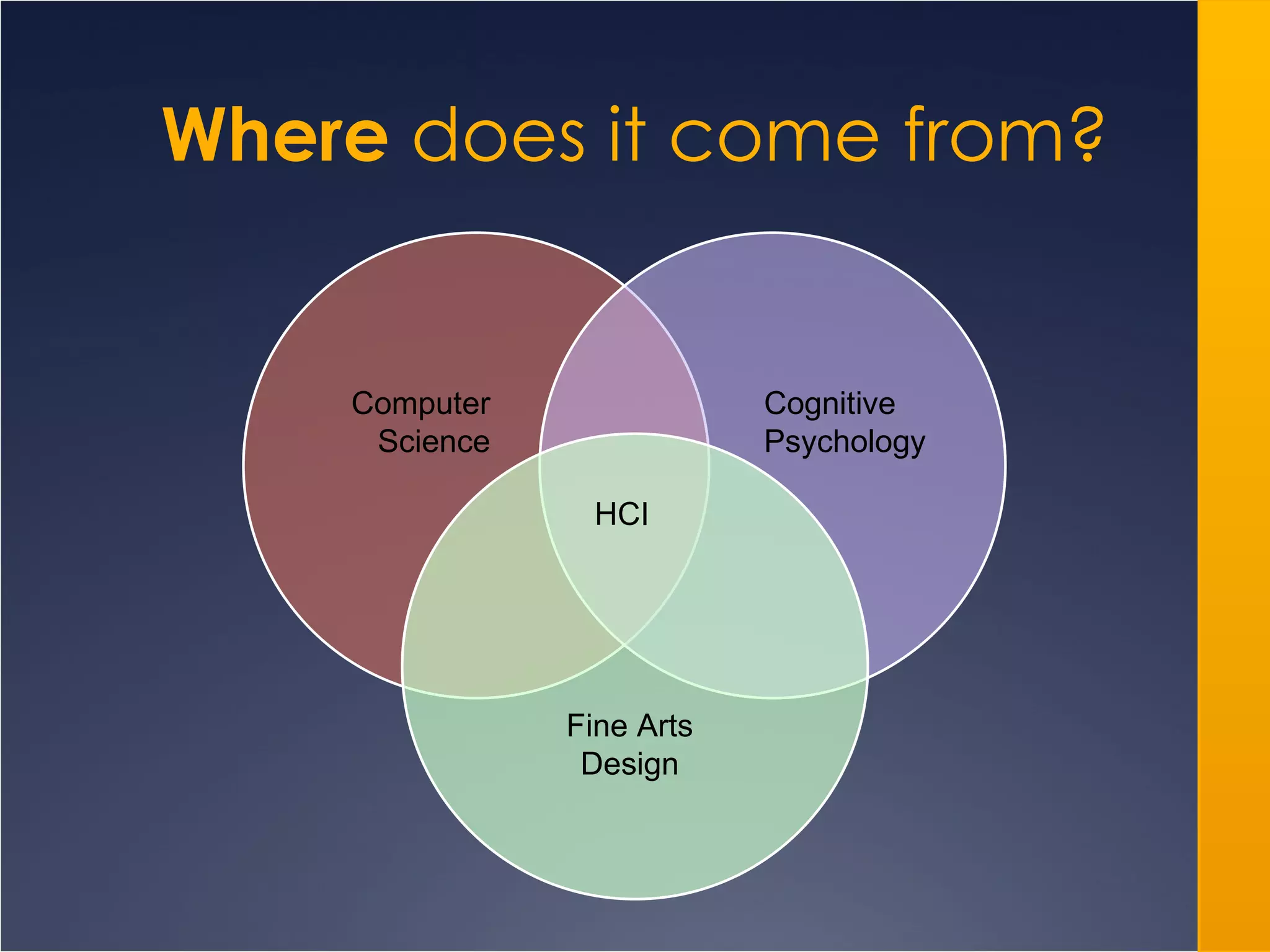
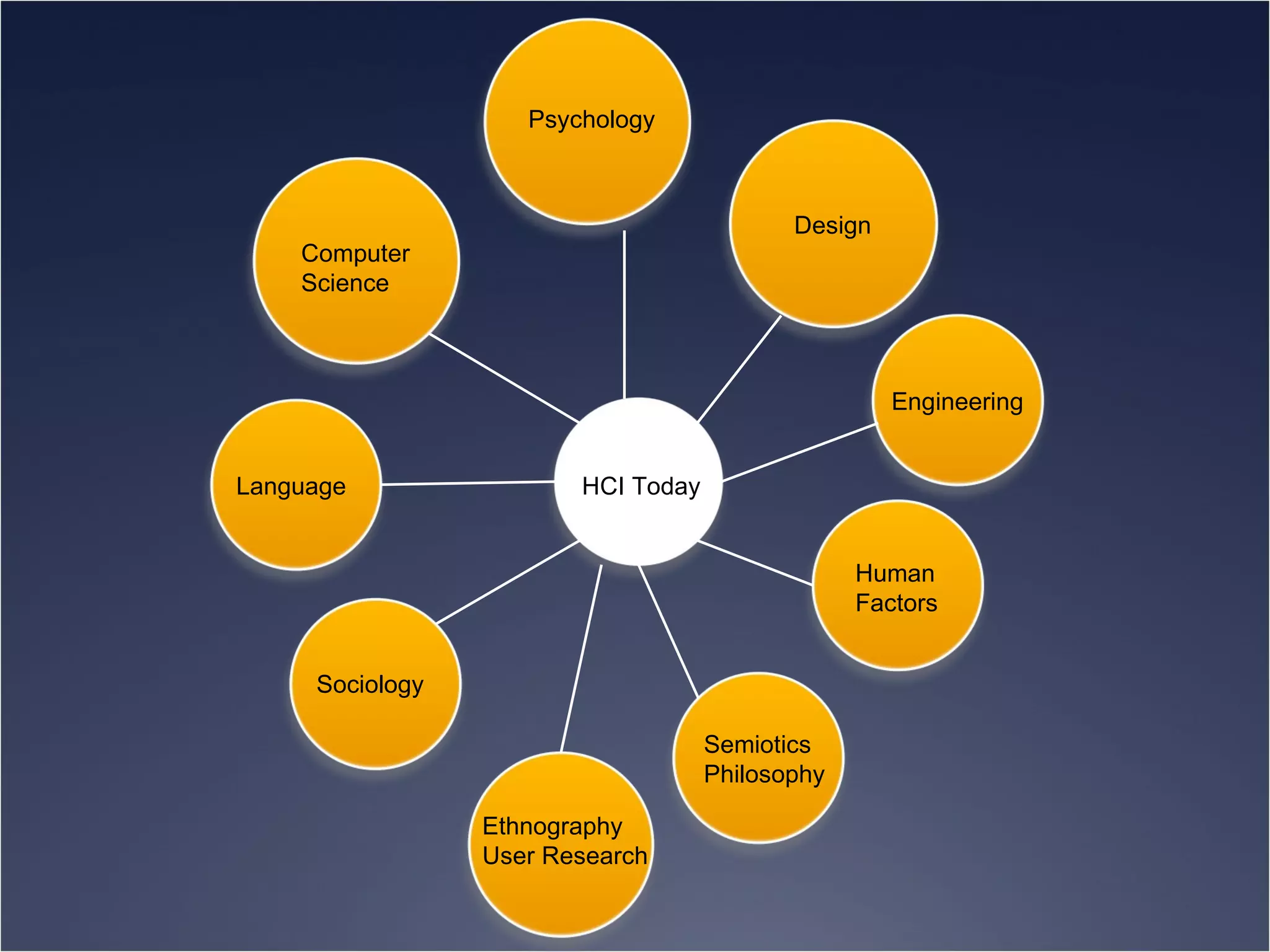
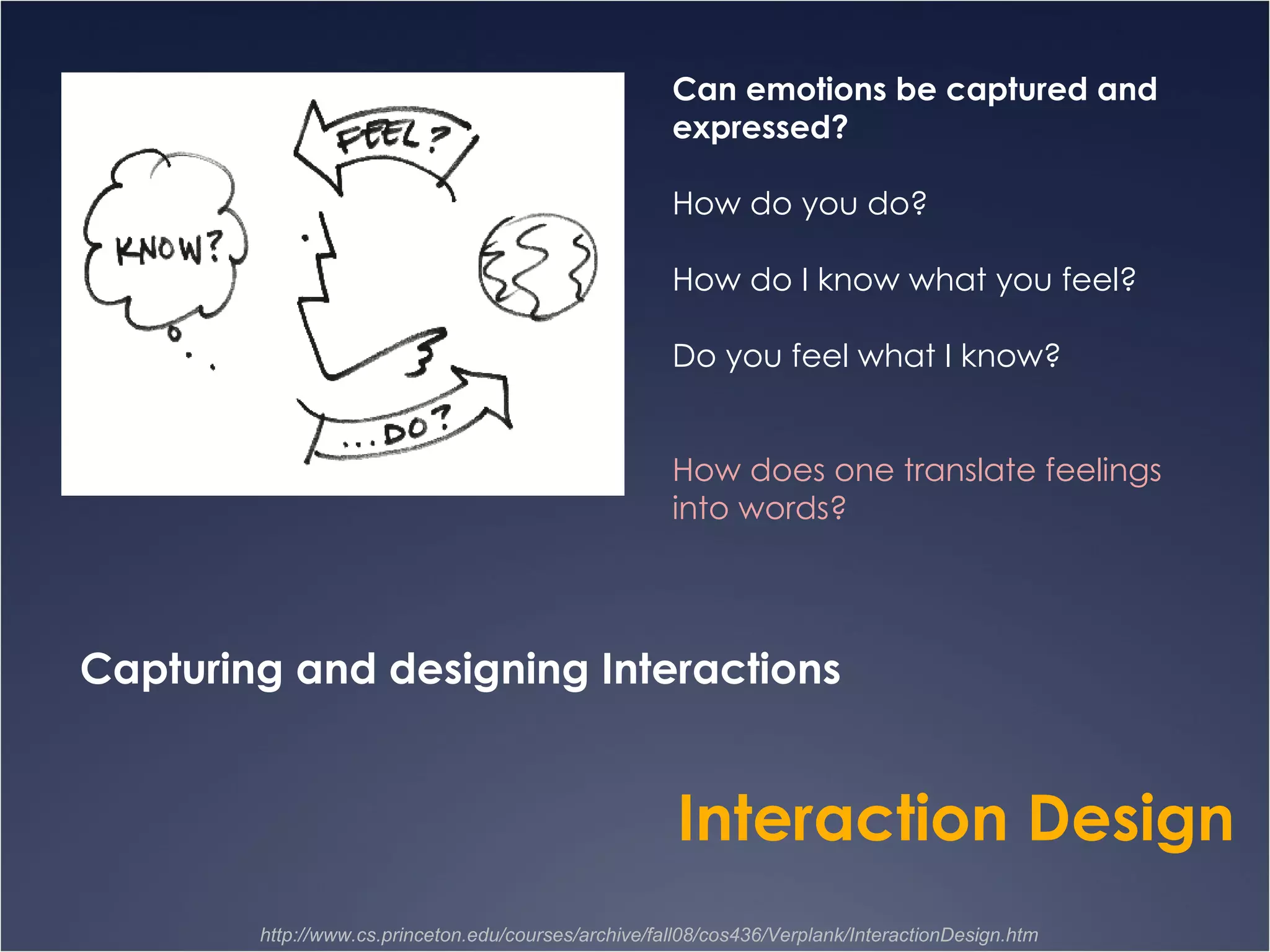
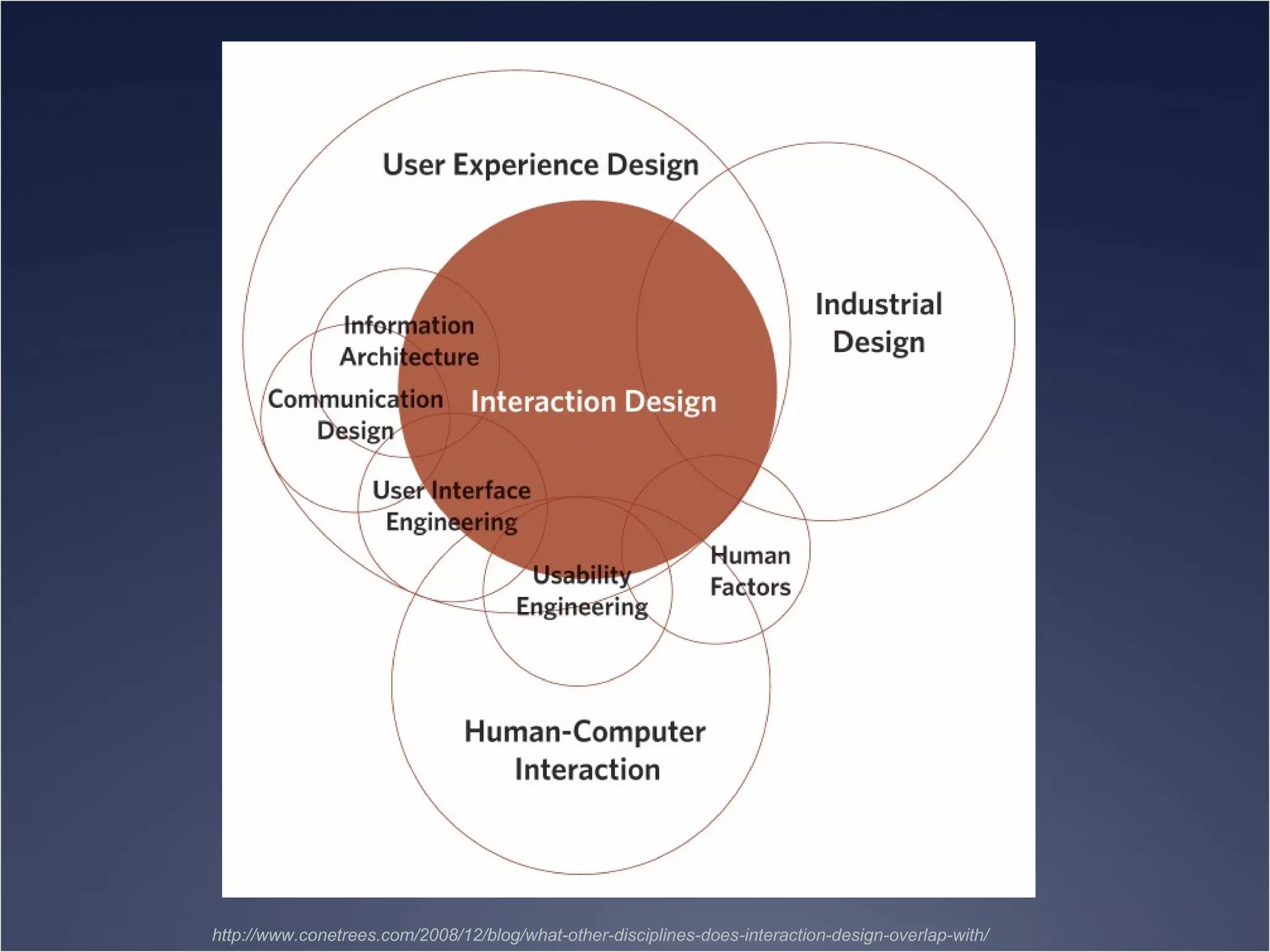
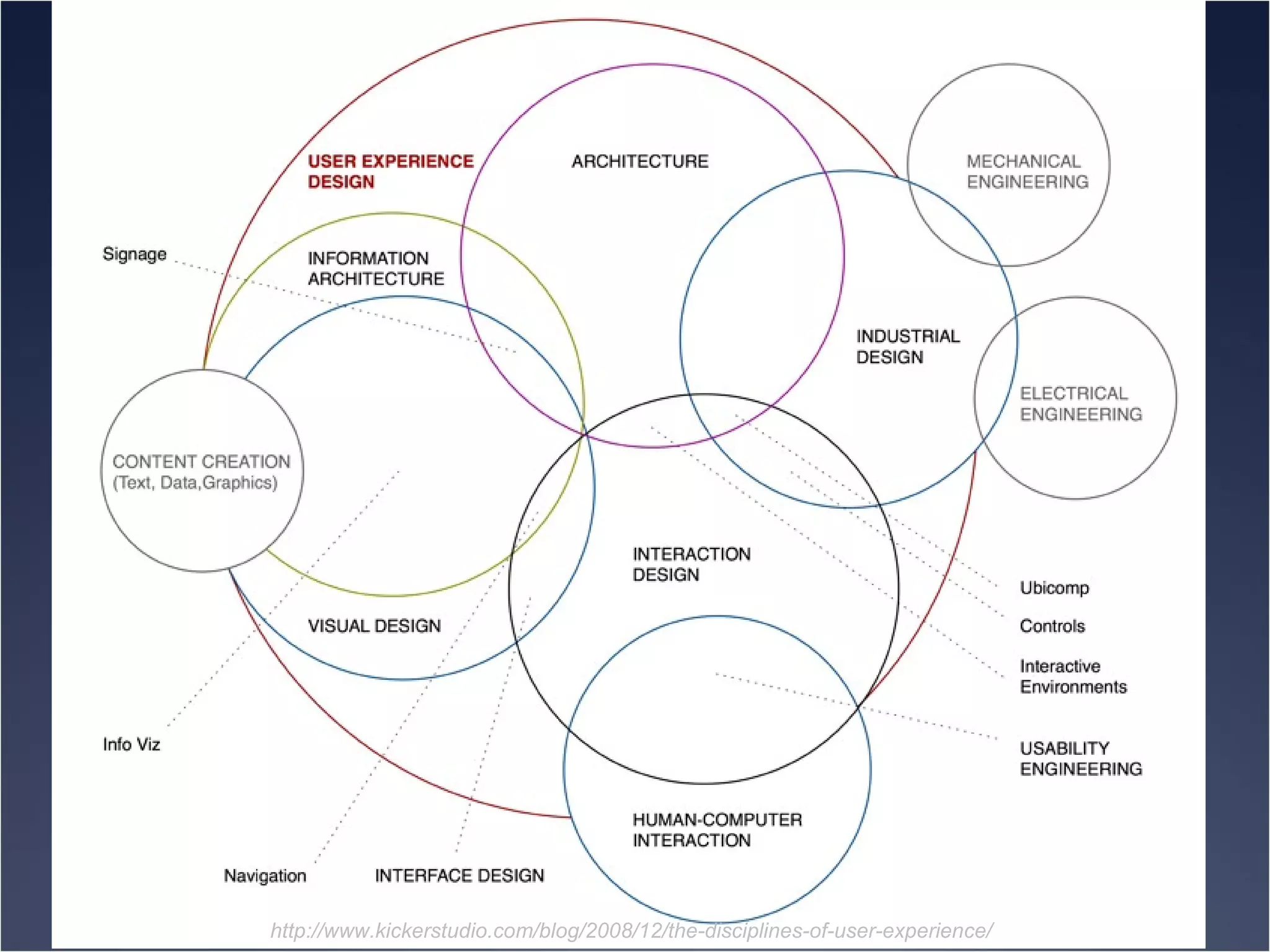
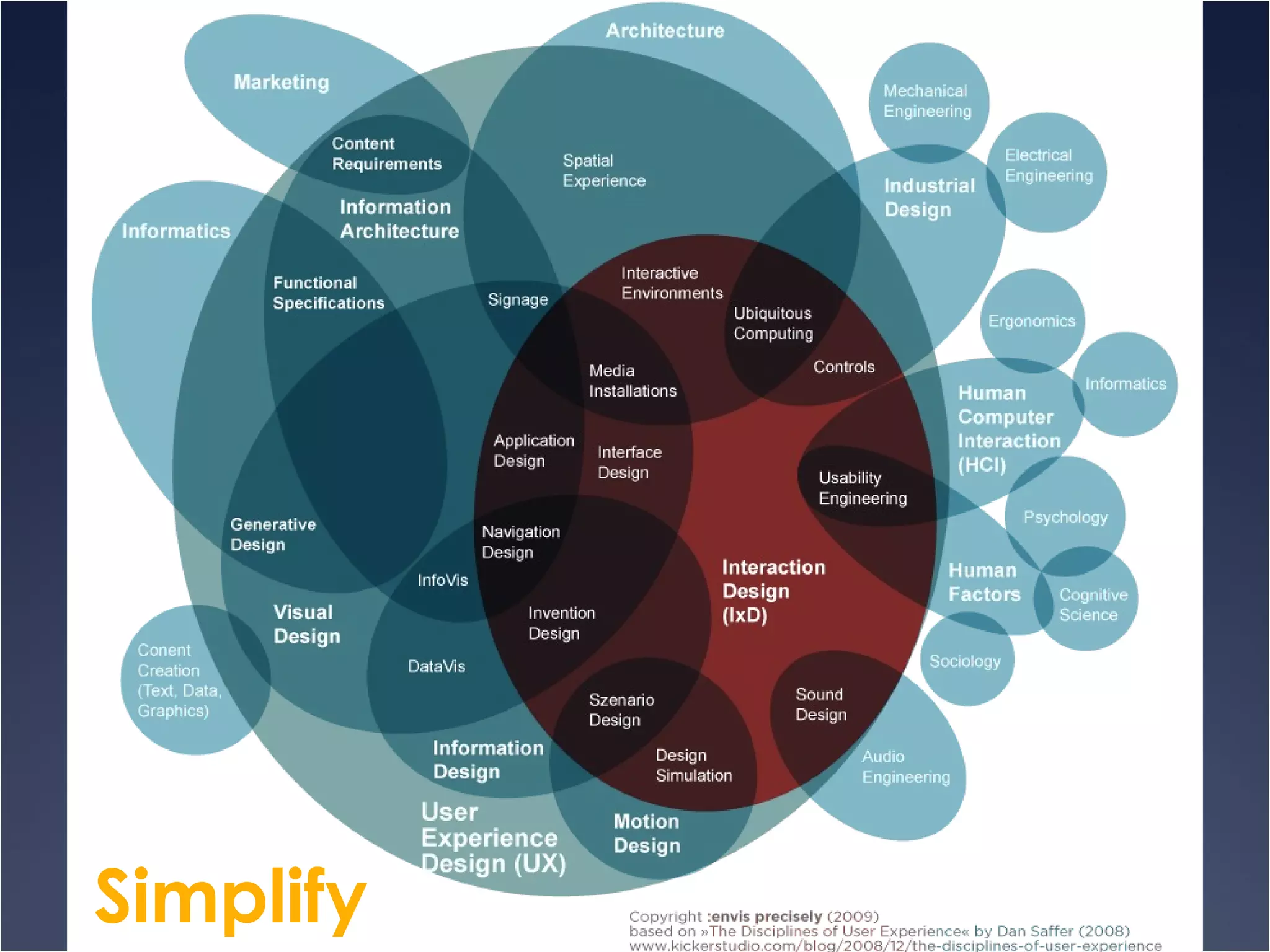
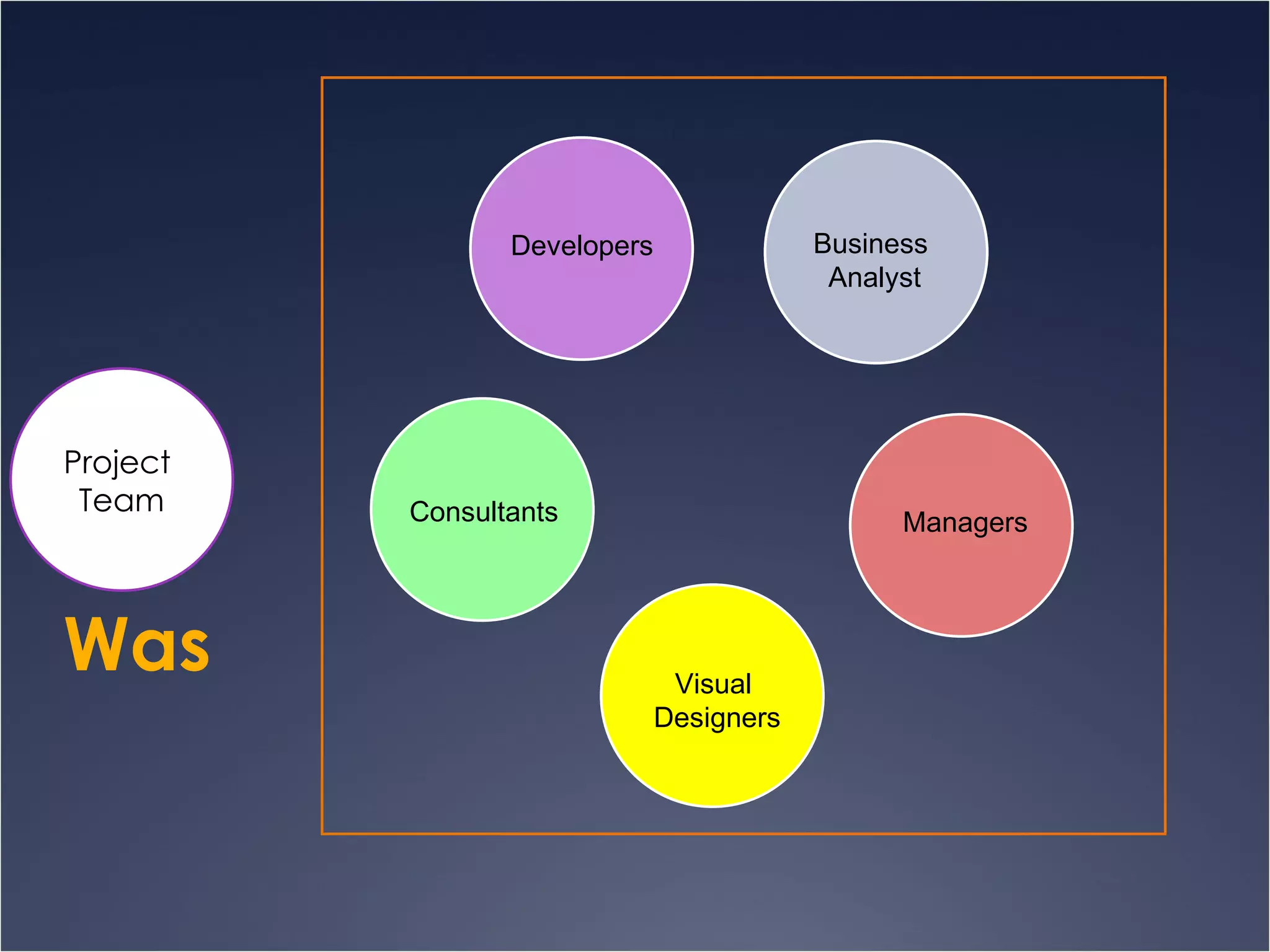
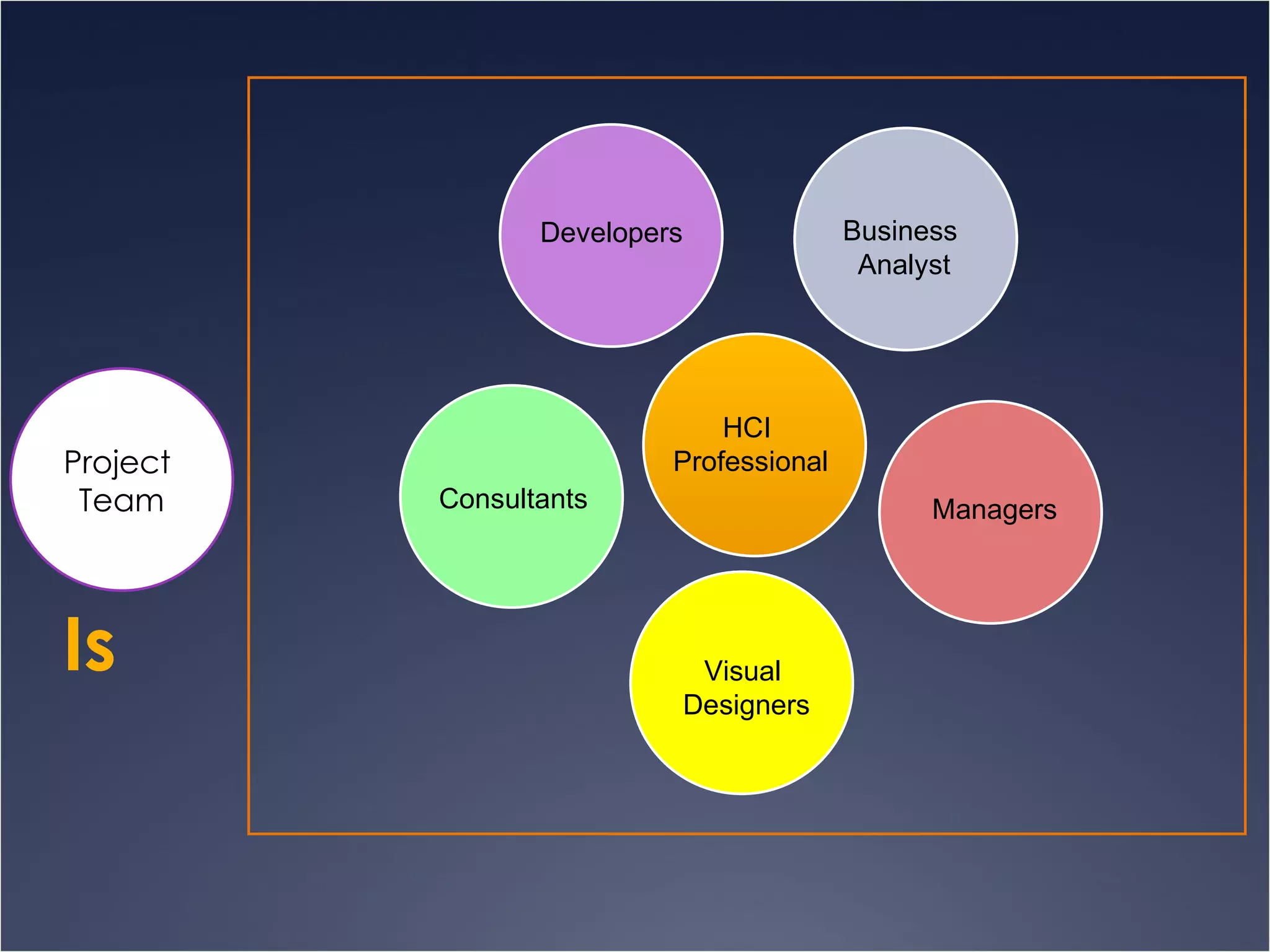
The document provides an overview of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), defining it as the study of interactions between people and computers. It discusses the historical development of HCI through three waves, focusing on user-centered design, context-based research, and expanding interactions to larger environments. Additionally, it outlines various roles and methodologies associated with HCI professionals, emphasizing the importance of user experience and interdisciplinary collaboration in designing effective interactive systems.





























![Thank You! [email_address] twitter.com/kshitiz | slideshare.net/kshitiz](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontohci-100708121158-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-HCI-42-2048.jpg)