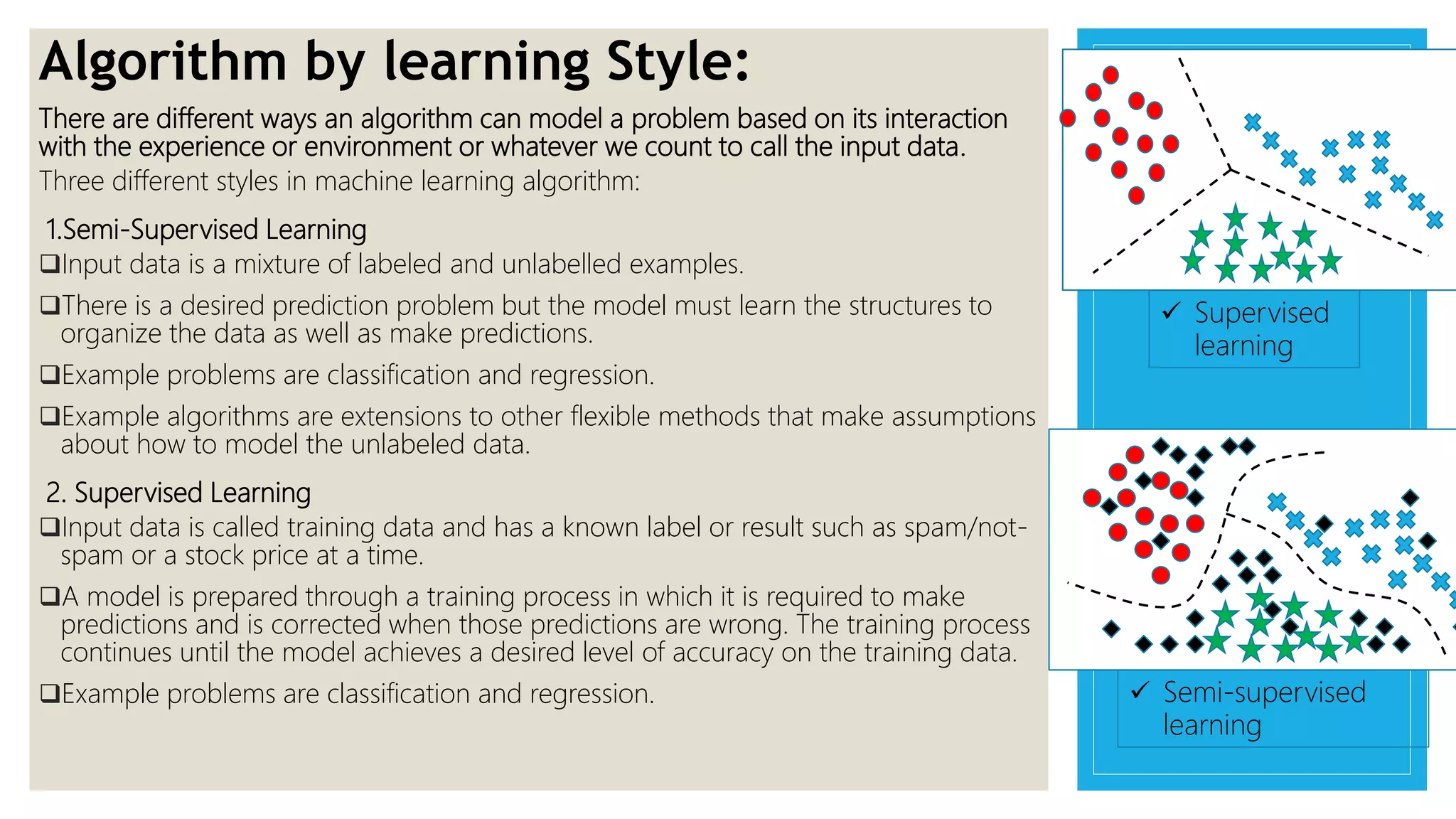
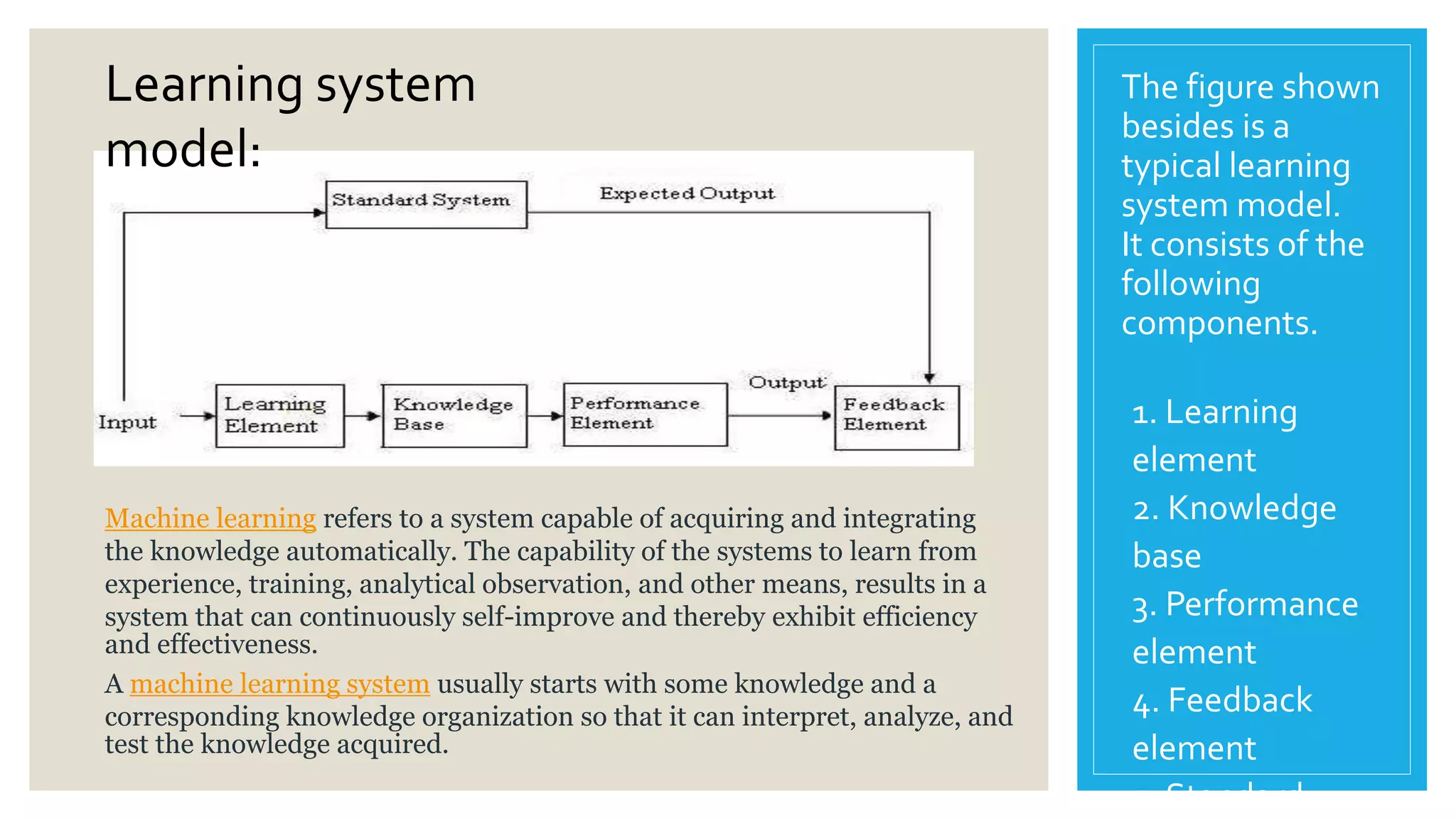
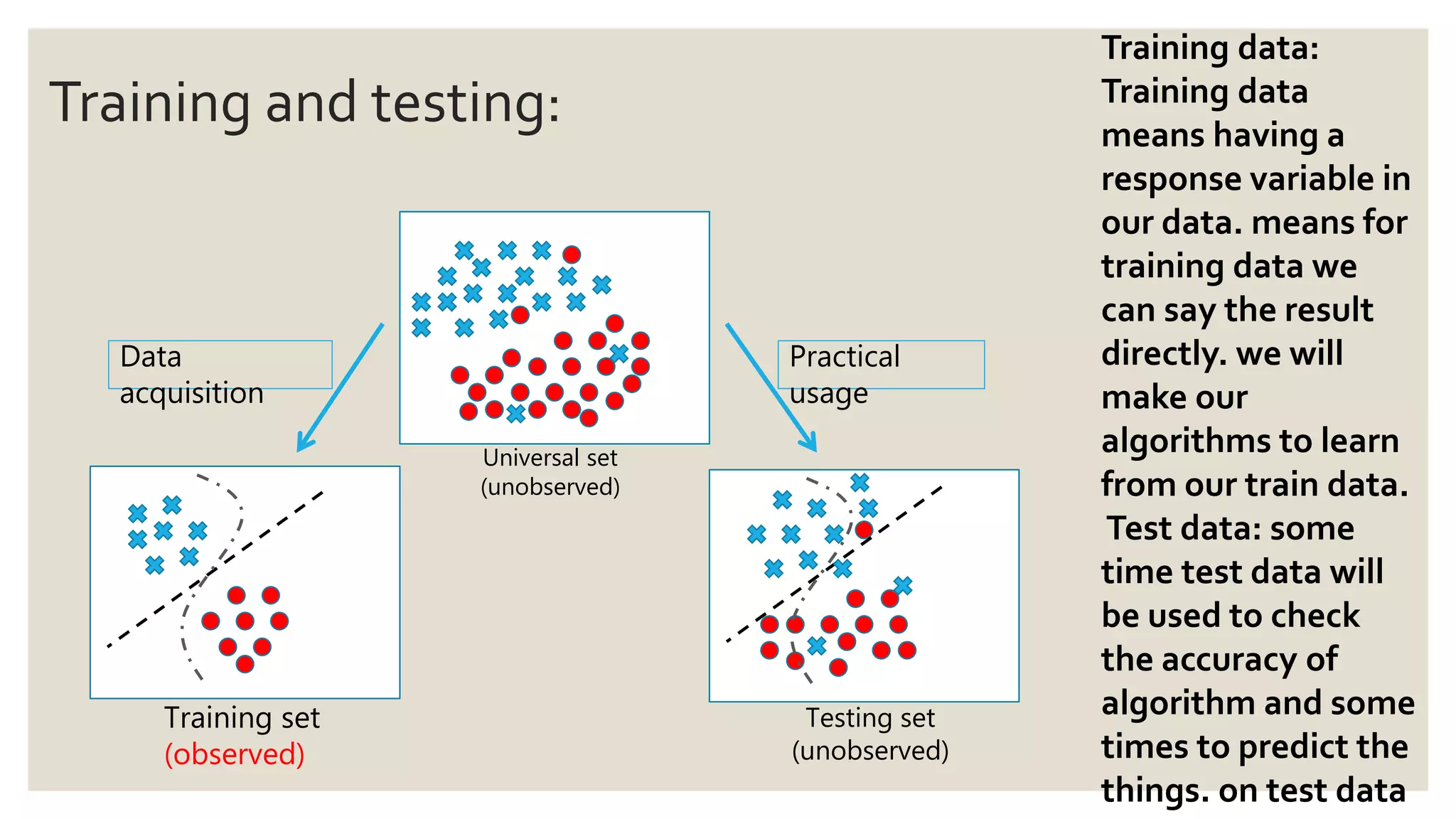
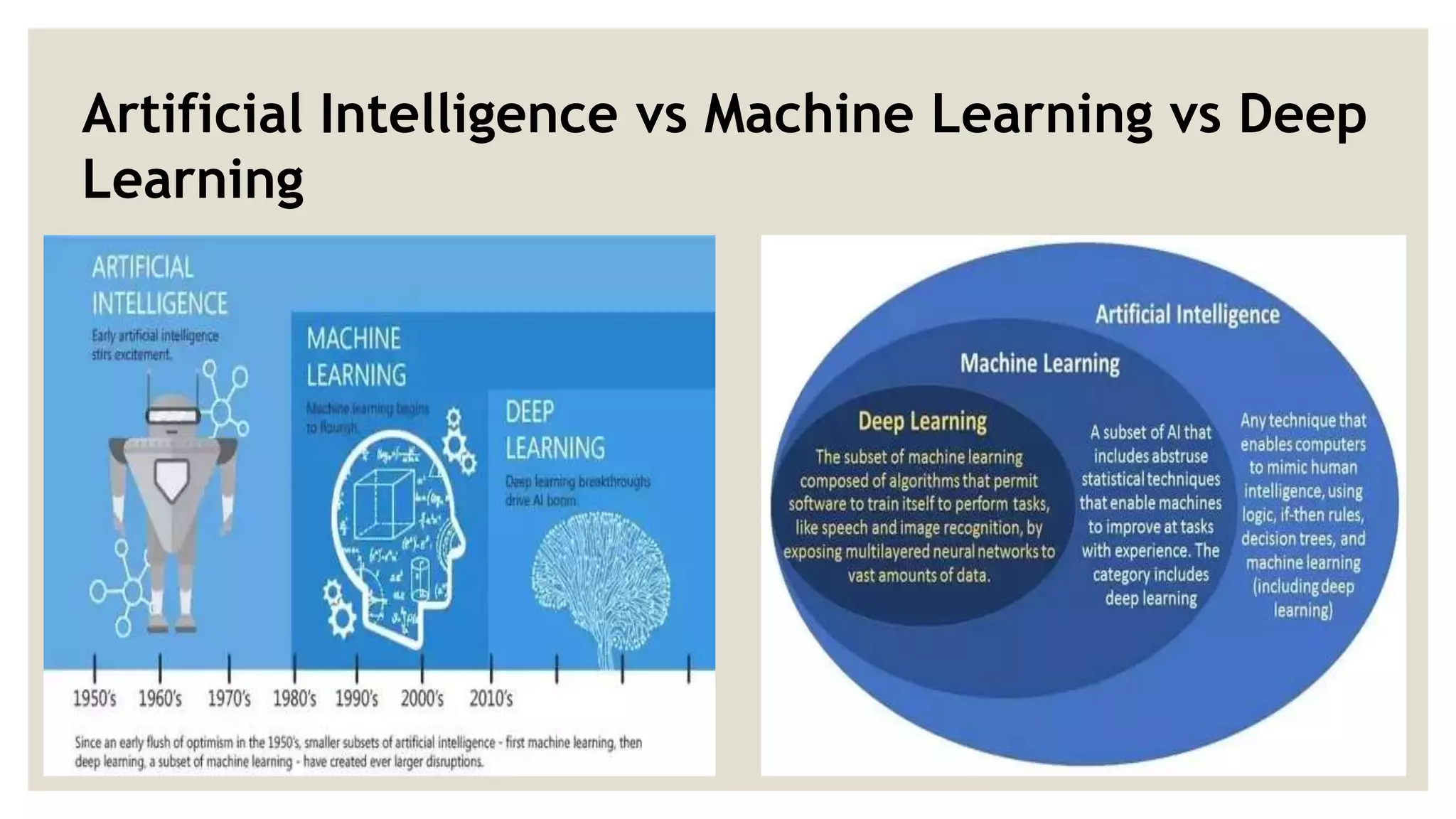
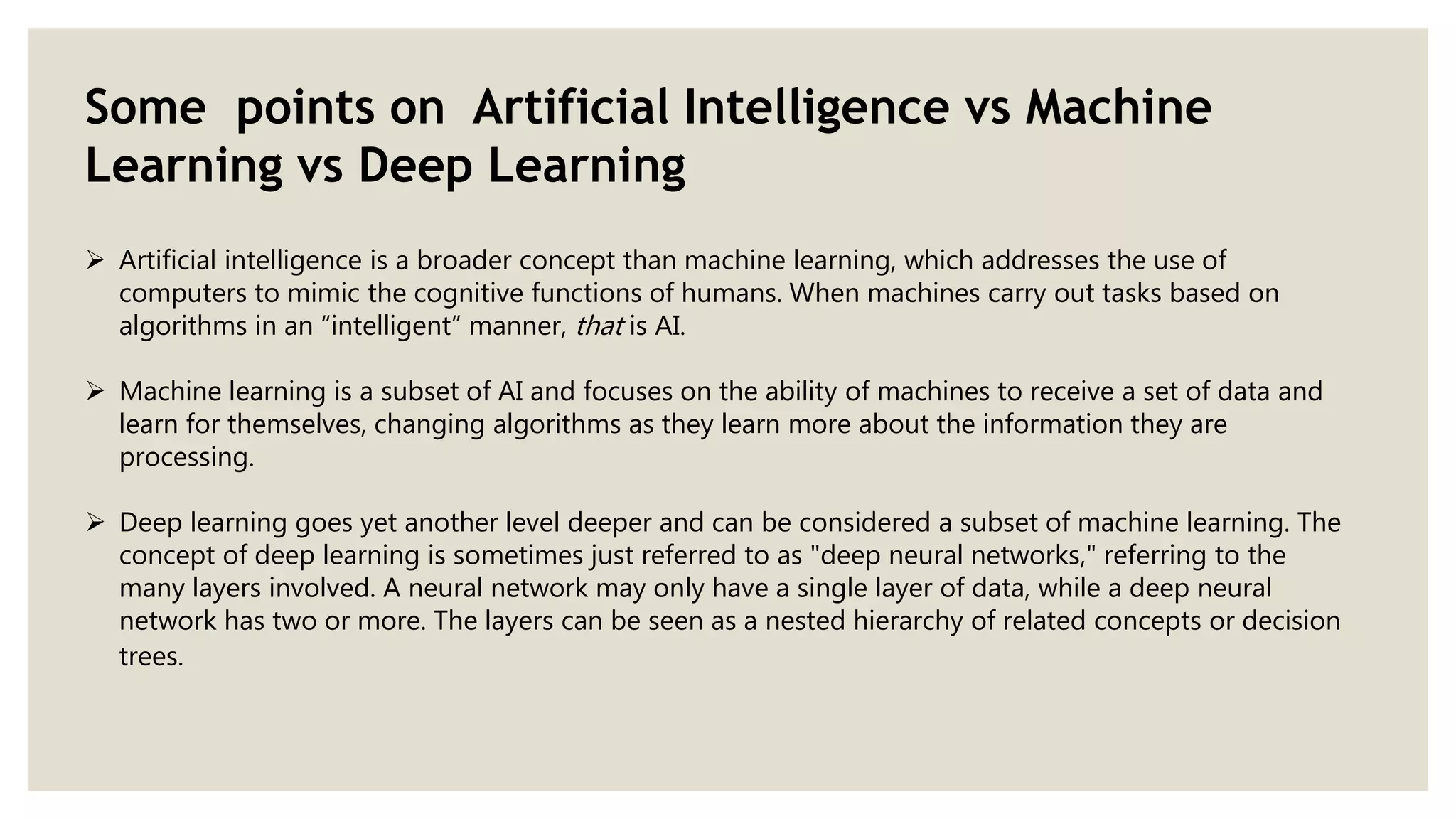
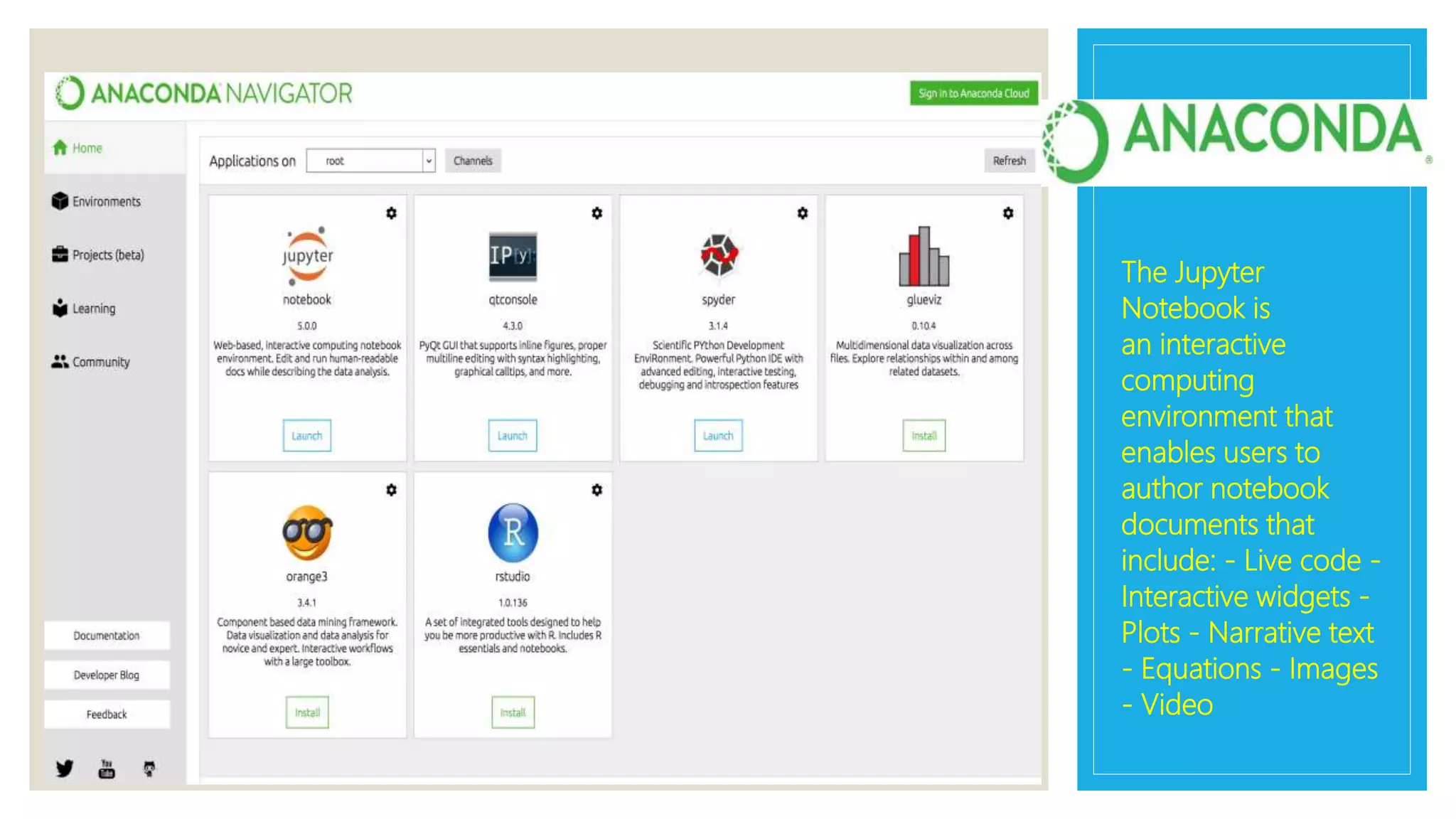
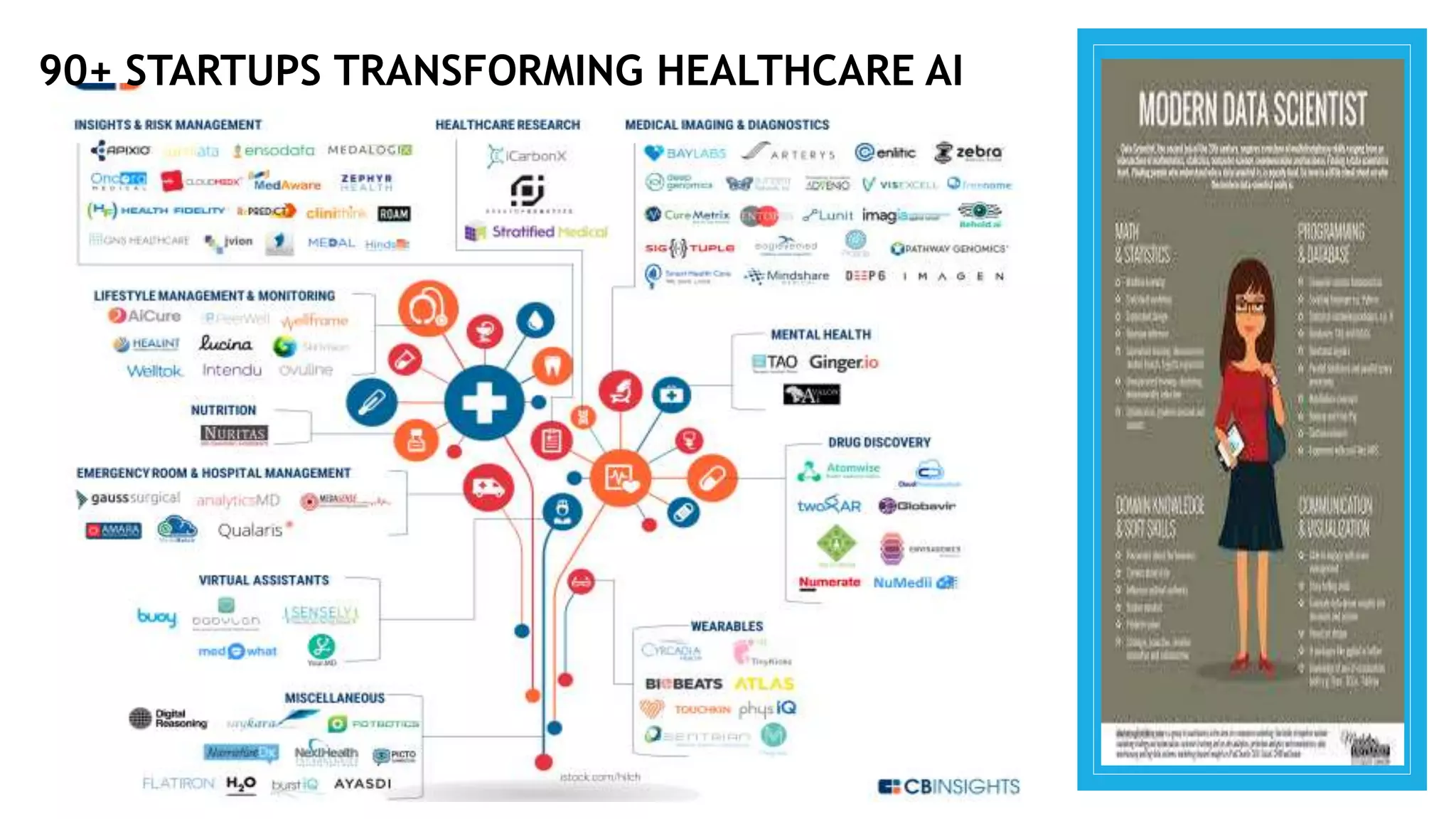
This document provides an overview of a presentation on machine learning given at Gurukul Kangri University in 2017. It defines machine learning as a field that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. It discusses different machine learning algorithms including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and semi-supervised learning. Examples of applications of machine learning discussed include data mining, natural language processing, image recognition, and expert systems. The document also contrasts artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning.

![
WHAT IS MACHINE LEARNING?
ARTHUR SAMUEL IN 1959:
“[MACHINE LEARNING IS THE] FIELD OF STUDY THAT GIVES
COMPUTERS THE ABILITY TO LEARN WITHOUT BEING EXPLICITLY
PROGRAMMED.”
AND MORE RECENTLY, IN 1997, TOM MITCHEL :
“A COMPUTER PROGRAM IS SAID TO LEARN FROM EXPERIENCE E
WITH RESPECT TO SOME TASK T AND SOME PERFORMANCE
MEASURE P, IF ITS PERFORMANCE ON T, AS MEASURED BY P,
IMPROVES WITH EXPERIENCE E.” -- TOM MITCHELL, CARNEGIE
MELLON UNIVERSITY:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ankit-181209144402/75/Intro-Overview-on-Machine-Learning-Presentation-3-2048.jpg)