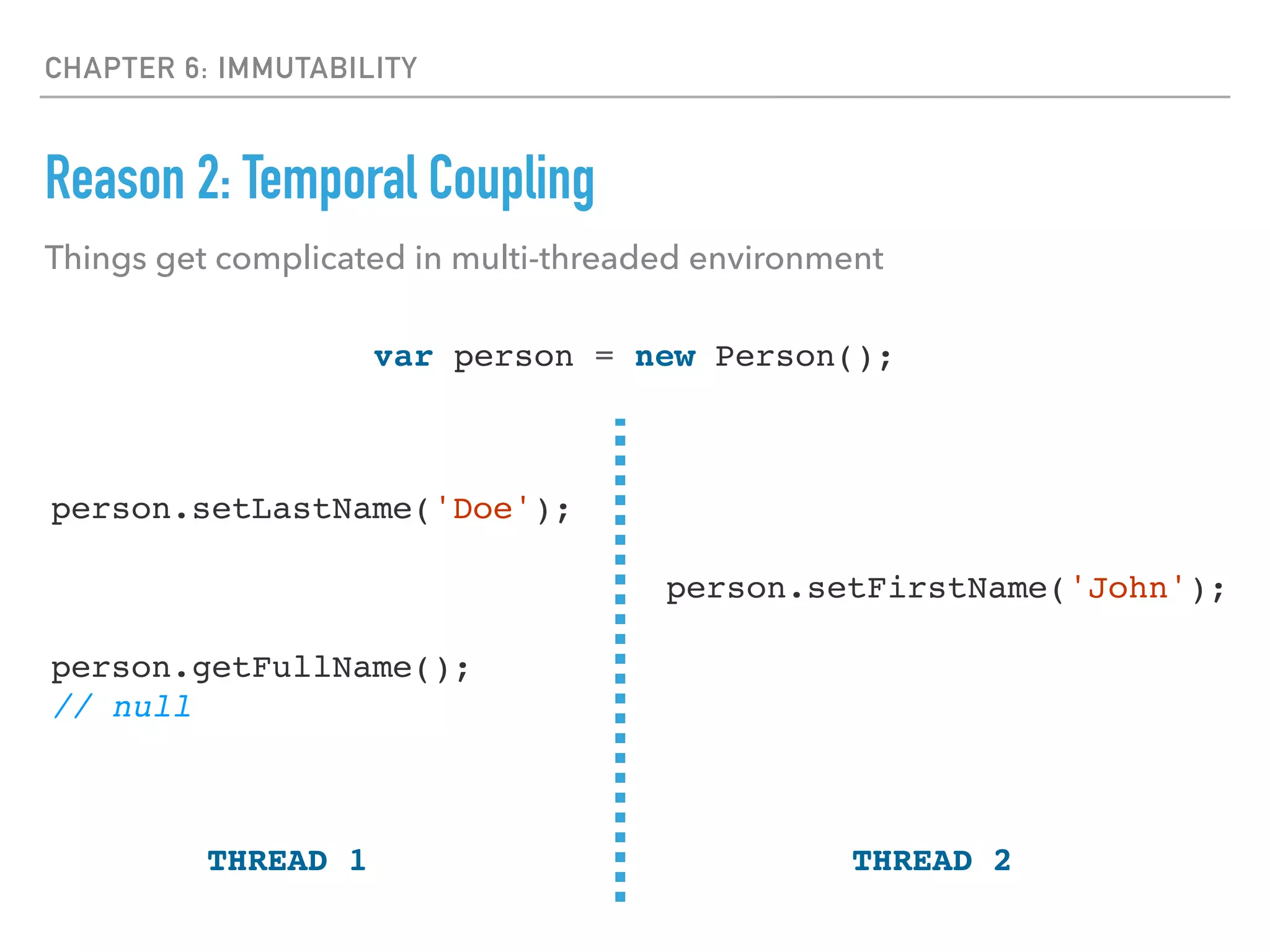
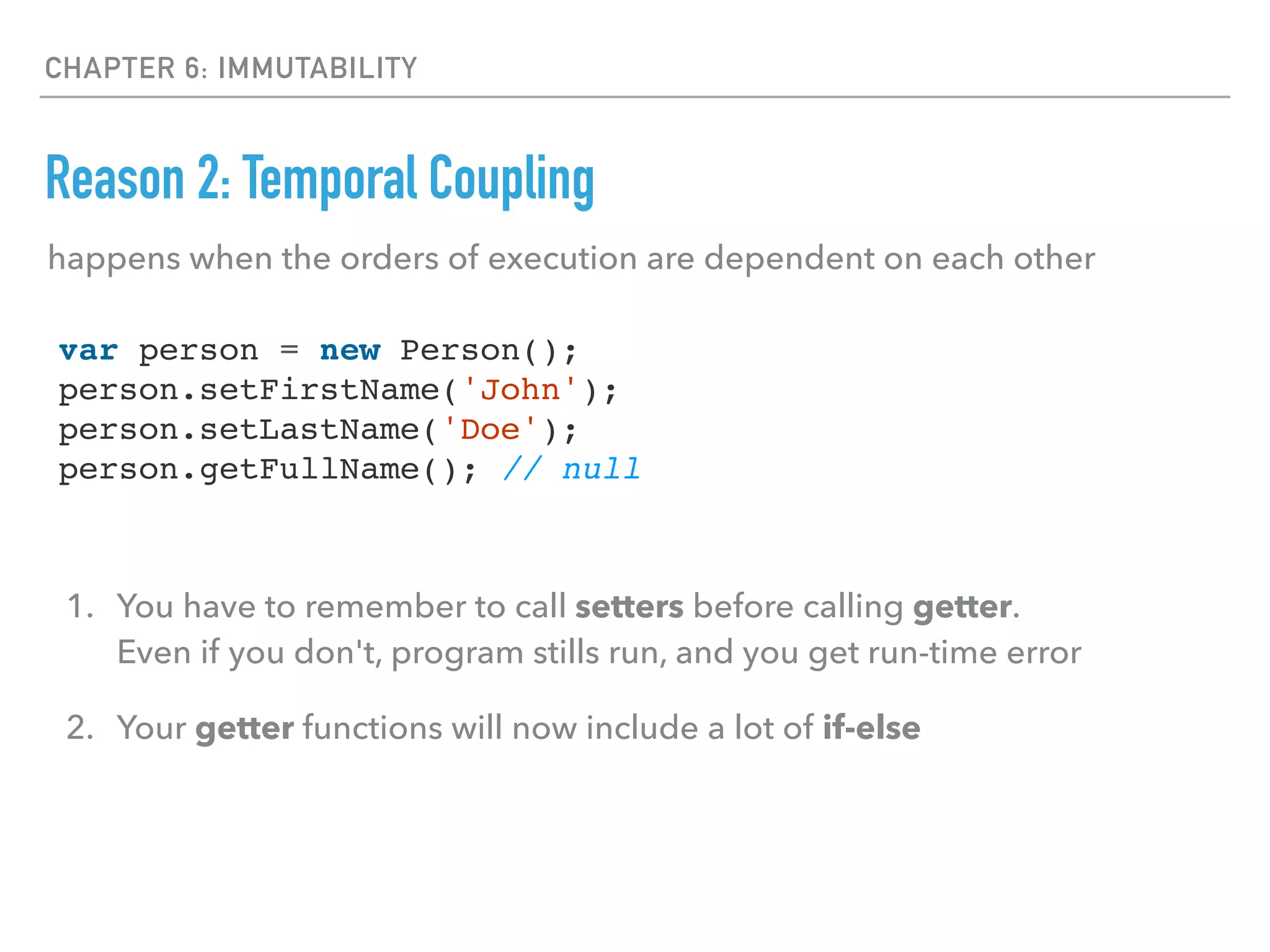
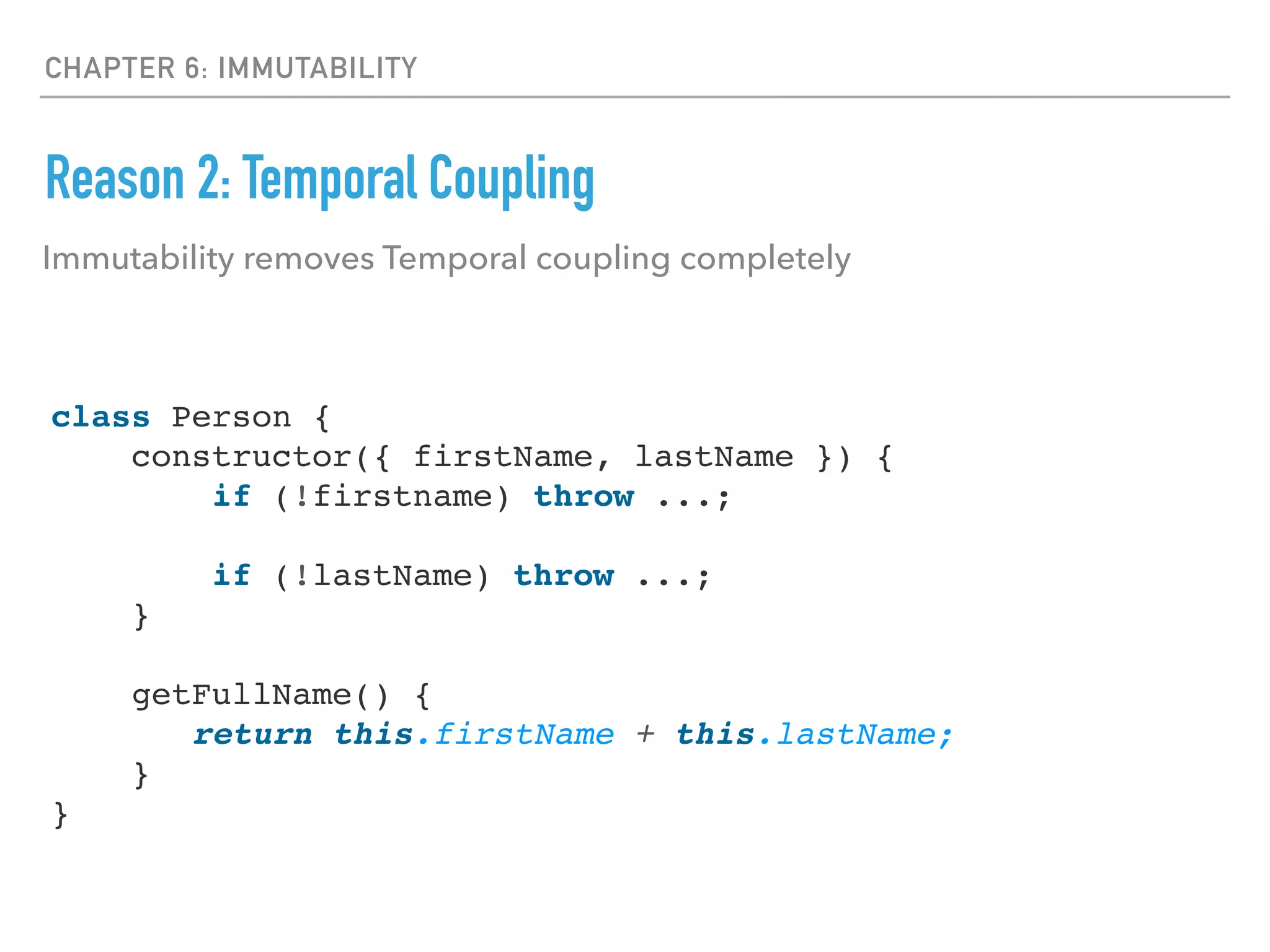
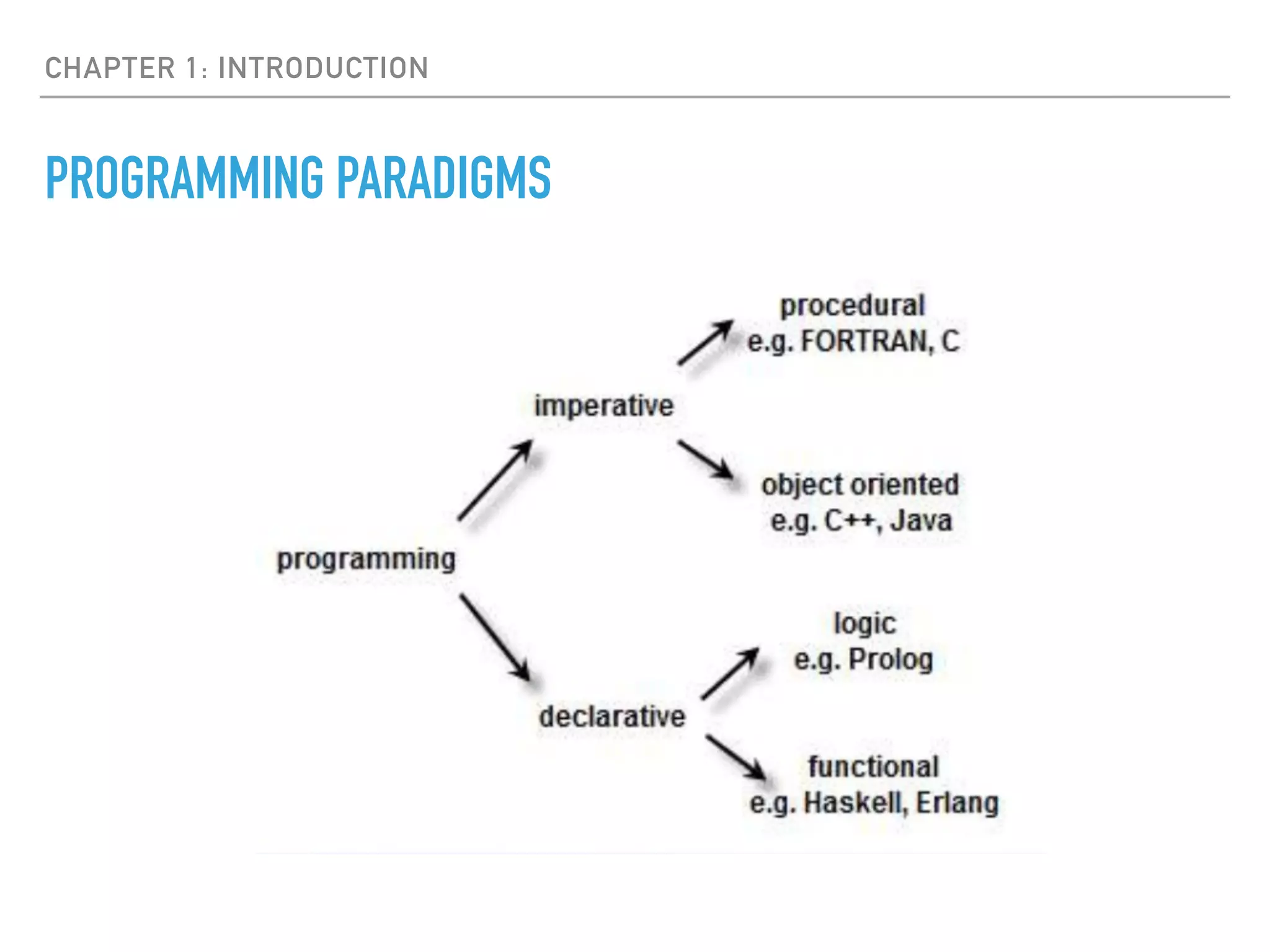
This document discusses key concepts in functional programming including:
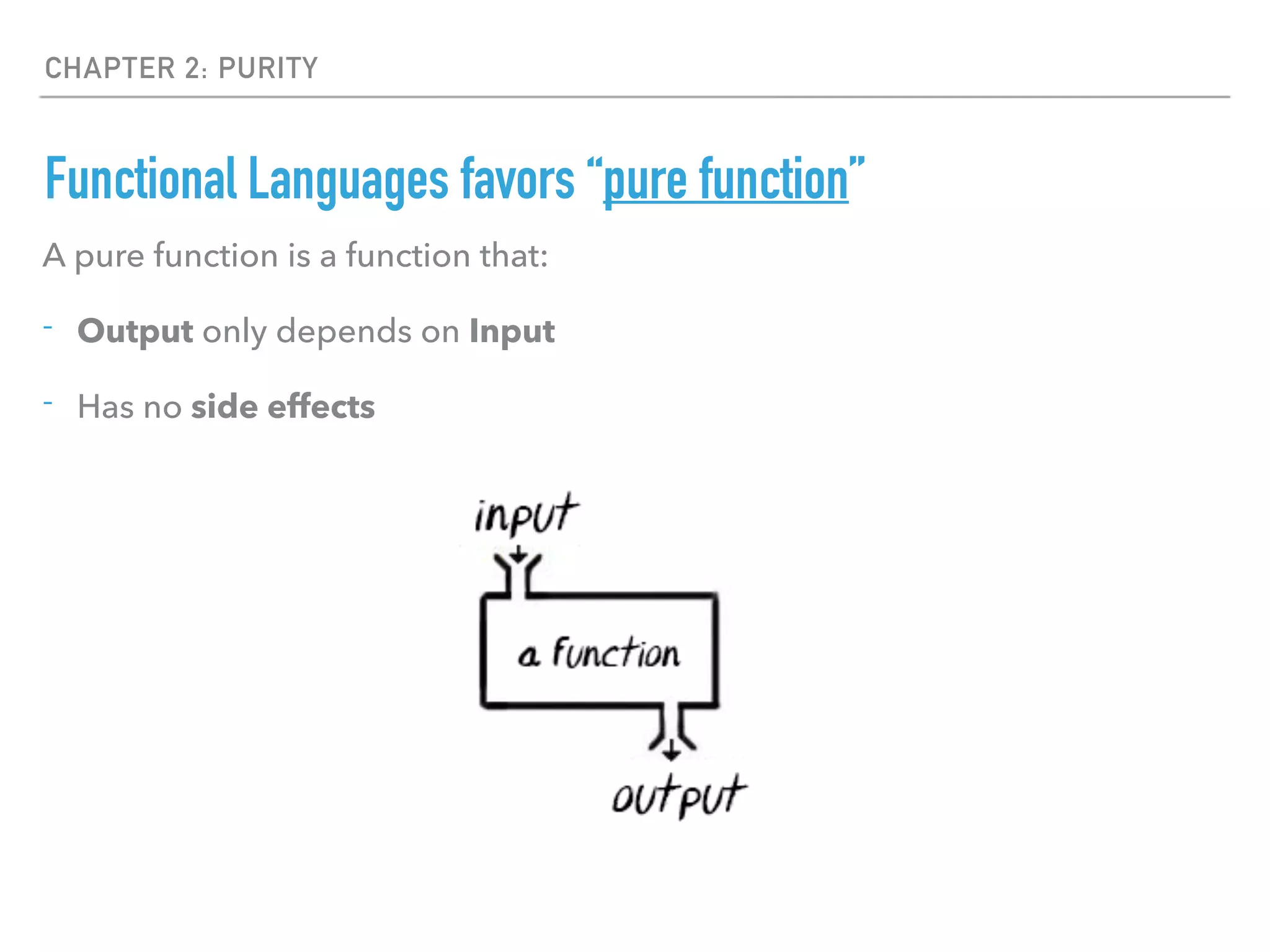
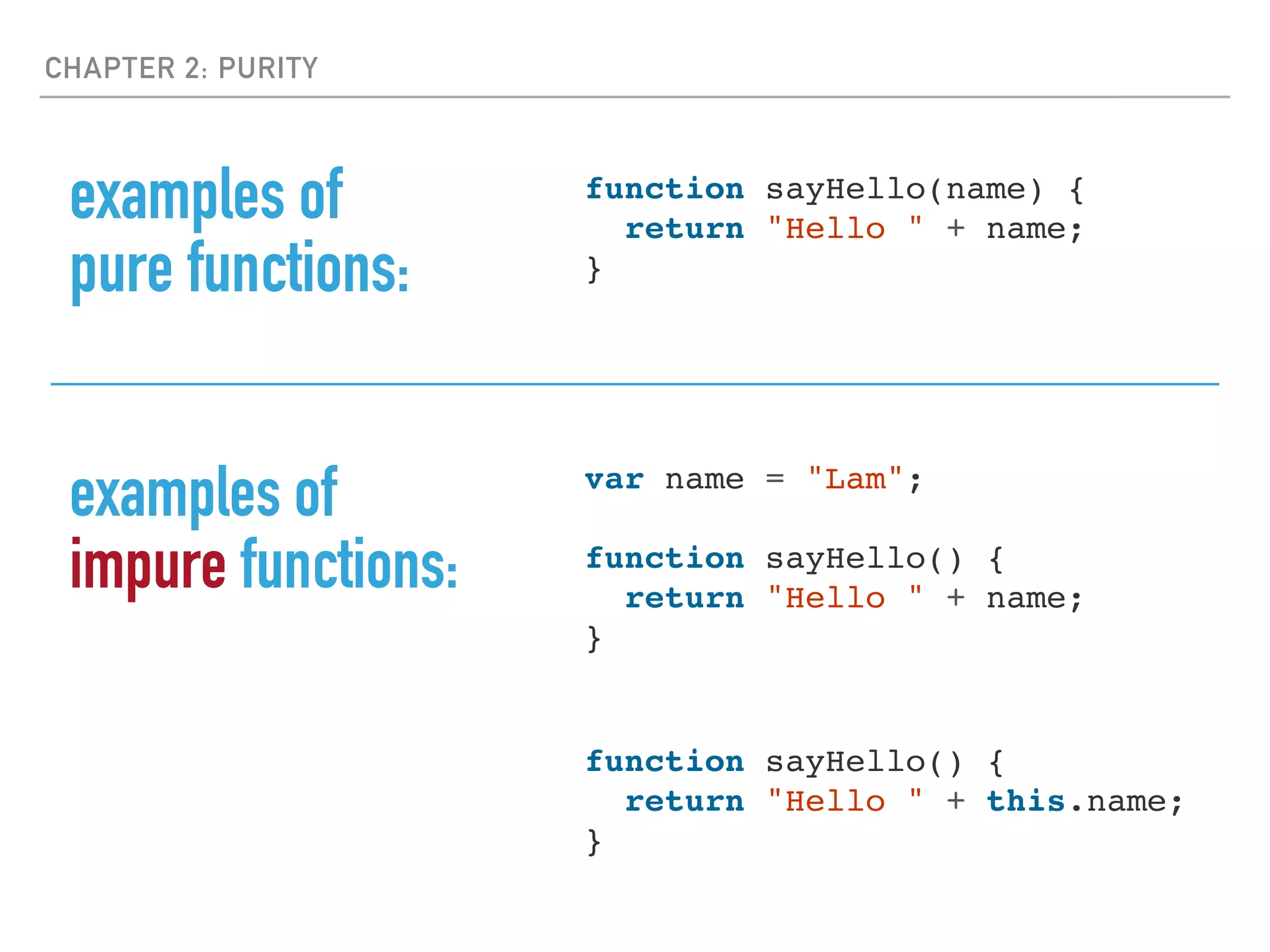
- Functional languages favor pure functions that have no side effects and always return the same output for a given input.
- Functions are first-class citizens that can be assigned to variables, passed as arguments to other functions, and returned from other functions.
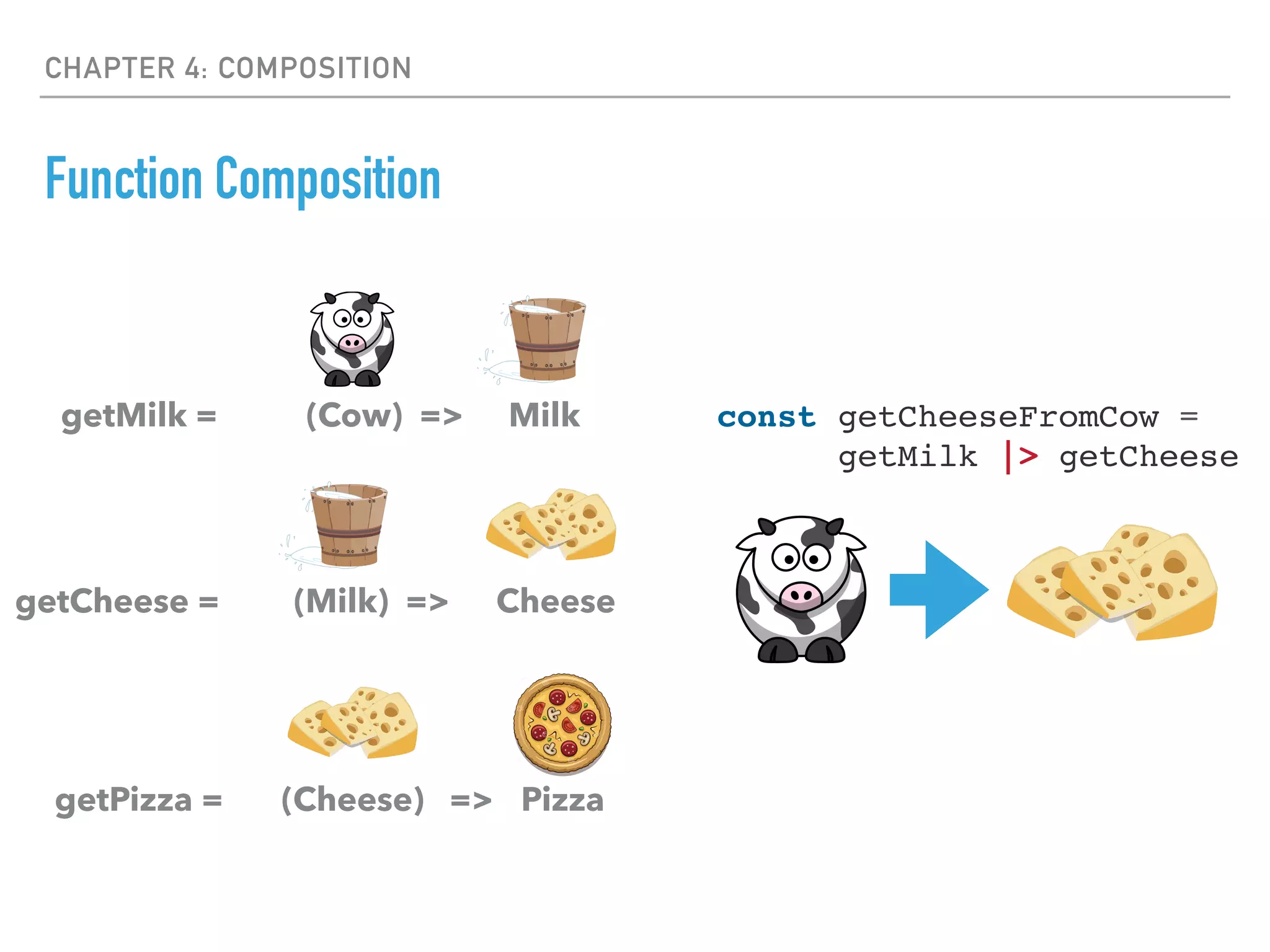
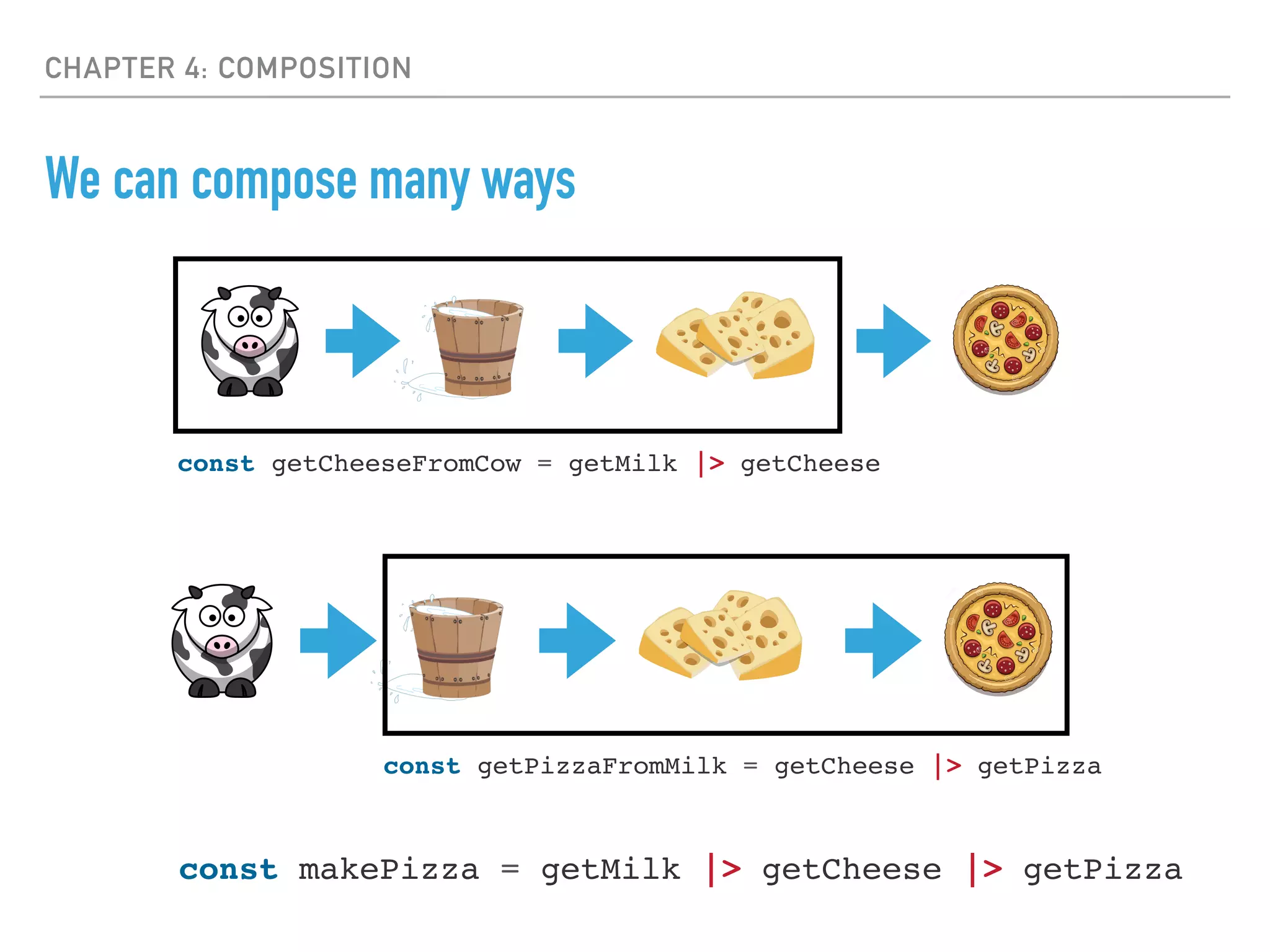
- Composition involves combining simple functions together to build more complex behaviors through function piping.
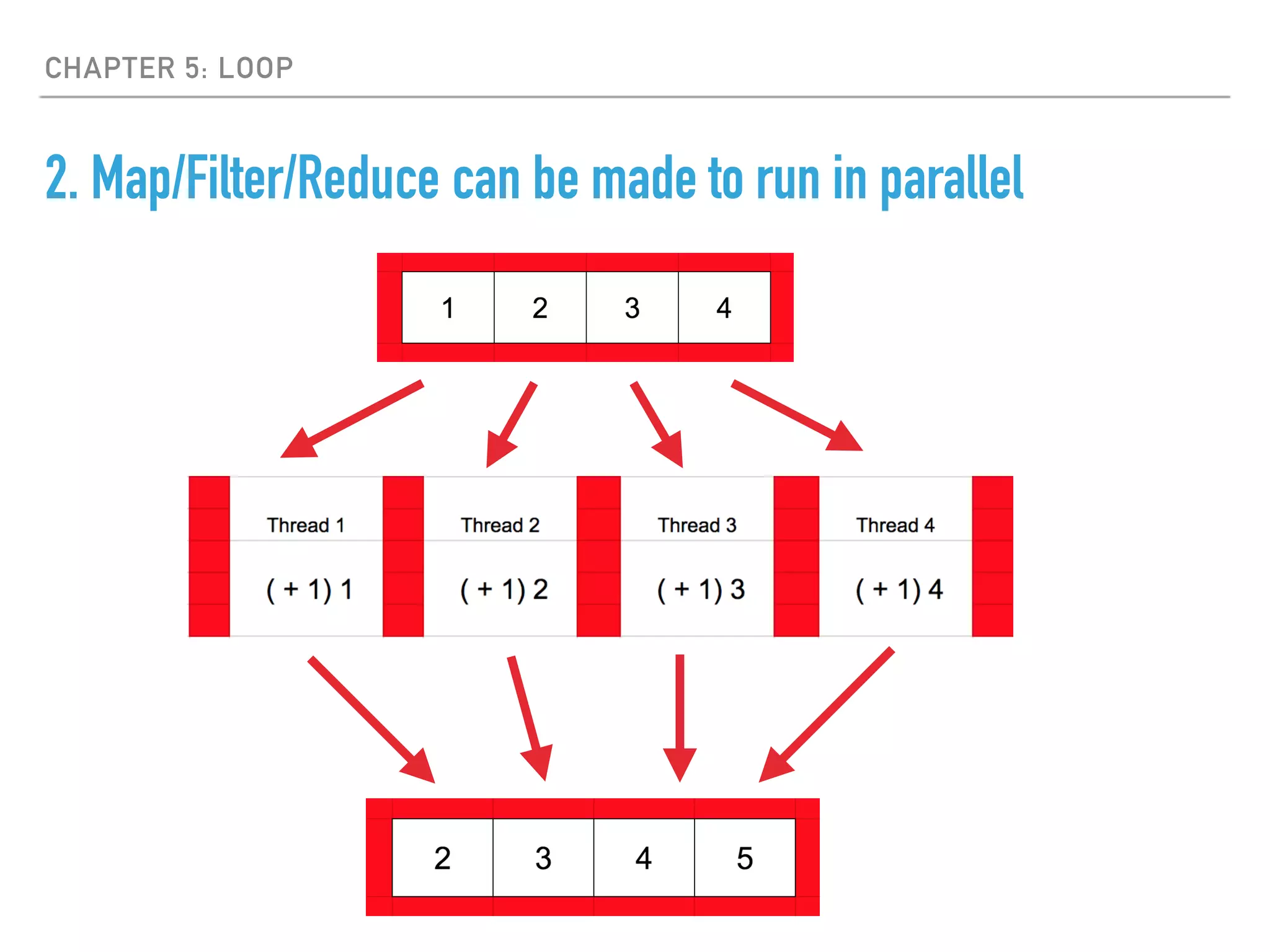
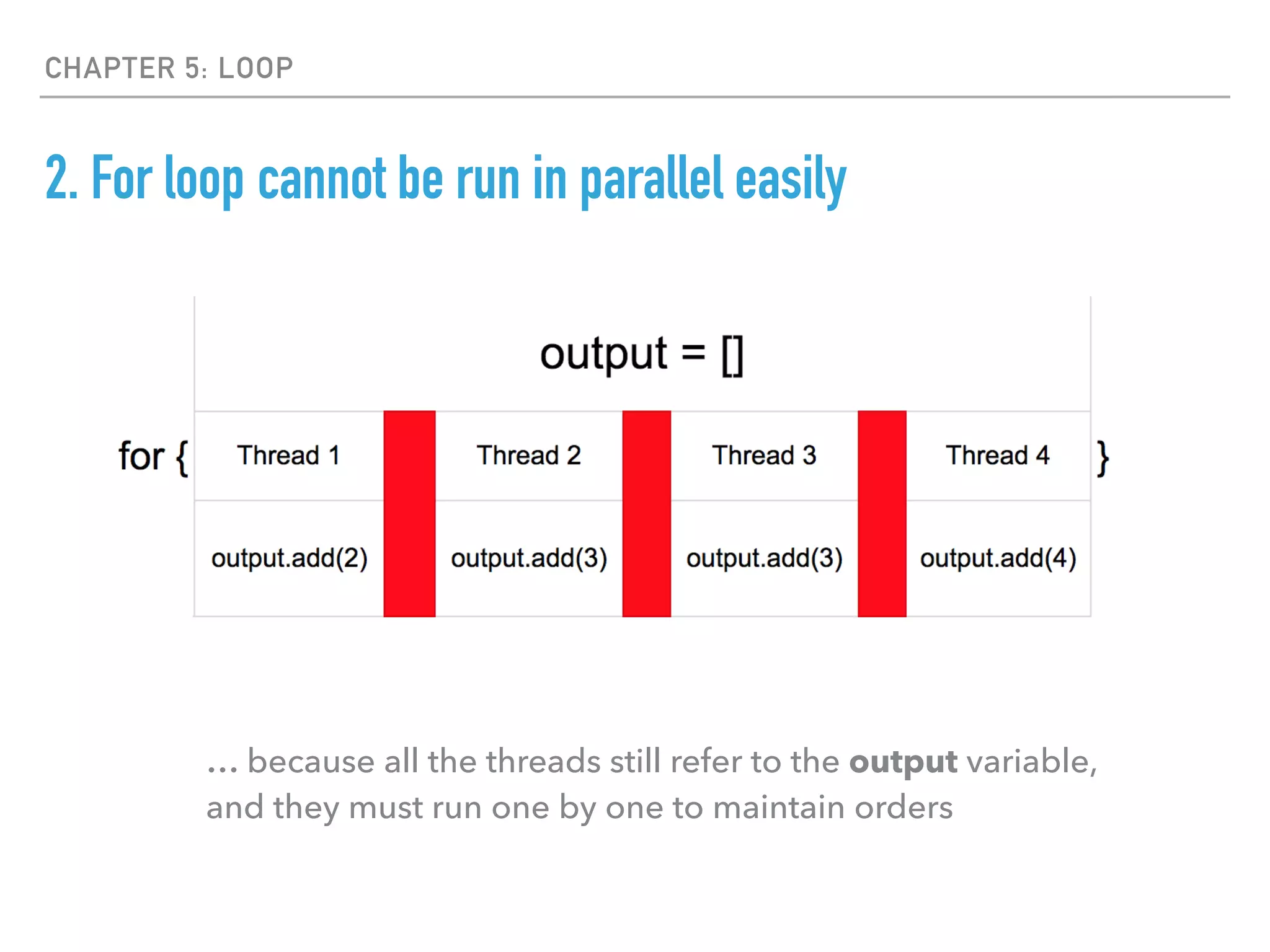
- Loops are avoided in favor of map, filter, and reduce functions to operate on collections in a declarative way that can run operations in parallel.
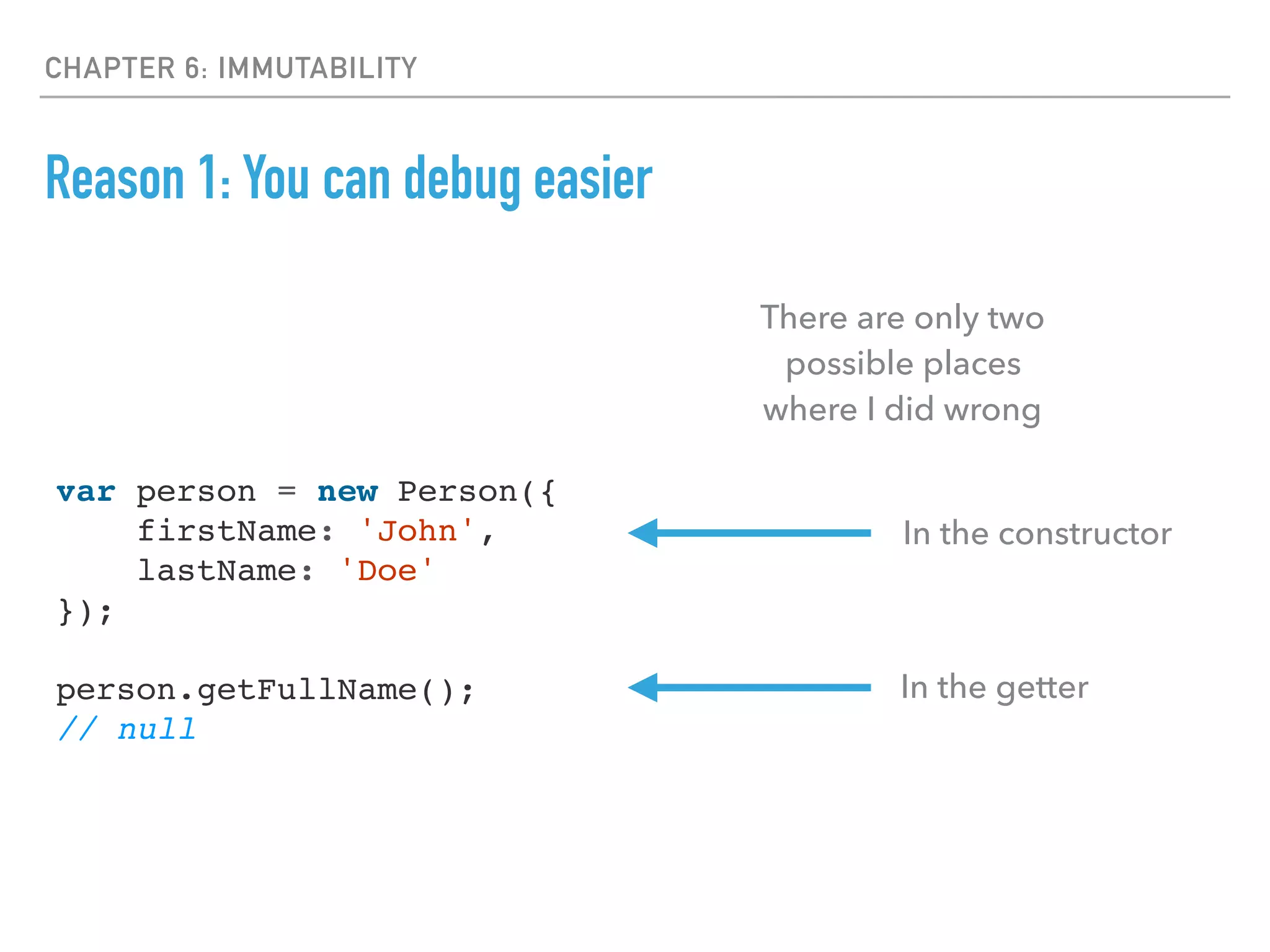
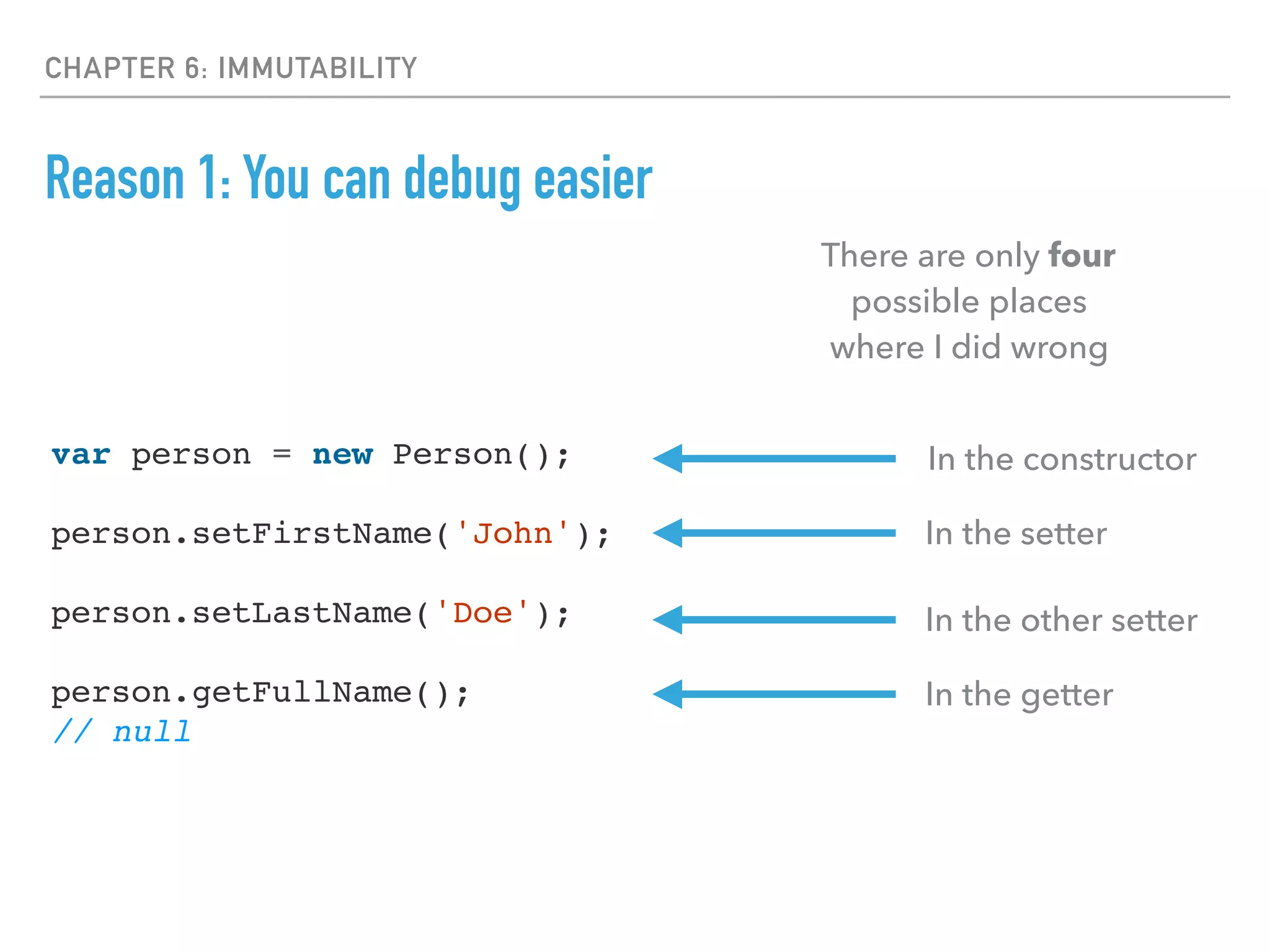
- Immutability is important to avoid bugs from side effects and make reasoning about programs easier.














![CHAPTER 4: COMPOSITION
Real world example (Functional Javascript way)
const sayHello = (name) => ‘Hello ‘ + name;
const addExcitement = (str) => str + ' !!!!!!!!!!!';
Crazy way
const capitalize = (str) => str.toUpperCase();
const name = 'nfq';
const transform = _.flow([
capitalize, sayHello, addExcitement
]);
transform(name); // 'Hello NFQ !!!!!!!!!'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-171207120647/75/Introduction-to-Functional-Programming-20-2048.jpg)




![CHAPTER 5: LOOP
1. For loop is usually longer and duplicated (example 1)
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var output = [];
for (var n of input) {
output.push(n + 1);
}
console.log(output); // [2, 3, 4, 5]
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var output = input.map(n => n + 1);
console.log(output); // [2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-171207120647/75/Introduction-to-Functional-Programming-25-2048.jpg)
![CHAPTER 5: LOOP
1. For loop is usually longer and duplicated (example 2)
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var output = [];
for (var n of input) {
if (n % 2 === 0) {
output.push(n);
}
}
console.log(output); // [2, 4]
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var output = input.filter(n => n % 2 === 0);
console.log(output); // [2, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-171207120647/75/Introduction-to-Functional-Programming-26-2048.jpg)
![CHAPTER 5: LOOP
1. For loop is usually longer and duplicated (example 3)
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var result = null;
for (var n of input) {
if (n === 3) {
result = n;
break;
}
}
console.log(result); // 3
var input = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var result = input.find(n => n === 3);
console.log(result); // 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functional-171207120647/75/Introduction-to-Functional-Programming-27-2048.jpg)