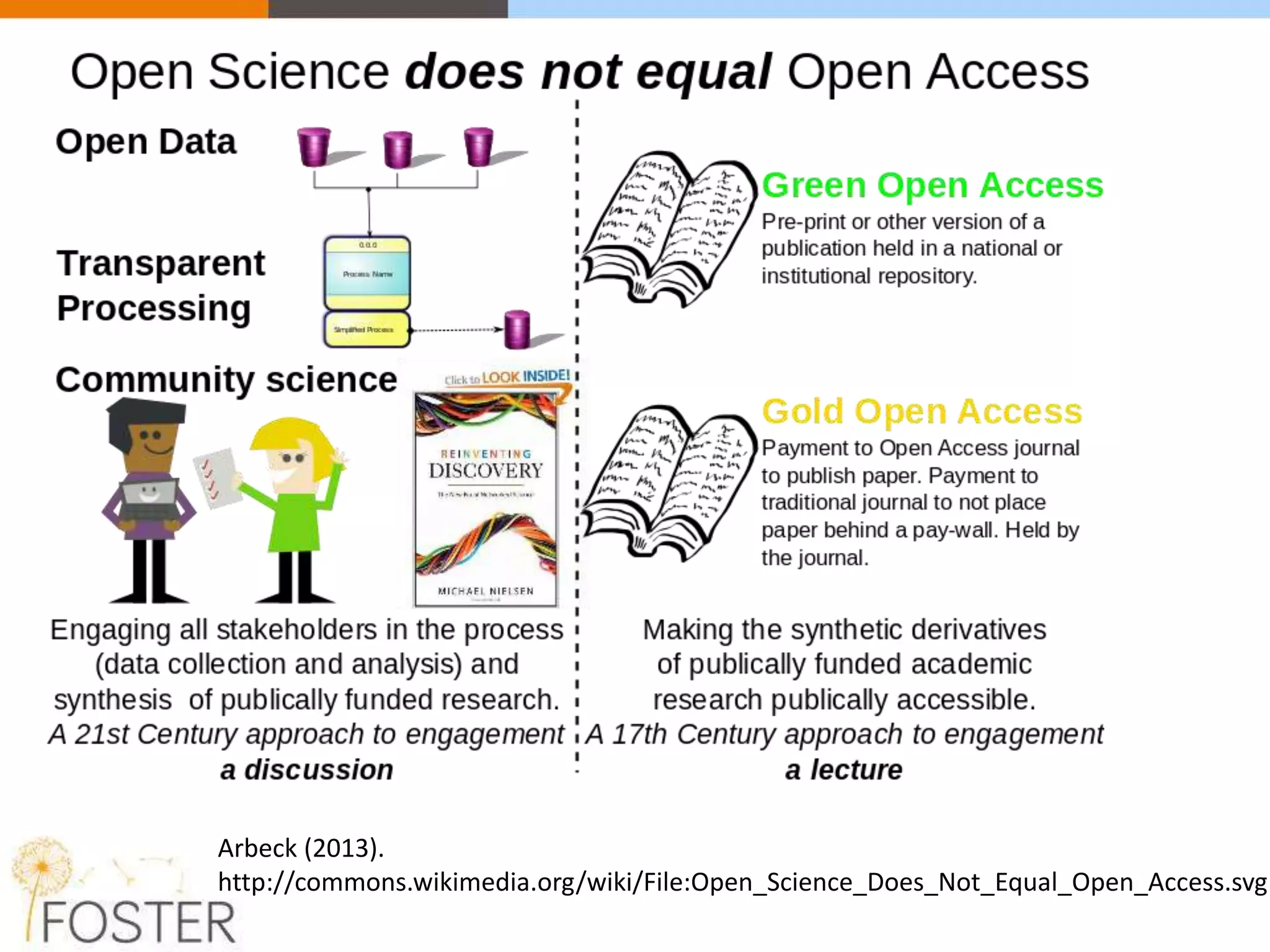
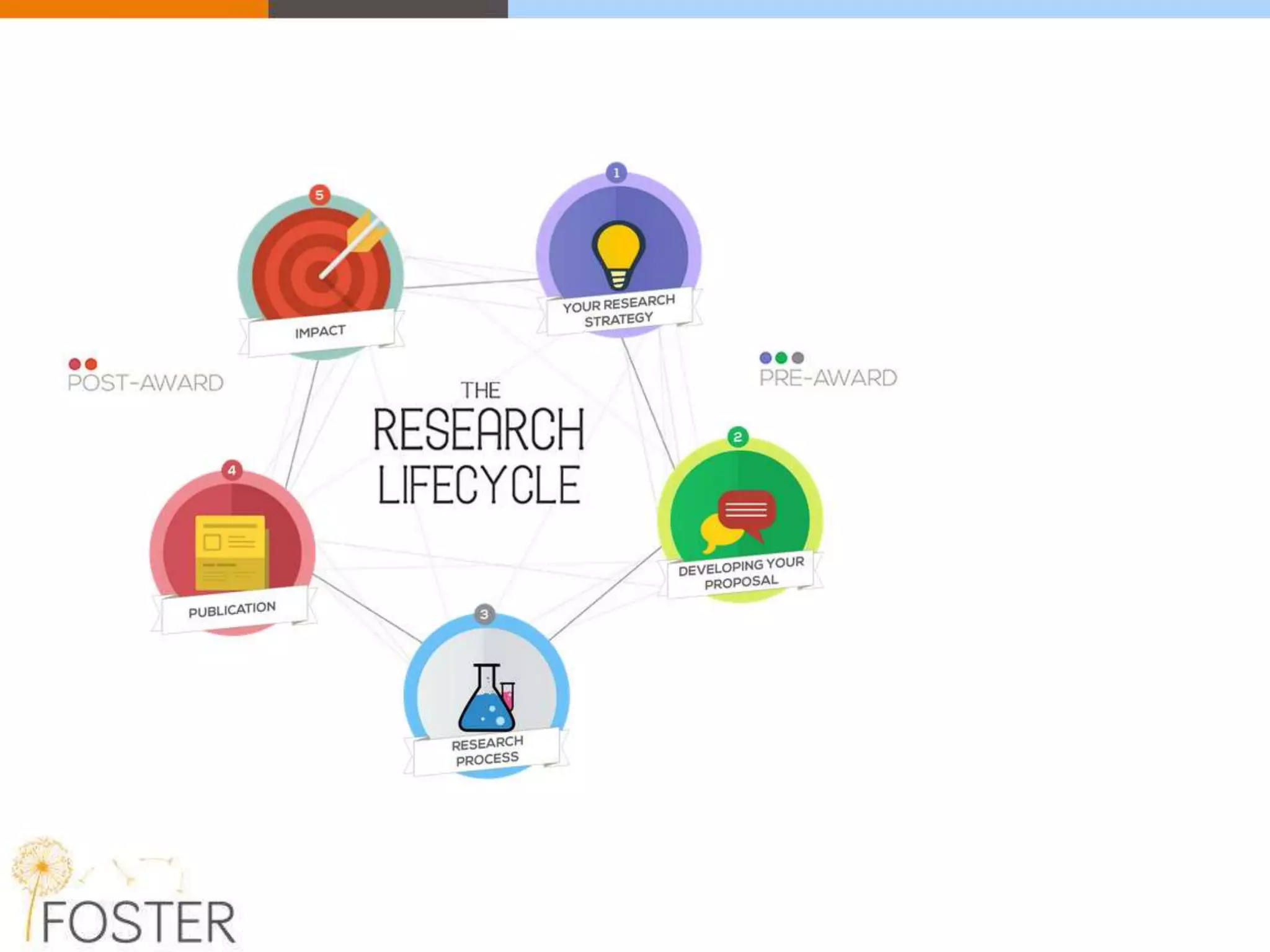
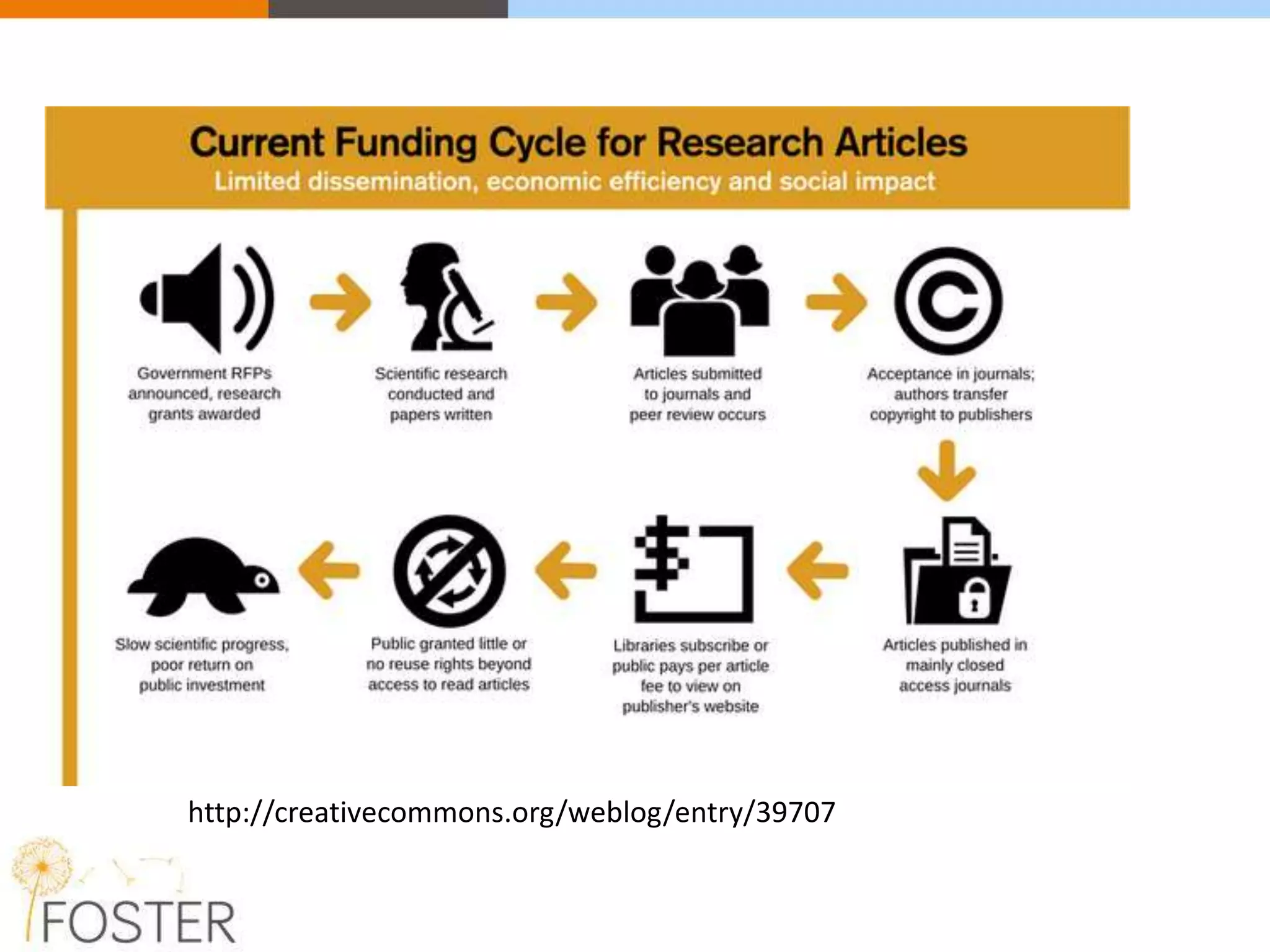
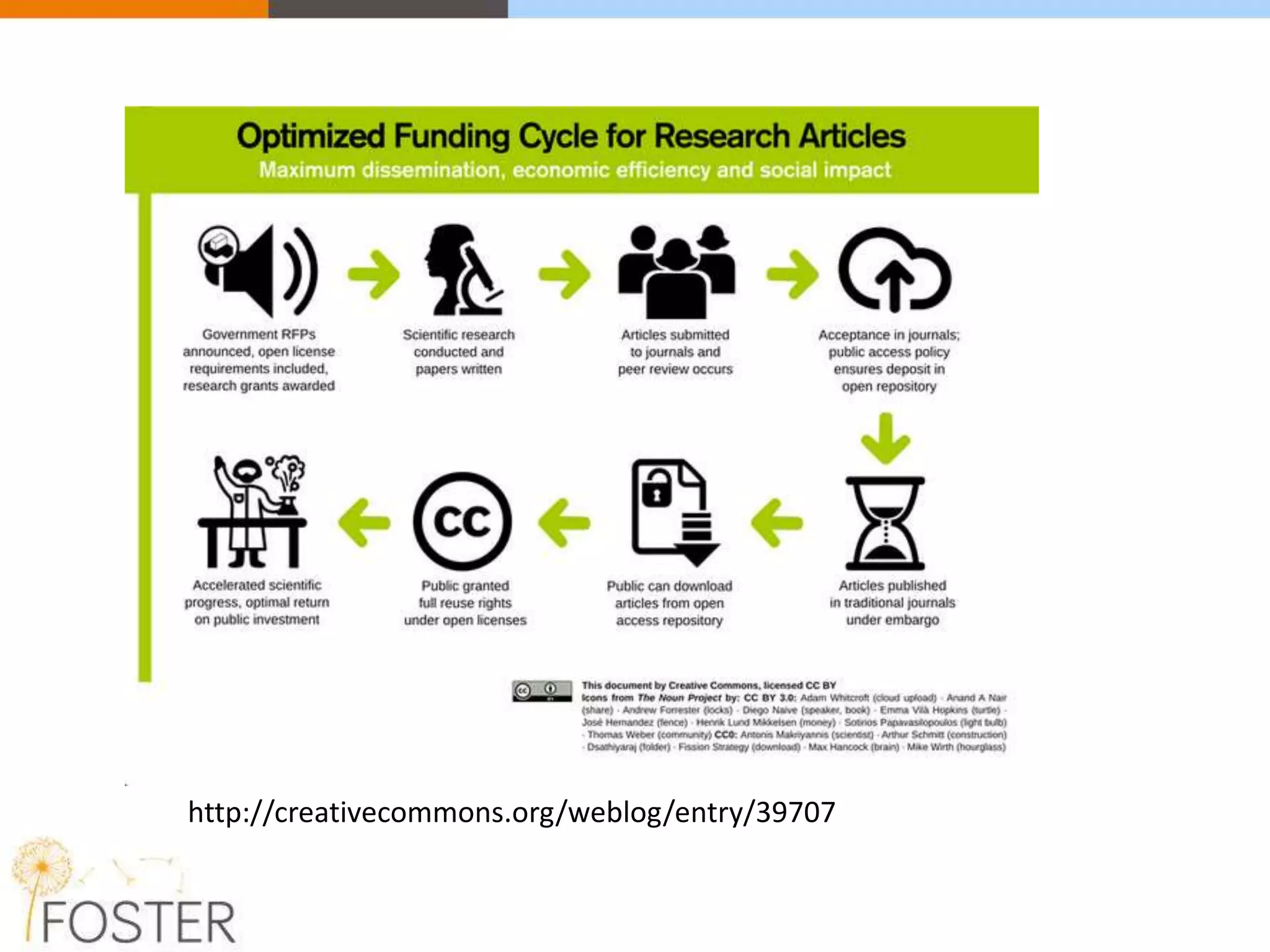
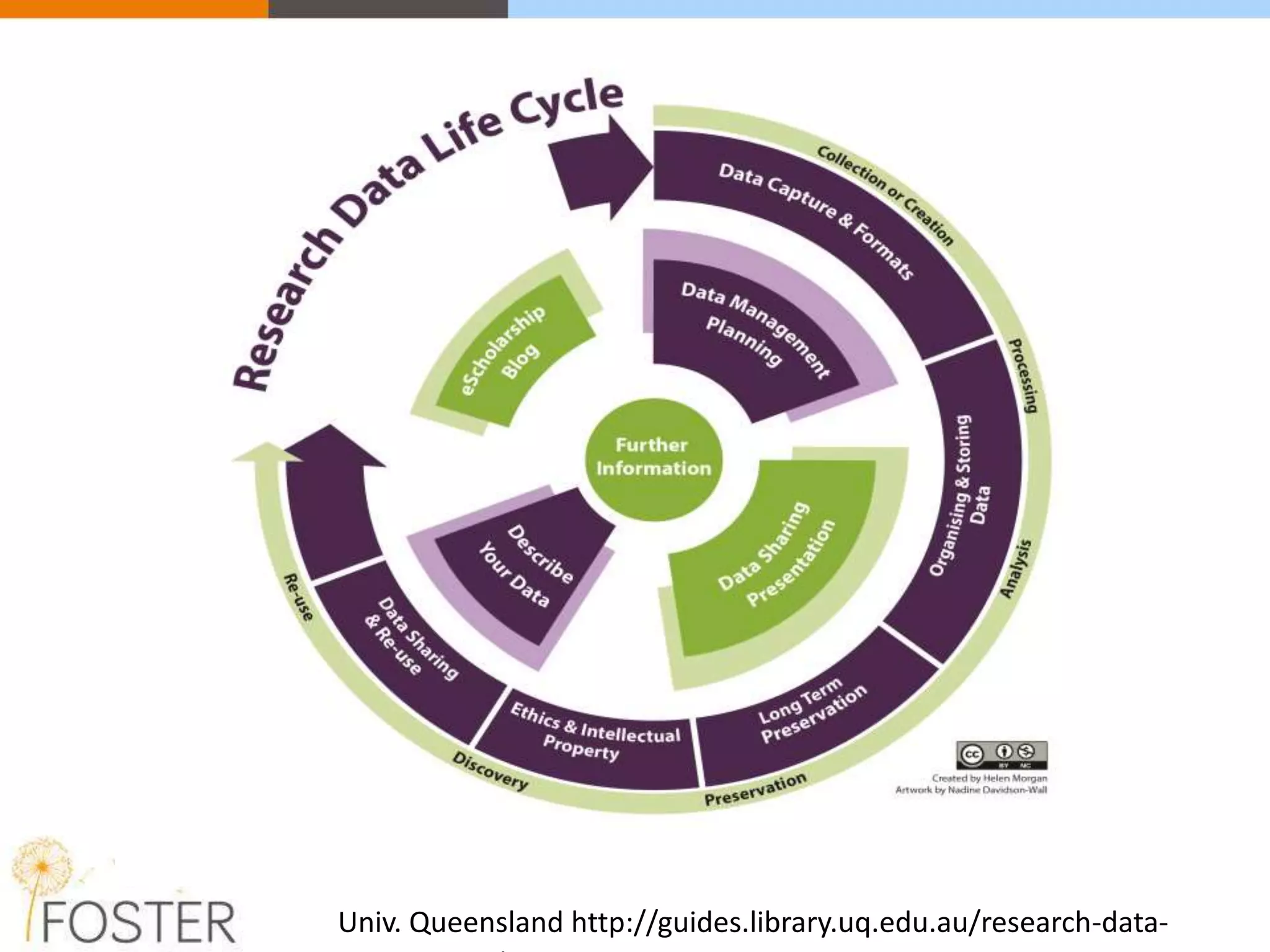
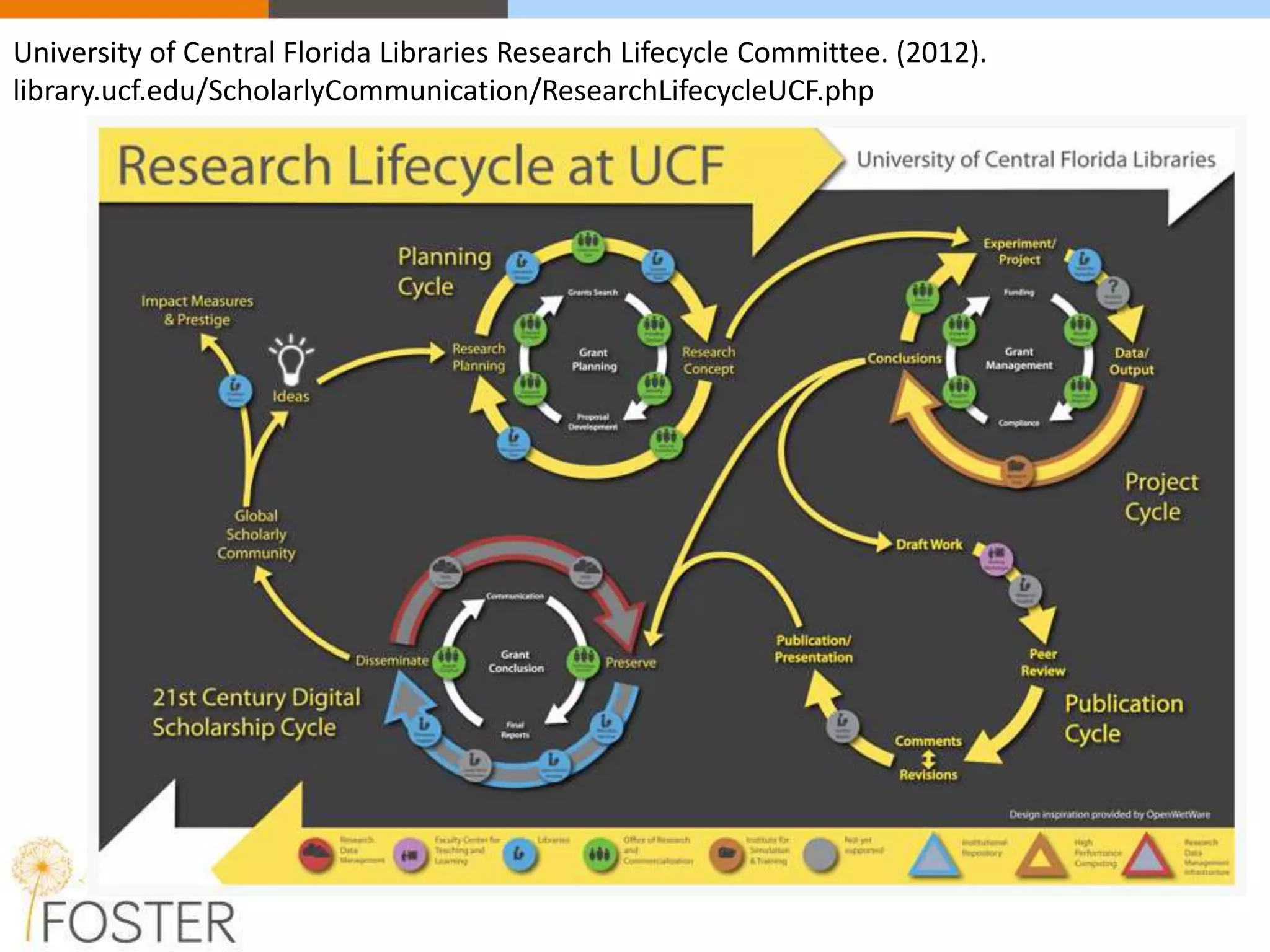
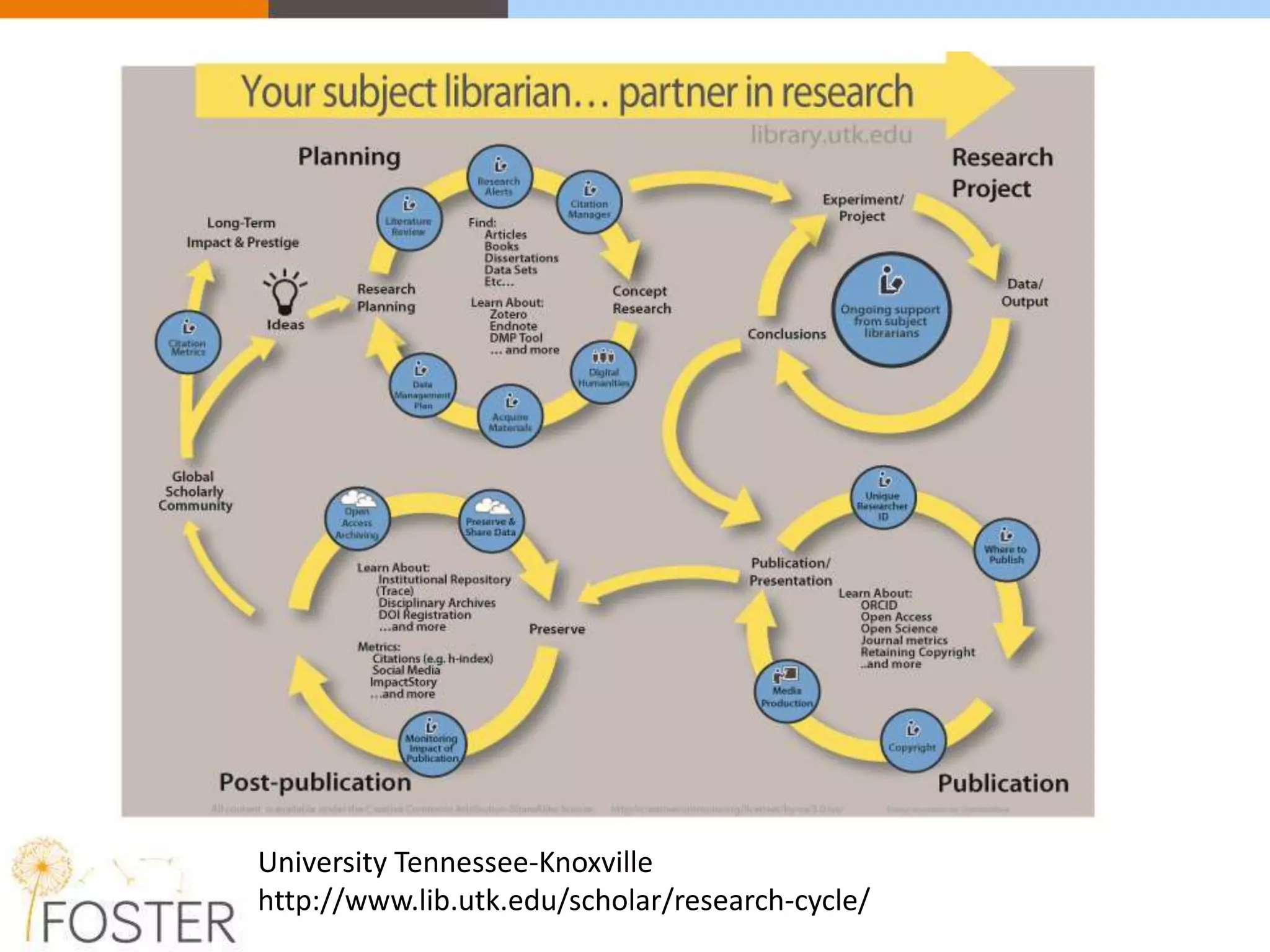
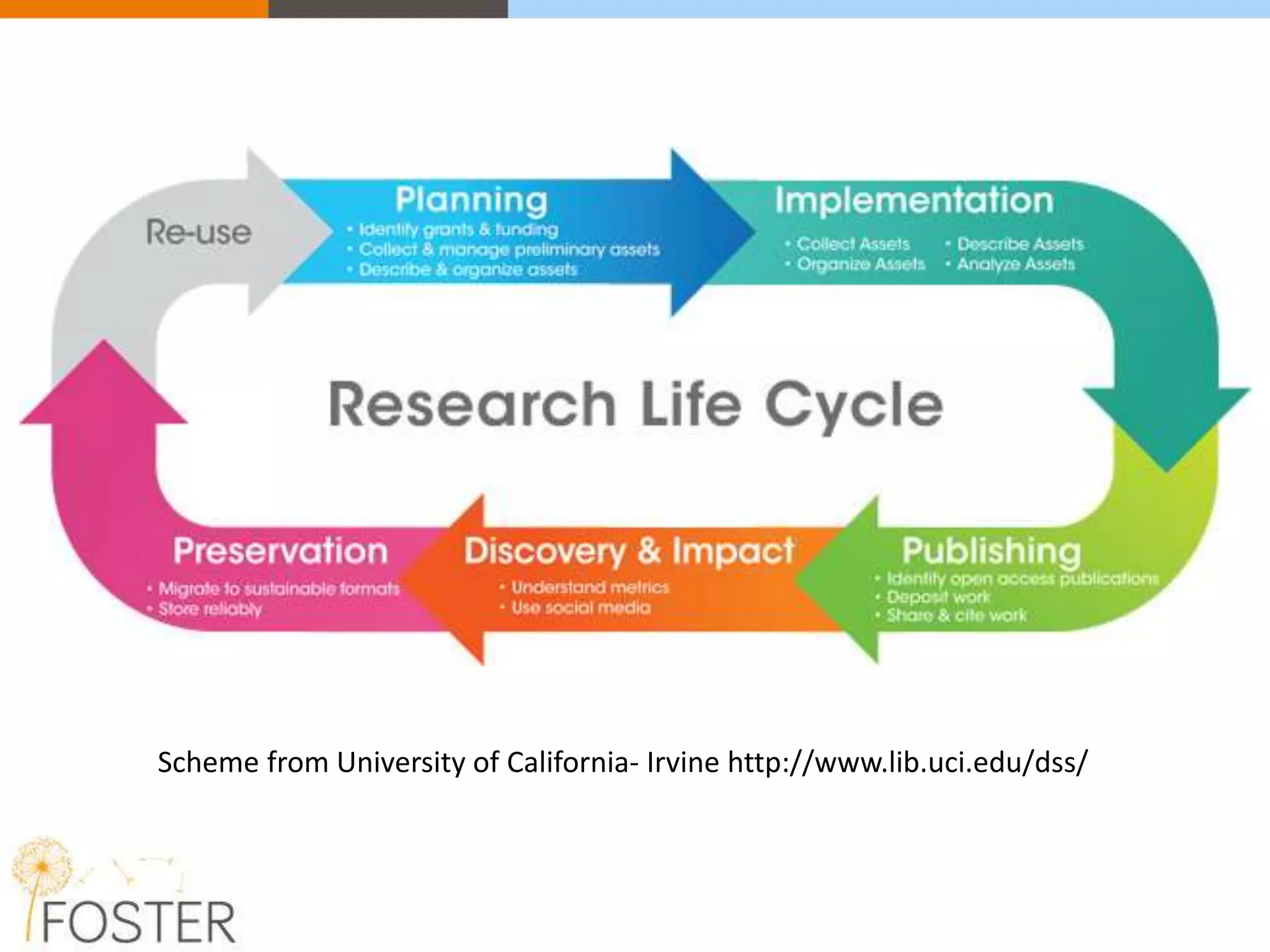
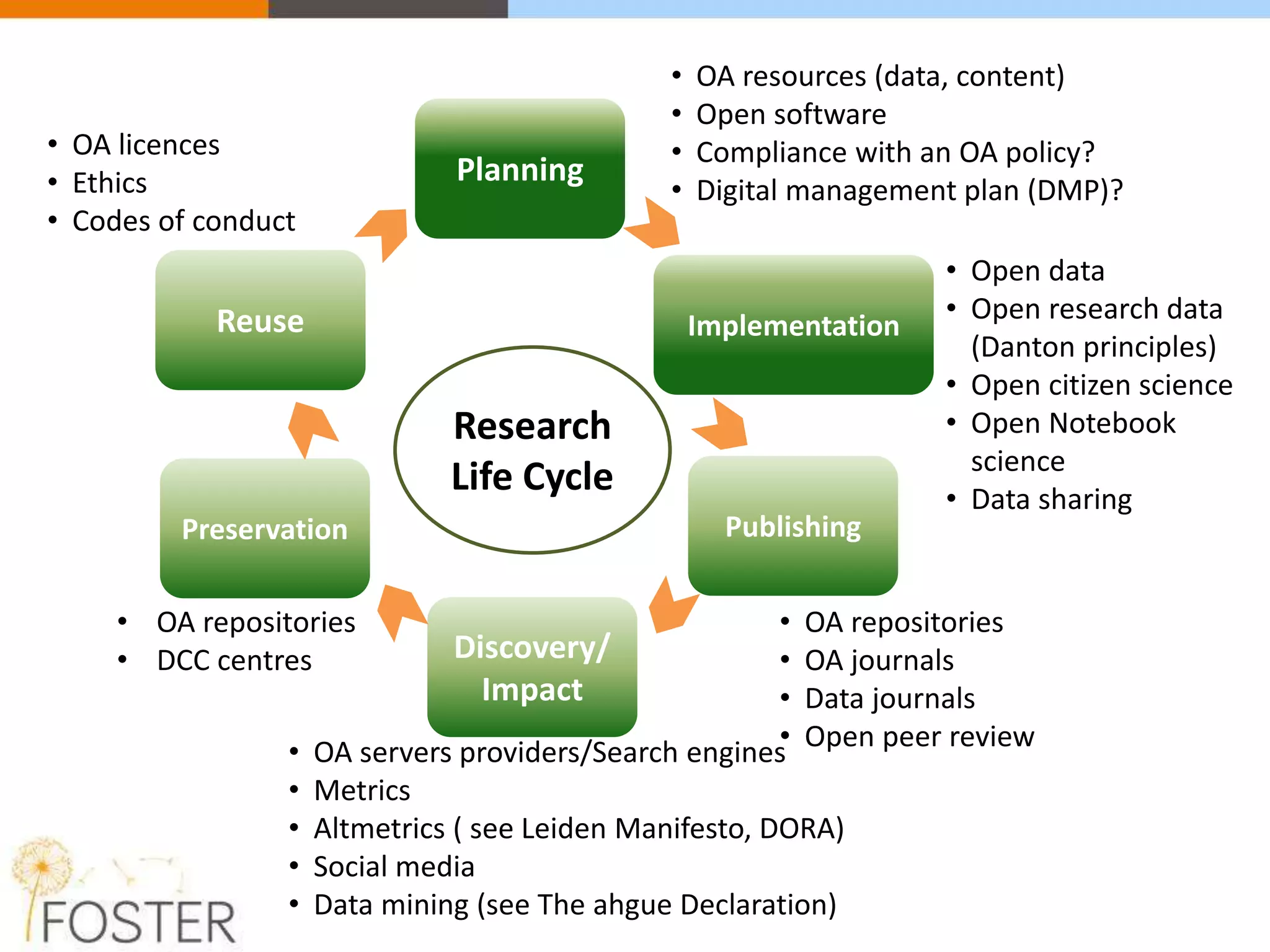
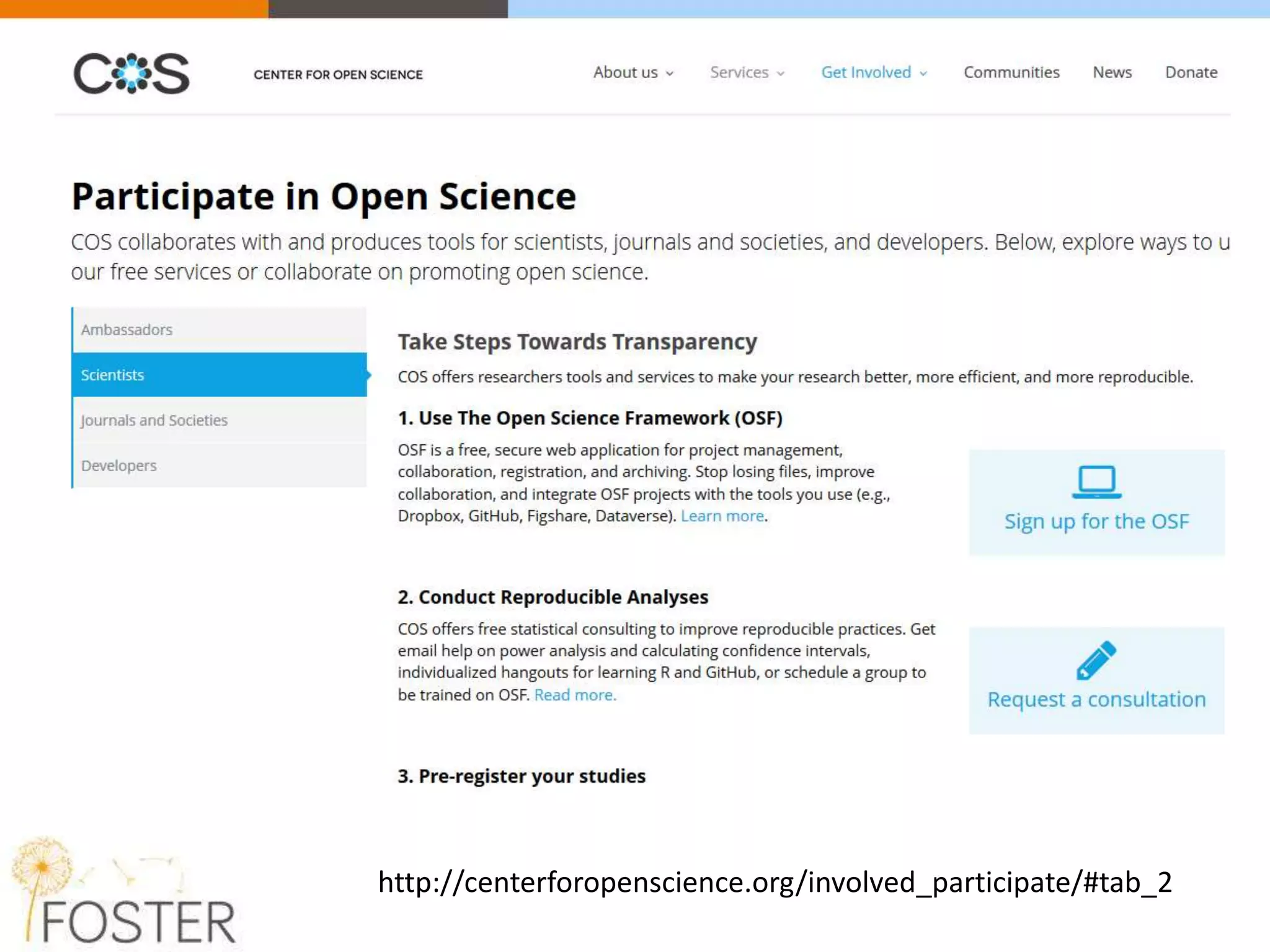
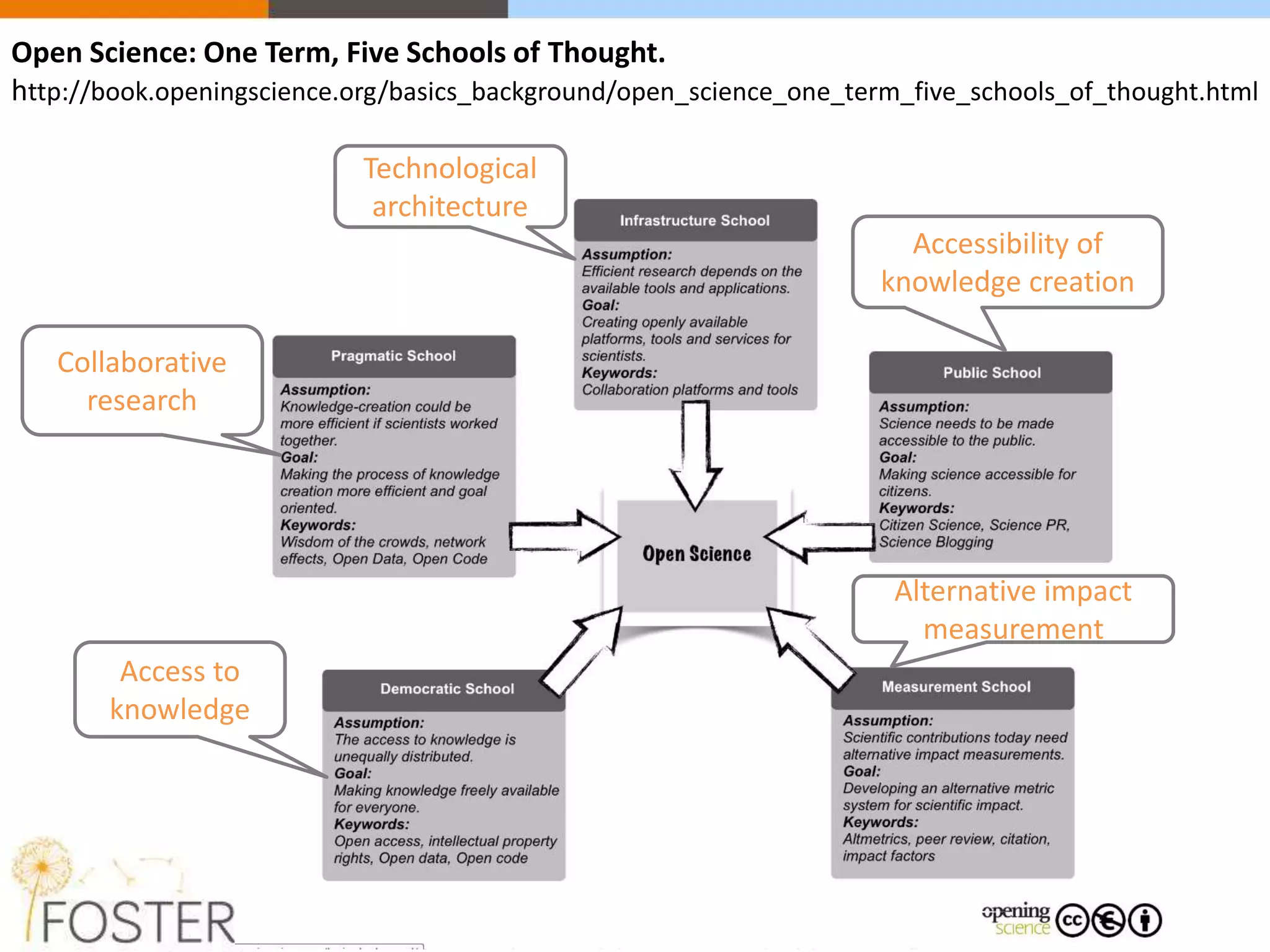
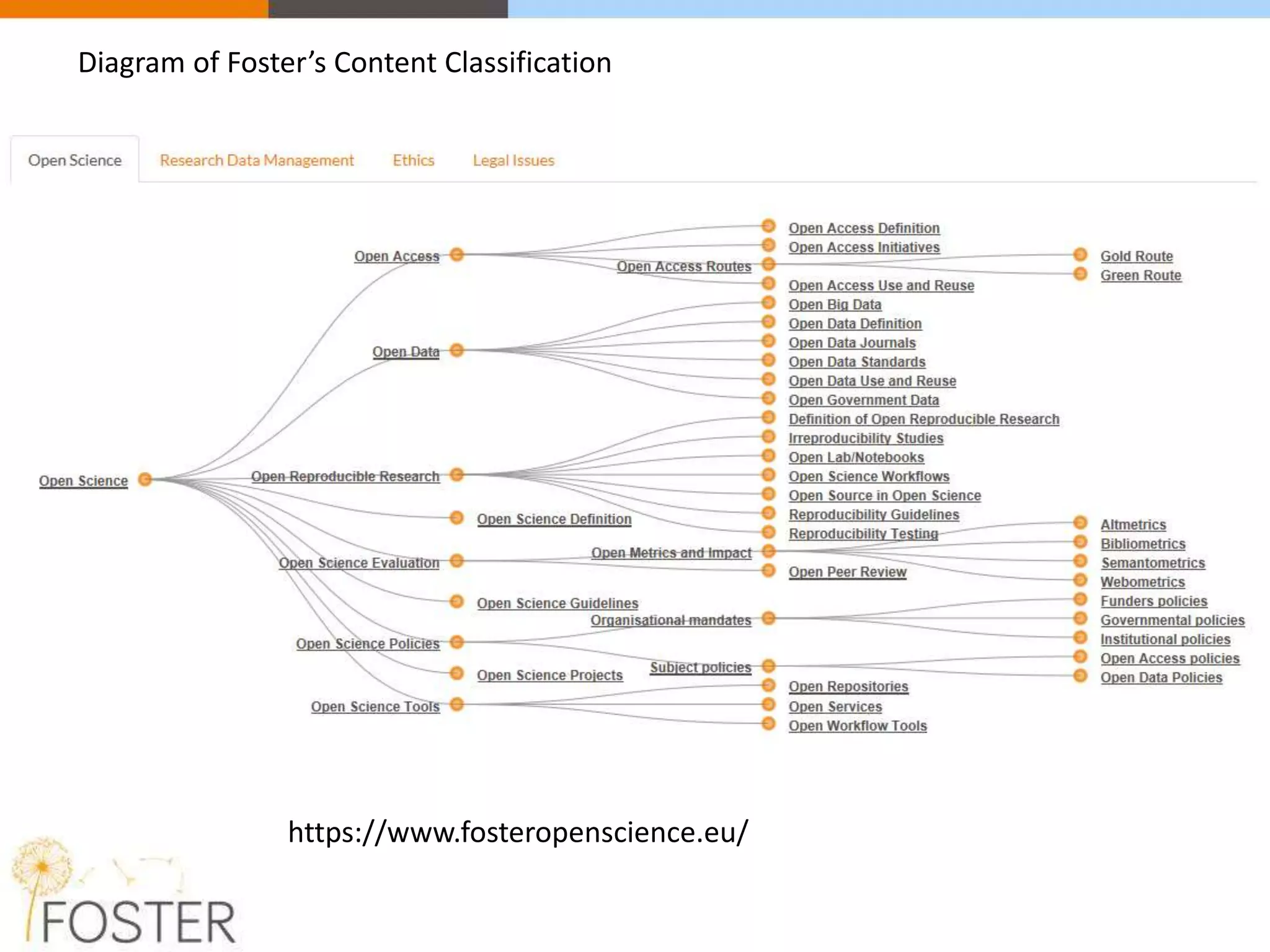
The FOSTER project, funded by Horizon 2020, aims to facilitate open science training for European researchers, especially targeting young researchers. It includes multiple European partners and focuses on supporting compliance with open access policies, integrating open access principles into research workflows, and strengthening institutional training capacity. Key objectives encompass fostering the adoption of open science practices across various research stages and ensuring alignment with European funding policies.