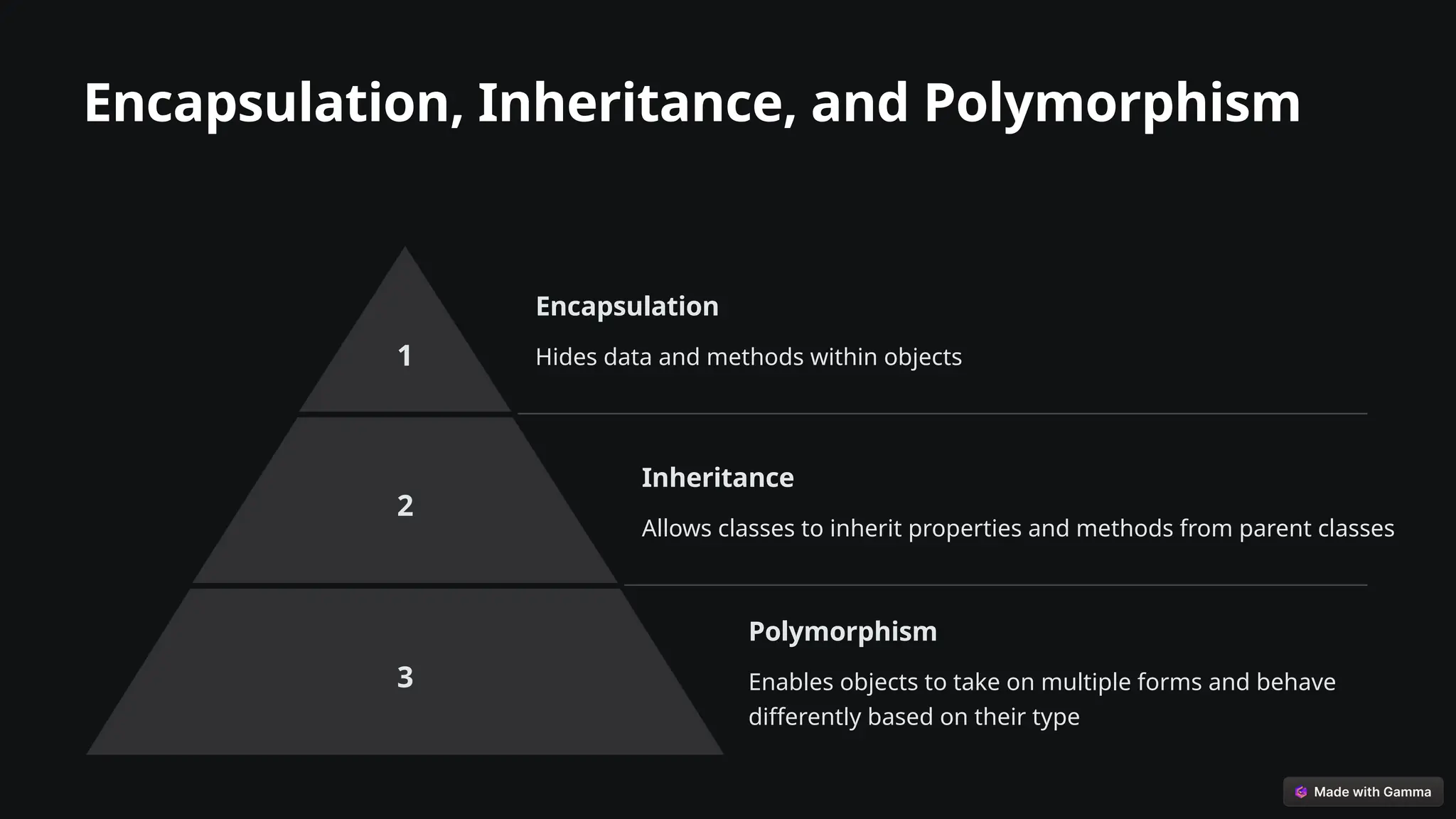
This presentation introduces the fundamentals of Java programming, focusing on core concepts, object-oriented principles, and practical applications through a sample project. It covers variables, data types, operators, control flow, and key OOP concepts such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, emphasizing their advantages in code reusability and maintainability. The sample project demonstrates these principles through a student management system, highlighting Java's power and versatility.