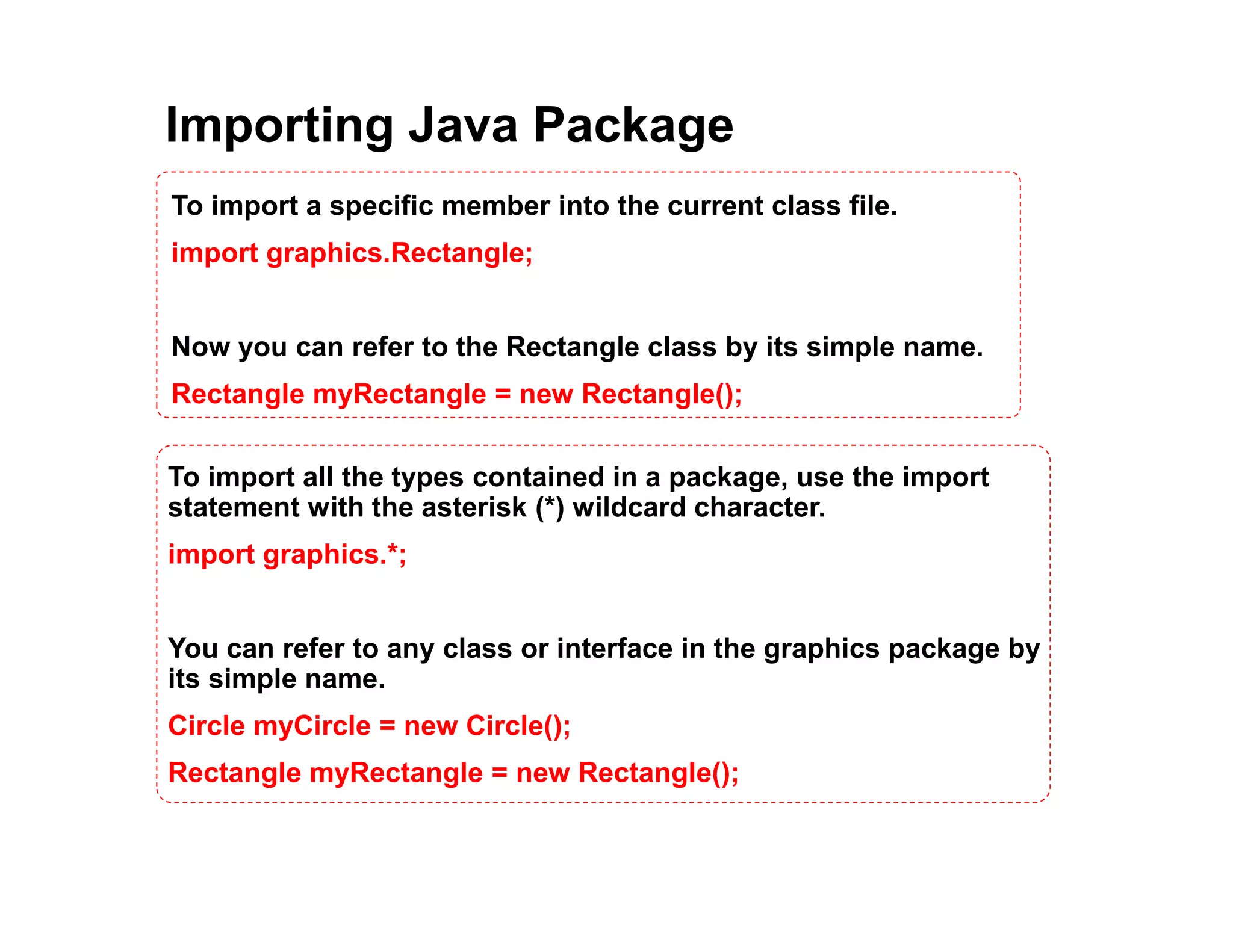
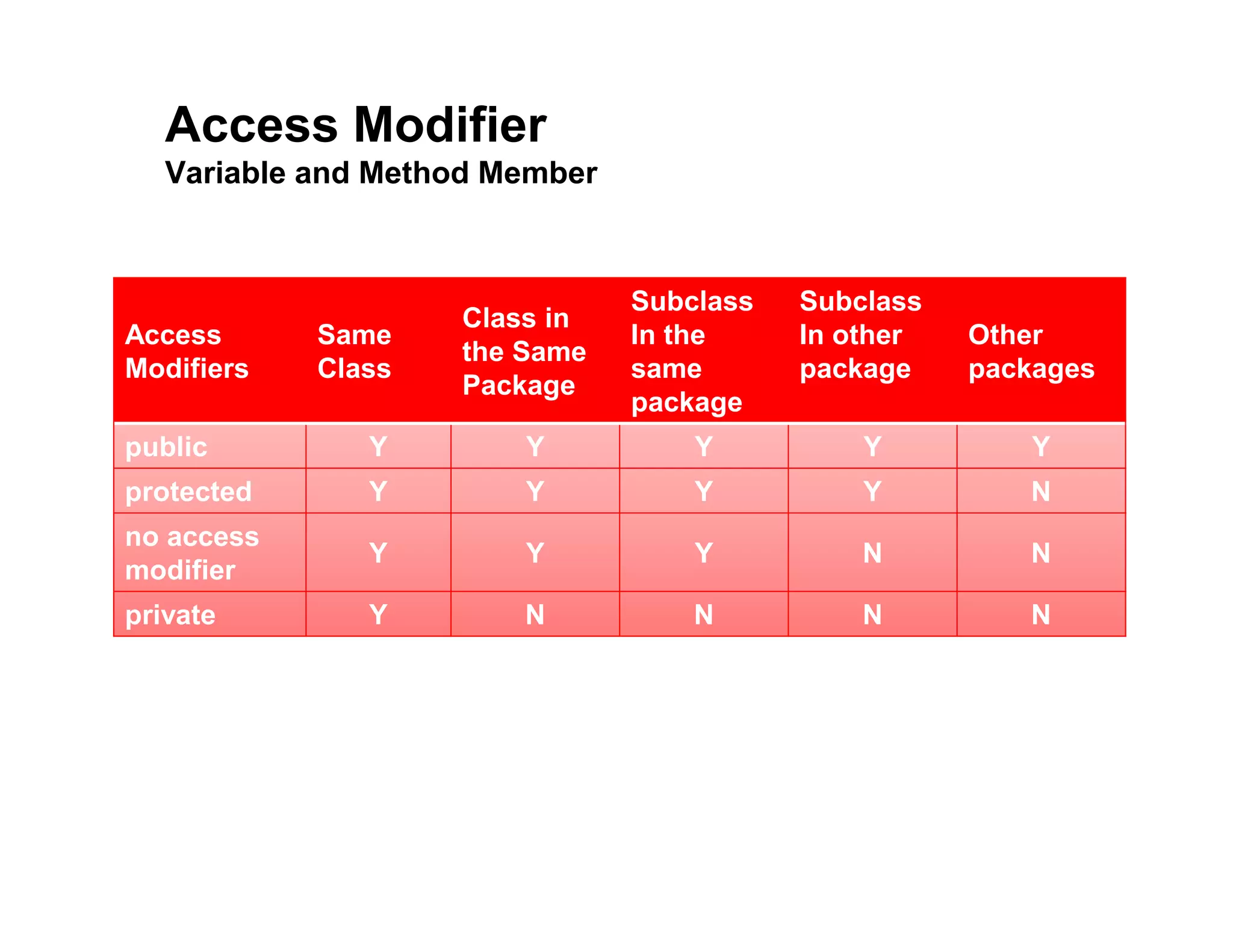
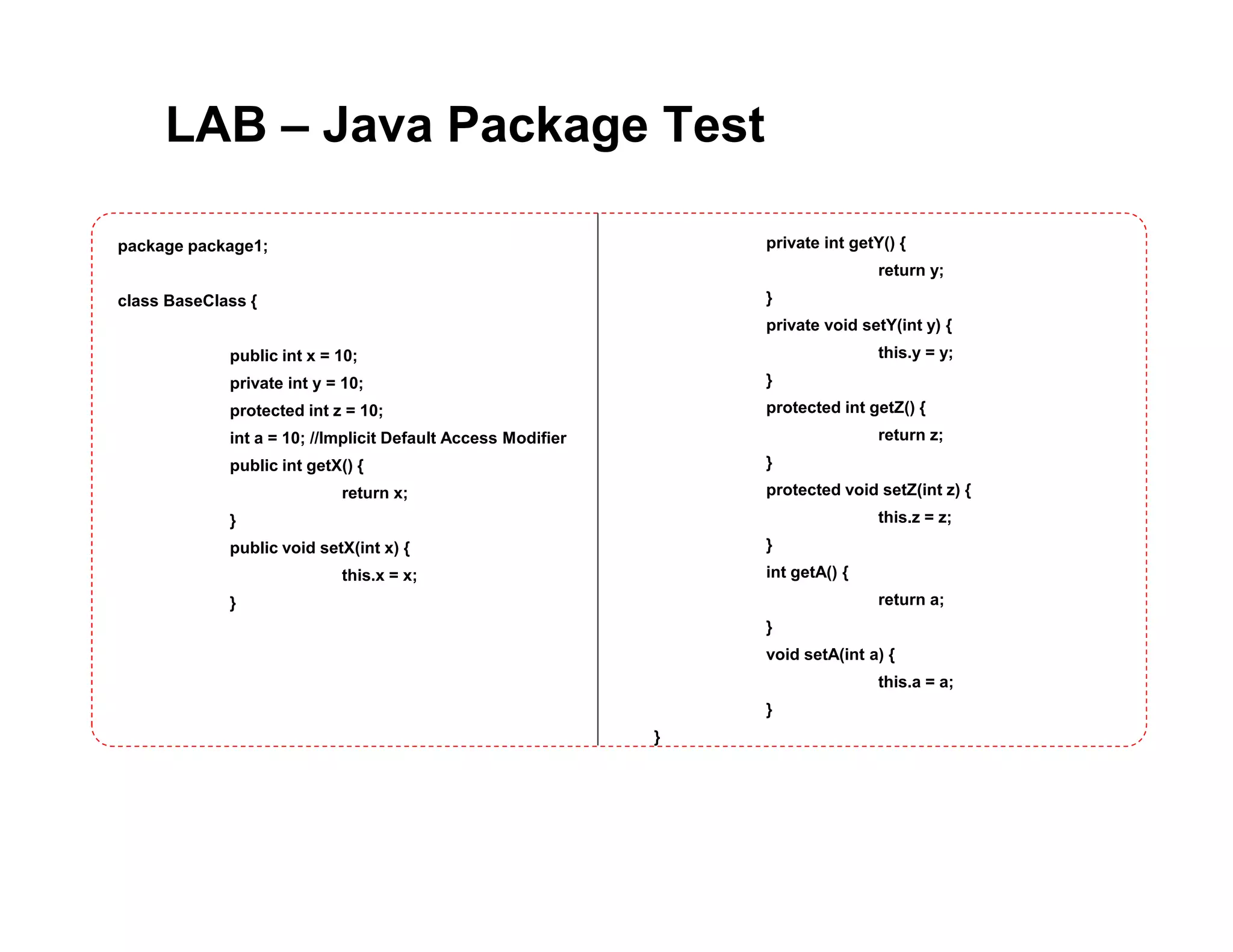
This document discusses Java packages and access control. It defines packages as namespaces that group related classes, and describes how to declare packages and import other packages. It then covers the four access modifiers in Java (public, protected, no modifier, private) and their effects on class, package, subclass and other package access. Code examples are provided to demonstrate how to define packages and use different access modifiers to control visibility and accessibility of classes, variables and methods in Java.



![package package1;
public class SubclassInSamePackage extends BaseClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
BaseClass rr = new BaseClass();
rr.z = 0;
SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage();
//Access Modifiers - Public
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
subClassObj.setX(20);
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
//Access Modifiers - Private
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are private
/* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);
subClassObj.setY(20);
System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/
//Access Modifiers - Protected
System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassObj.z);
subClassObj.setZ(30);
System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassObj.z);
//Access Modifiers - Default
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.a);
subClassObj.setA(20);
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.a);
}
}
Output
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 20
Value of z is : 10
Value of z is : 30
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05accesscontrolinjavav1-151031160655-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-05-access-control-in-java-9-2048.jpg)
![package package2;
import package1.*;
public class SubClassInDifferentPackage extends SubclassInSamePackage {
public int getZZZ() {
return z;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
SubClassInDifferentPackage subClassDiffObj = new SubClassInDifferentPackage();
SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage();
//Access specifiers - Public
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
subClassObj.setX(30);
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
//Access specifiers - Private
// if we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are private
/* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);
subClassObj.setY(20);
System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/
//Access specifiers - Protected
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are protected.
/* System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);
subClassObj.setZ(30);
System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);*/
System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassDiffObj.getZZZ());
//Access Modifiers - Default
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are default.
/*
System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);
subClassObj.setA(20);
System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);*/
}
}
Output
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 30
Value of z is : 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05accesscontrolinjavav1-151031160655-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-05-access-control-in-java-10-2048.jpg)
![package package2;
import package1.*;
public class ClassInDifferentPackage {
public static void main(String args[]) {
SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage();
//Access Modifiers - Public
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
subClassObj.setX(30);
System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x);
//Access Modifiers - Private
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are private
/* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);
subClassObj.setY(20);
System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/
//Access Modifiers - Protected
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are protected.
/* System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);
subClassObj.setZ(30);
System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);*/
//Access Modifiers - Default
// If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton
// error as the fields and methods being accessed are default.
/* System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);
subClassObj.setA(20);
System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);*/
}
}
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05accesscontrolinjavav1-151031160655-lva1-app6891/75/Java-Programming-05-access-control-in-java-11-2048.jpg)
