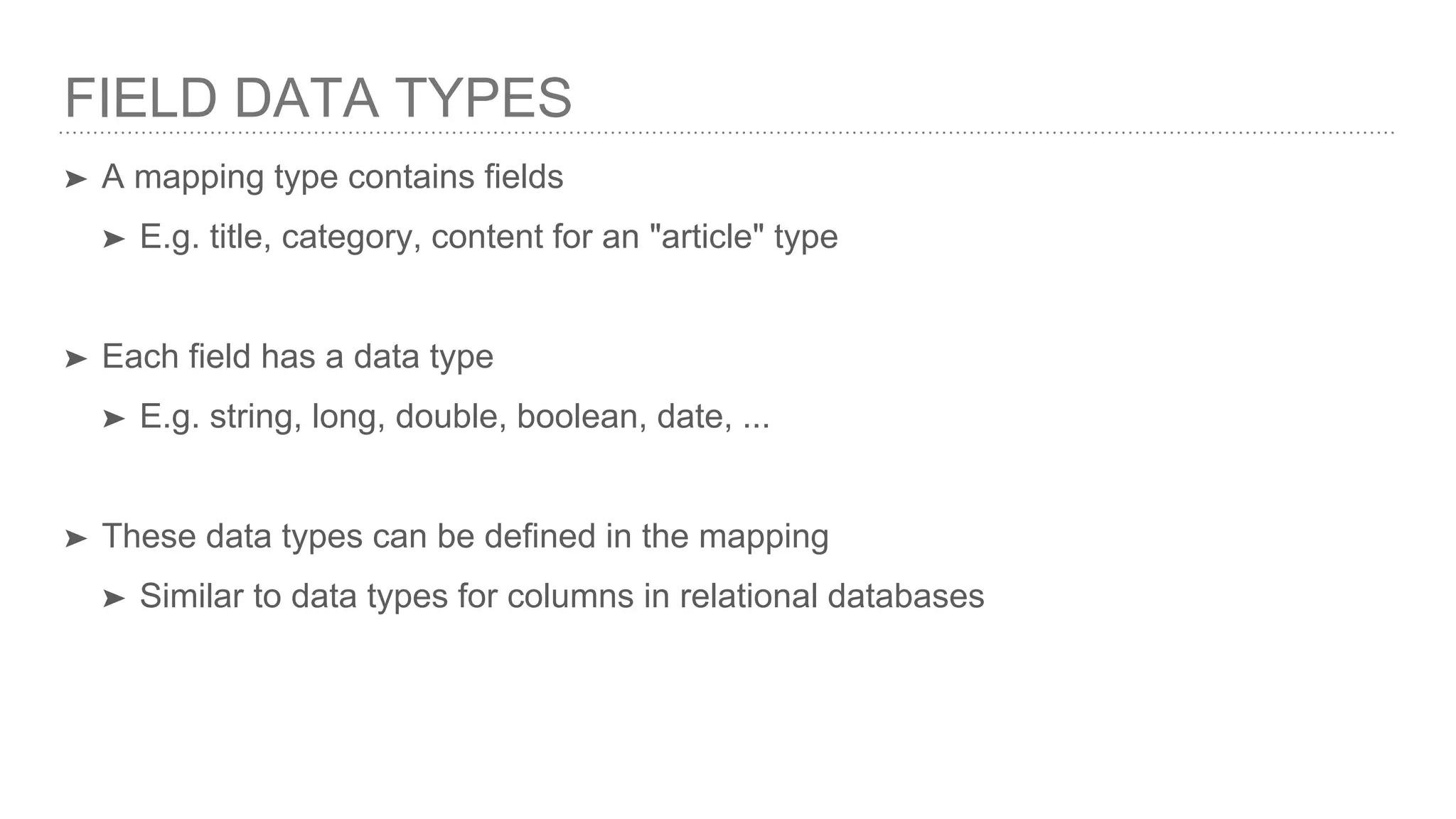
The document provides an introduction to mapping in Elasticsearch, explaining its definition and importance in storing and indexing documents akin to relational database schemas. It covers various aspects such as field data types, meta fields, dynamic and explicit mappings, and highlights potential pitfalls or 'mapping gotchas.' Overall, it serves as a foundational guide for understanding how to effectively manage data structures within Elasticsearch.