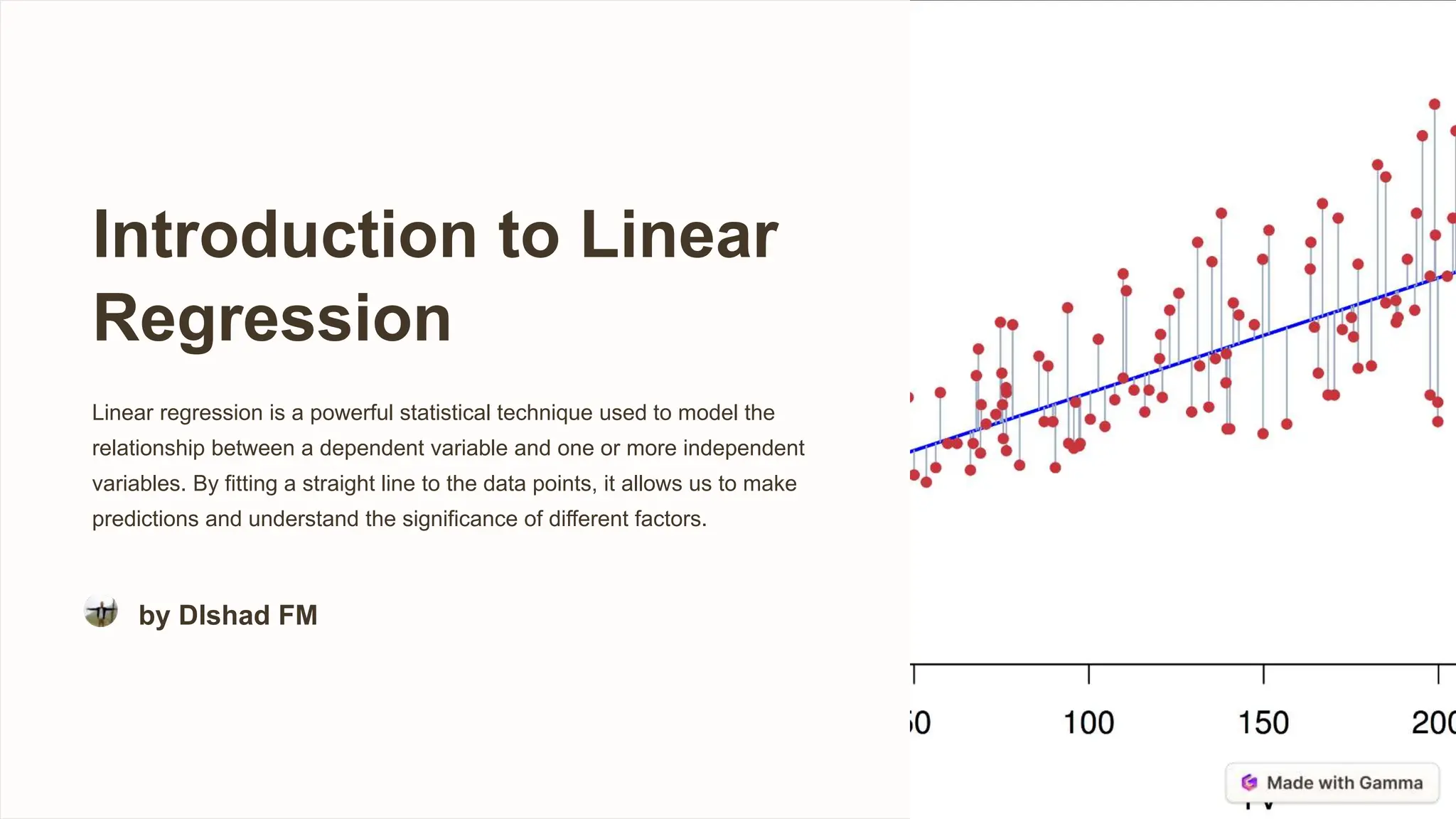
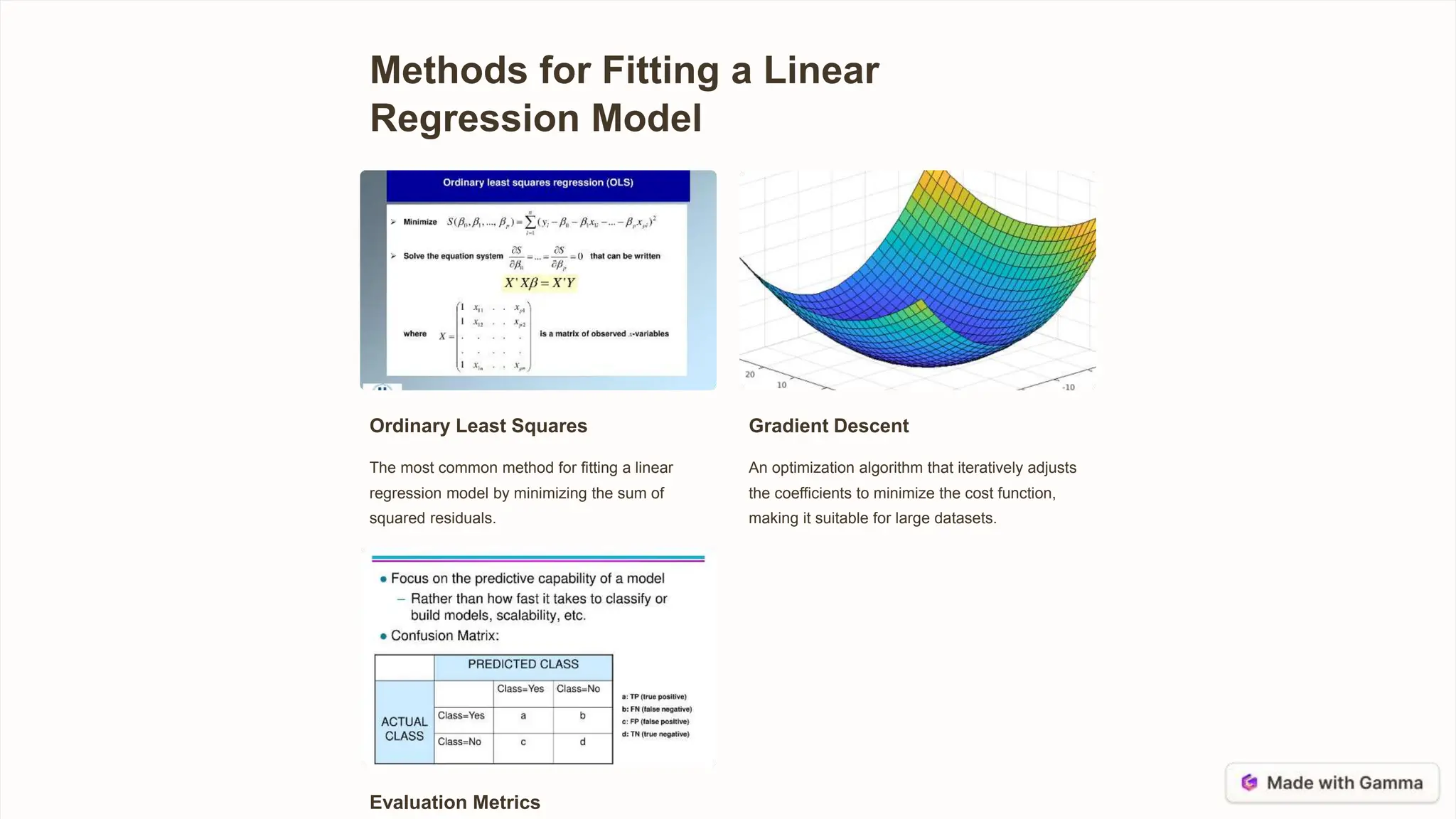
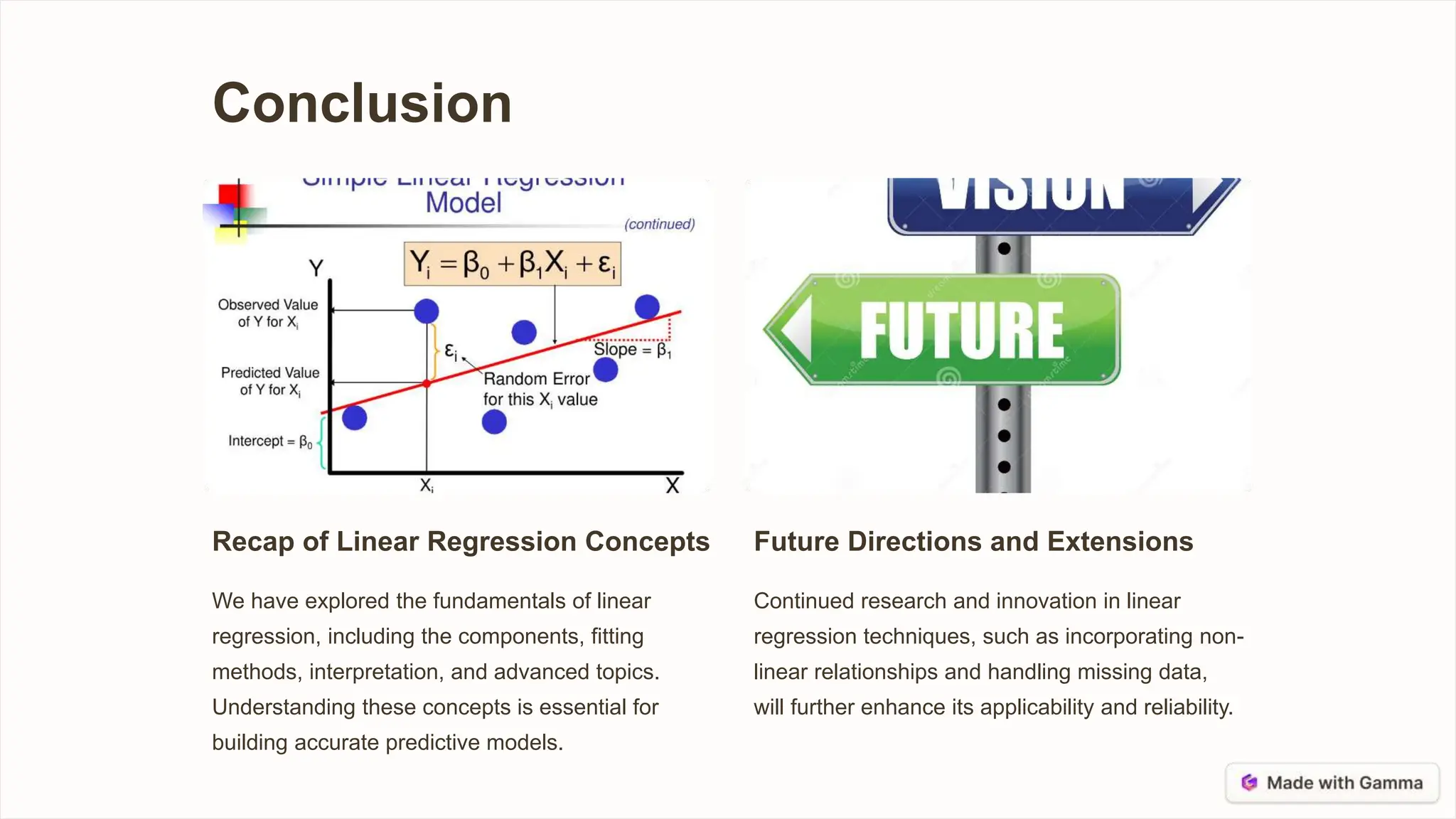
Linear regression is a statistical technique used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables by fitting a straight line to the data points. It allows predictions and understanding of factor significance. The dependent variable is what is being predicted, while independent variables may help explain its variability. Coefficients represent changes in the dependent variable per independent variable change, and the intercept is the dependent variable value when independents are zero. Linear regression relies on assumptions like linearity and normality that may be violated for complex relationships. Methods like ordinary least squares and gradient descent fit regression models by minimizing residuals or cost functions. Evaluation metrics and significance tests help interpret results and variable importance.