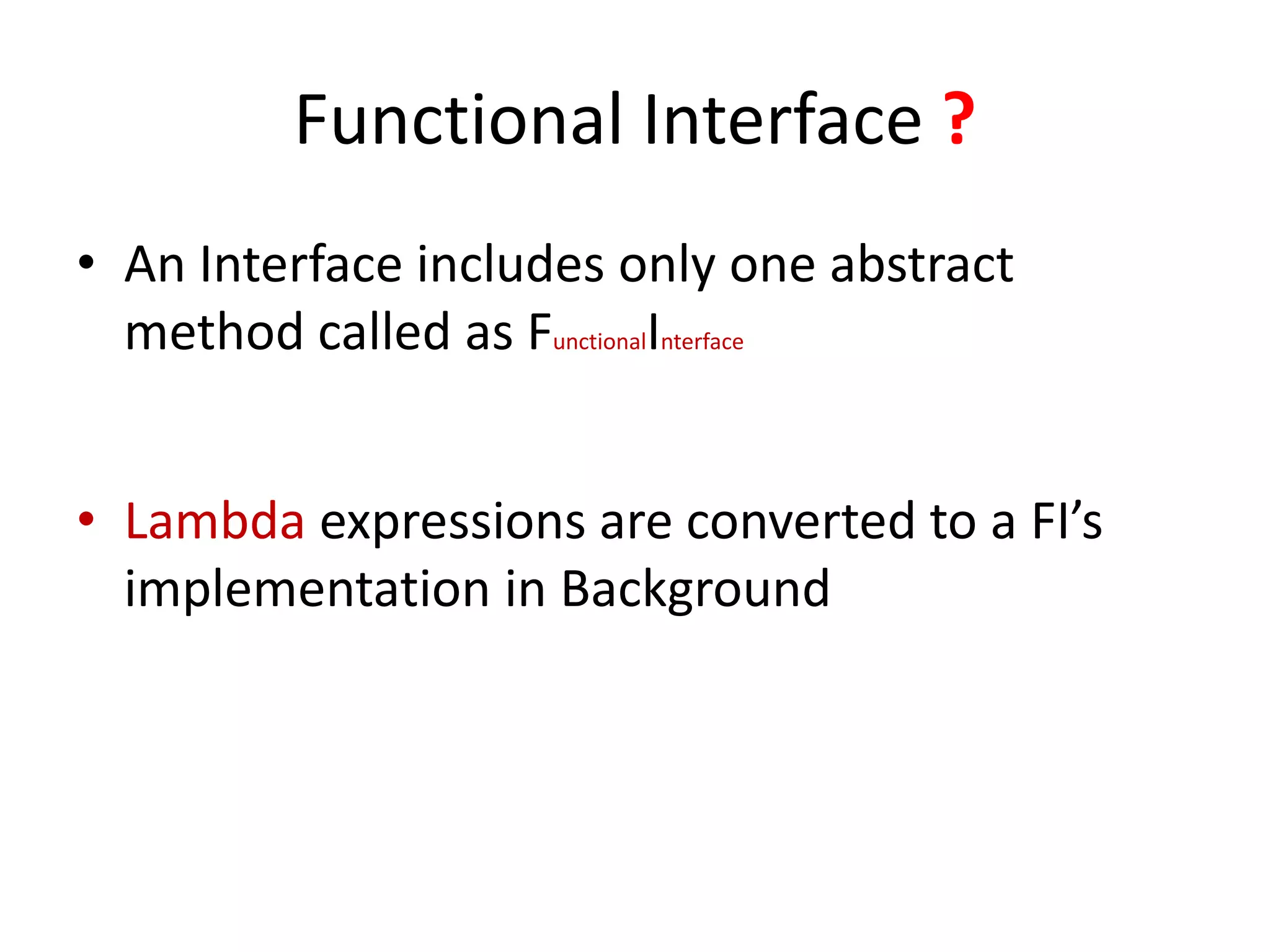
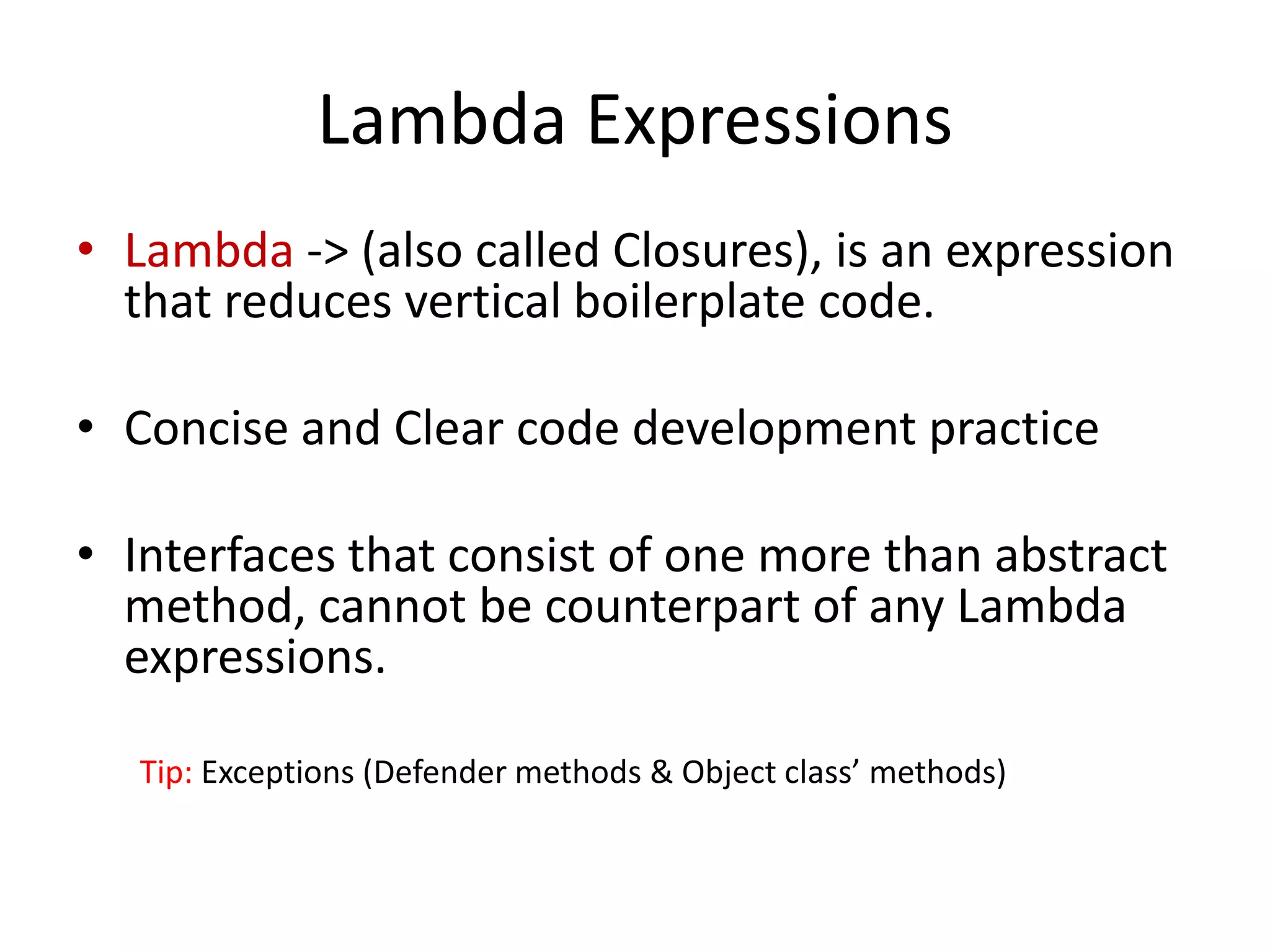
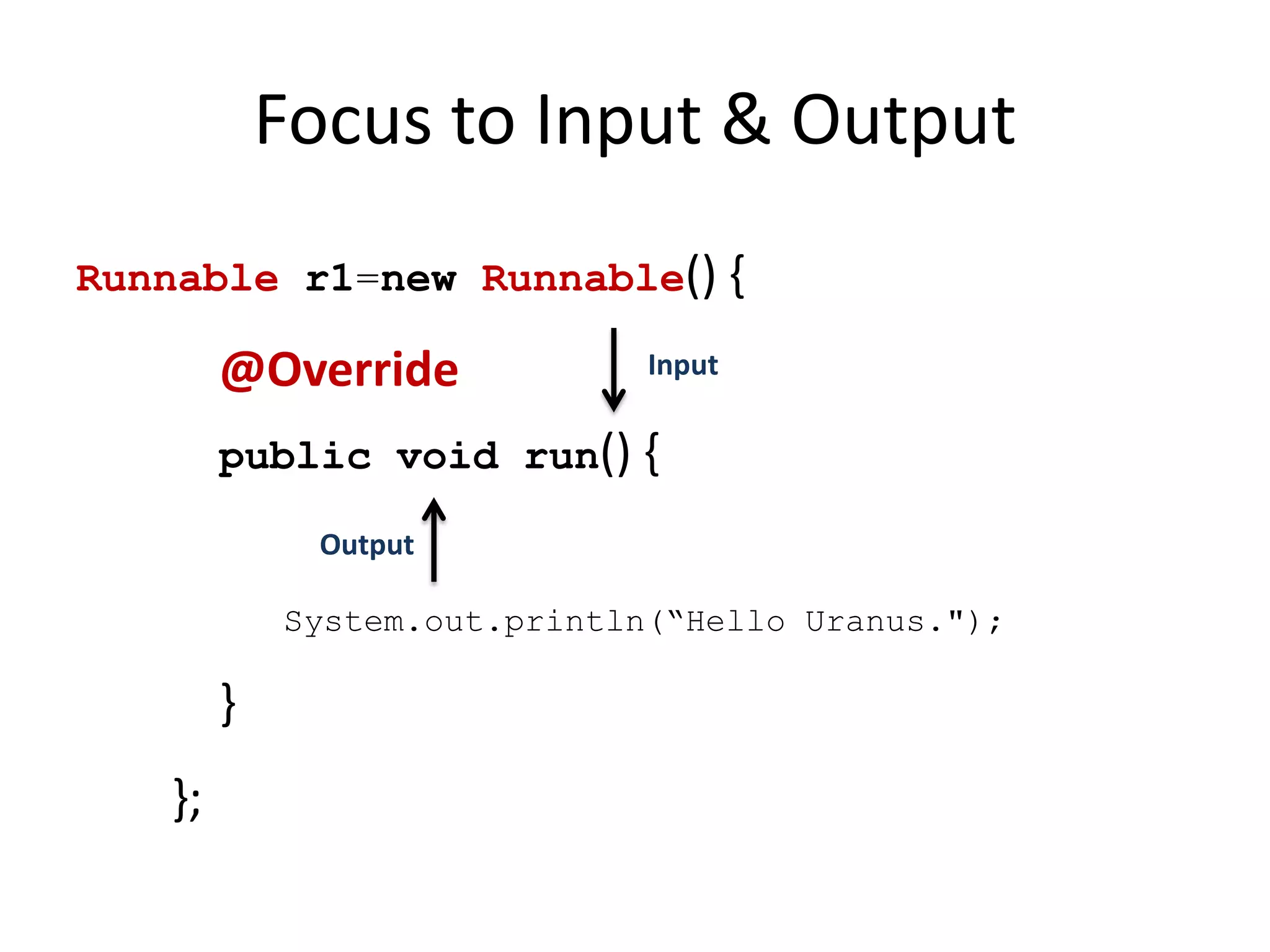
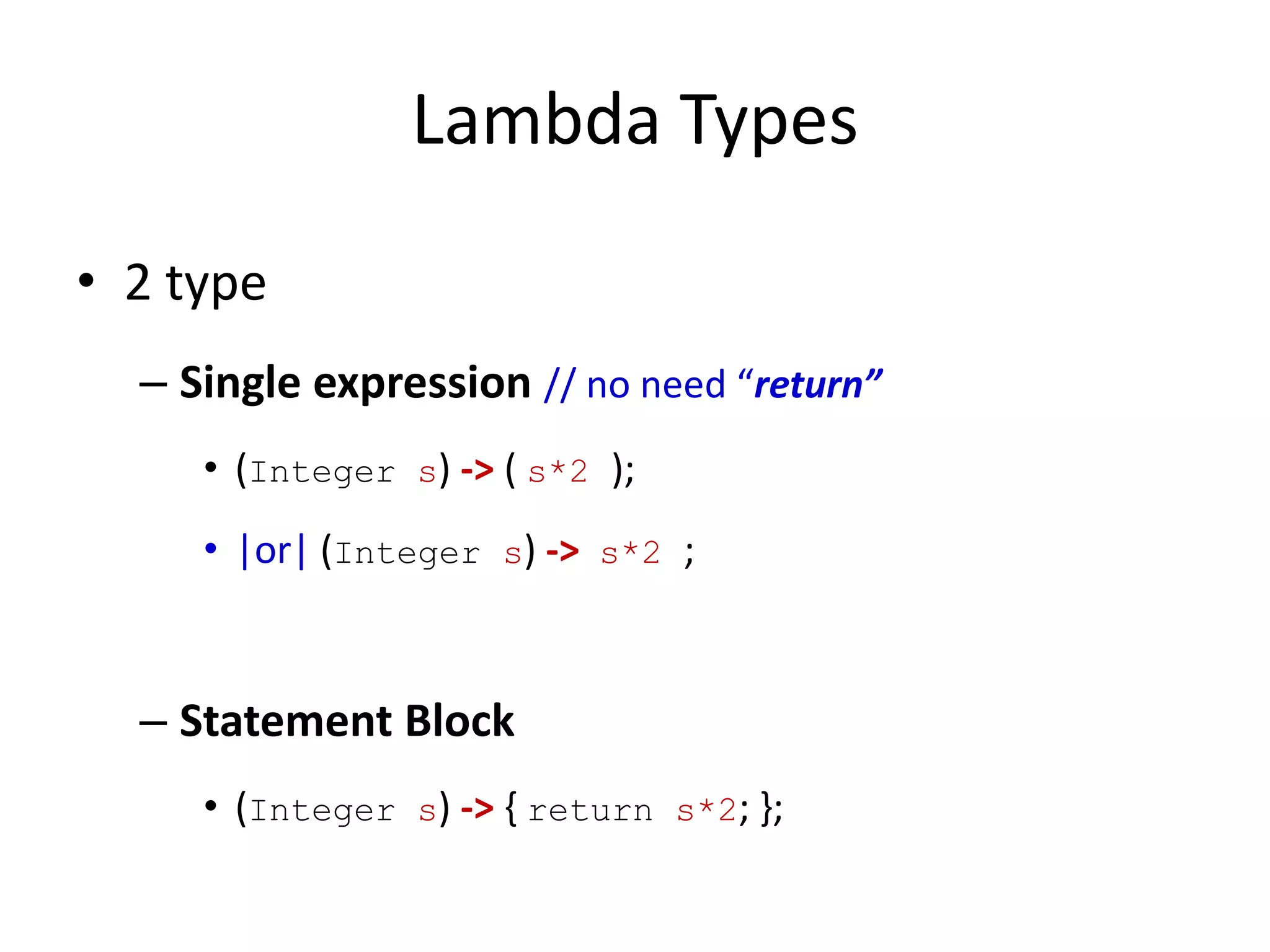
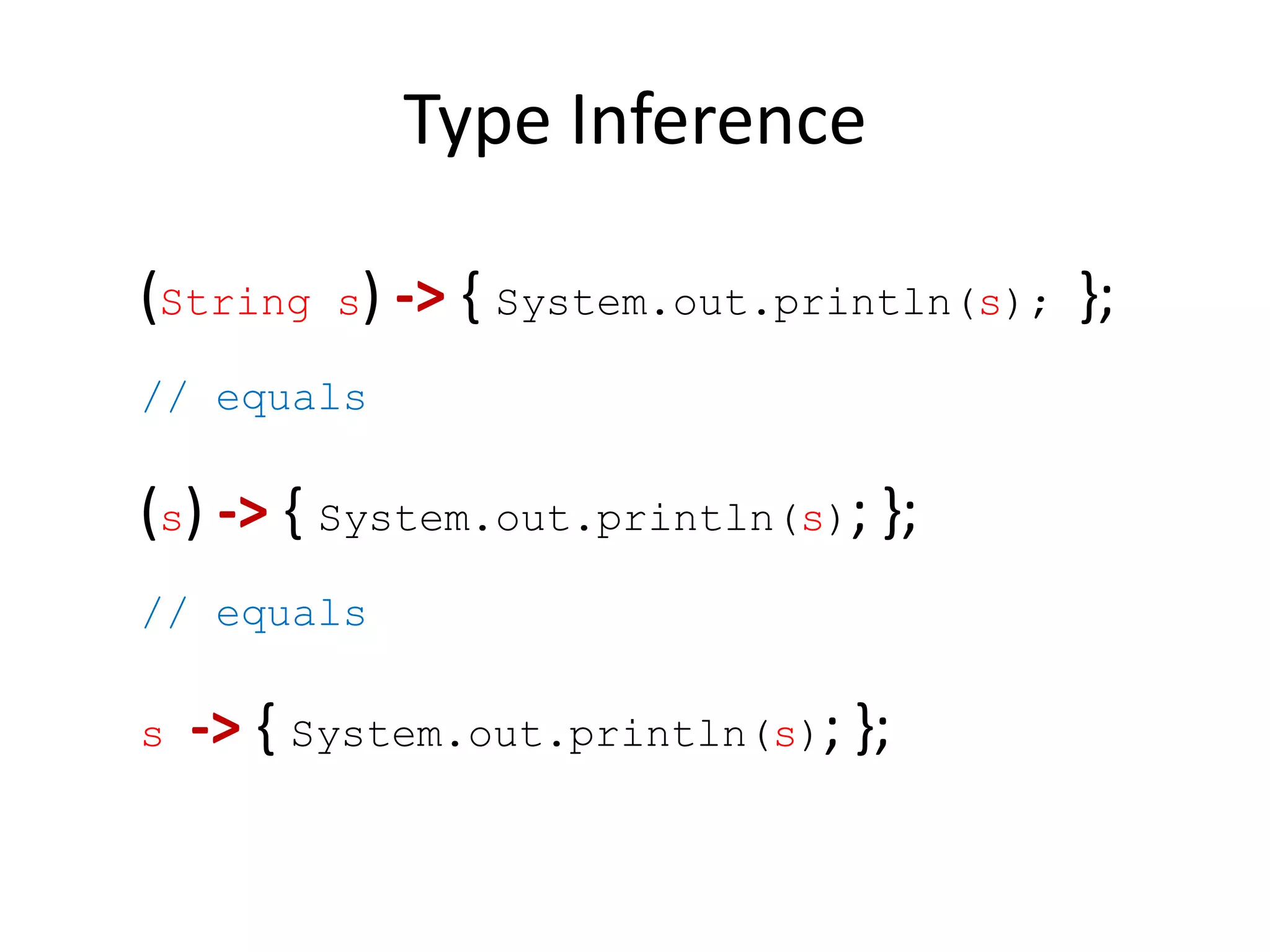
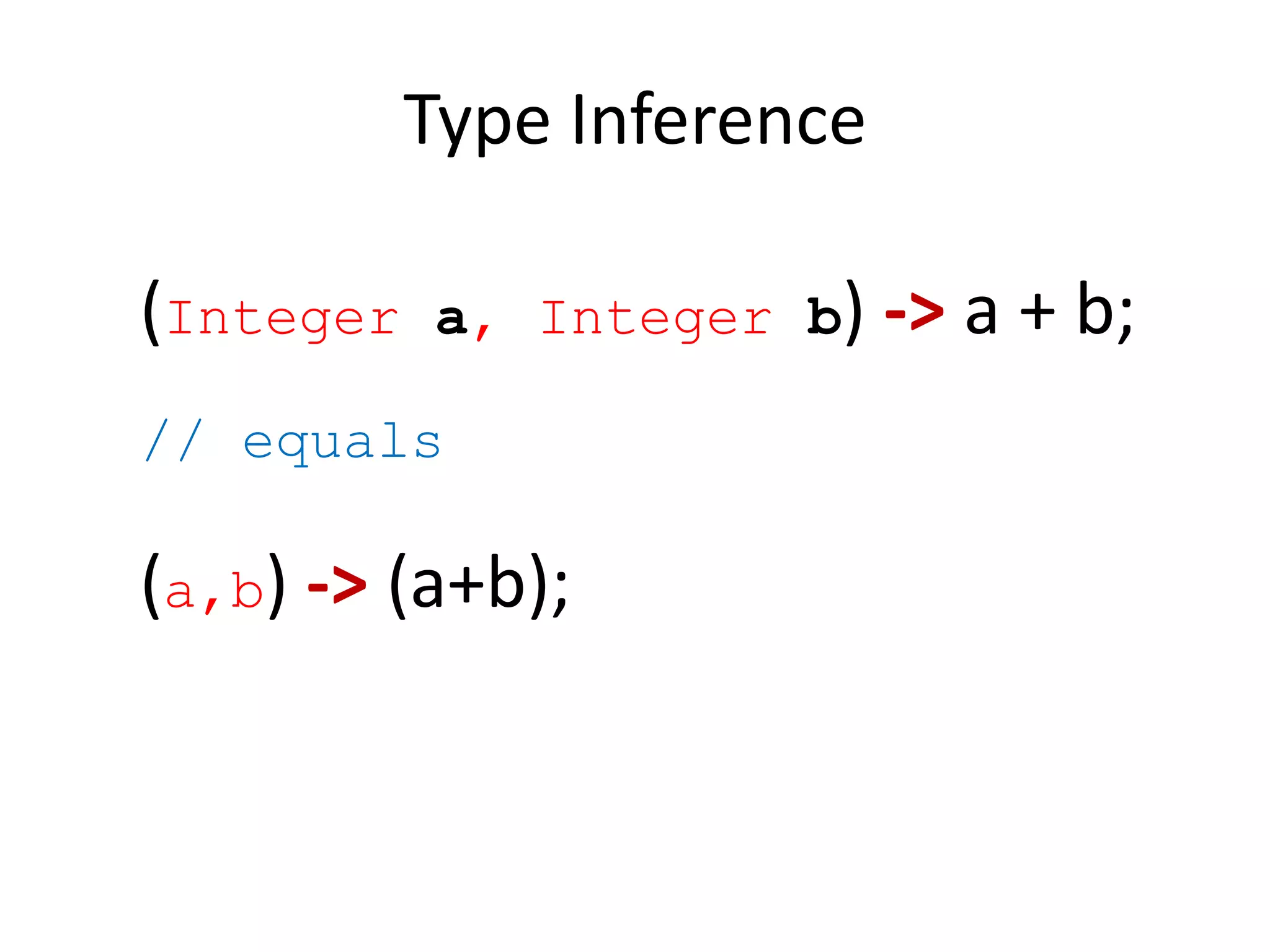
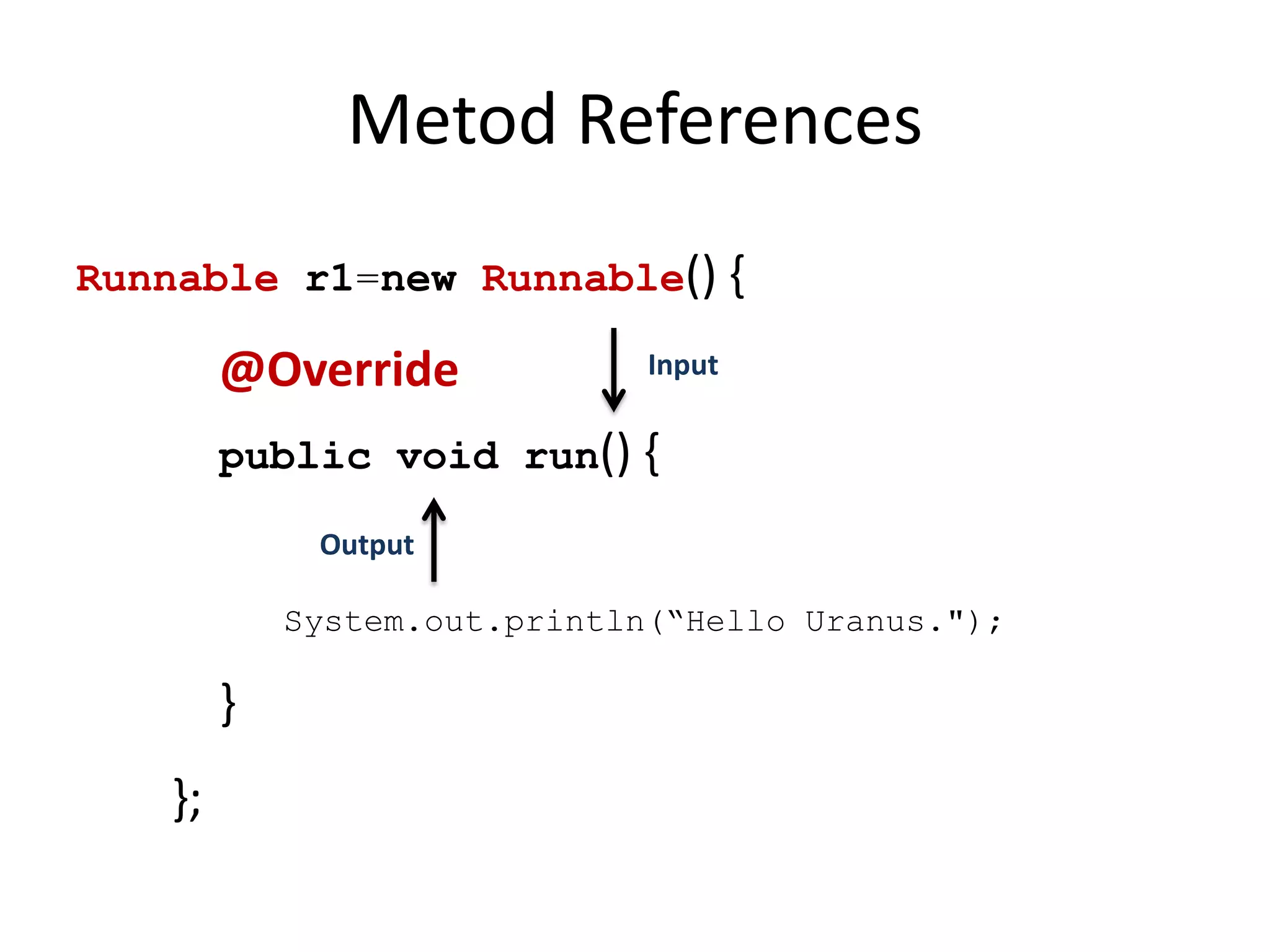
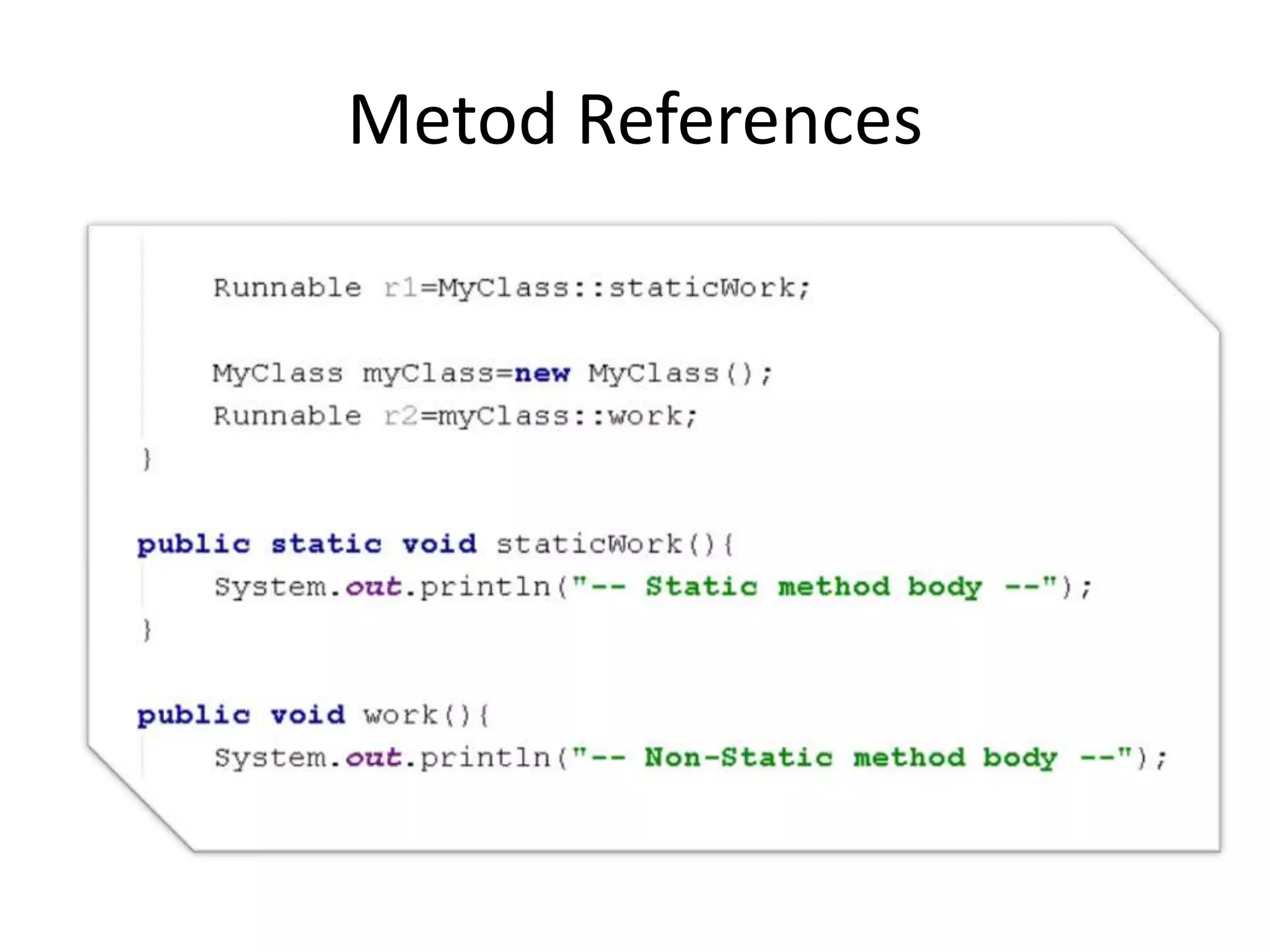
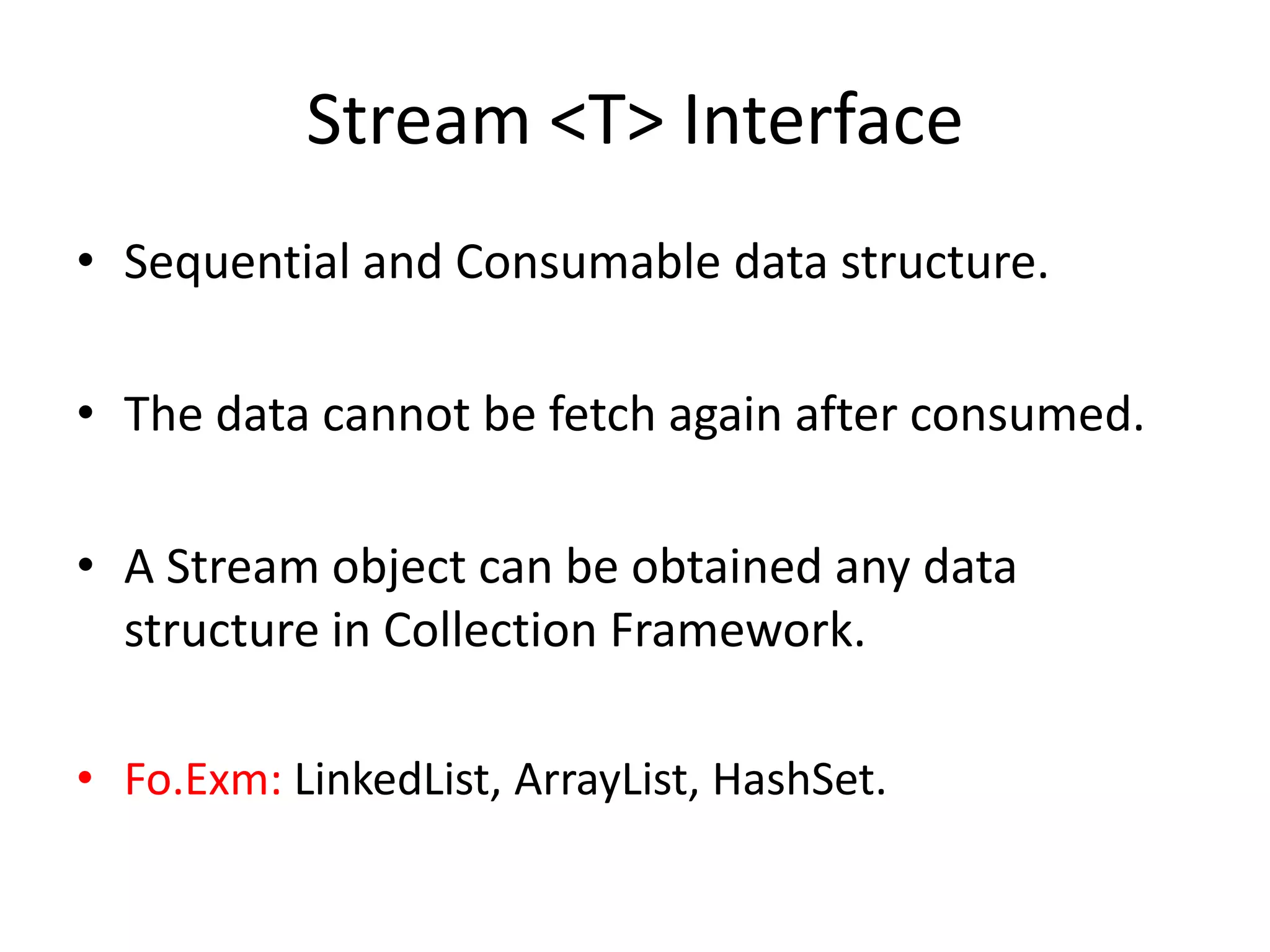
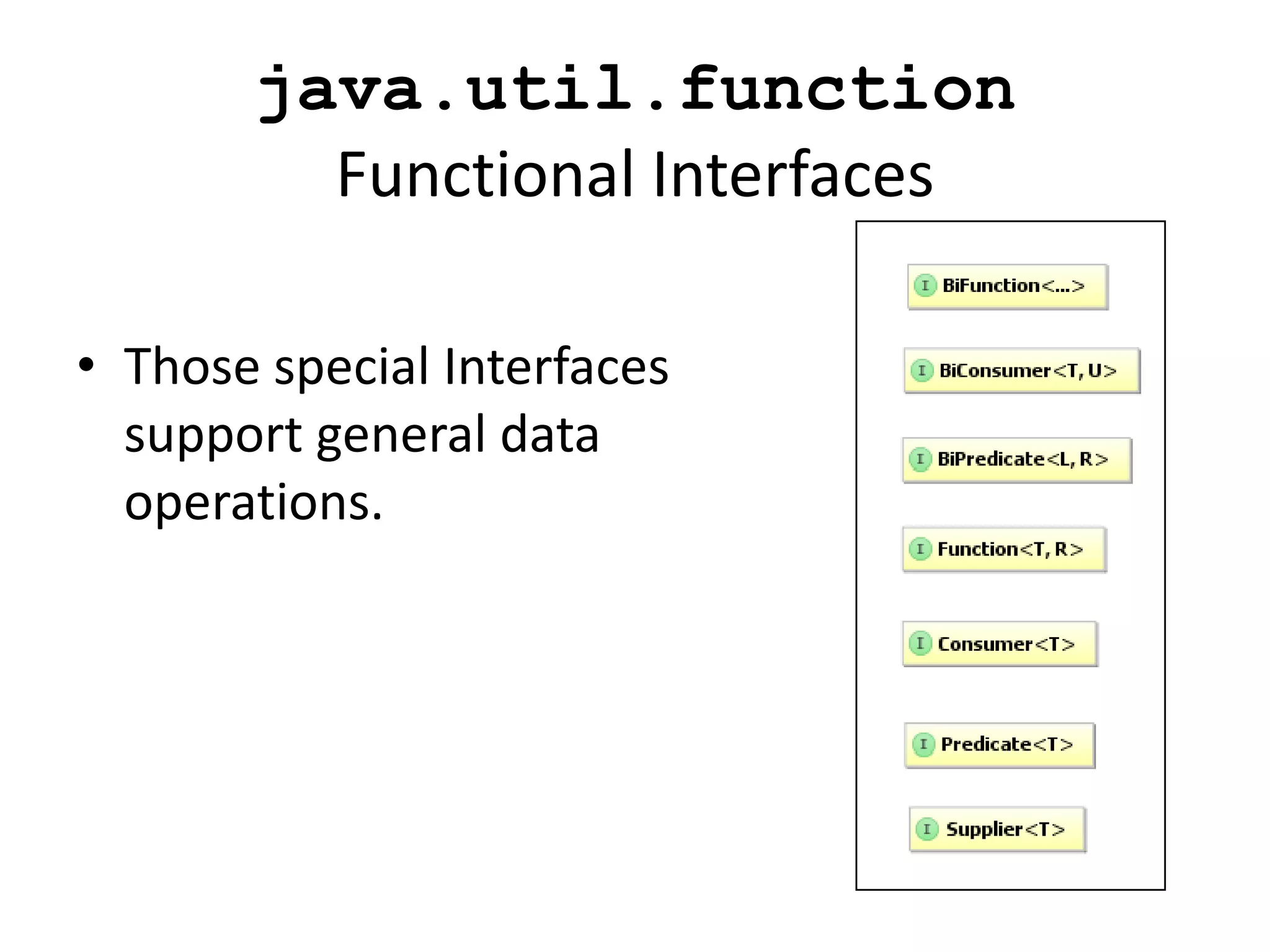
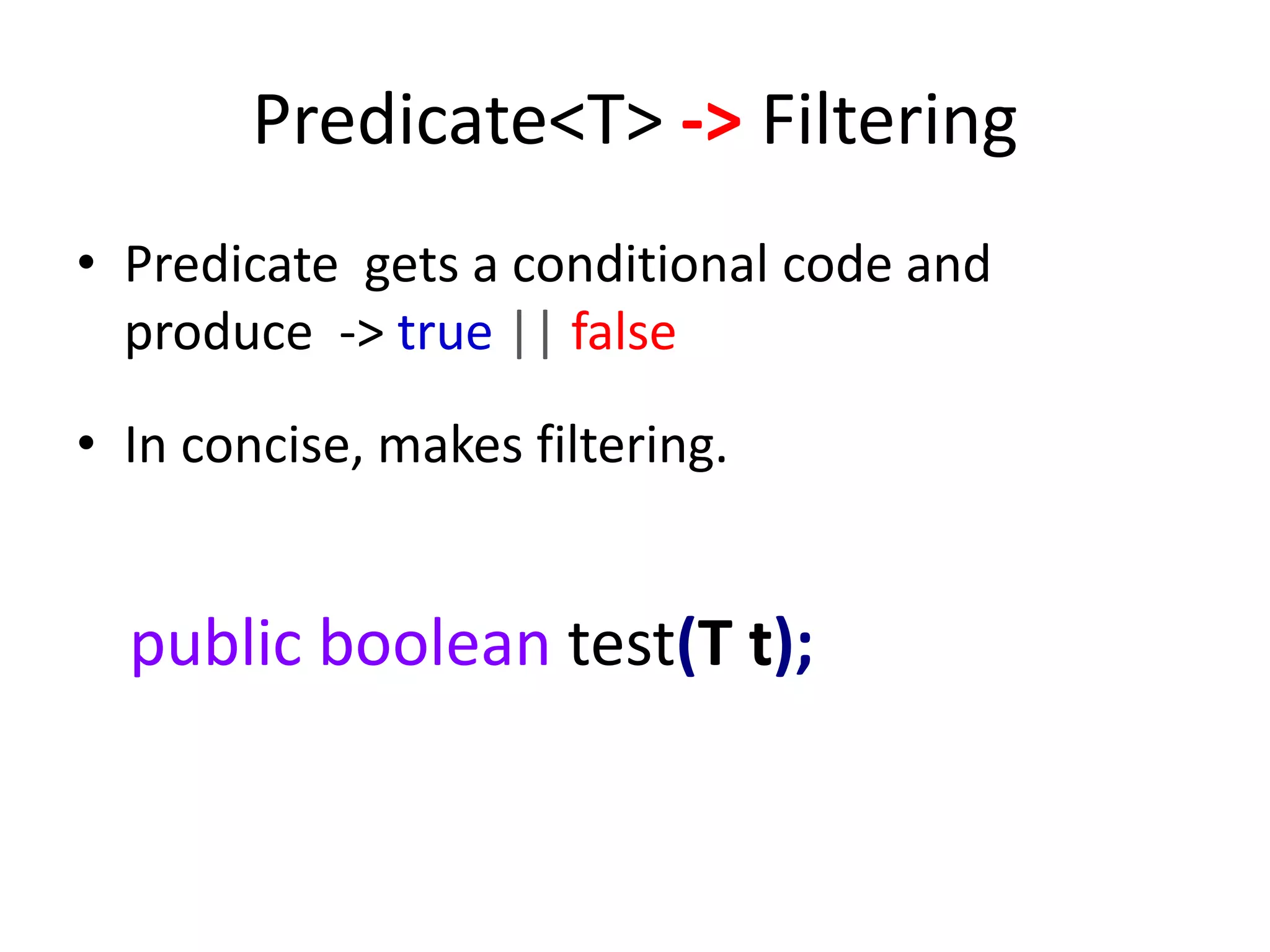
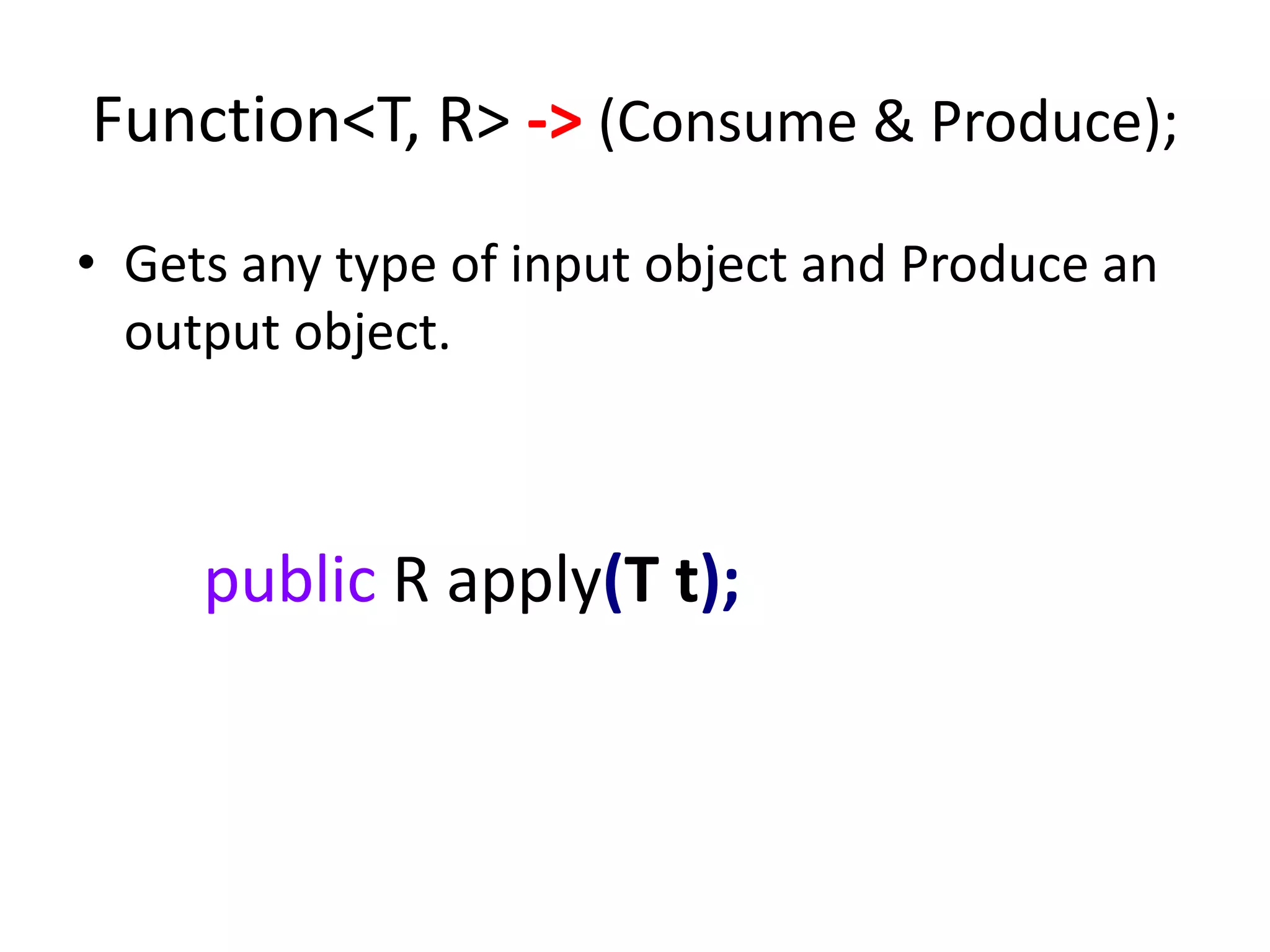
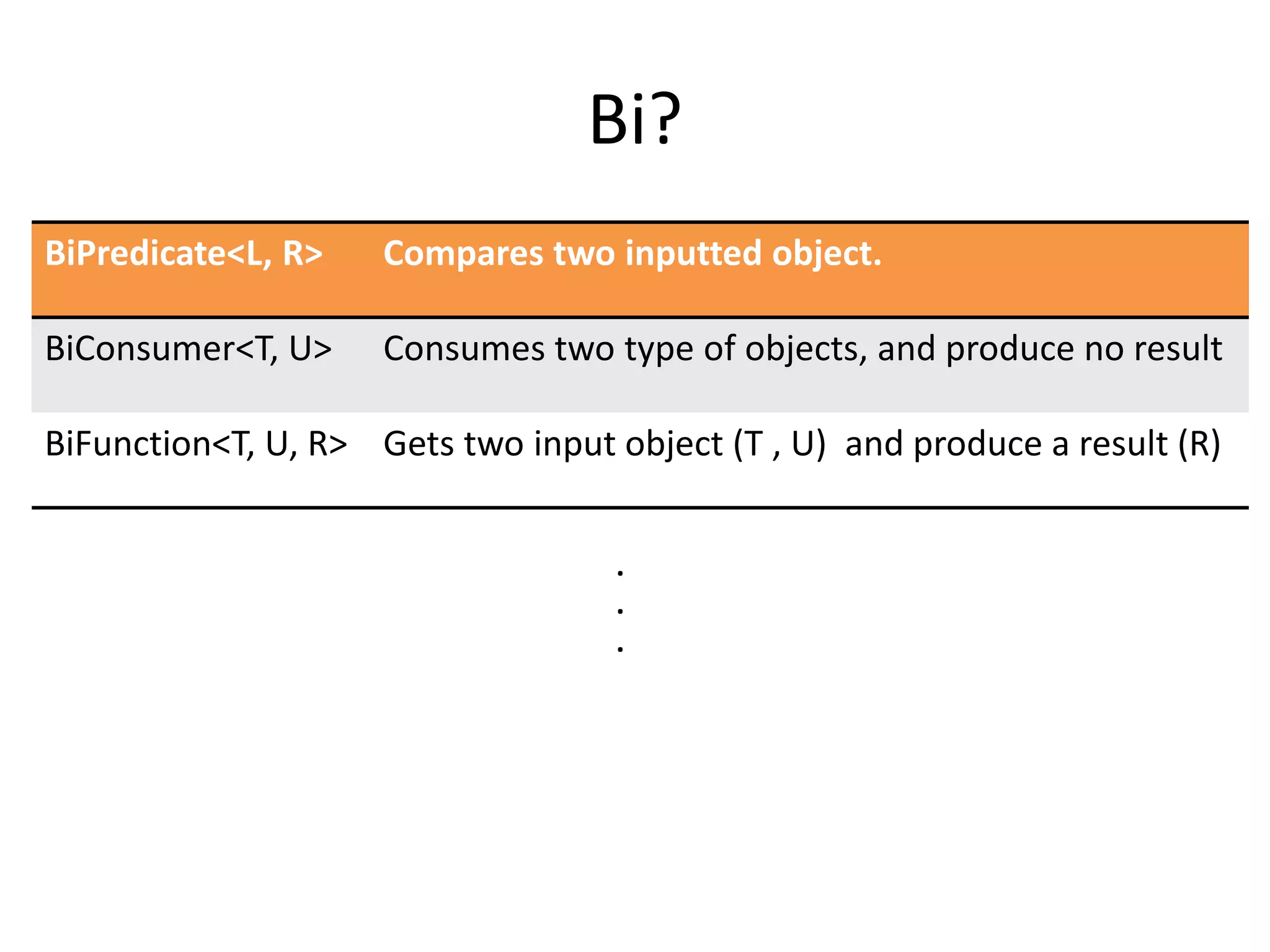
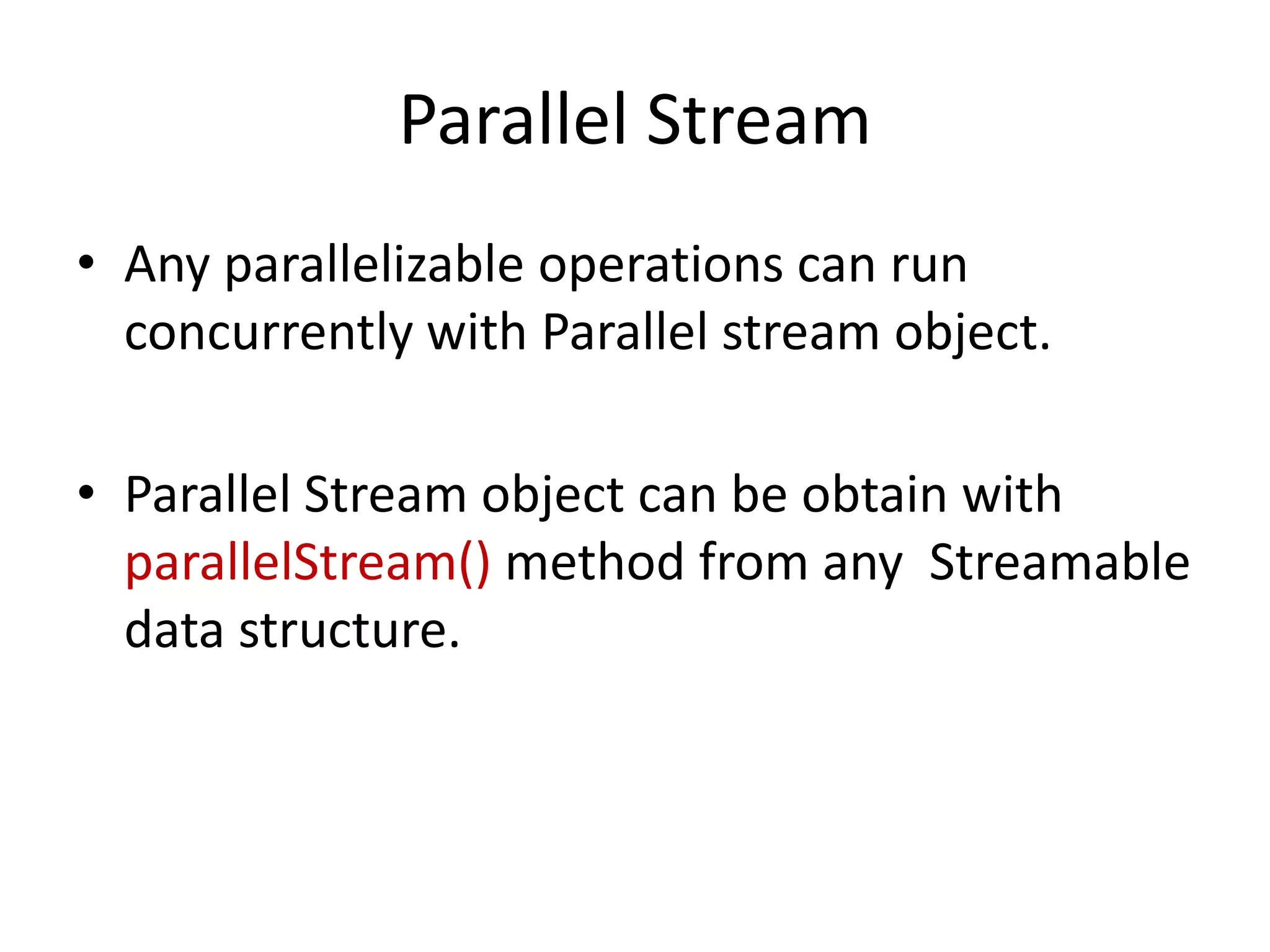
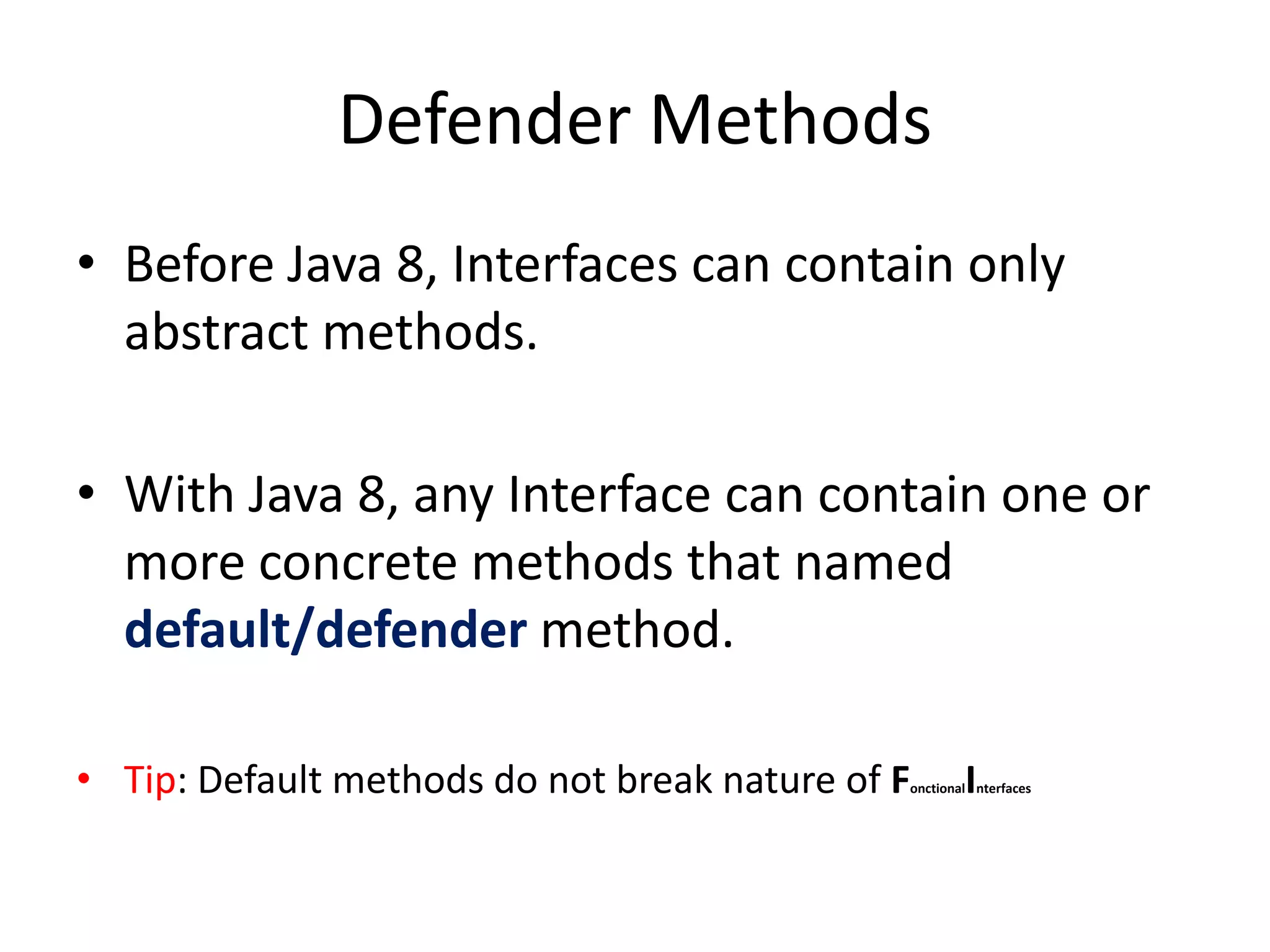
Lambda expressions were introduced in Java 8 as a way to write concise code for functional interfaces. They allow passing code as data and reducing boilerplate code. Other Java 8 features include default methods that allow interfaces to have method implementations, and streams that provide a functional way to process collections of data in a declarative way. Parallel streams allow concurrent processing of data. Lambda expressions, default methods, and streams improved Java's support for functional programming.