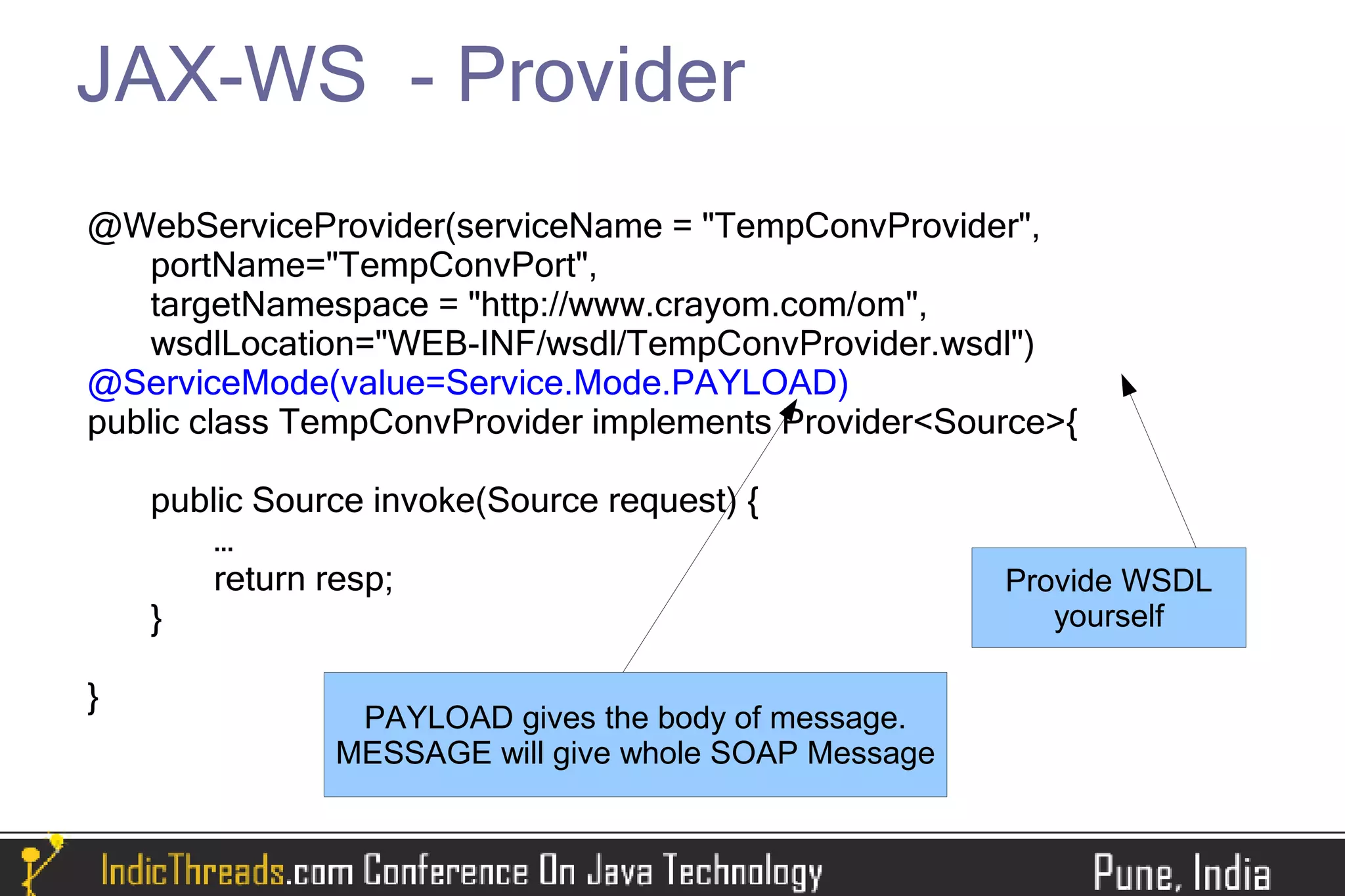
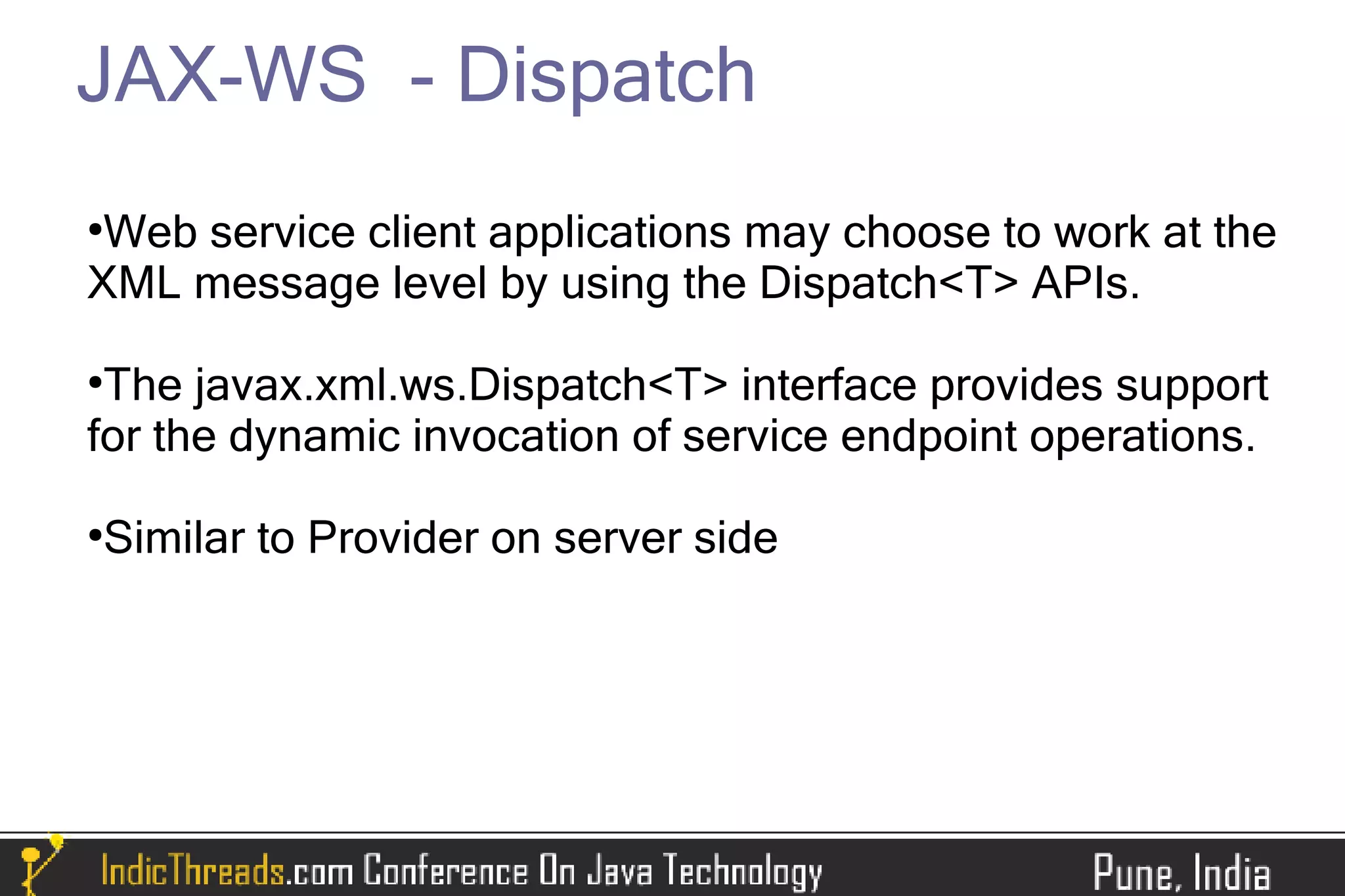
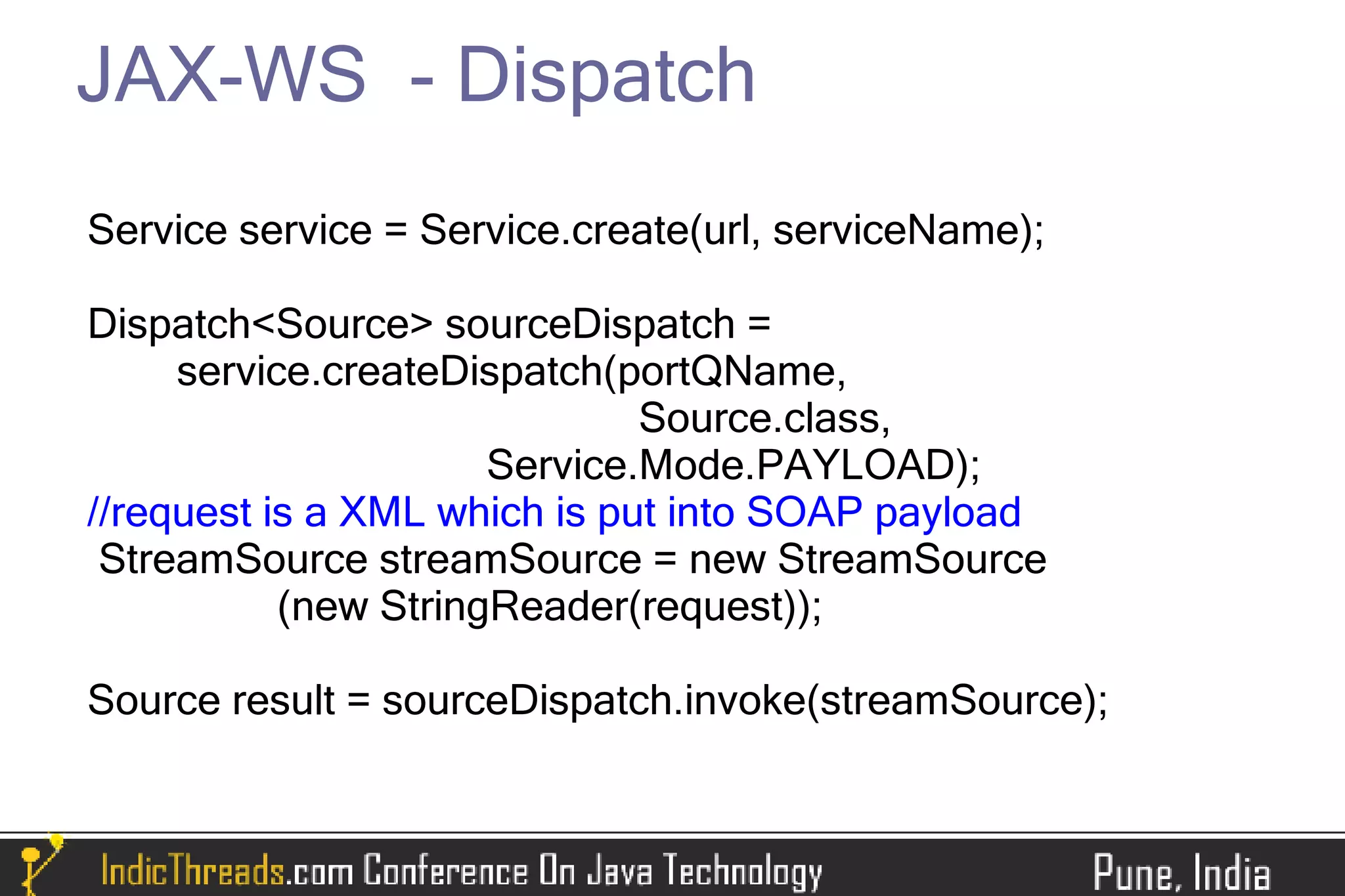
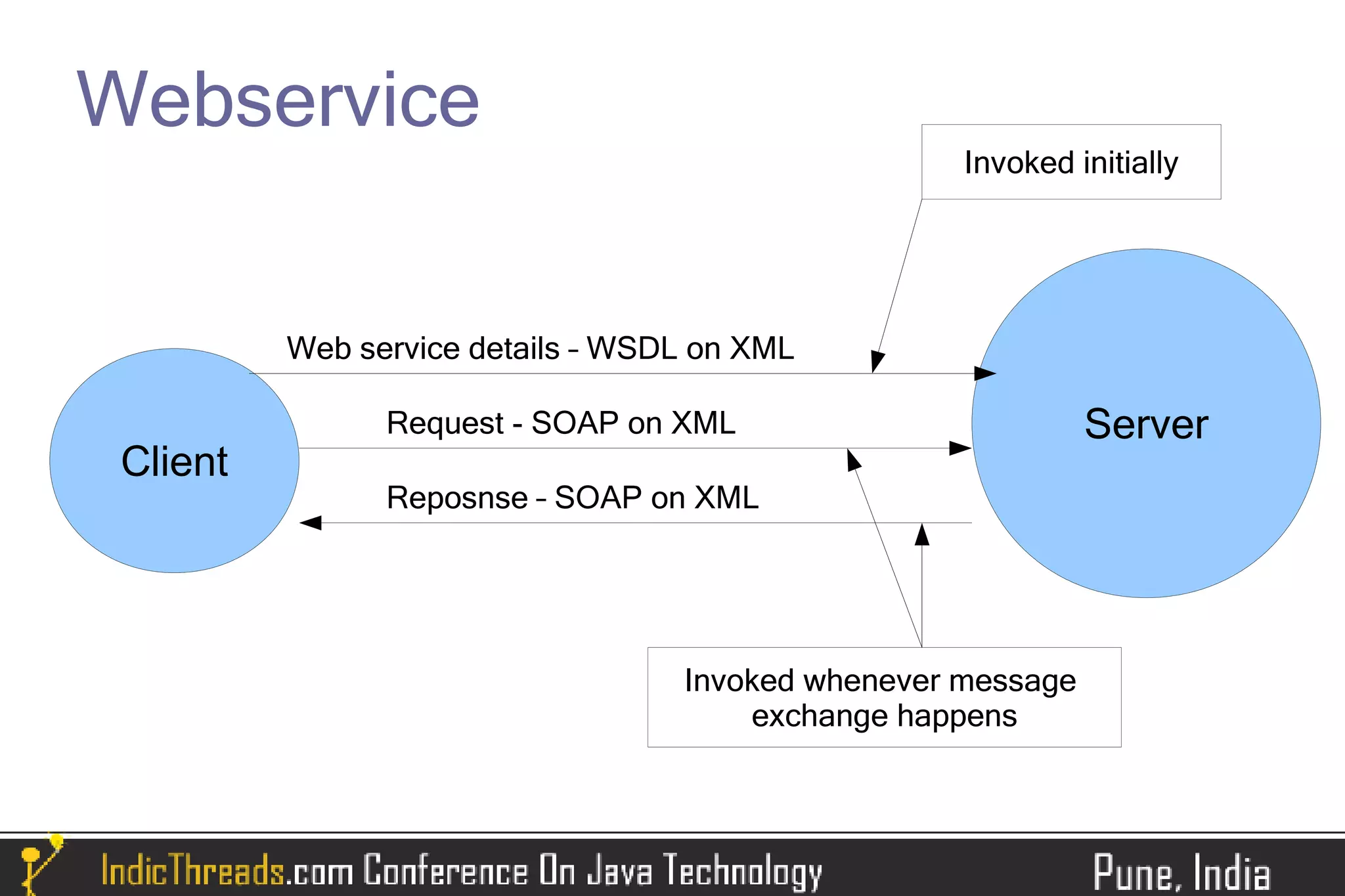
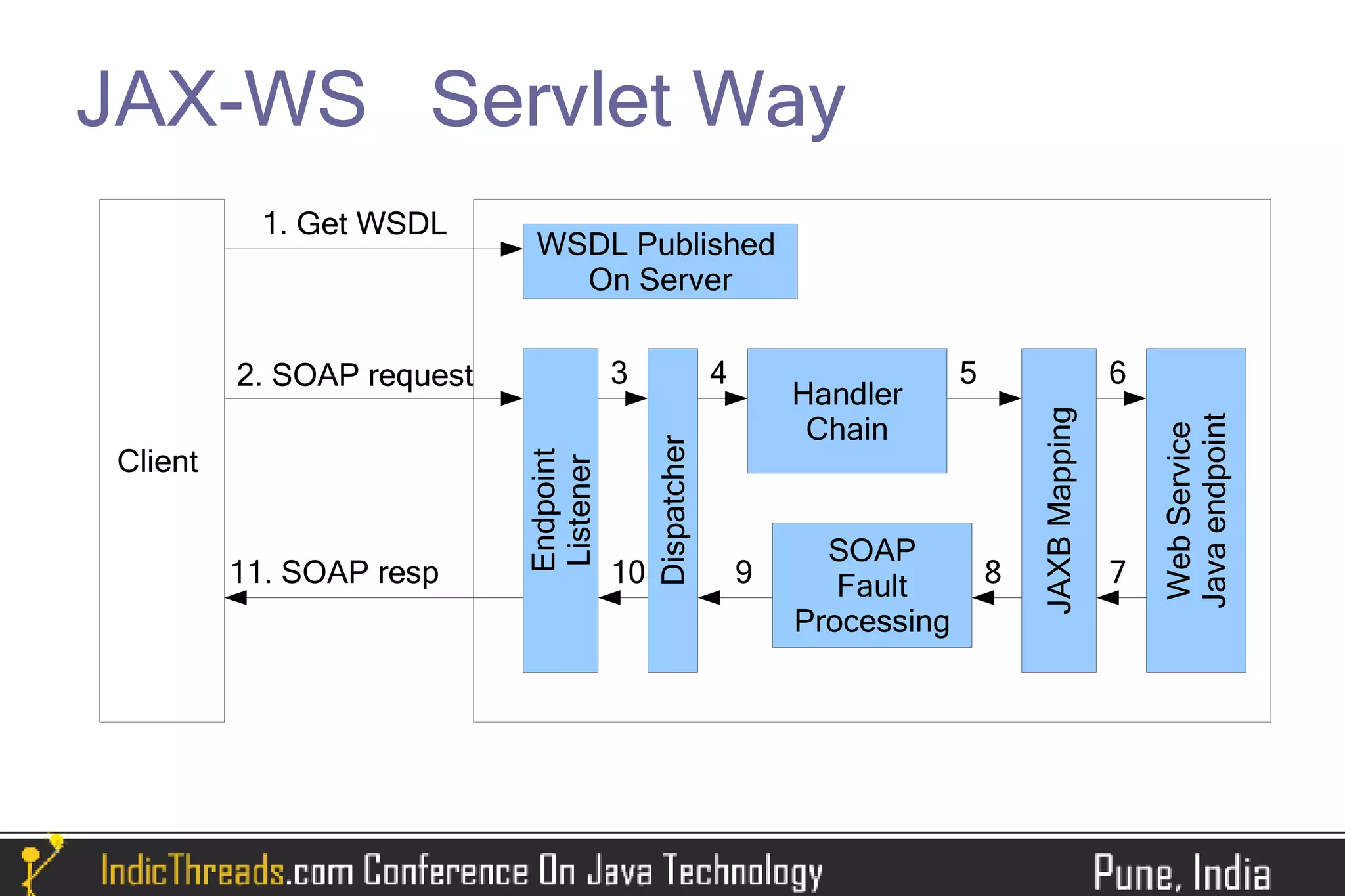
The document provides a comprehensive overview of implementing SOAP-based web services using JAX-WS, detailing both server and client-side processes. It discusses the stages of understanding web services, the use of annotations, WSDL generation, and different methods for deploying and invoking web services. Key features such as SOAP message handling, error management, and asynchronous communication are also highlighted.











![JAX-WS – JavaSE Endpoint
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemperatureConverter tc= new
TemperatureConverter();
//Java comes with an embedded Http server
//which is used to host the service
Endpoint endpoint = Endpoint.publish
("http://localhost:8080/tempConv", tc);
//Keeping commented, keeps the server running
/*endpoint.stop();*/
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indicthreads-java-jax-ws-091214063721-phpapp01/75/Java-web-services-using-JAX-WS-15-2048.jpg)