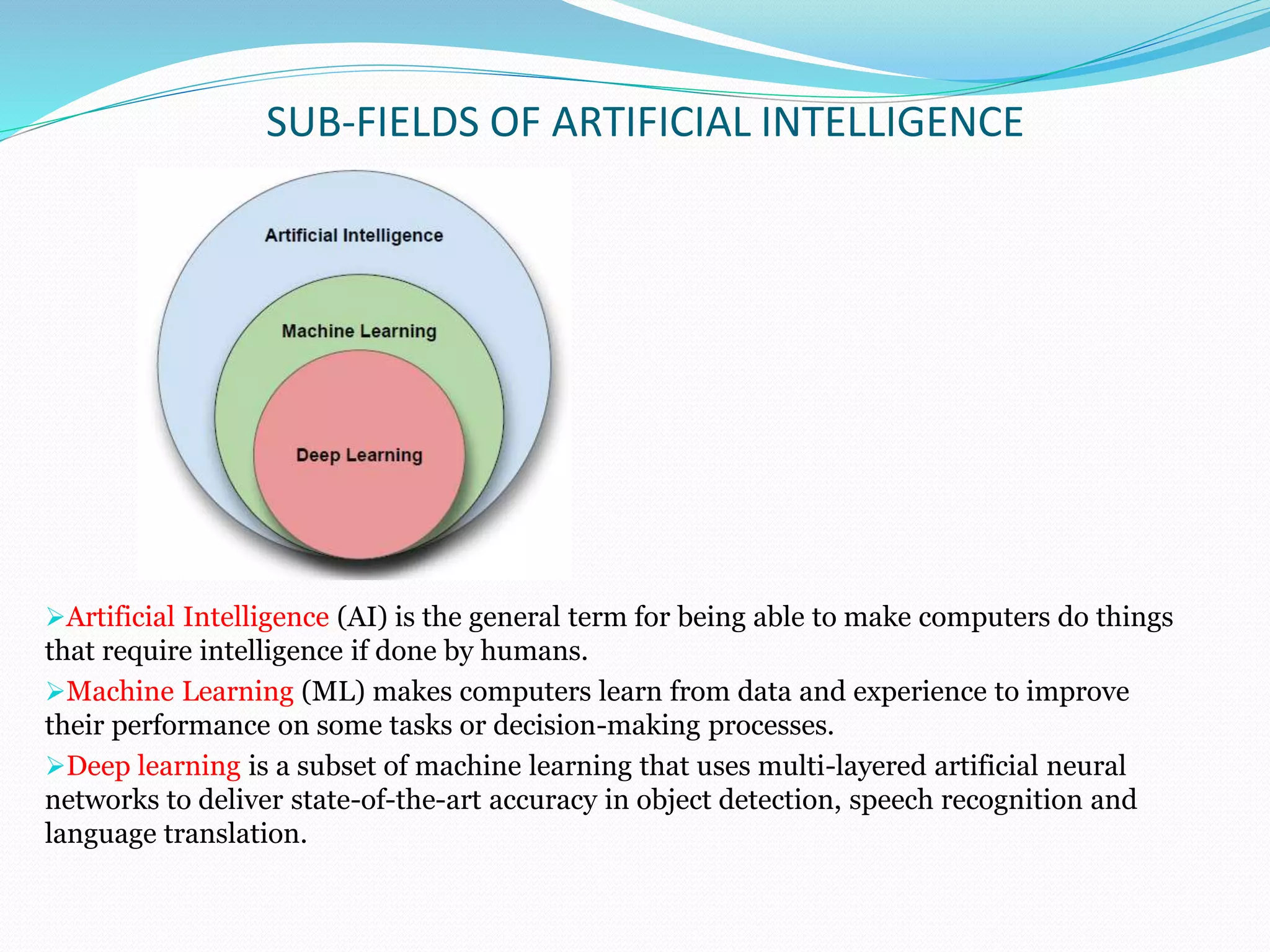
The document provides a comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence (AI), discussing its definition, history, goals, types, and current status. It highlights the various applications of AI across industries, its advantages and disadvantages, as well as the potential risks and ethical implications. The document concludes that AI is a dominant technology poised to significantly impact various sectors in the future.