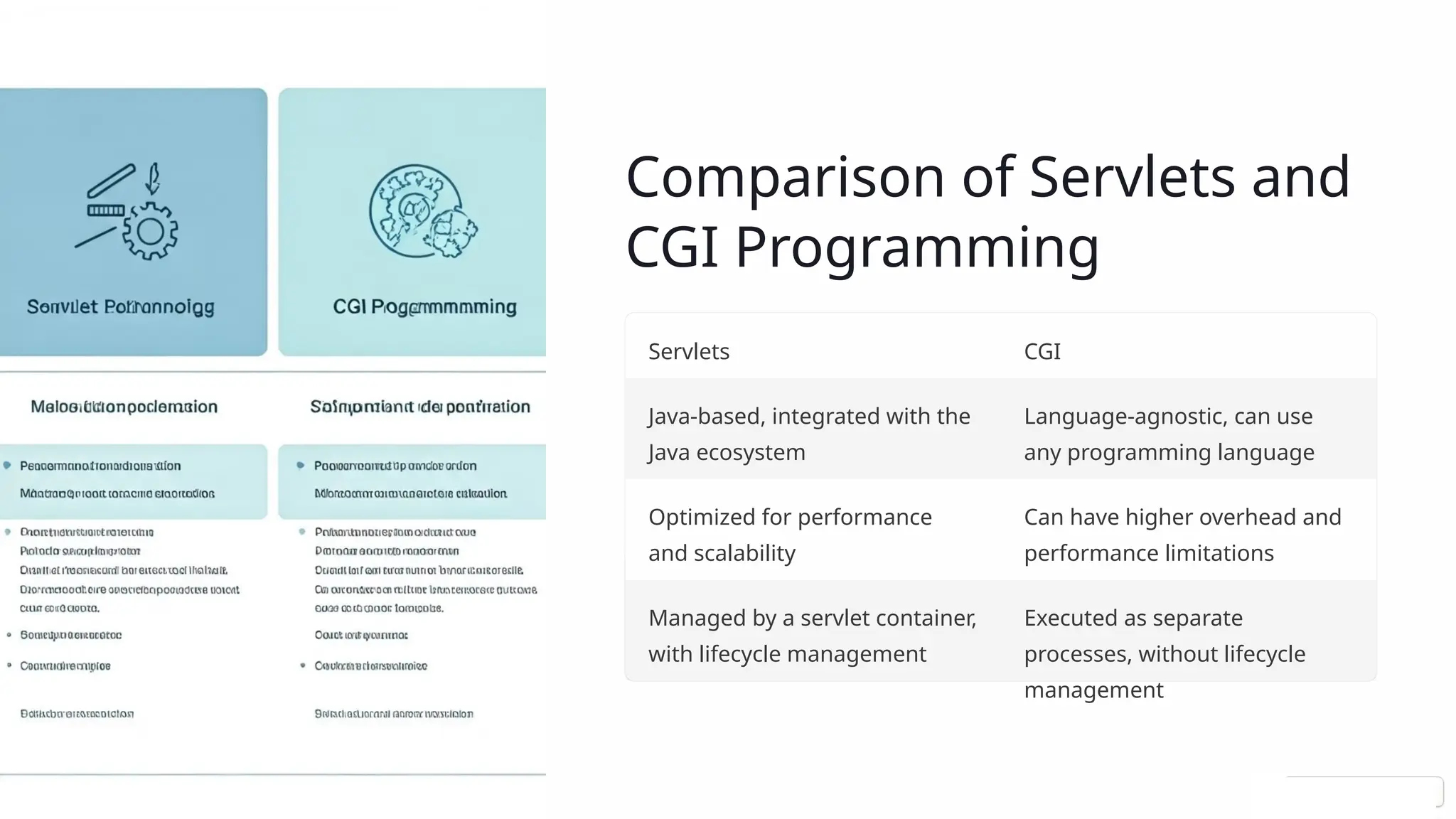
The document presents an overview of Java servlets and CGI programming, highlighting their differences, advantages, and best practices for web application development. It details servlet technology, including the servlet lifecycle, request handling, configuration, deployment, and common design patterns. Additionally, it compares servlets with CGI, emphasizing performance and scalability benefits of servlets within the Java ecosystem.