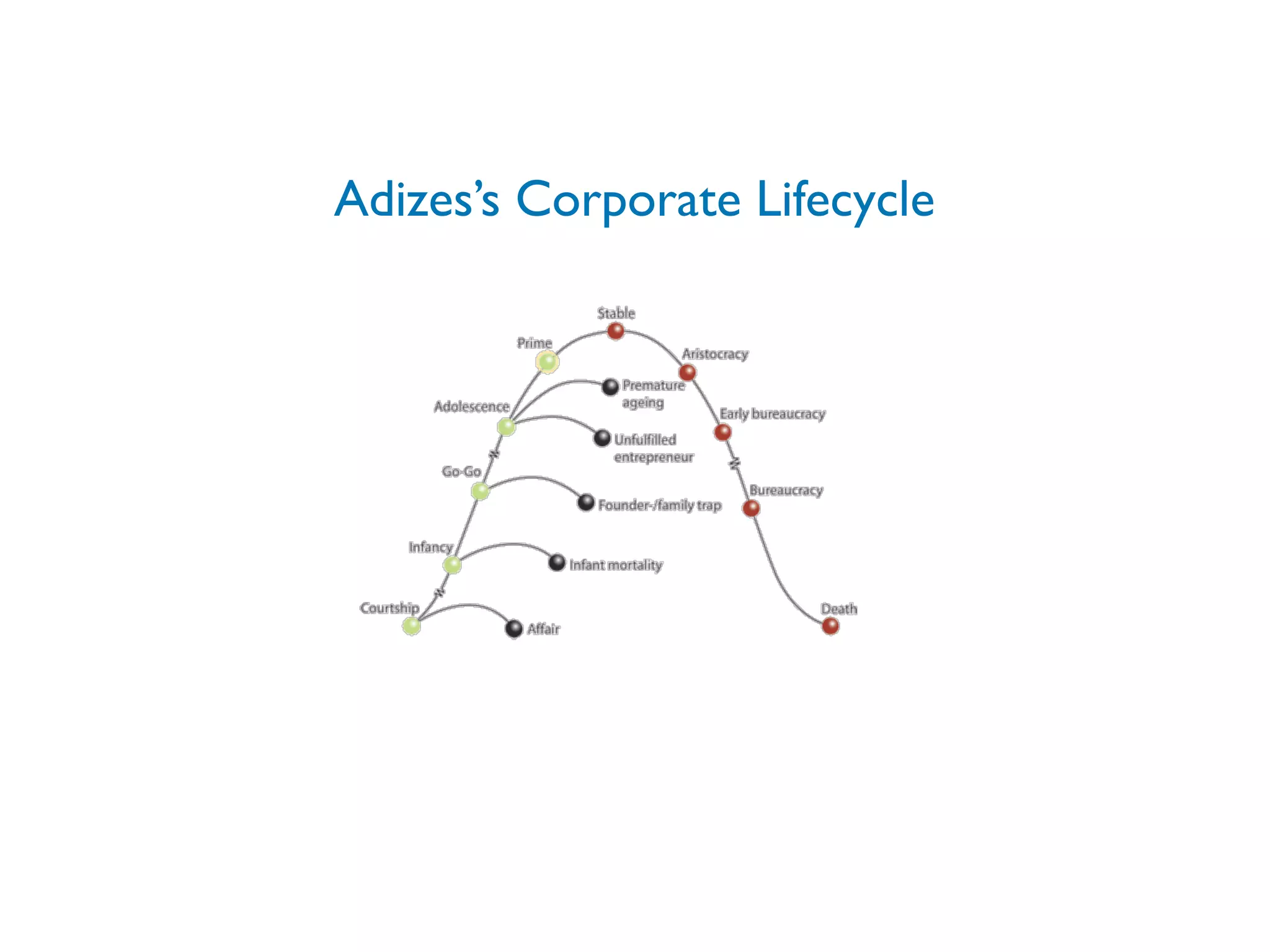
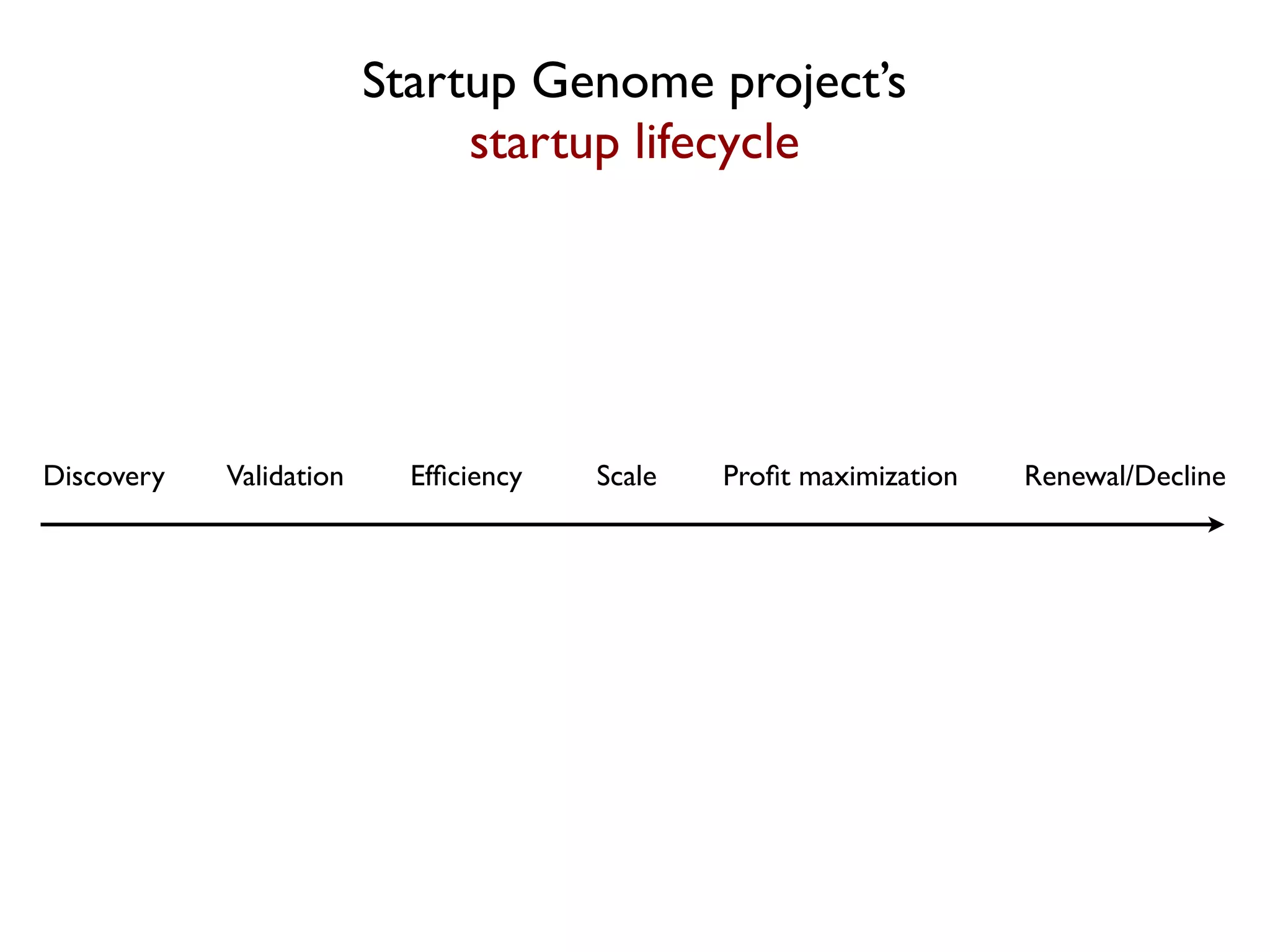
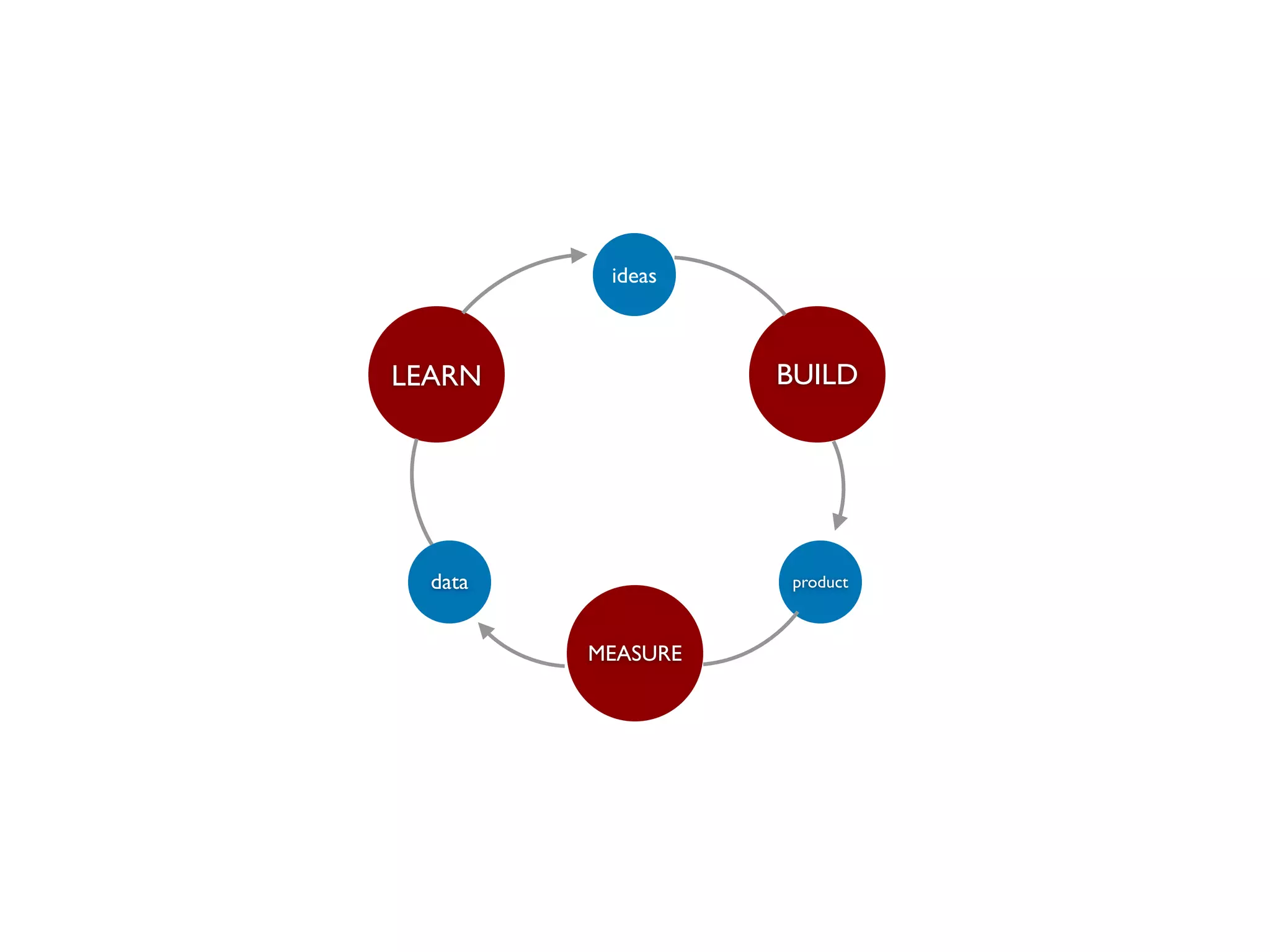
The document discusses the startup lifecycle, focusing on innovation, customer validation, and the various stages from discovery to scaling a business. It emphasizes the importance of solving real problems and adapting the product based on customer feedback. Additionally, it outlines the process of optimizing business models and acquisition channels for sustainable growth, highlighting the need for validated learning and efficient execution.