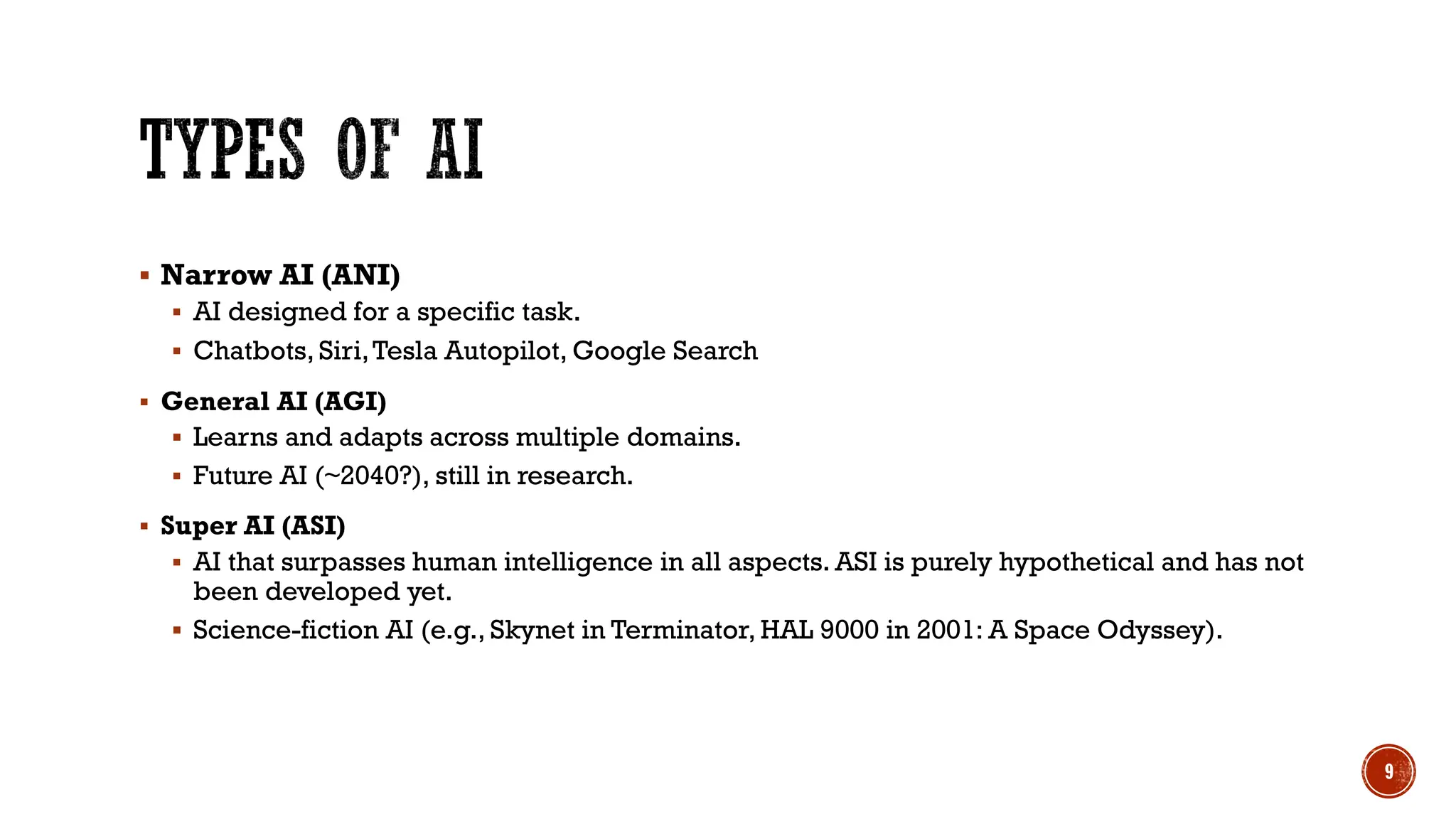
This lecture cover the introduction to artificial intelligence for beginners, its key features, brief history, importance, daily life applications, types of artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, overview of artificial intelligence technologies and algorithms.