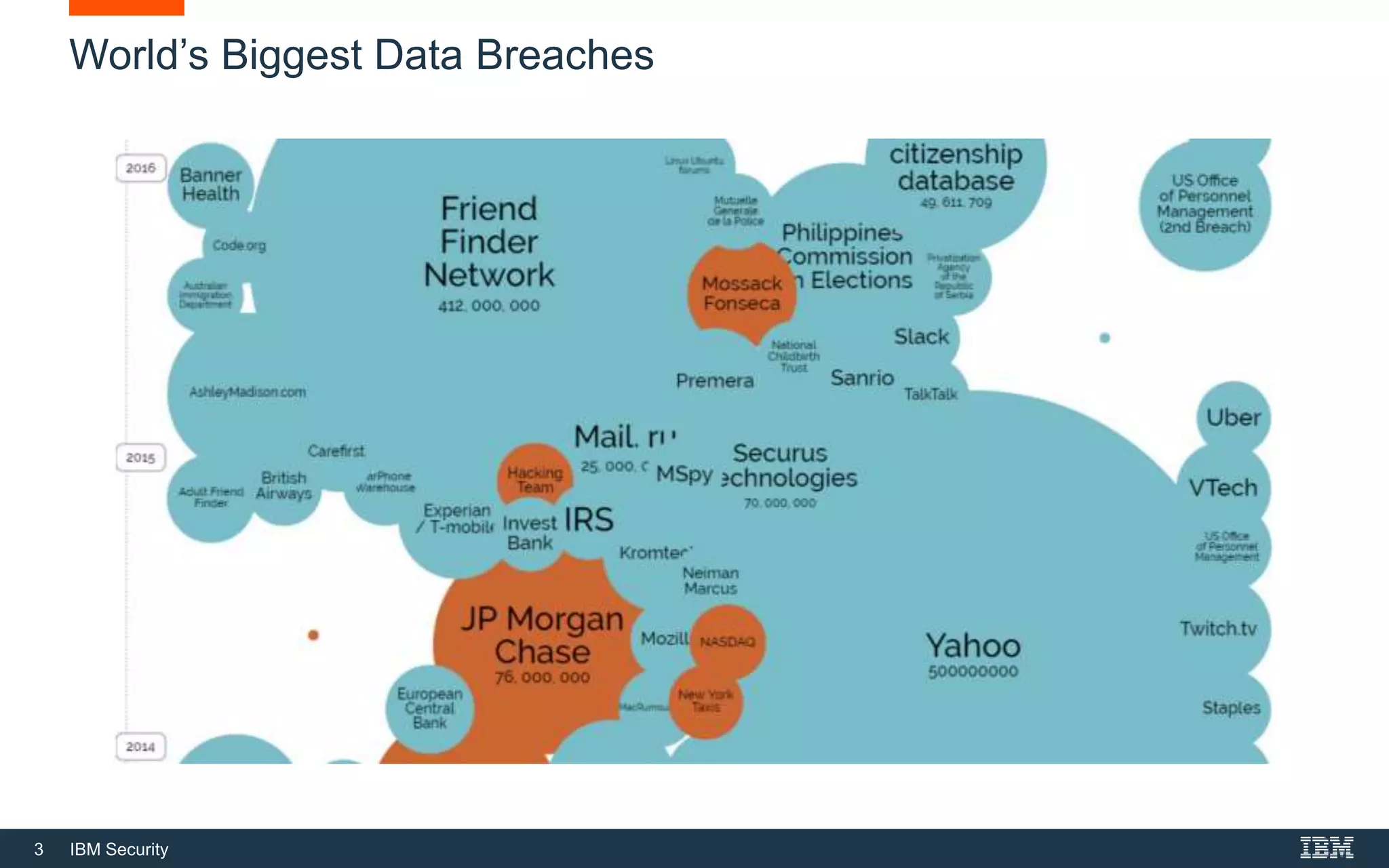
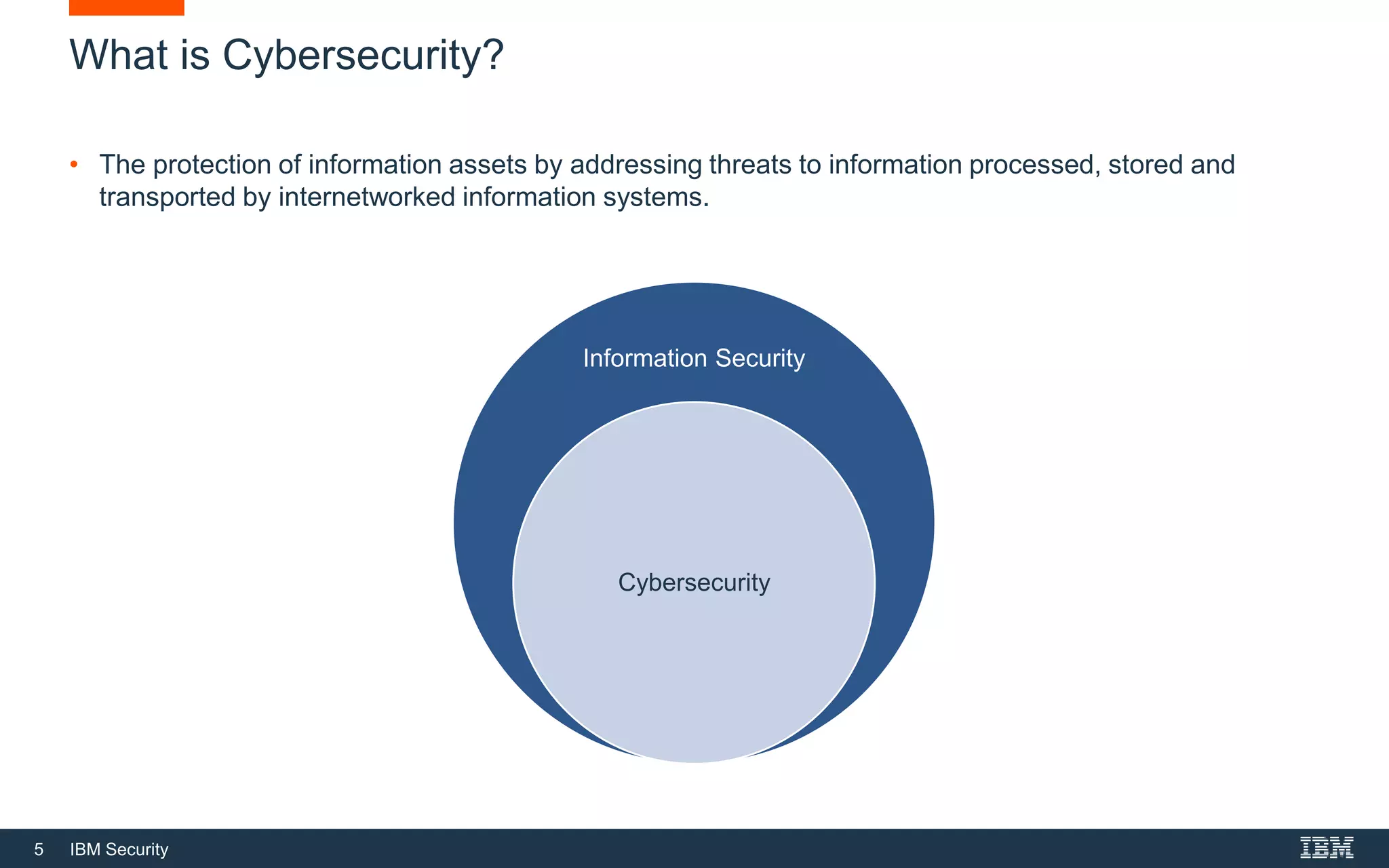
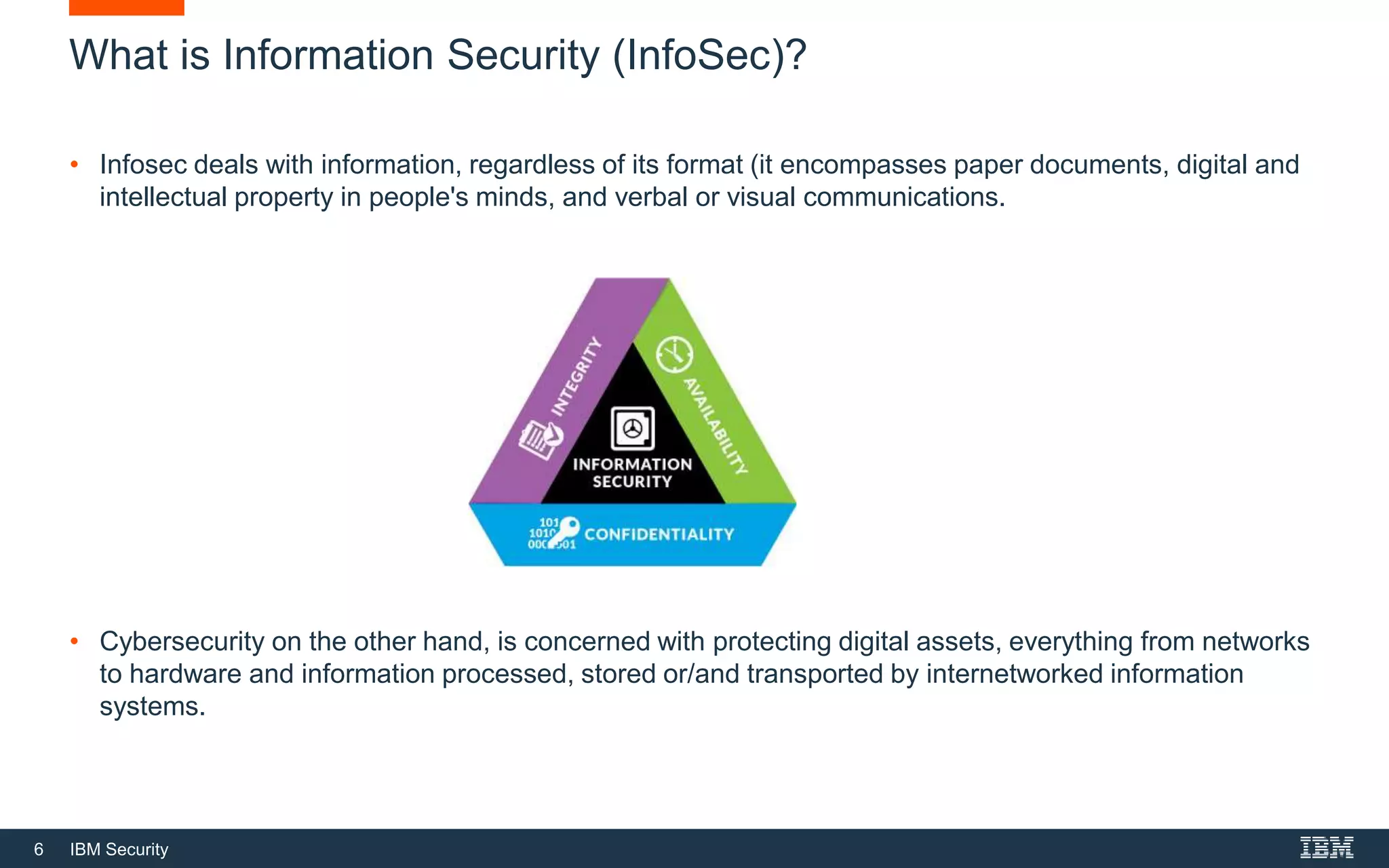
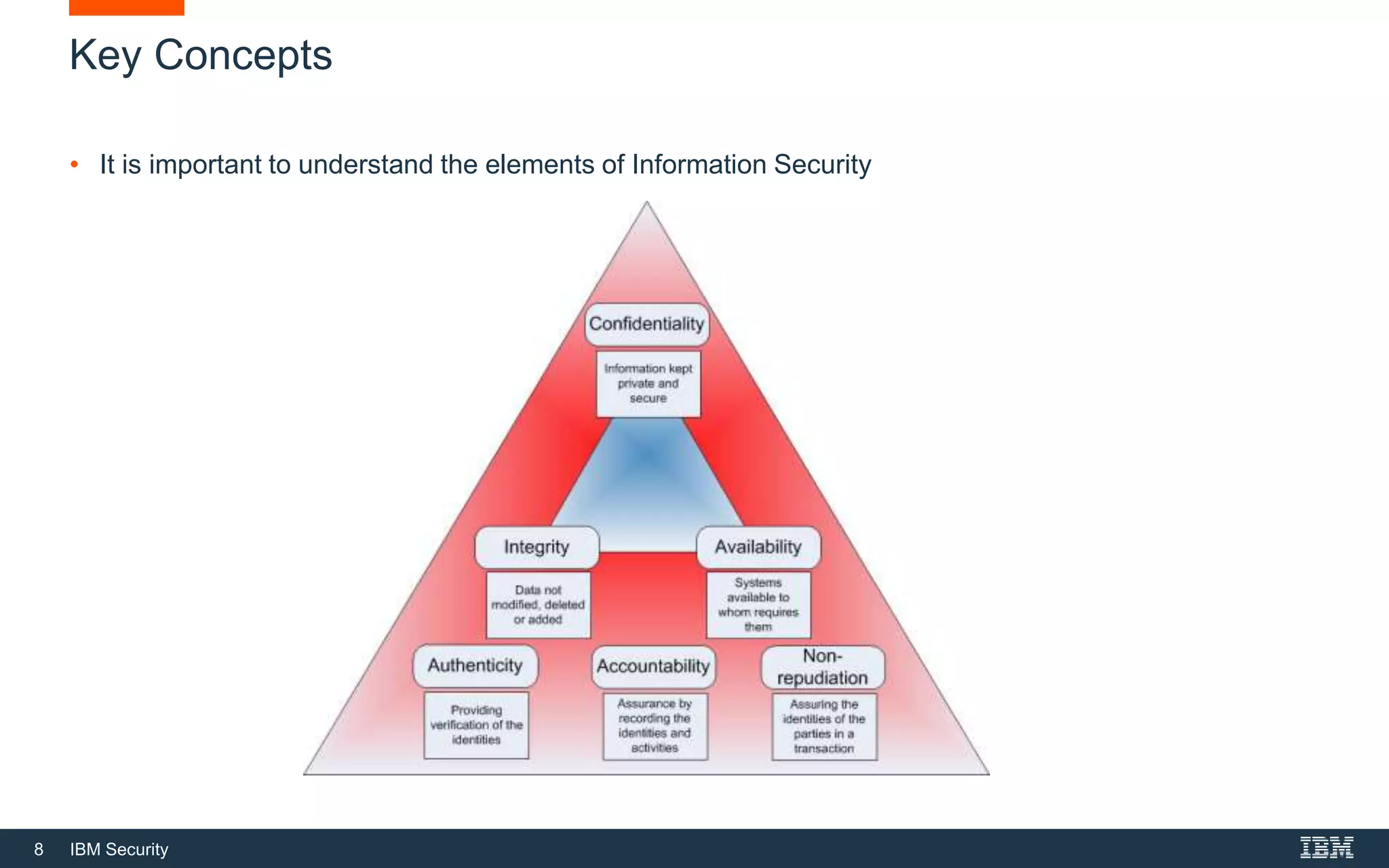
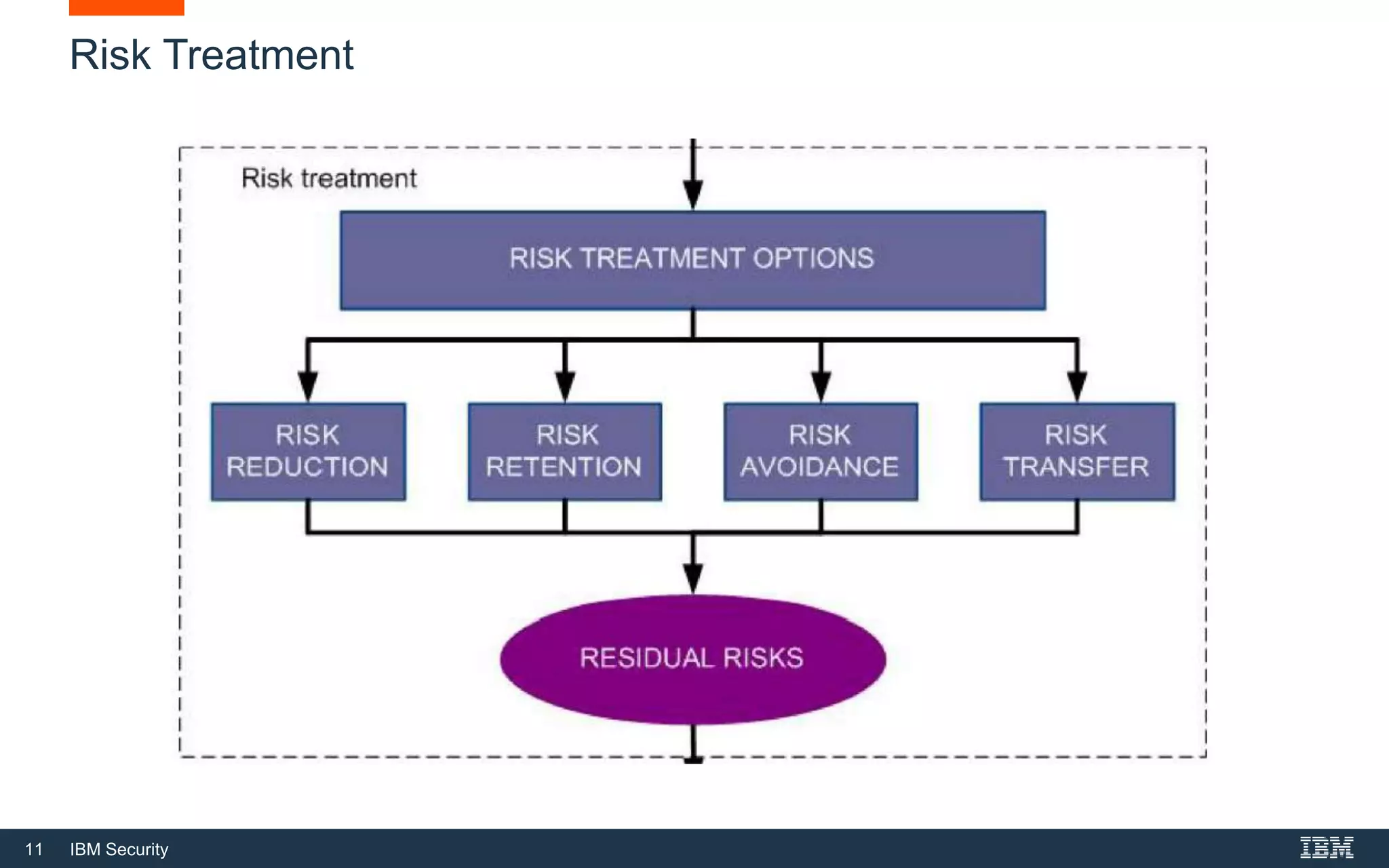
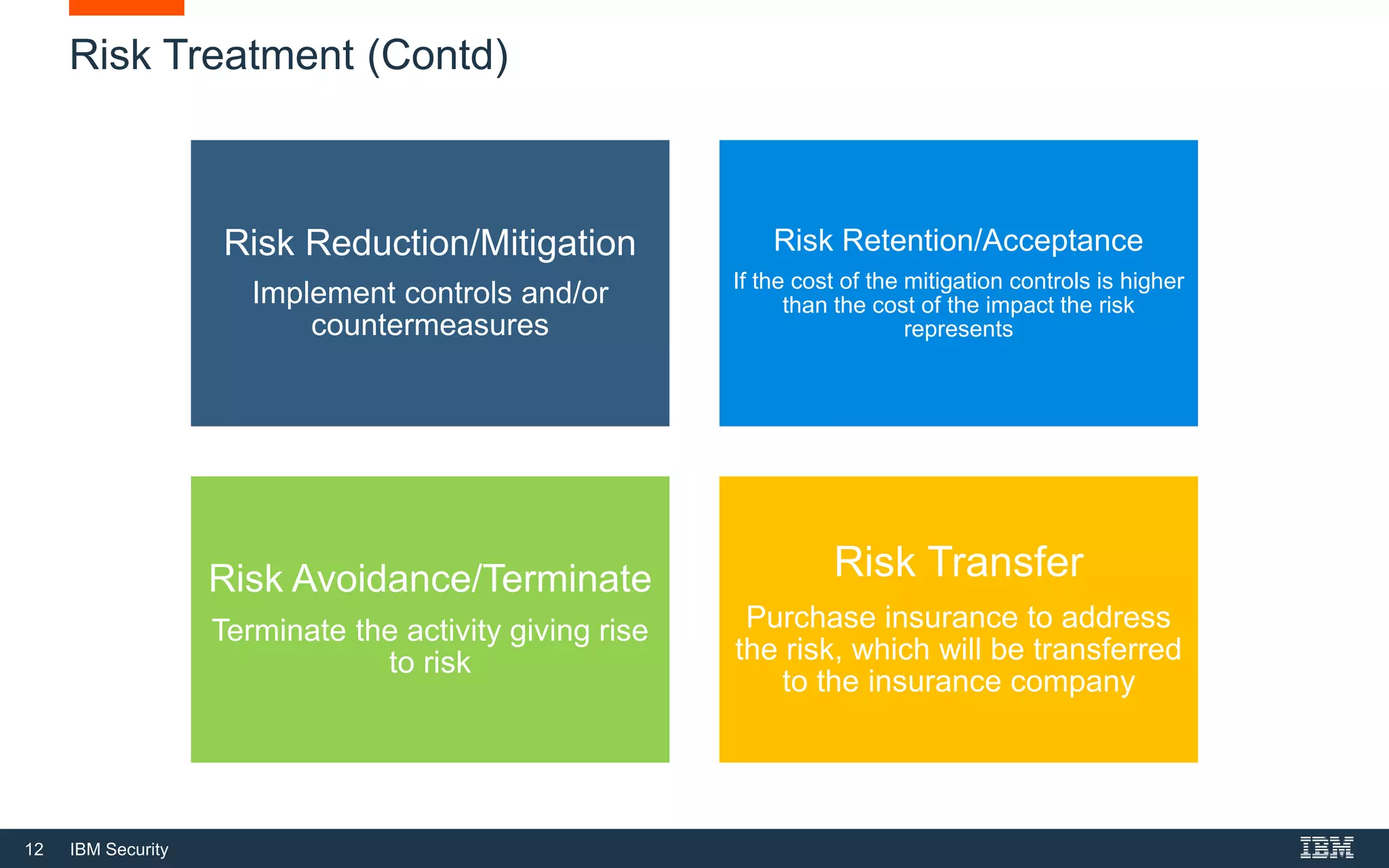
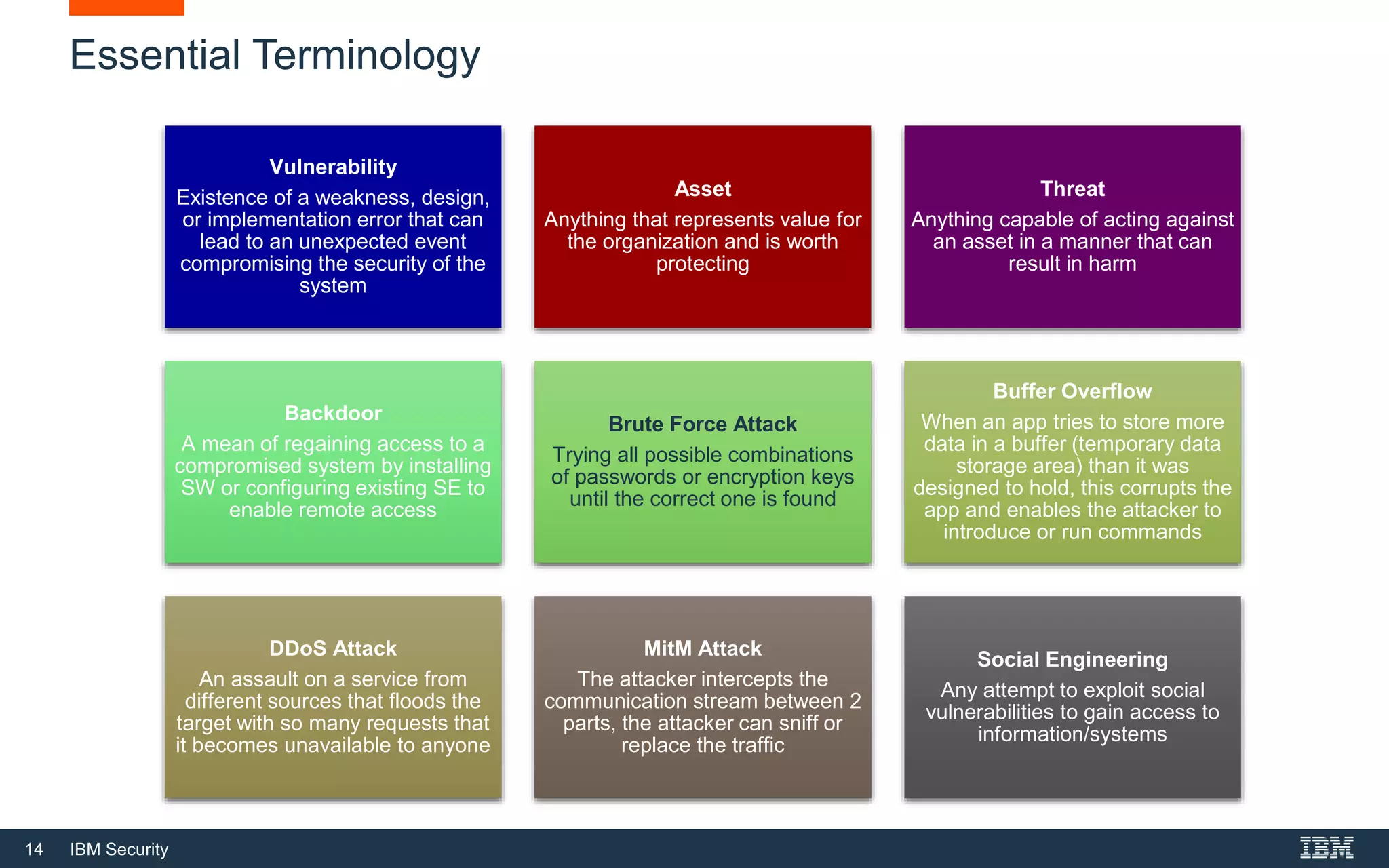
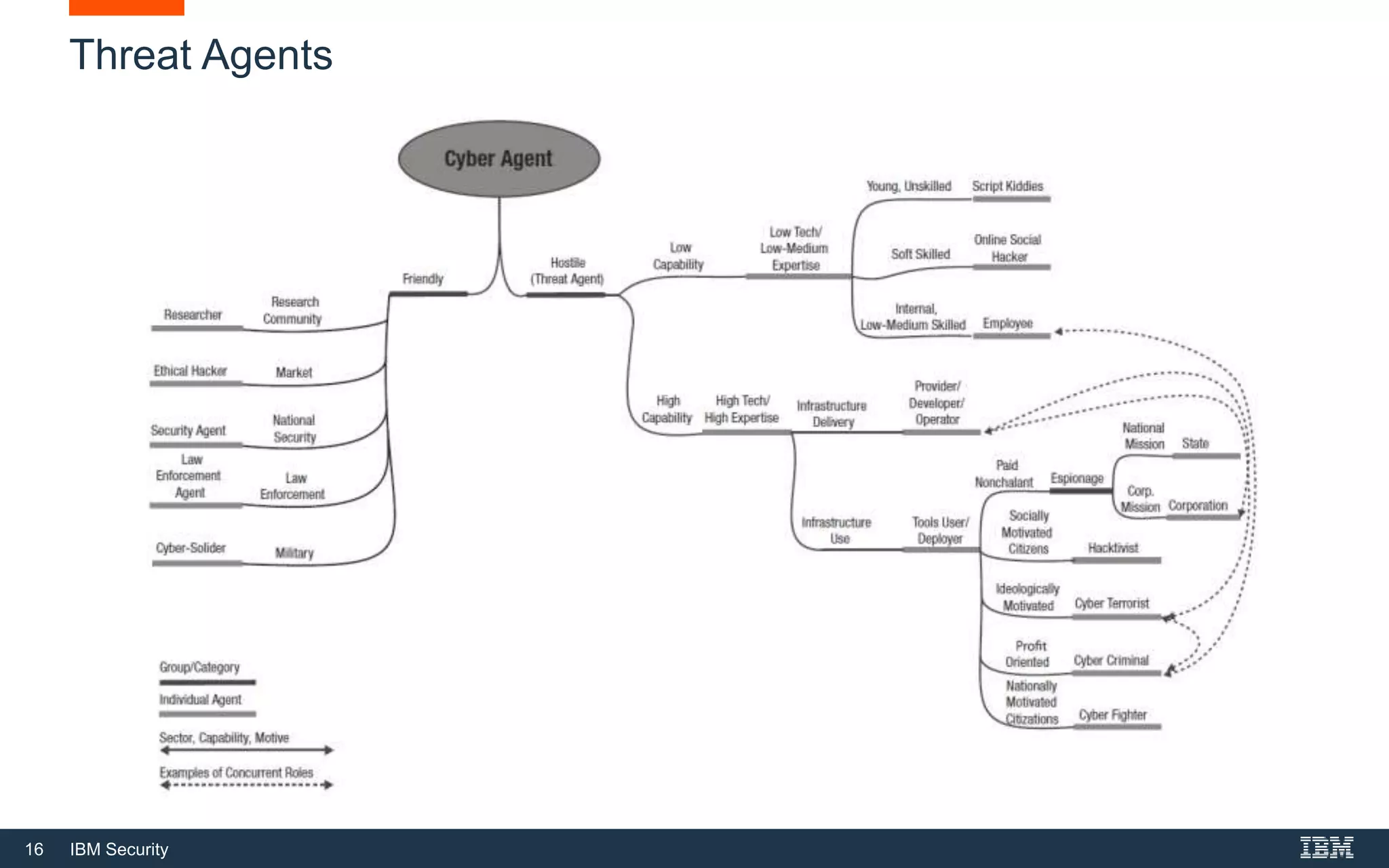
This document provides an overview of cybersecurity fundamentals. It discusses key topics like the definition of cybersecurity and information security, protecting digital assets, risk management concepts, essential cybersecurity terminology, cybersecurity roles and responsibilities, and common threat agents. The goal is to give attendees an introduction to fundamental cybersecurity concepts.