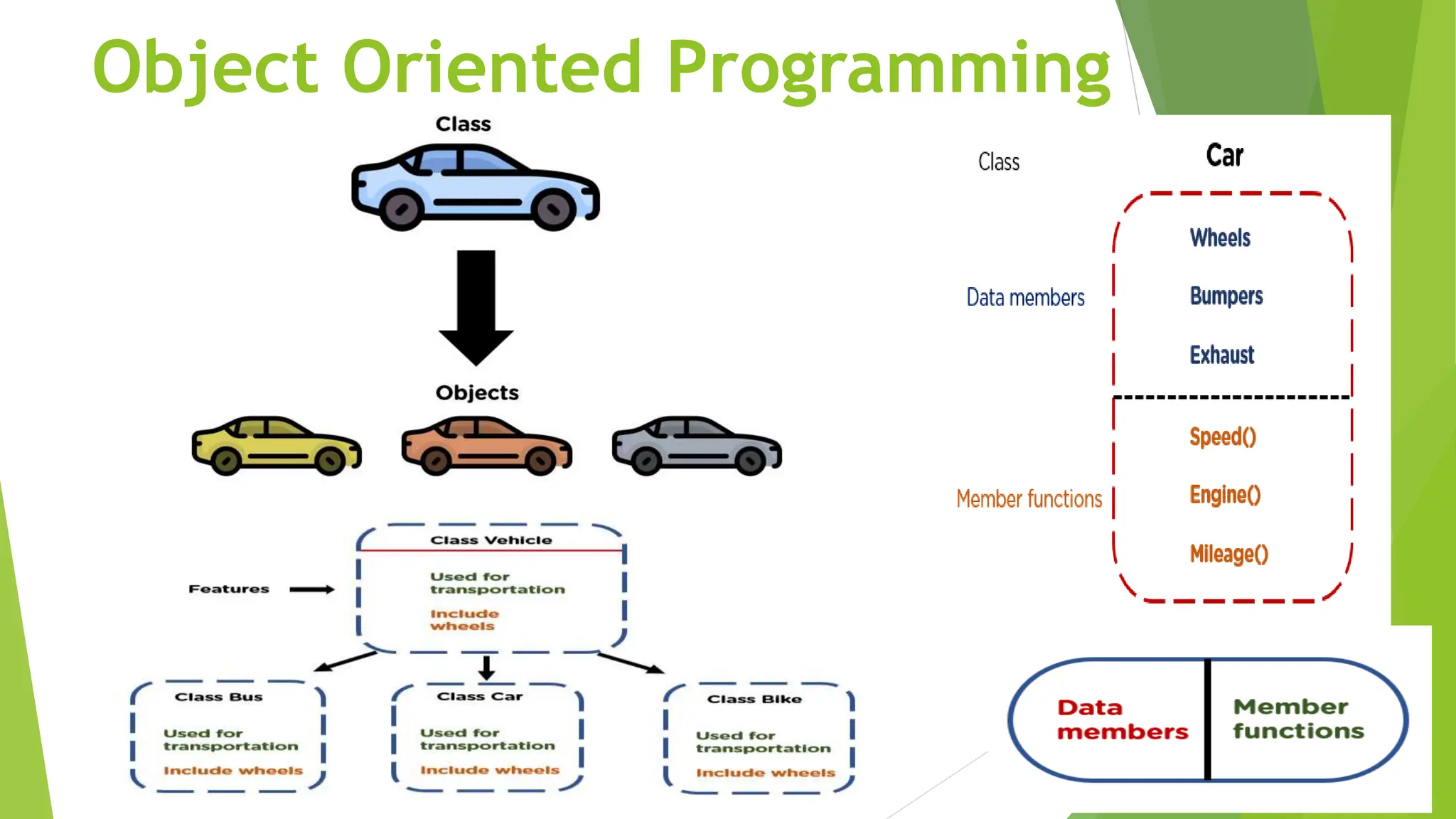
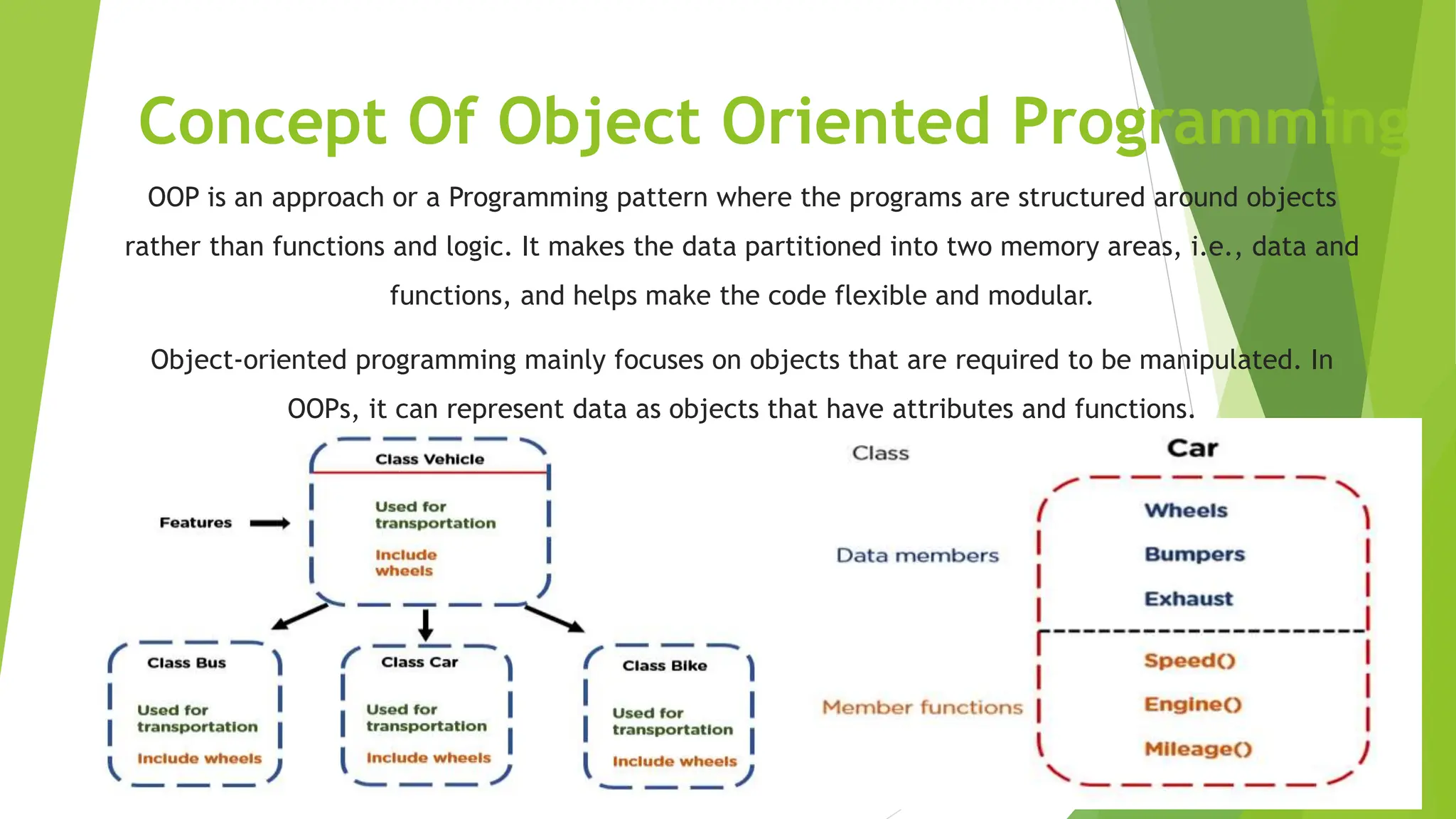
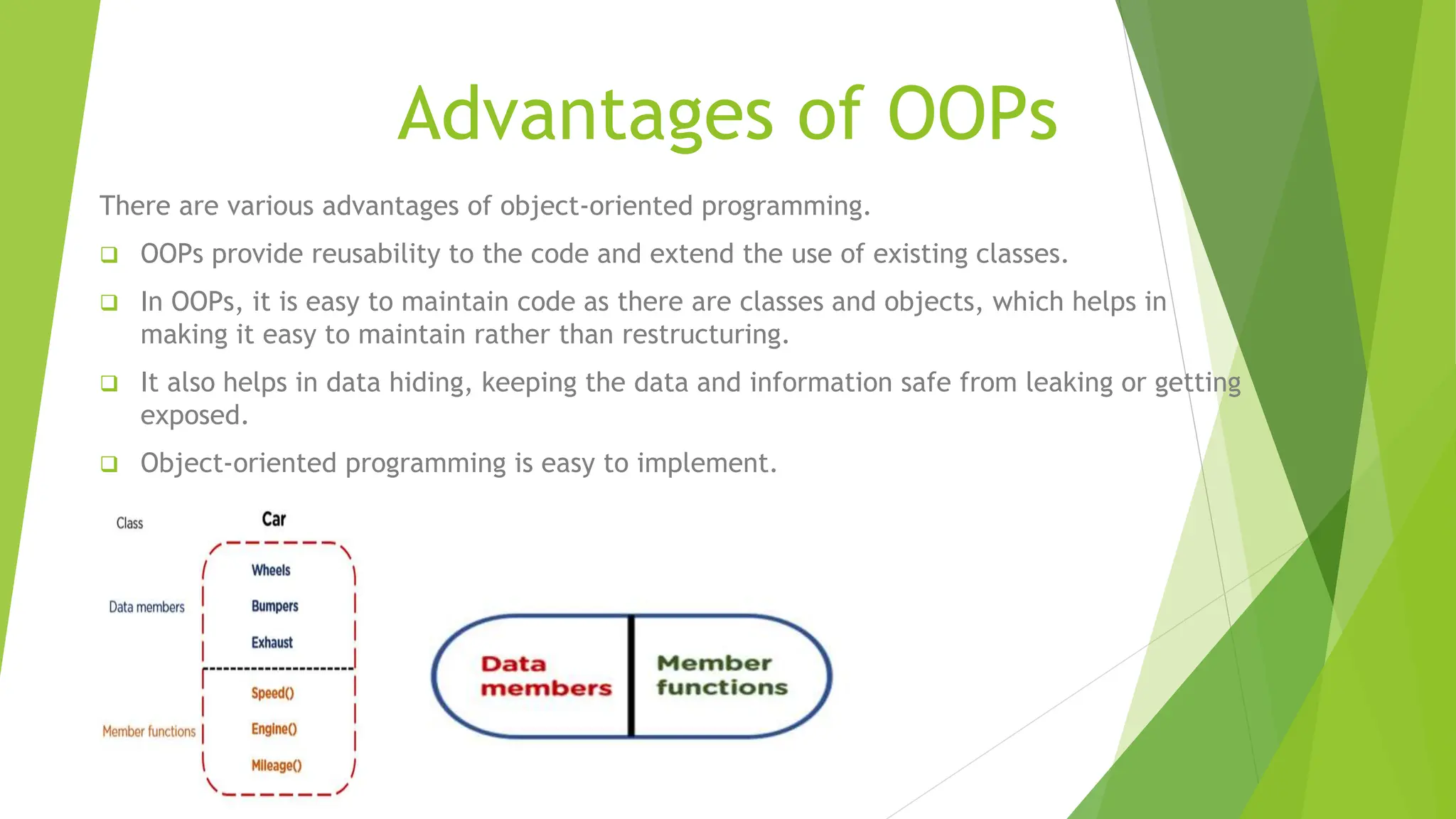
This document compares structured programming and object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting key features, advantages, and concepts of both paradigms. Structured programming focuses on modular functions and flow control, while OOP emphasizes objects, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, making it suitable for complex applications. The choice between the two paradigms is influenced by project requirements, complexity, and team expertise.