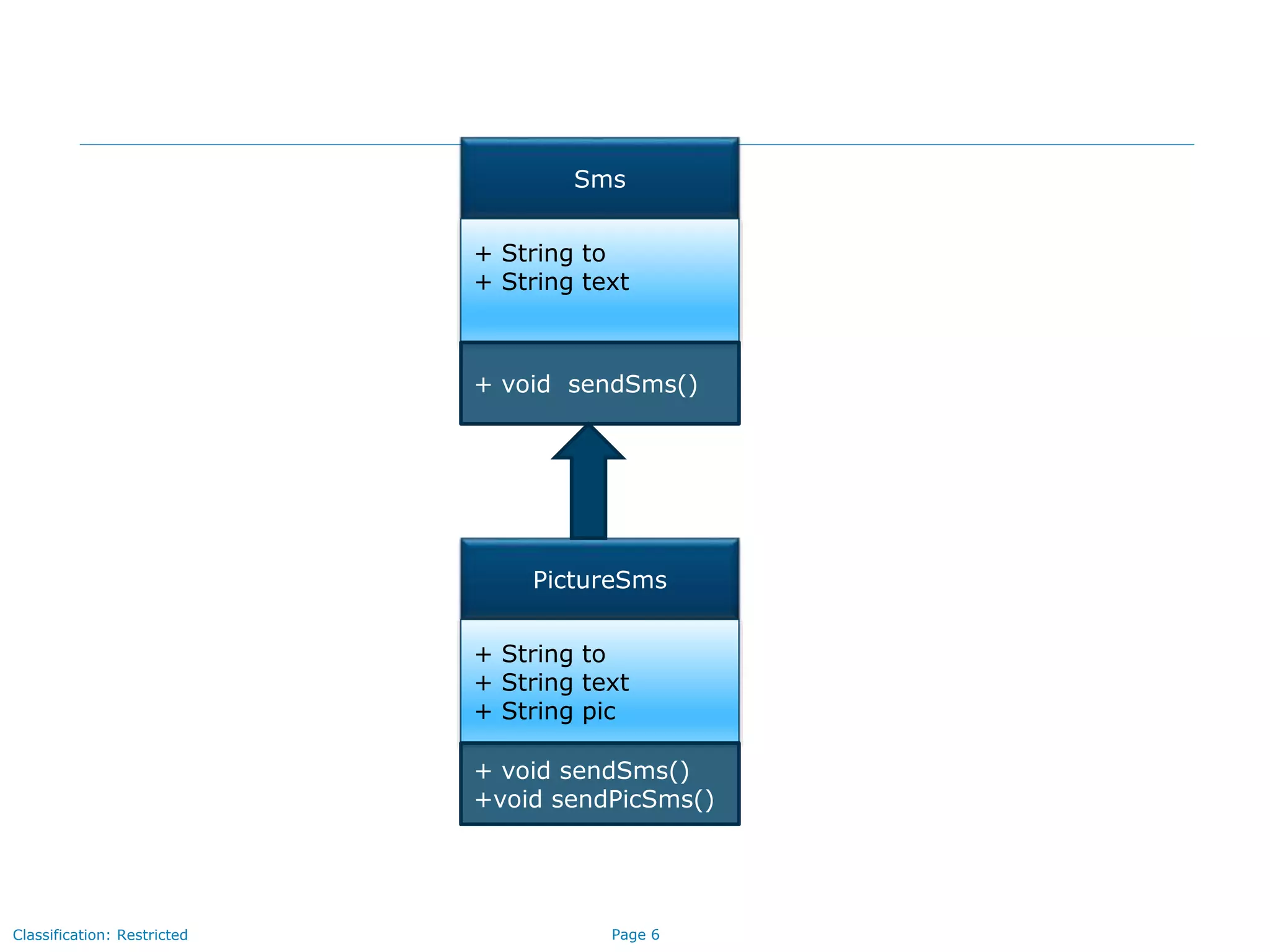
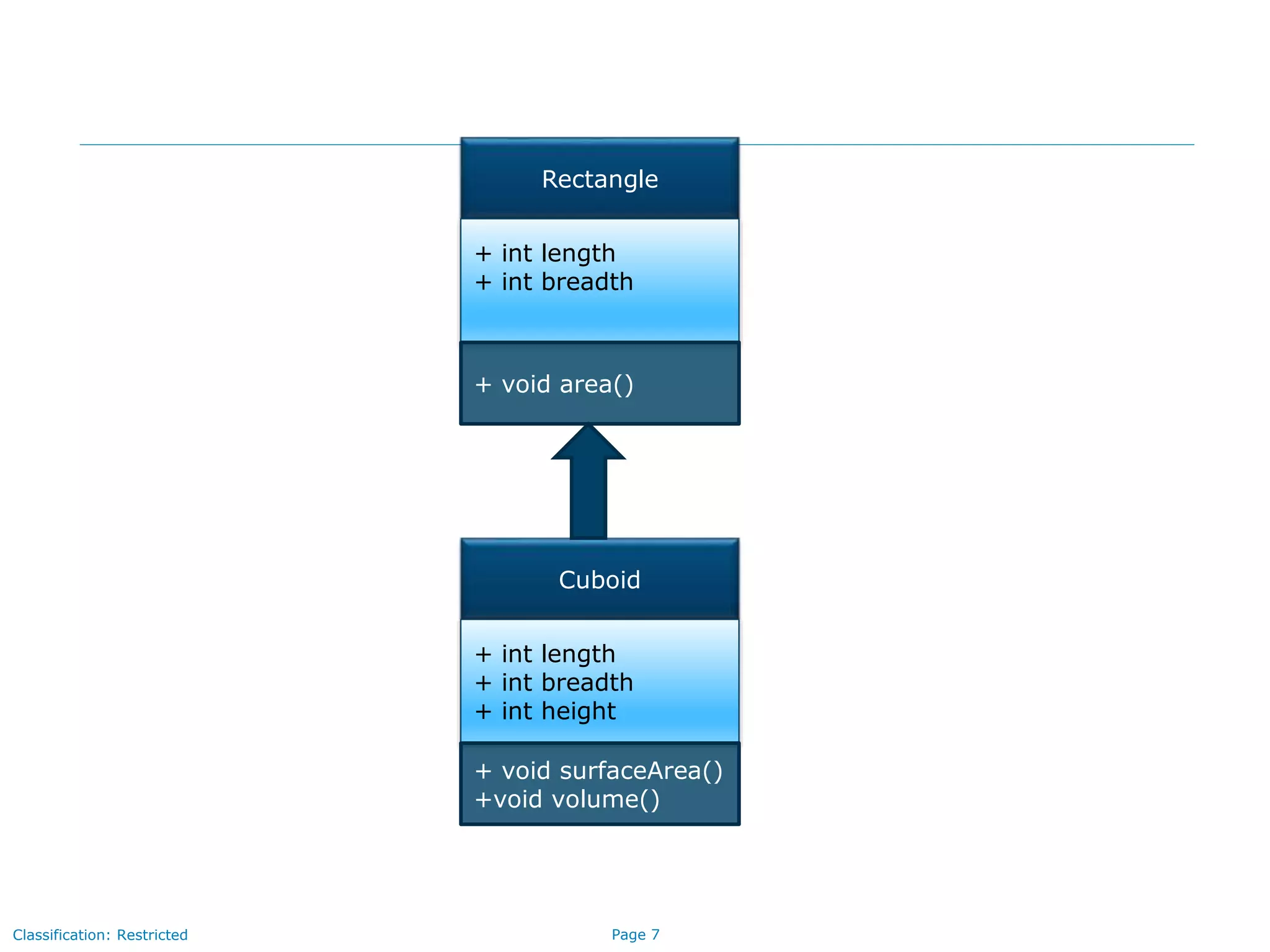
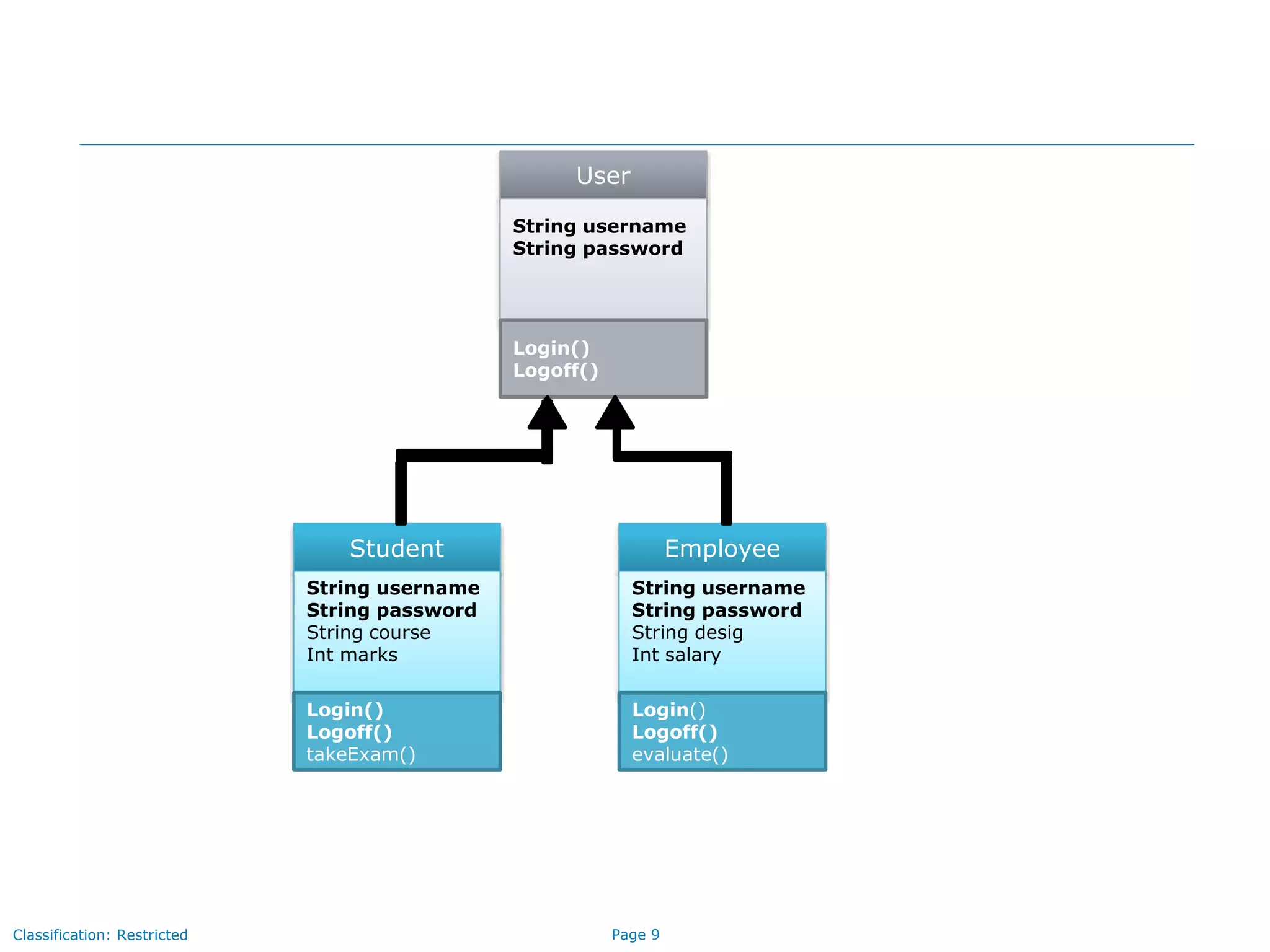
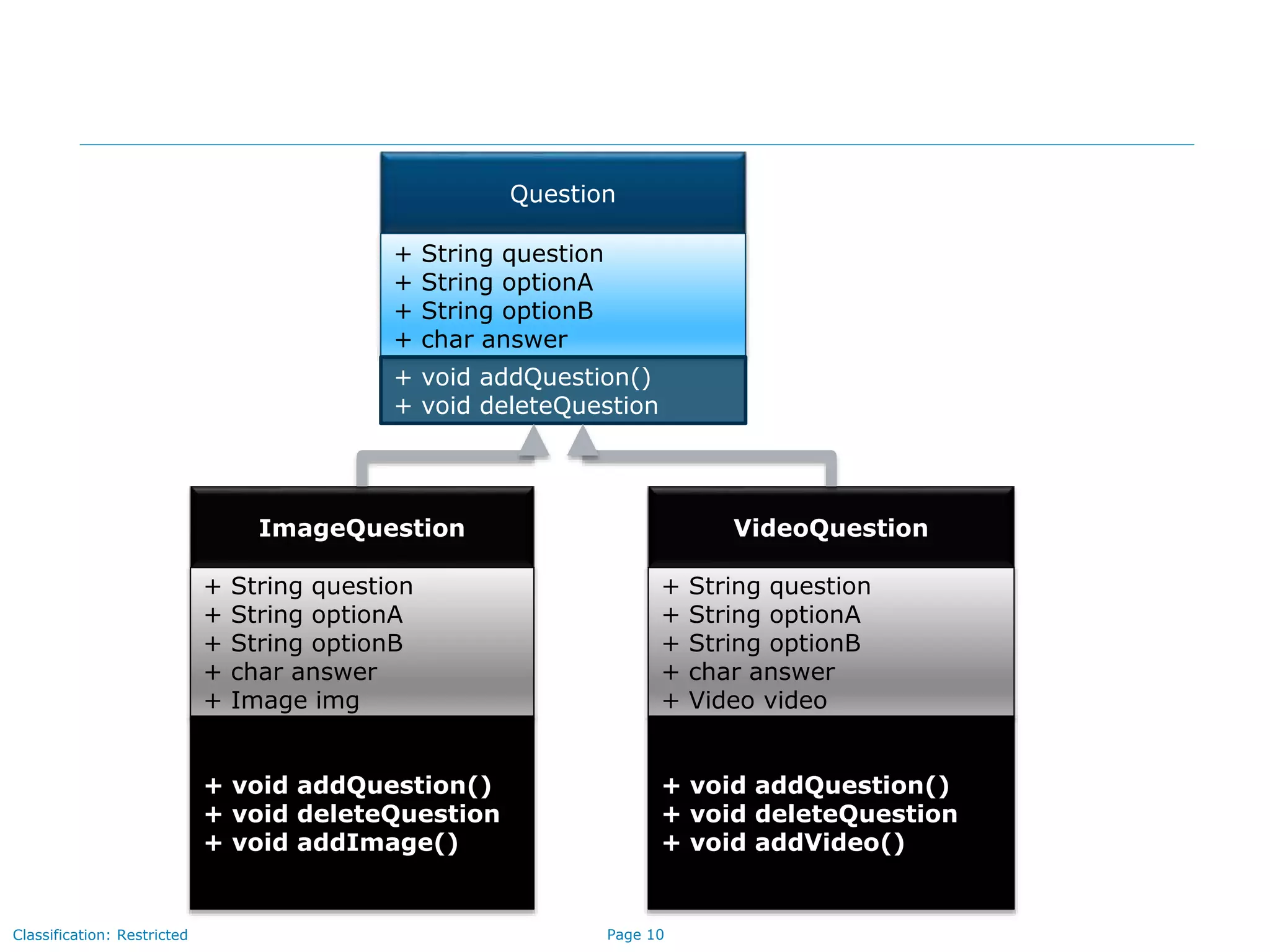
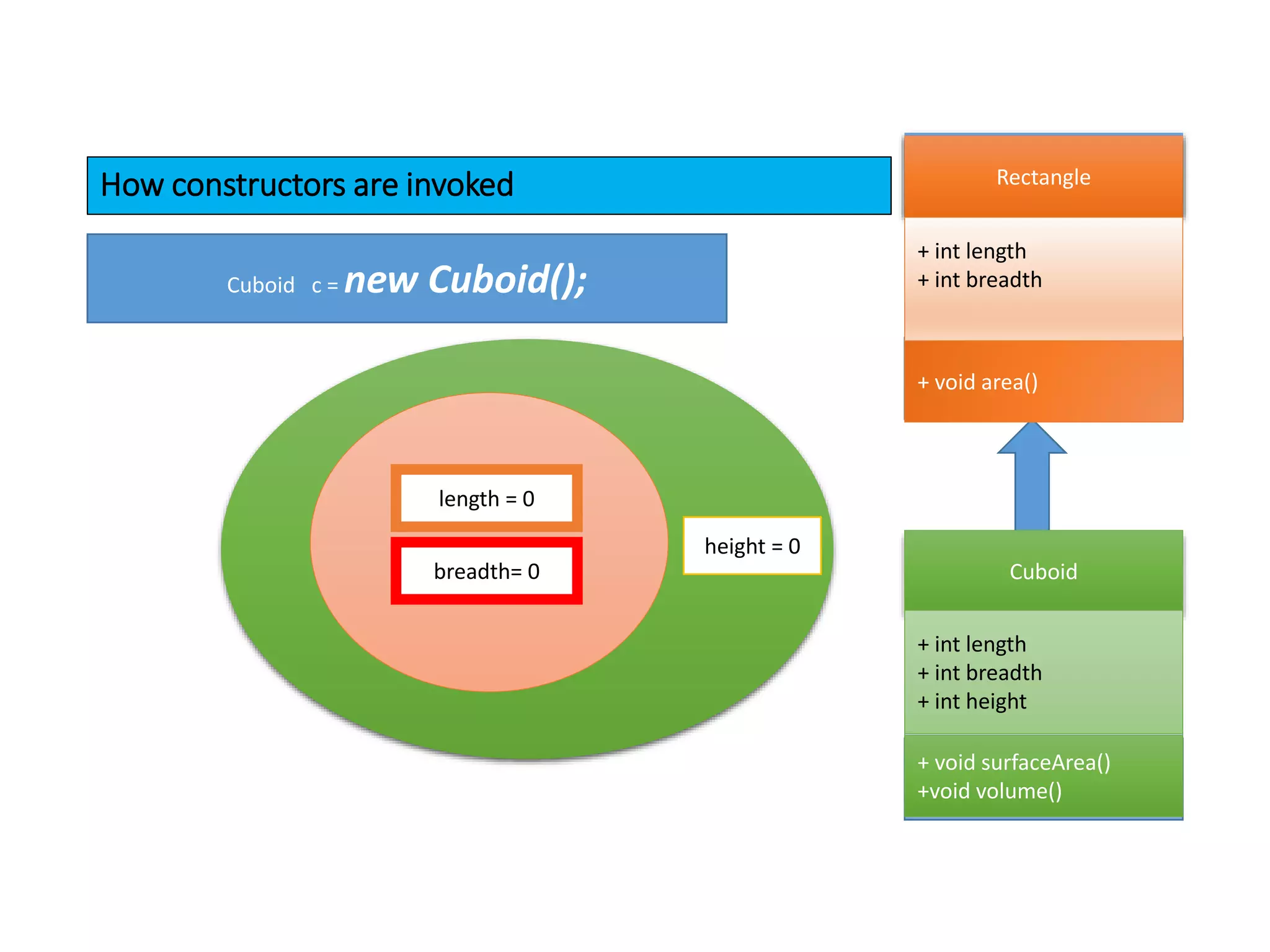
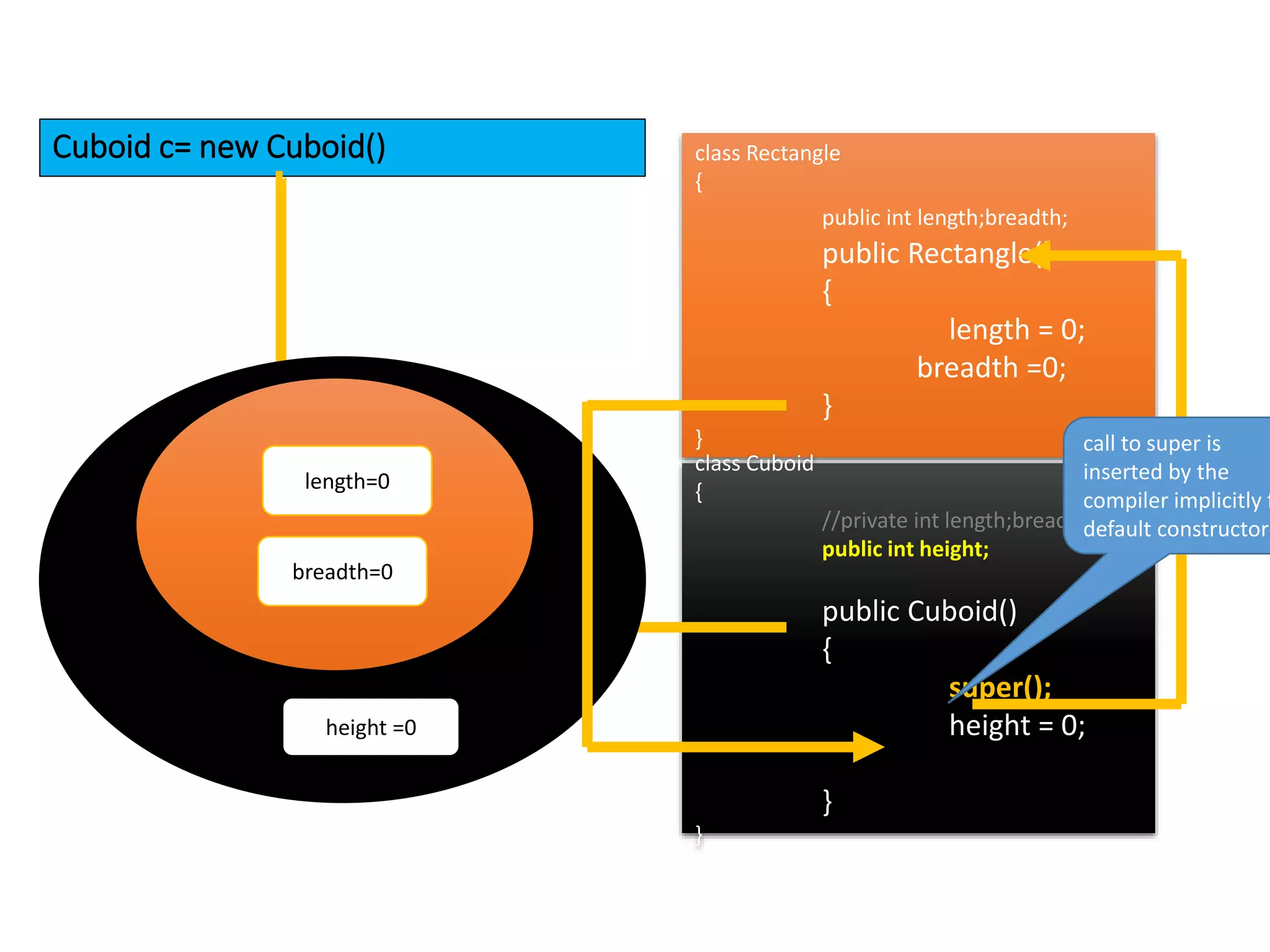
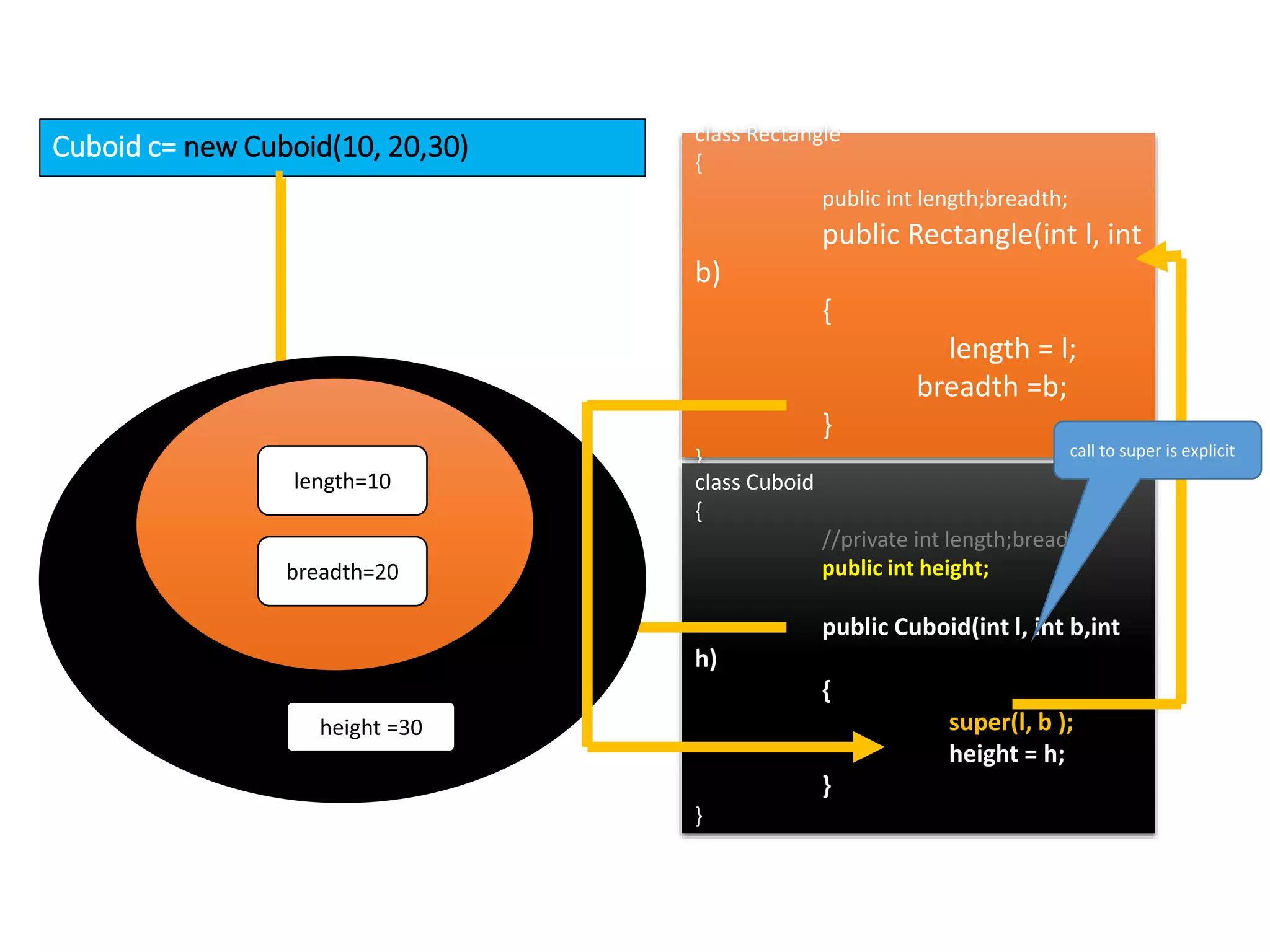
The document outlines key concepts in Java/J2EE programming, focusing on encapsulation and inheritance. It details how encapsulation is implemented and the role of base and child classes in inheritance, including accessing and overriding features. Additionally, it discusses constructors, specifically how they are invoked in child classes using the 'super' keyword.