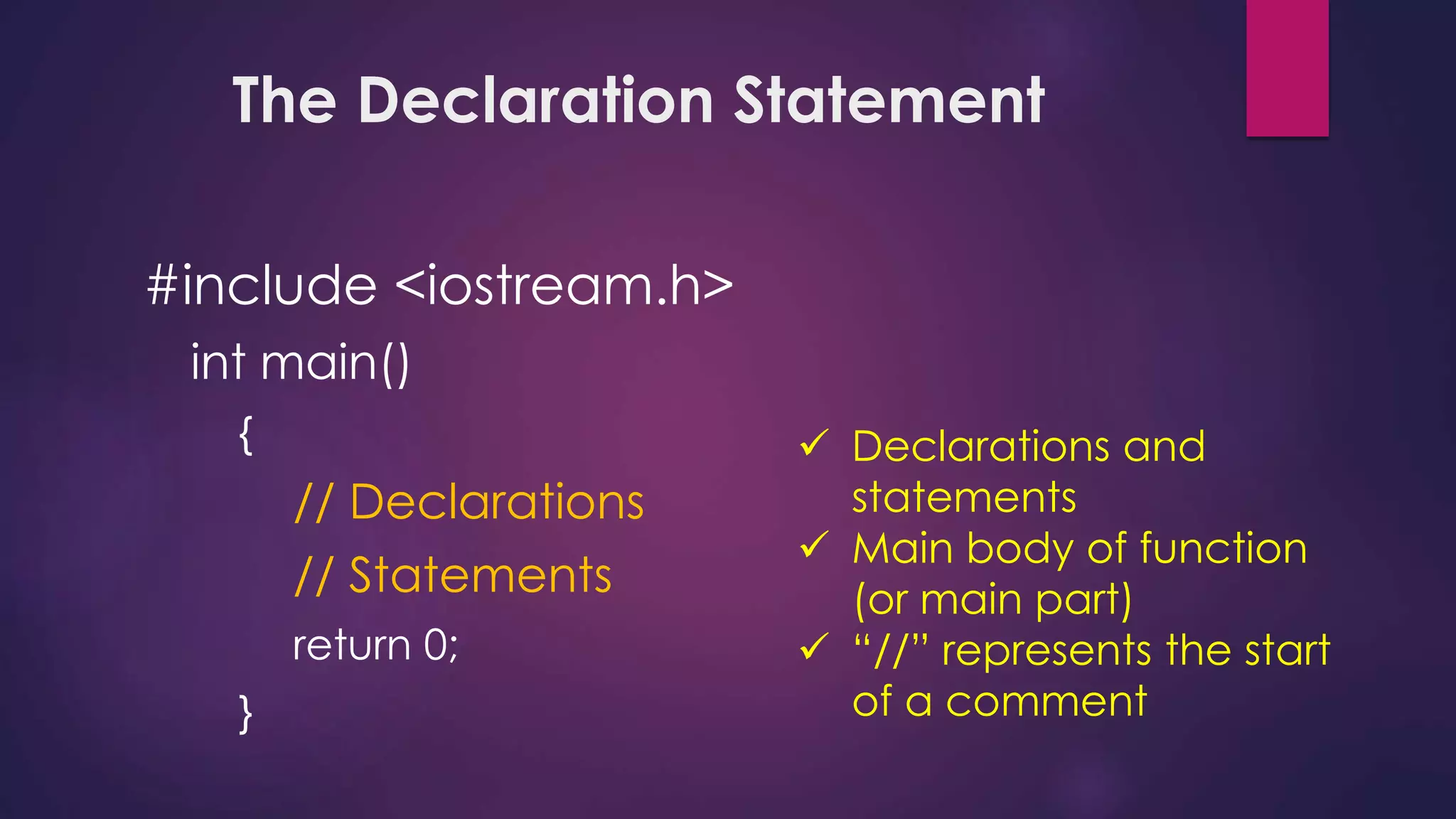
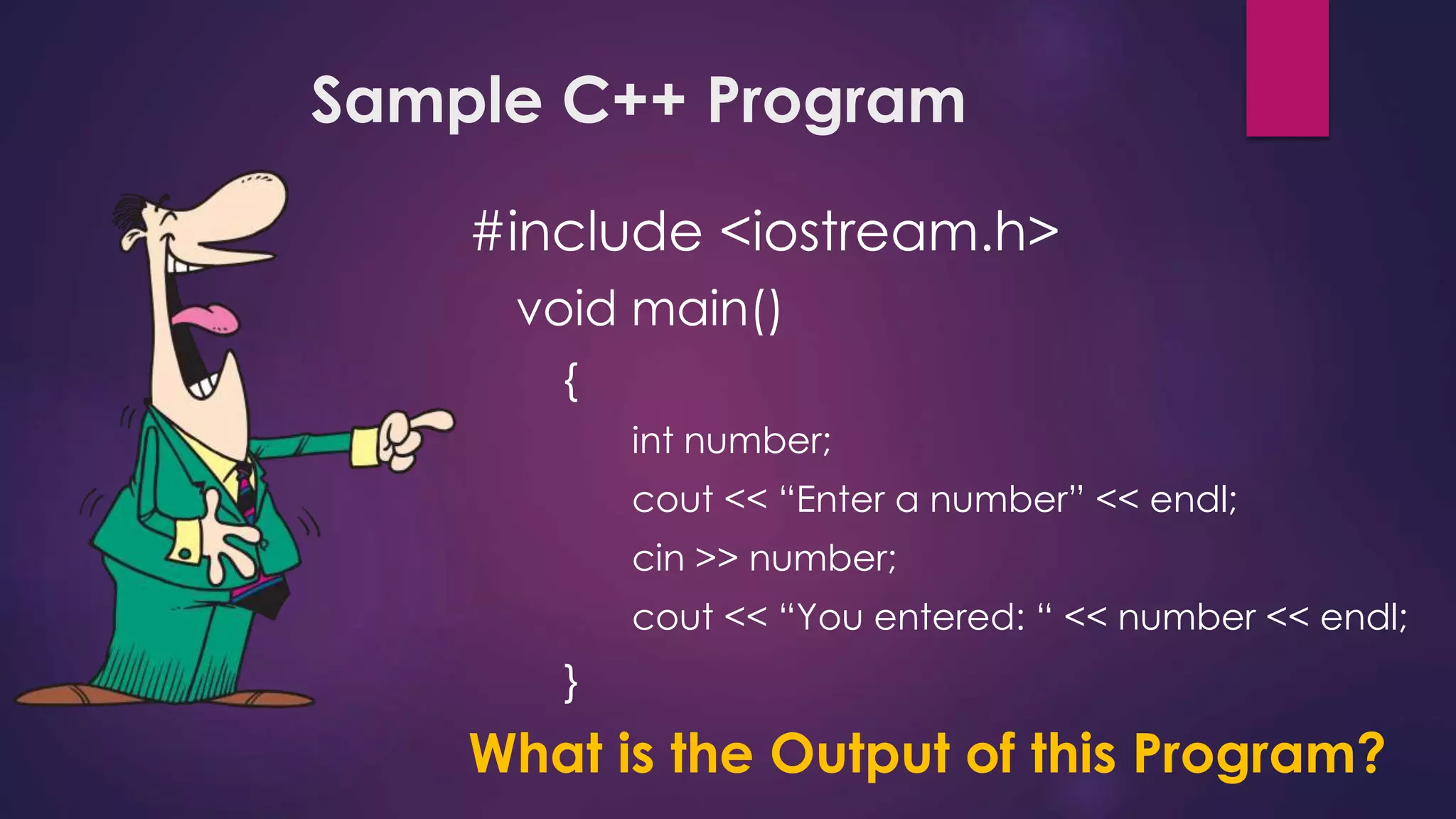
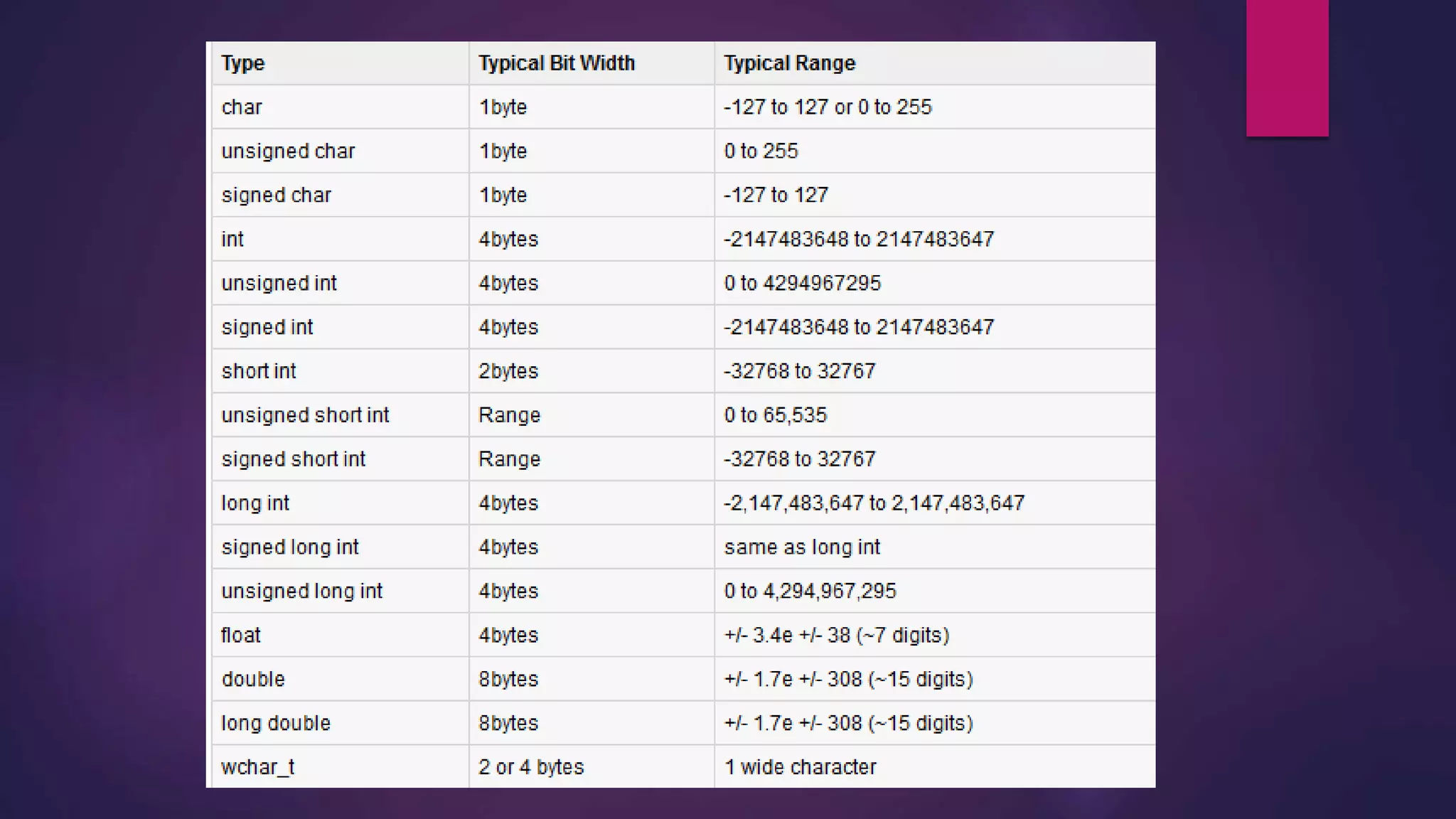
Here is a potential solution to the problem in C++:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num1, num2, num3;
cout << "Enter three numbers: ";
cin >> num1 >> num2 >> num3;
int total = num1 + num2 + num3;
float average = total / 3.0;
cout << "The numbers entered were: " << num1 << ", " << num2 << ", " << num3 << endl;
cout << "Their average is: " << average;
return 0;
}
Some key points:
- Use cin to input the 3 numbers from the