- Ruby on Rails is an open-source web framework that is optimized for programmer happiness and sustainable productivity. It uses conventions over configurations to favor writing beautiful code.
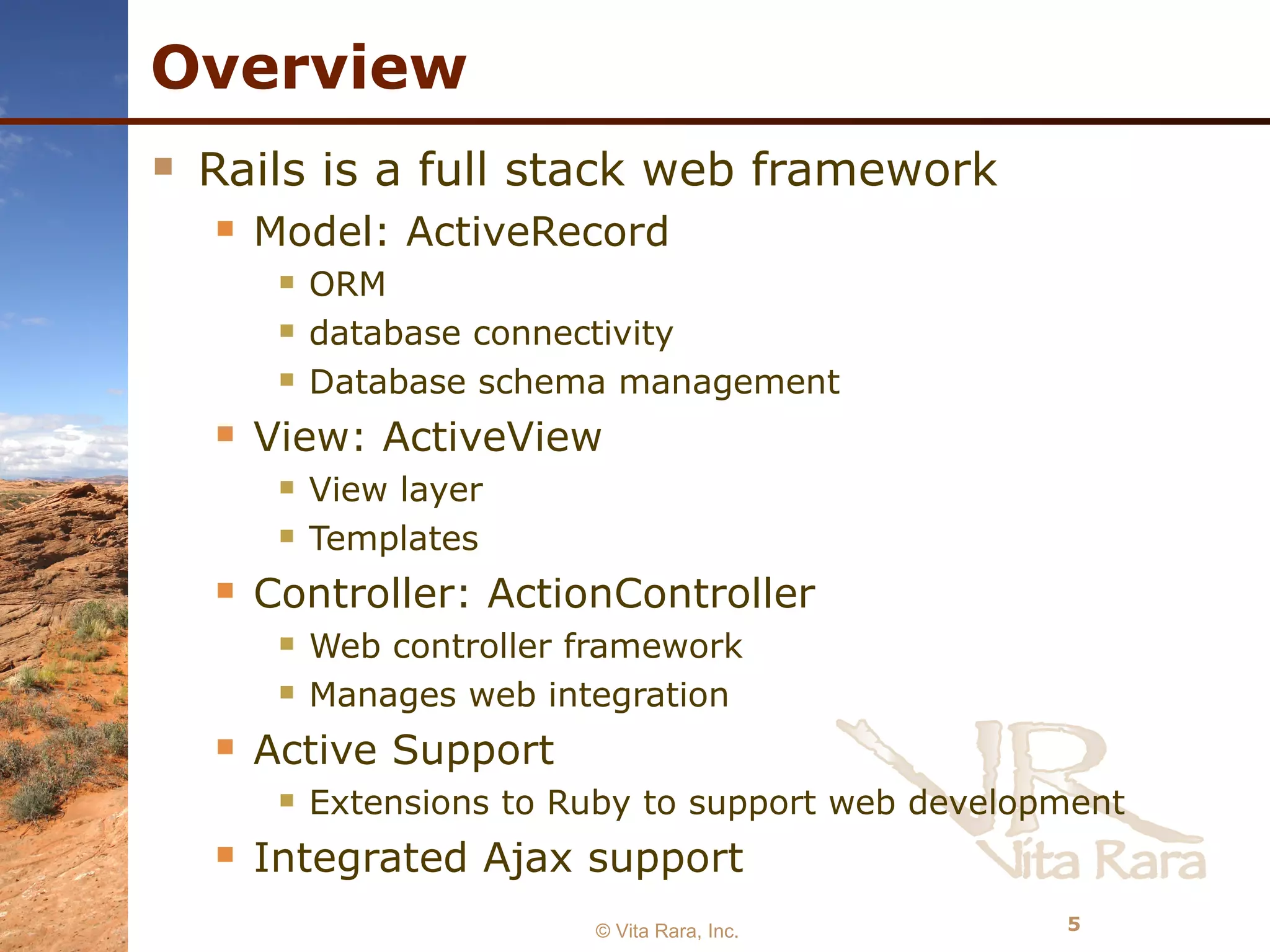
- Rails includes tools like ActiveRecord for ORM, ActiveView for templating, and ActionController for handling web requests. It also provides integrated support for AJAX, RESTful web services, and testing.
- The framework emphasizes conventions like MVC patterns and uses Ruby code for everything including database access and JavaScript integration for a simpler development experience.






![Finding Models User.find(:first) User.find(:all) User.find(1) User.find_by_login(‘mark’) User.find(:all, :conditions => [ “login = ? AND password = ?”, login, password]) © Vita Rara, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtorails-100416134115-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Ruby-on-Rails-17-2048.jpg)








![A Simple Controller © Vita Rara, Inc. class PrioritiesController < InternalController def show @priority = current_account.priorities.find(params[:id]) end def new @priority = Priority. new end def create @priority = Priority. new (params[:priority]) if @priority.save flash[:notice] = 'The priority was successfully created.' redirect_to account_url else render :action => "new" end end ... end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtorails-100416134115-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Ruby-on-Rails-34-2048.jpg)
![Sessions A hash stored on the server, typically in a database table or in the file system. Keyed by the cookie _session_id Avoid storing complex Ruby objects, instead put id:s in the session and keep data in the database, i.e. use session[:user_id] rather than session[:user] © Vita Rara, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtorails-100416134115-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Ruby-on-Rails-35-2048.jpg)







![Contact Information Mark Menard [email_address] http://www.vitarara.net / 518 369 7356 © Vita Rara, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtorails-100416134115-phpapp02/75/Intro-to-Ruby-on-Rails-48-2048.jpg)