The document provides an introduction to Dublin Core metadata, including:
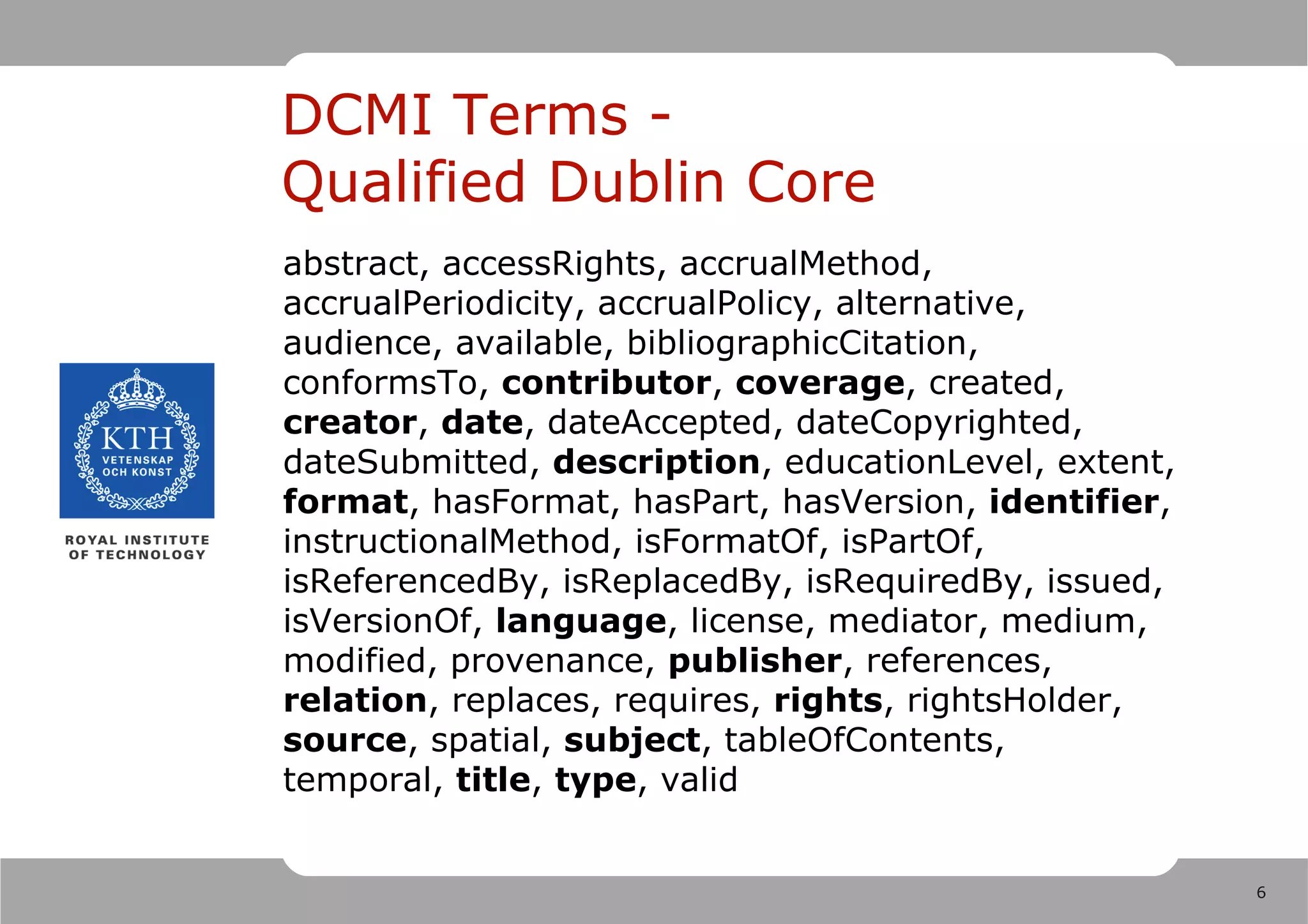
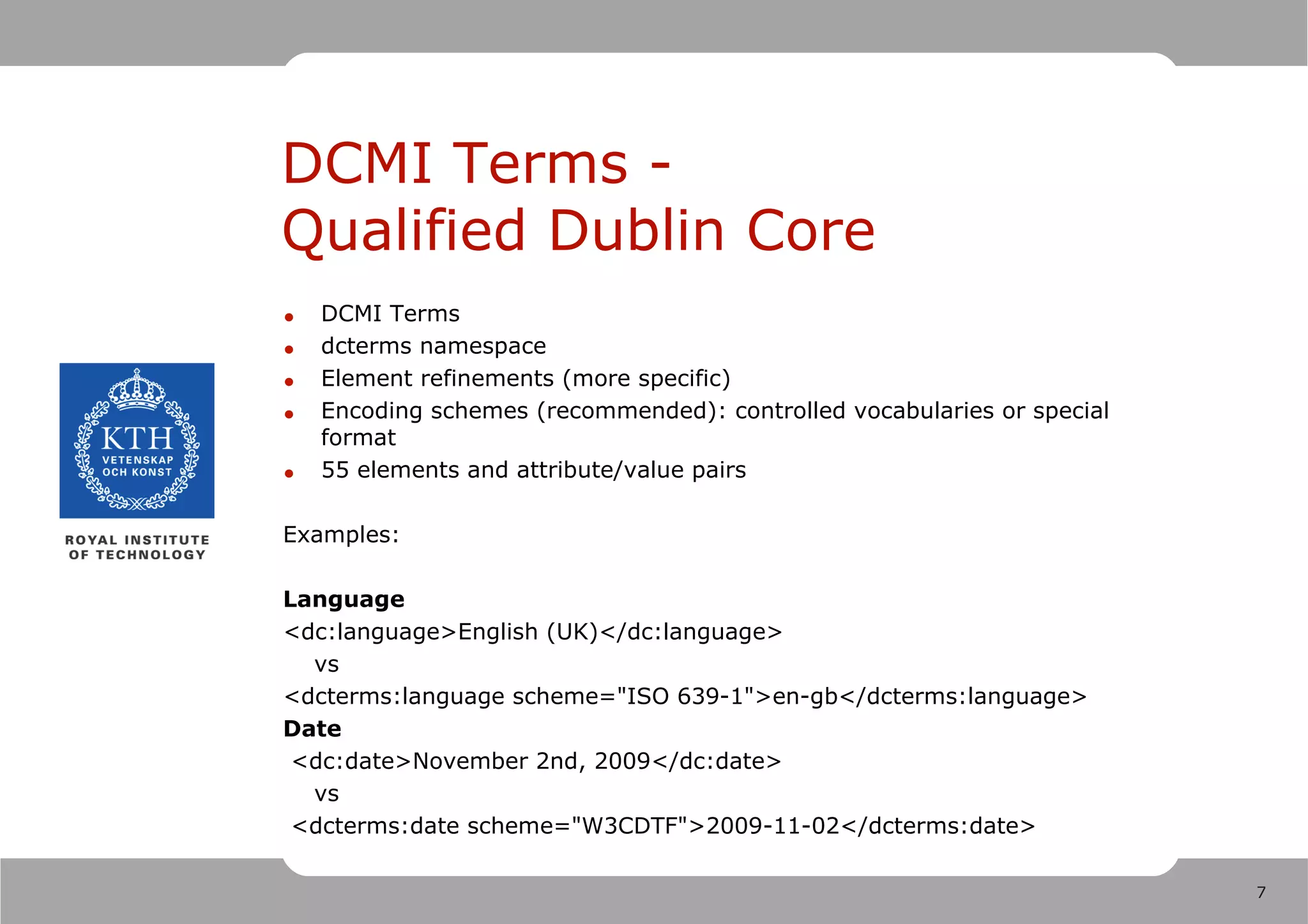
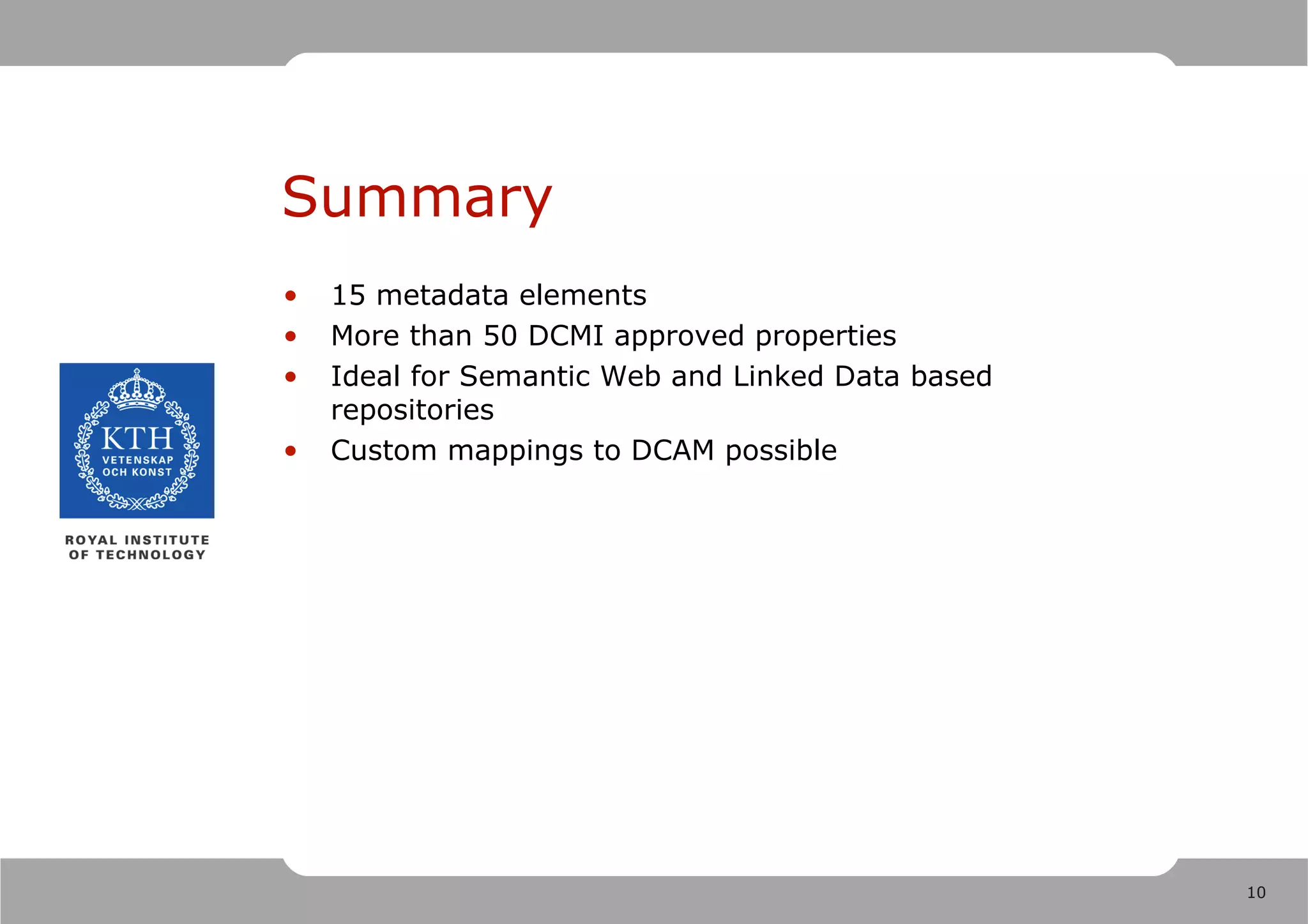
1) Dublin Core is a set of metadata standards including 15 simple elements and over 50 qualified elements for describing resources.
2) Dublin Core metadata can be used to improve resource discovery and is recommended for metadata harvesting and the semantic web.
3) Custom mappings can be made from other metadata standards like LOM to the Dublin Core Abstract Model to make metadata interoperable.