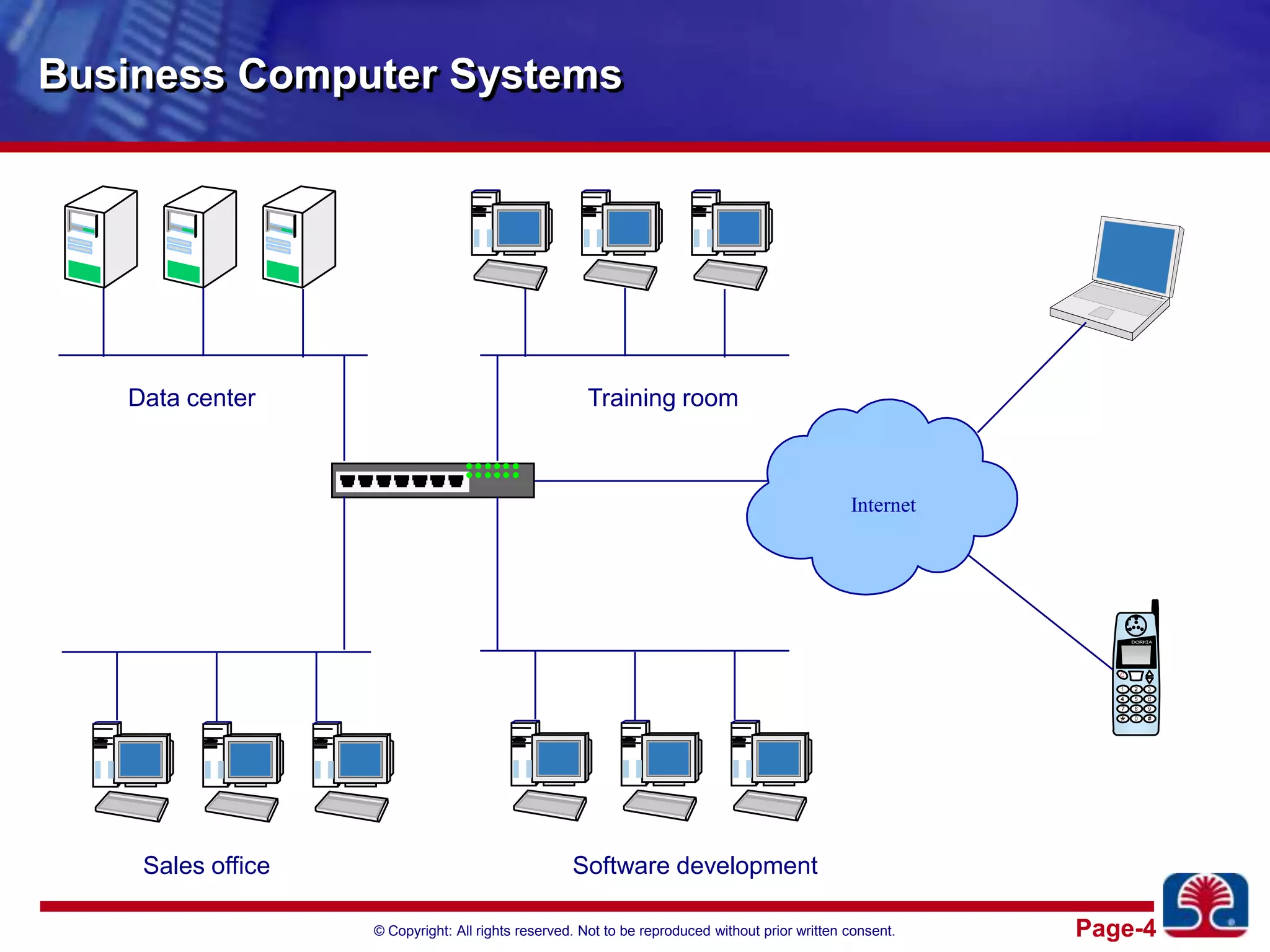
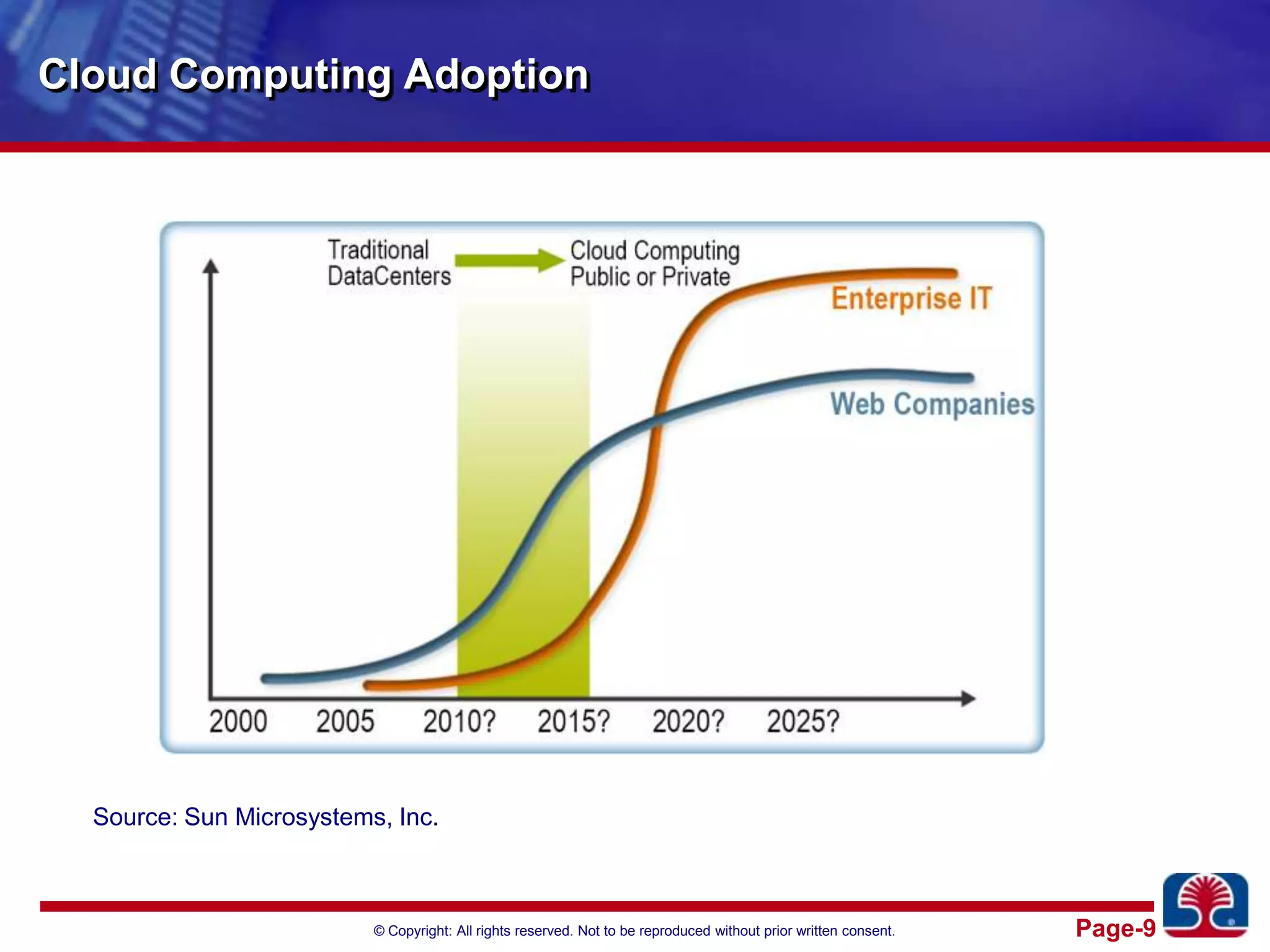
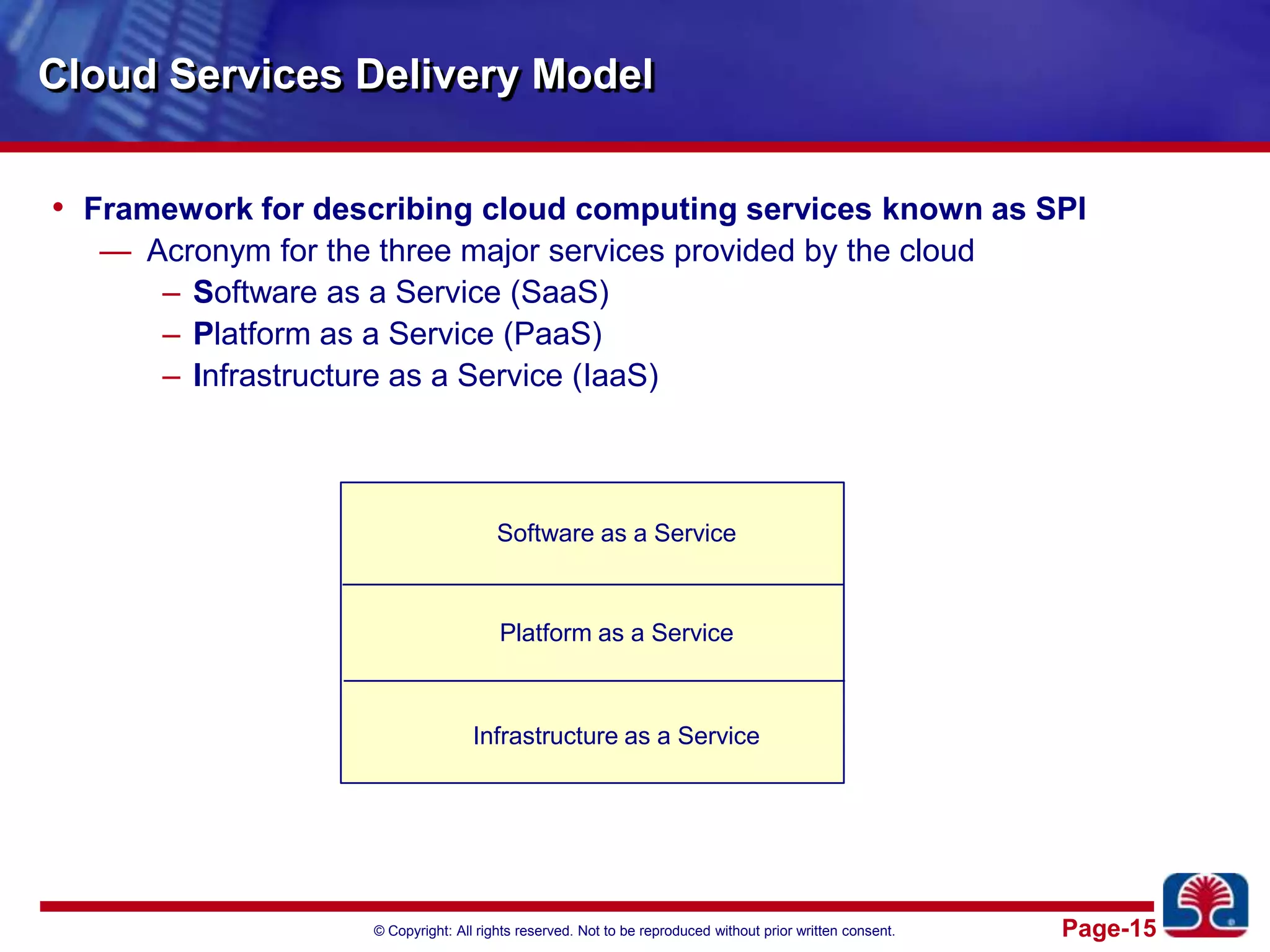
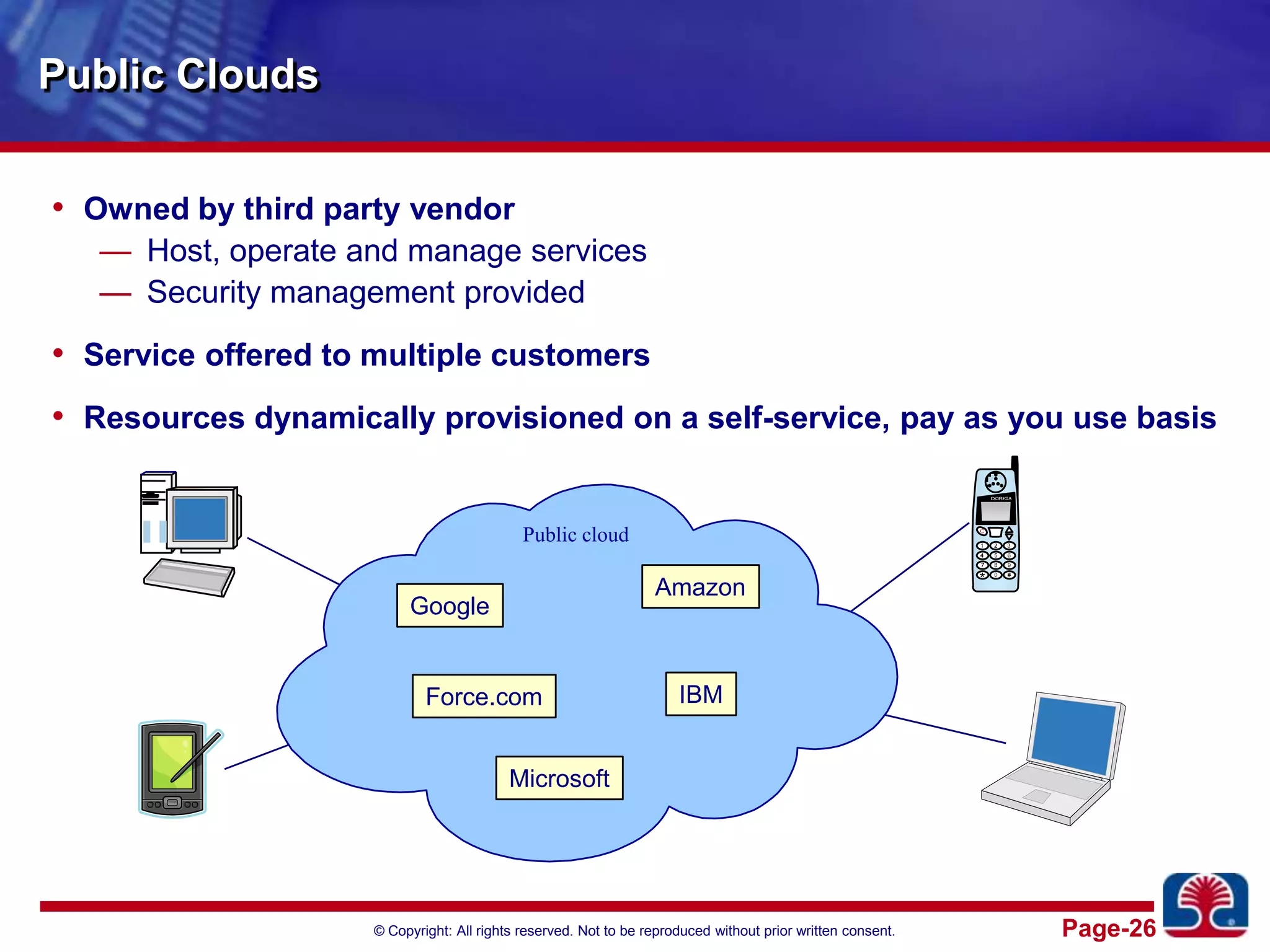
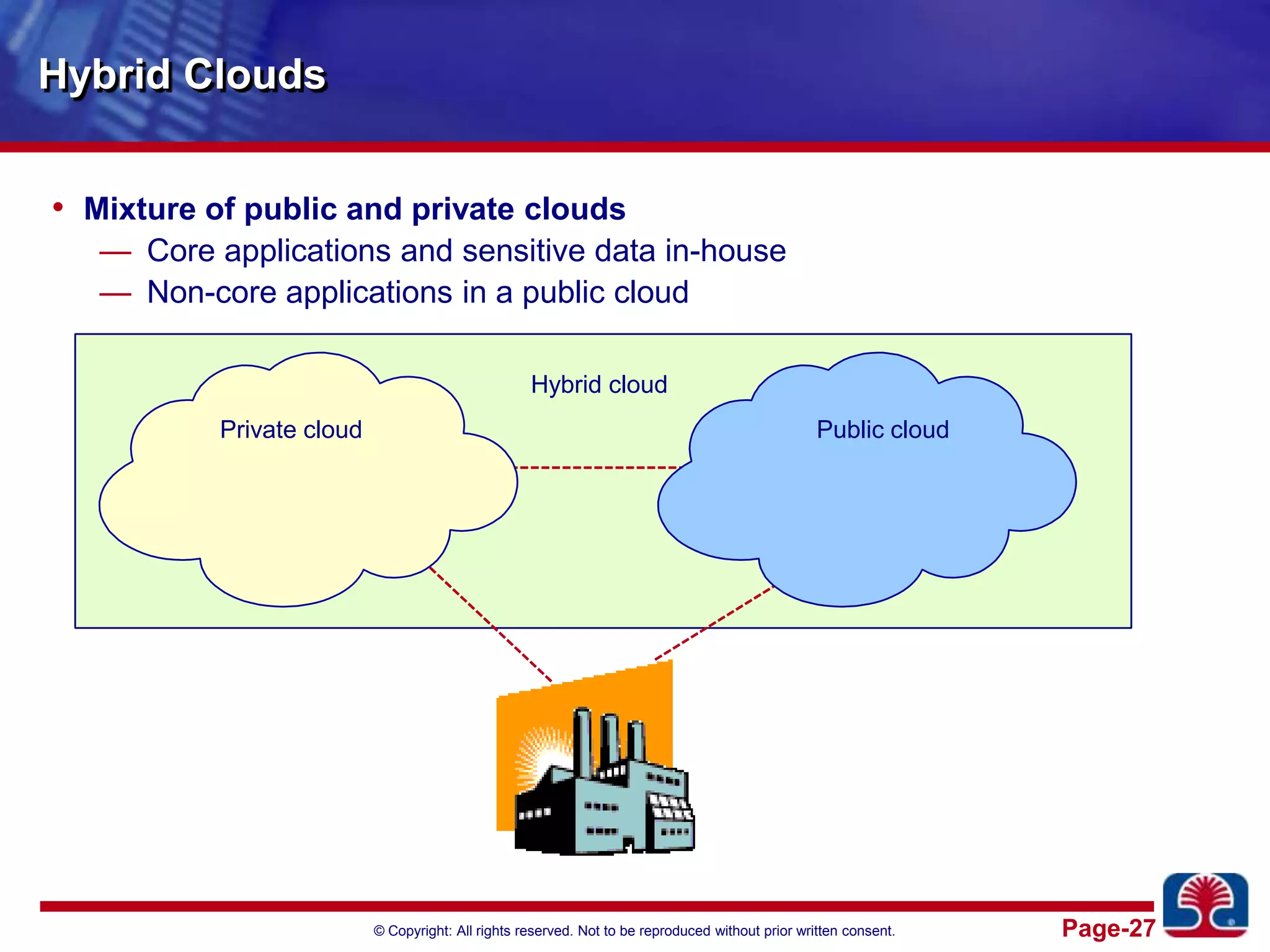
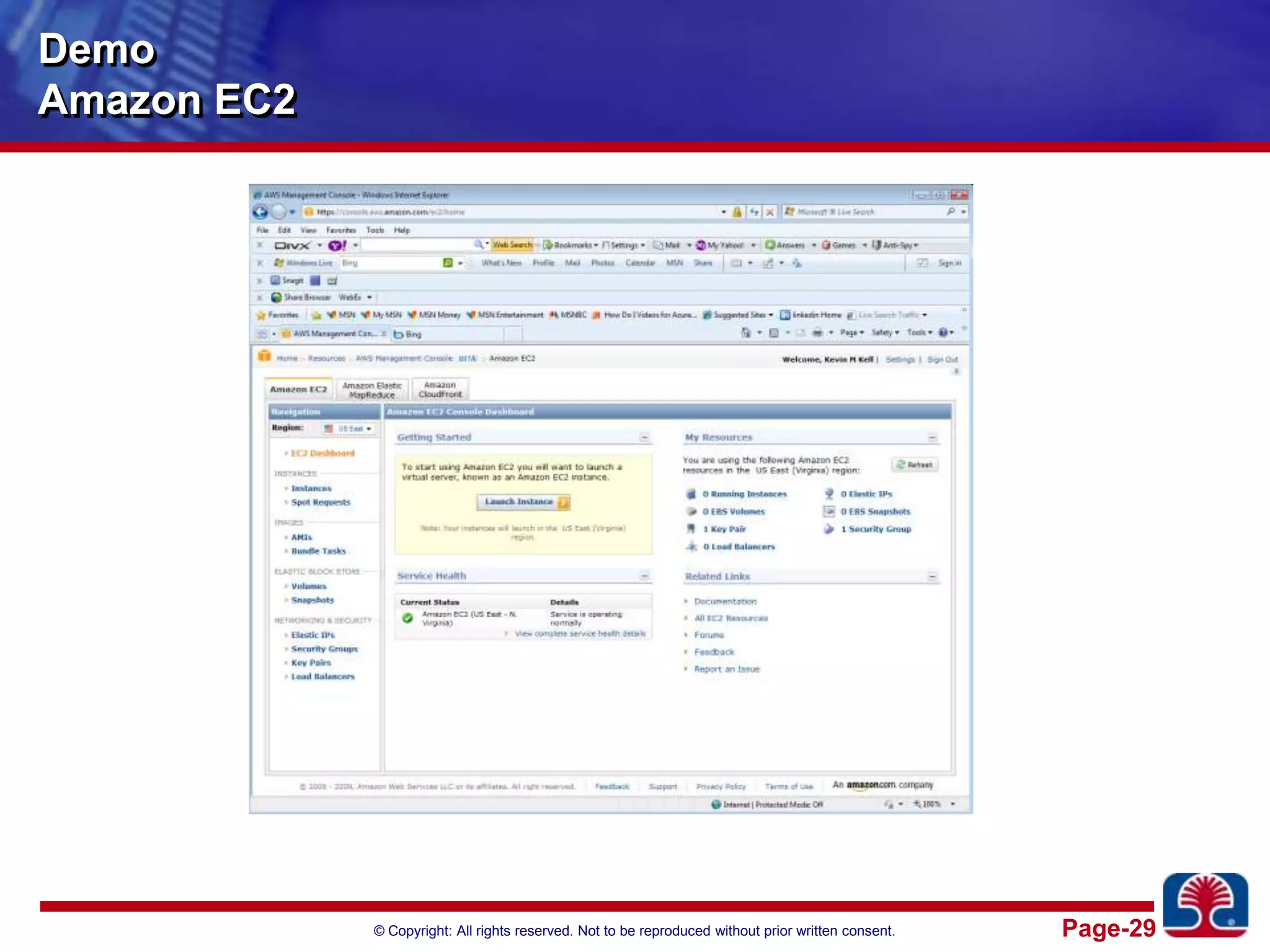
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing. It discusses the benefits of cloud computing like pay-as-you-go models and operational expense instead of capital expense. It defines cloud computing and introduces its essential characteristics, service models of SaaS, PaaS and IaaS, and deployment models of private, public and hybrid clouds. It demonstrates using Amazon EC2 as an example of infrastructure as a service.