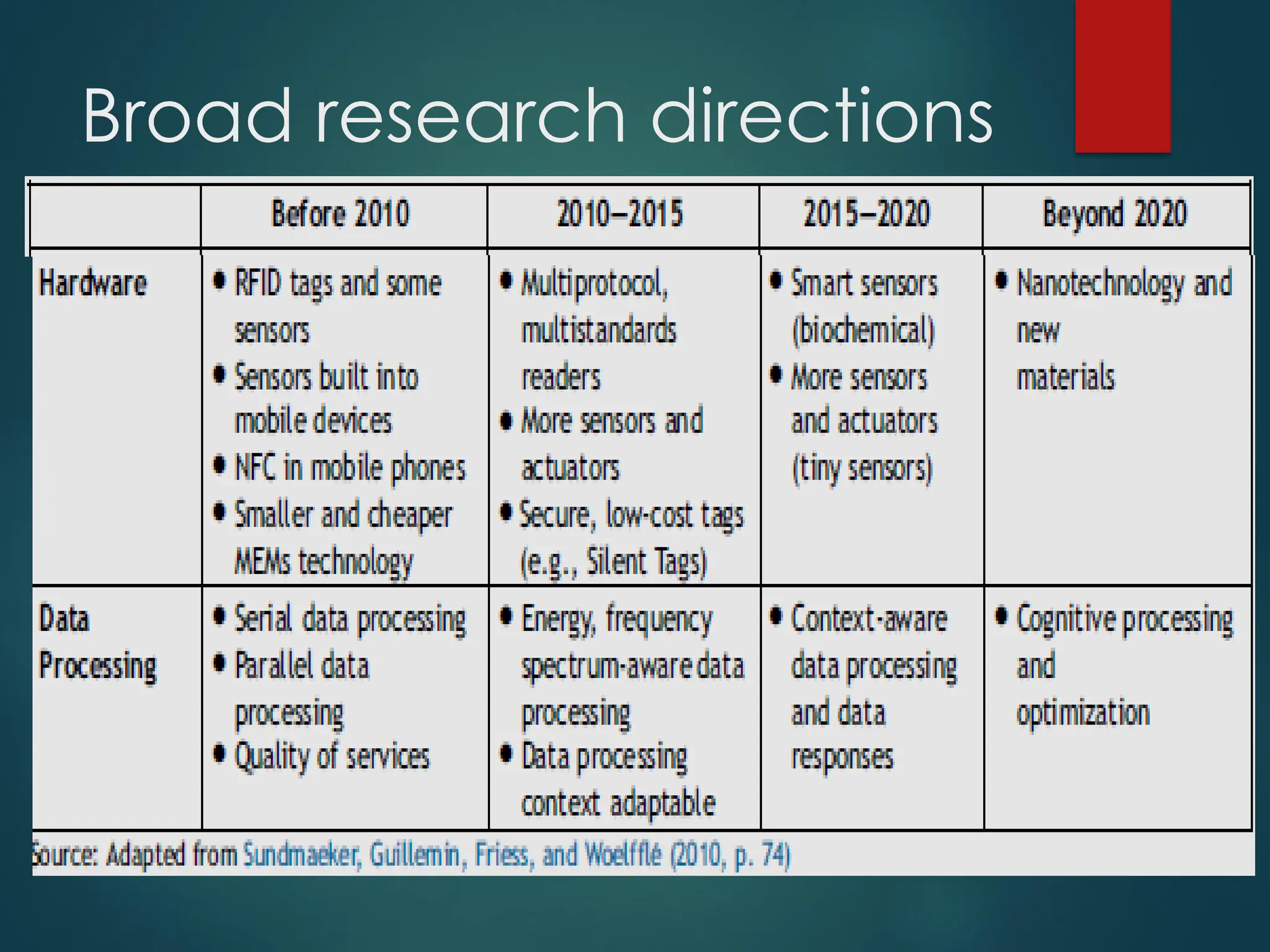
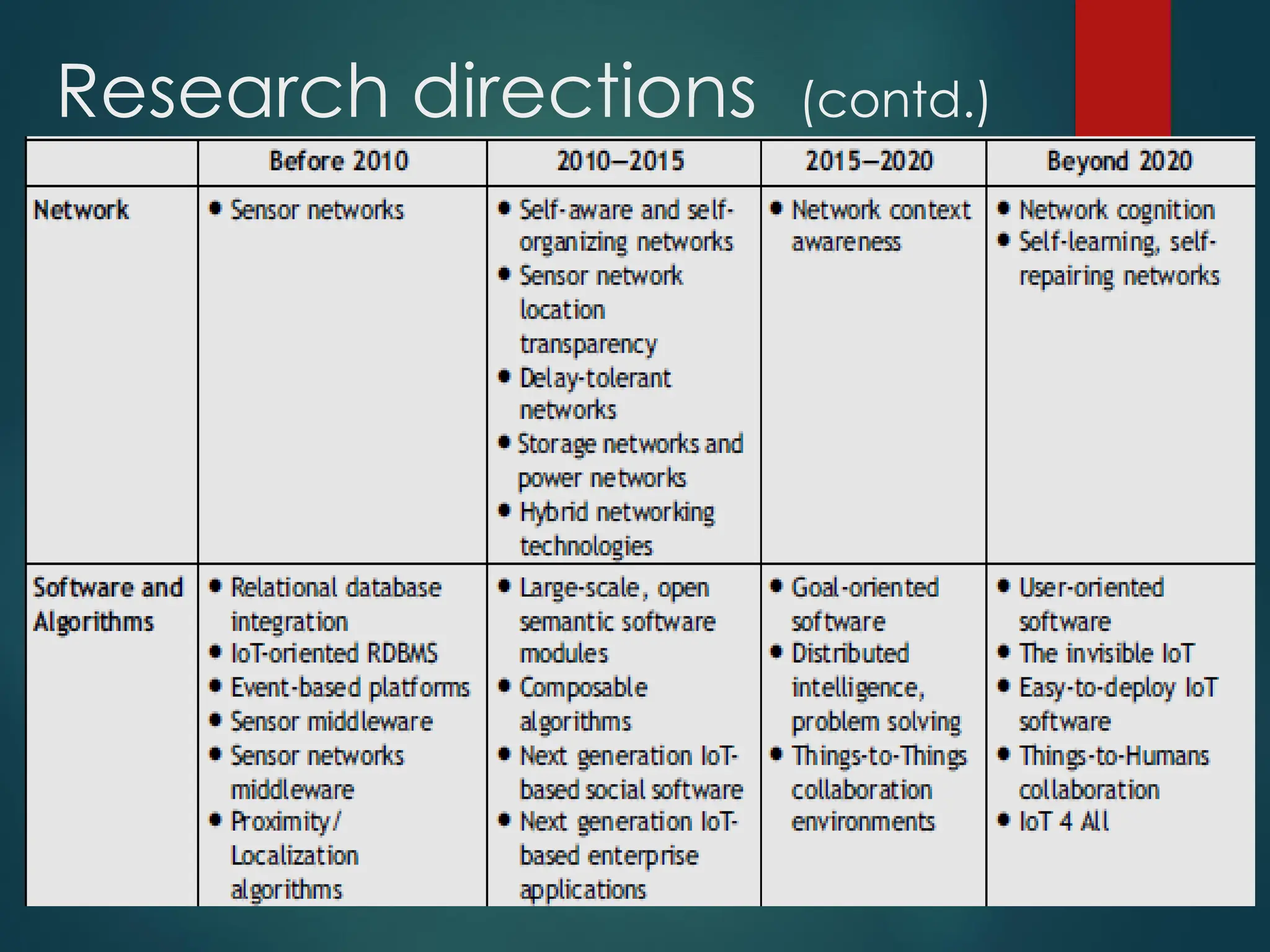
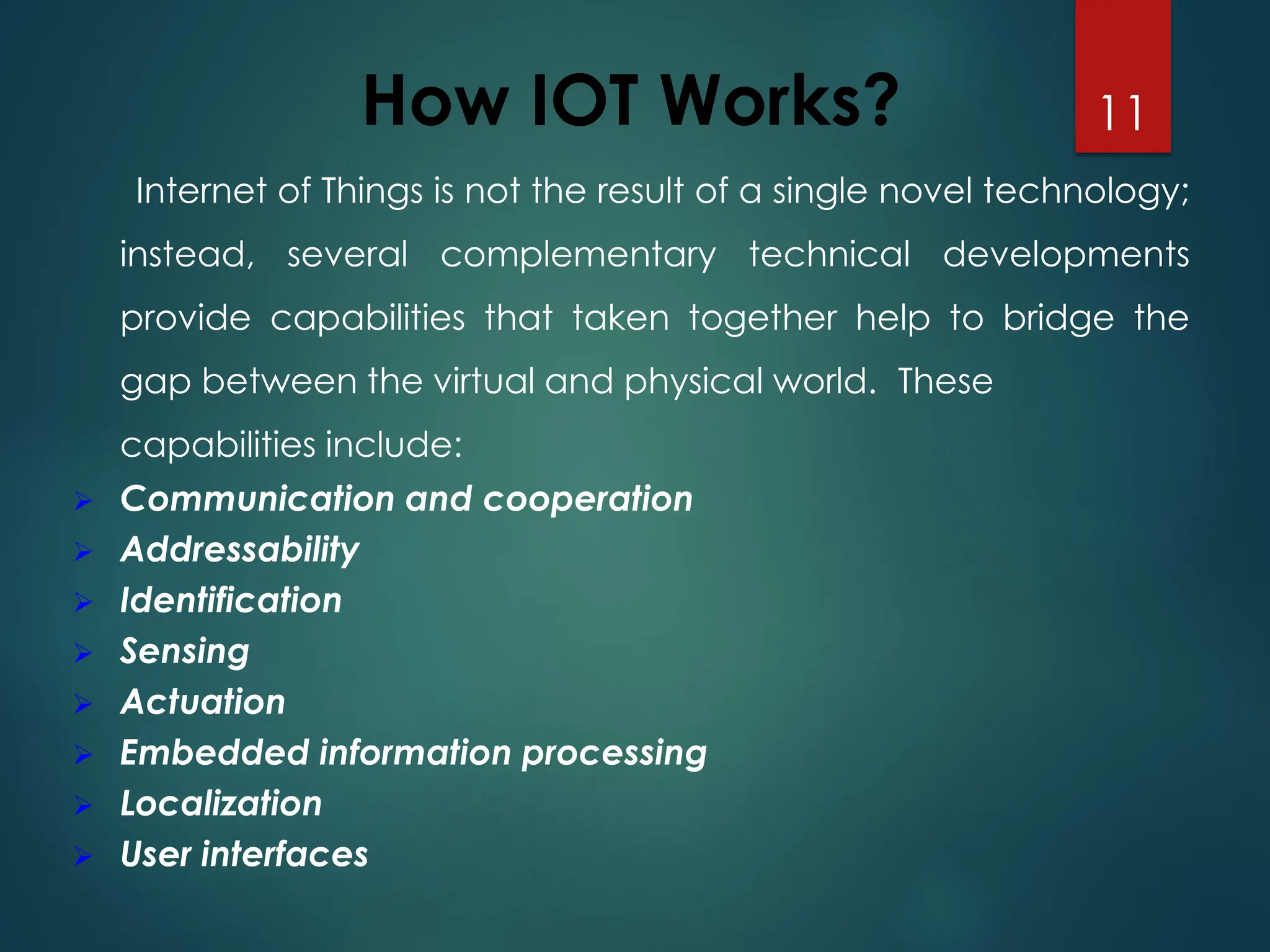
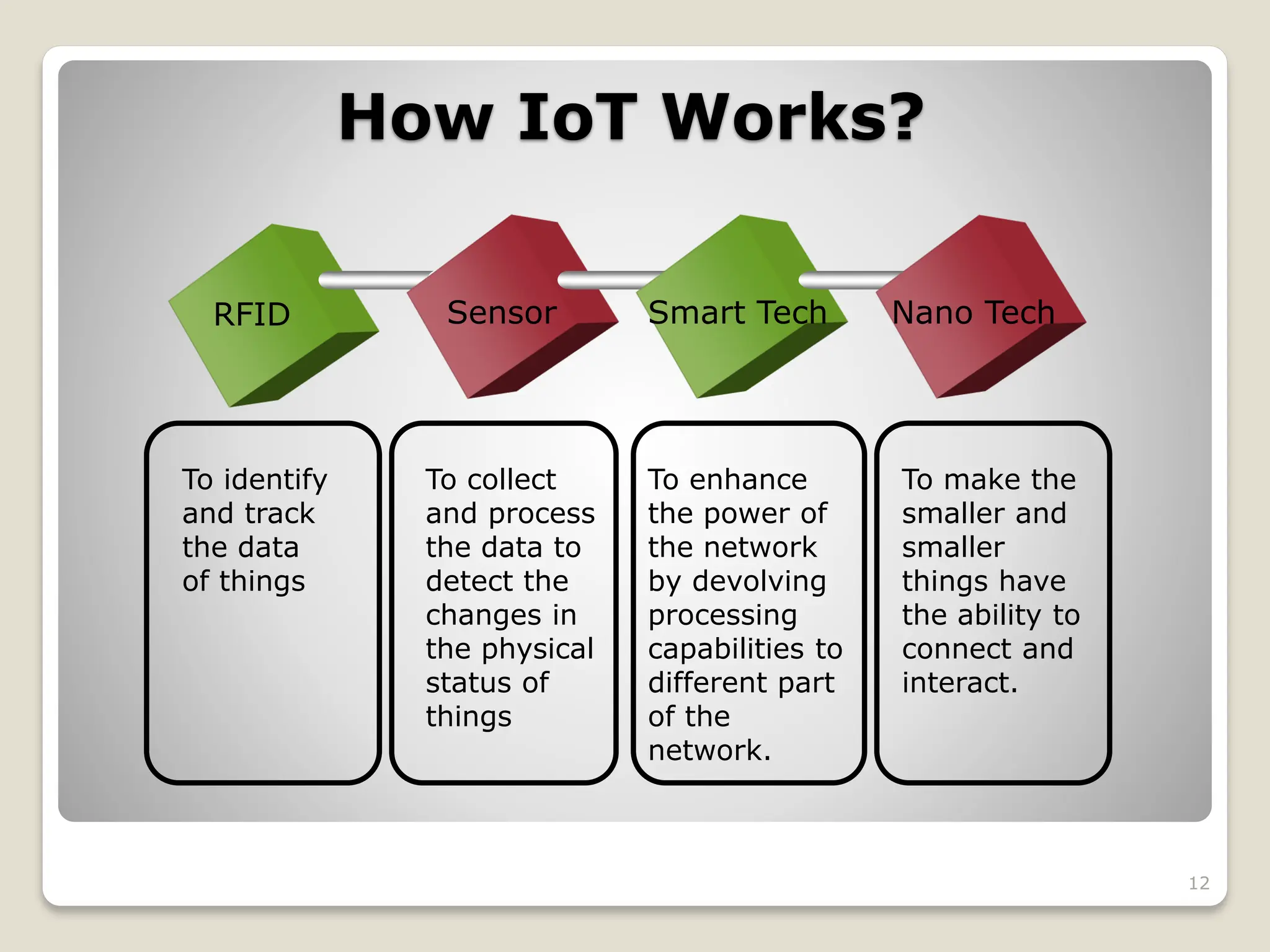
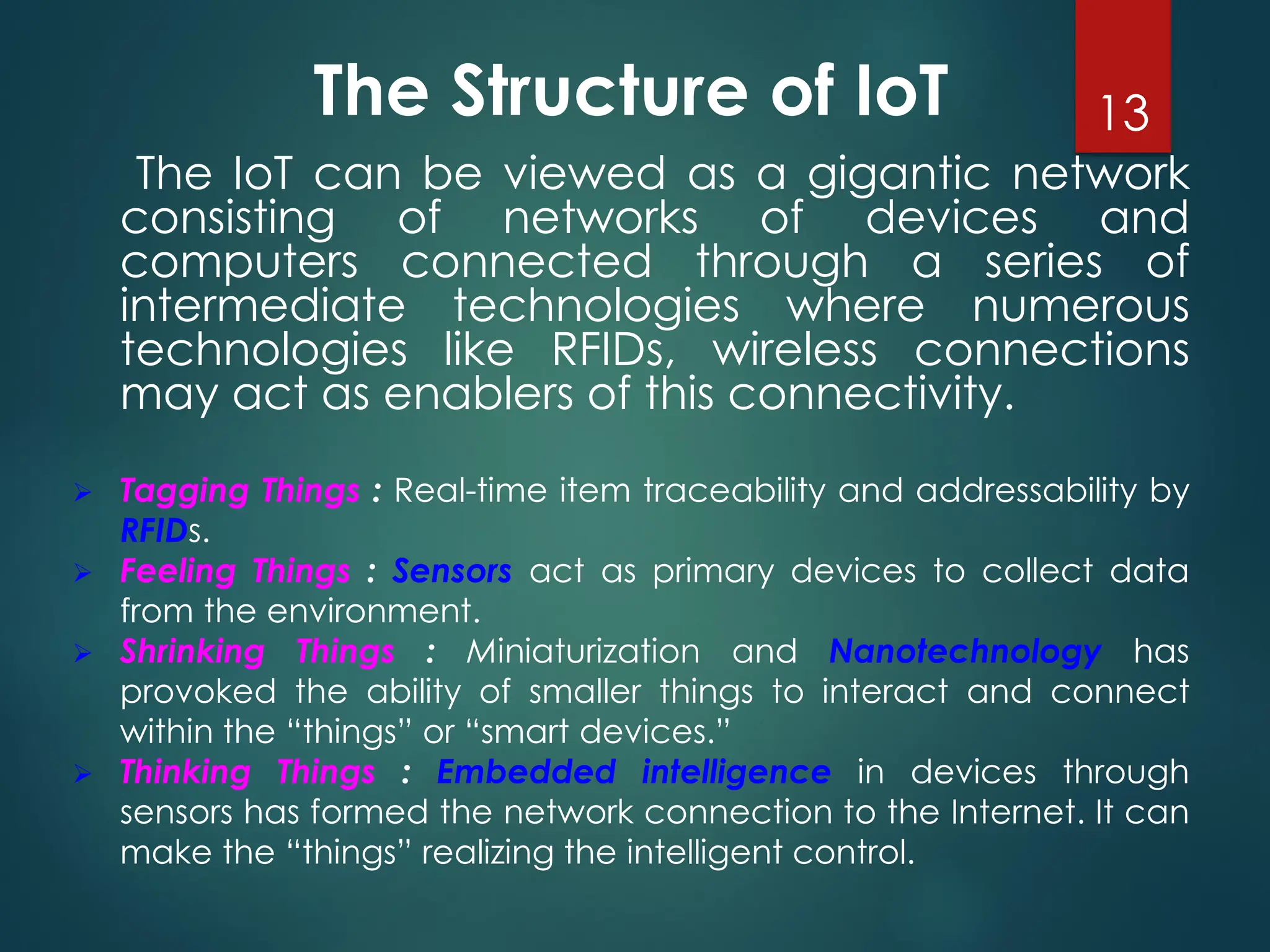
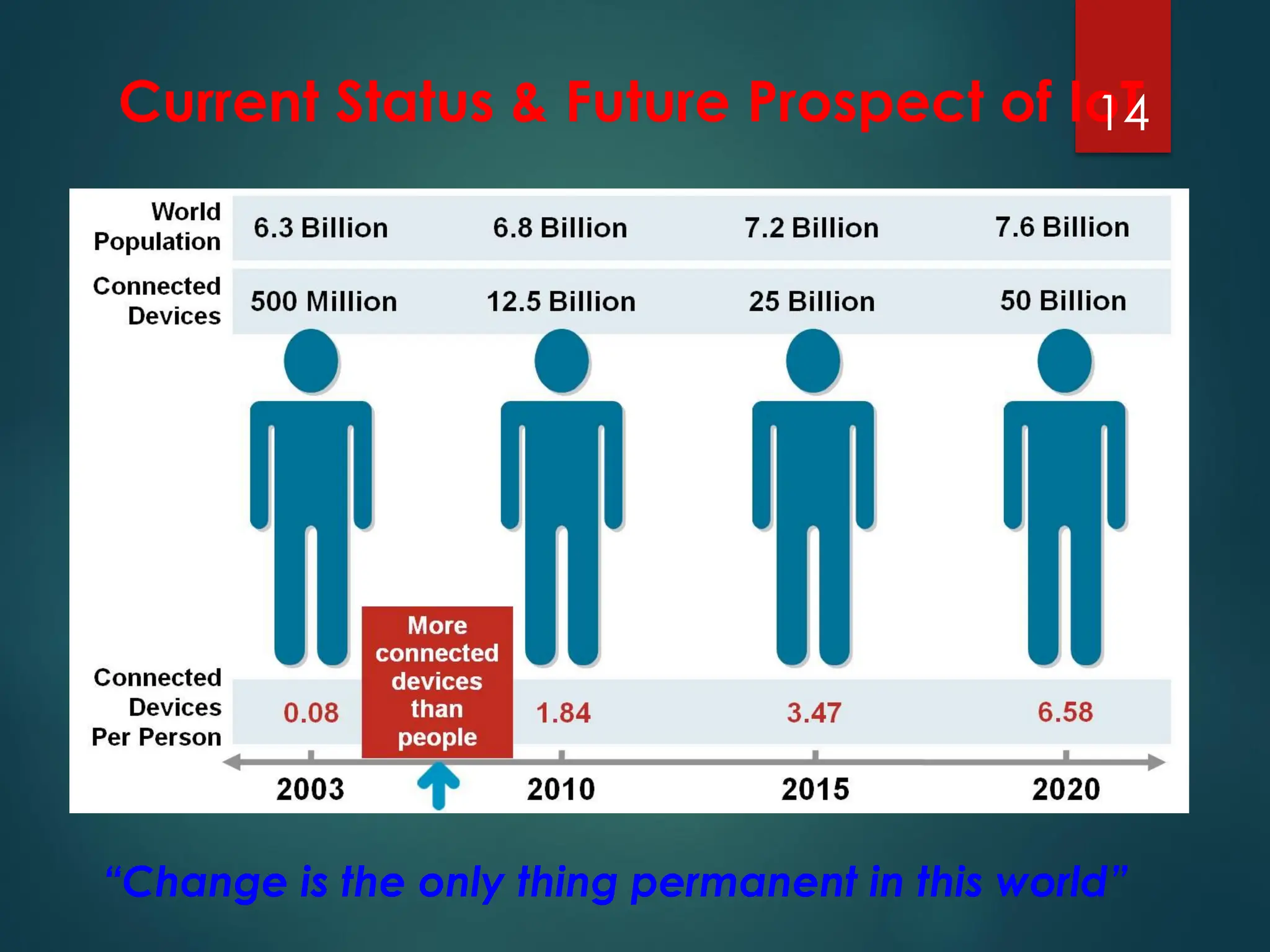
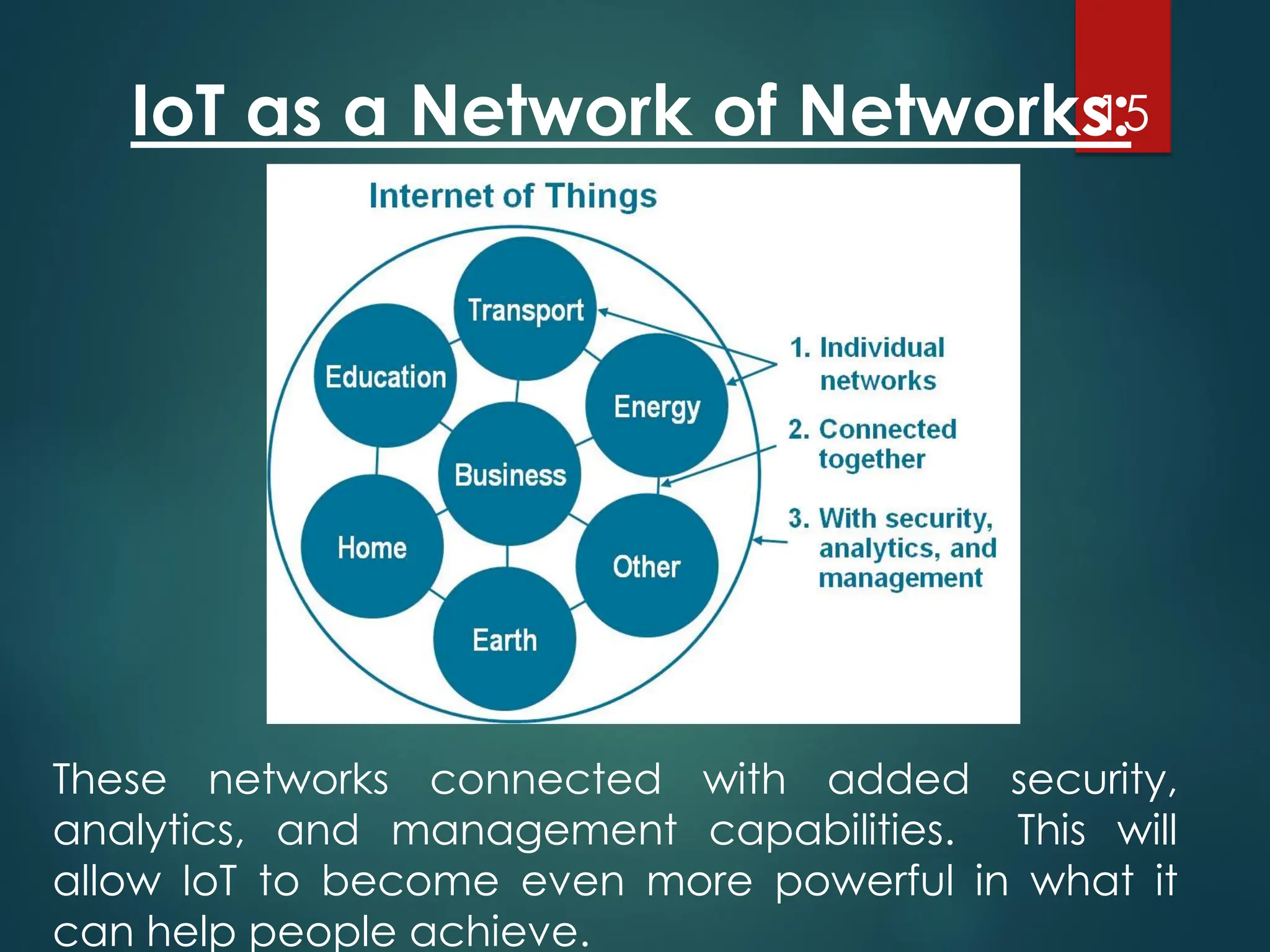
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects embedded with technology that enables data collection and exchange. It includes a wide variety of devices, such as medical implants and smart appliances, working together to enhance efficiency and facilitate remote control. The IoT ecosystem consists of numerous components like device manufacturers, cloud service providers, and analytics tools, with ongoing advancements driving its growth and application.