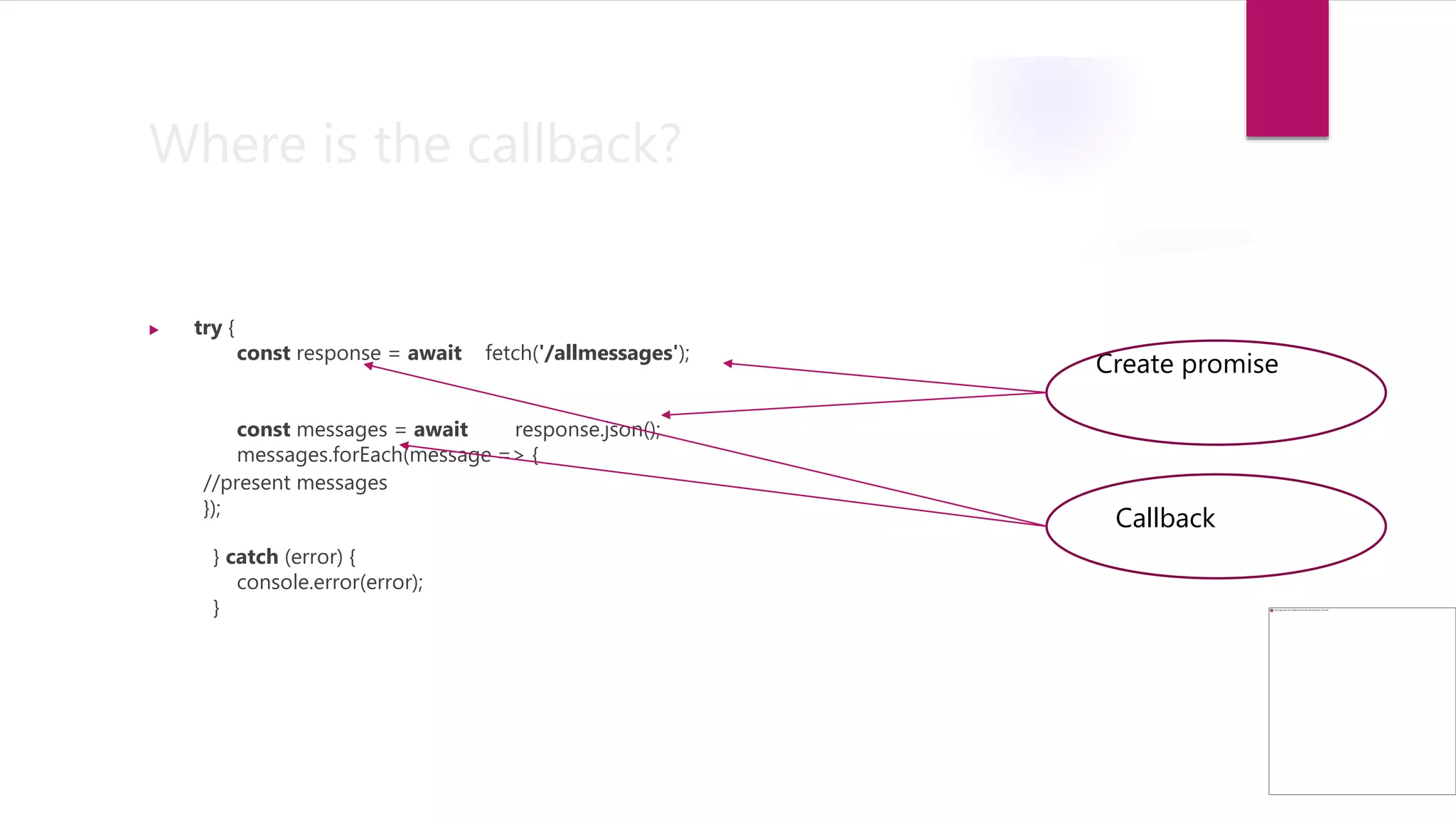
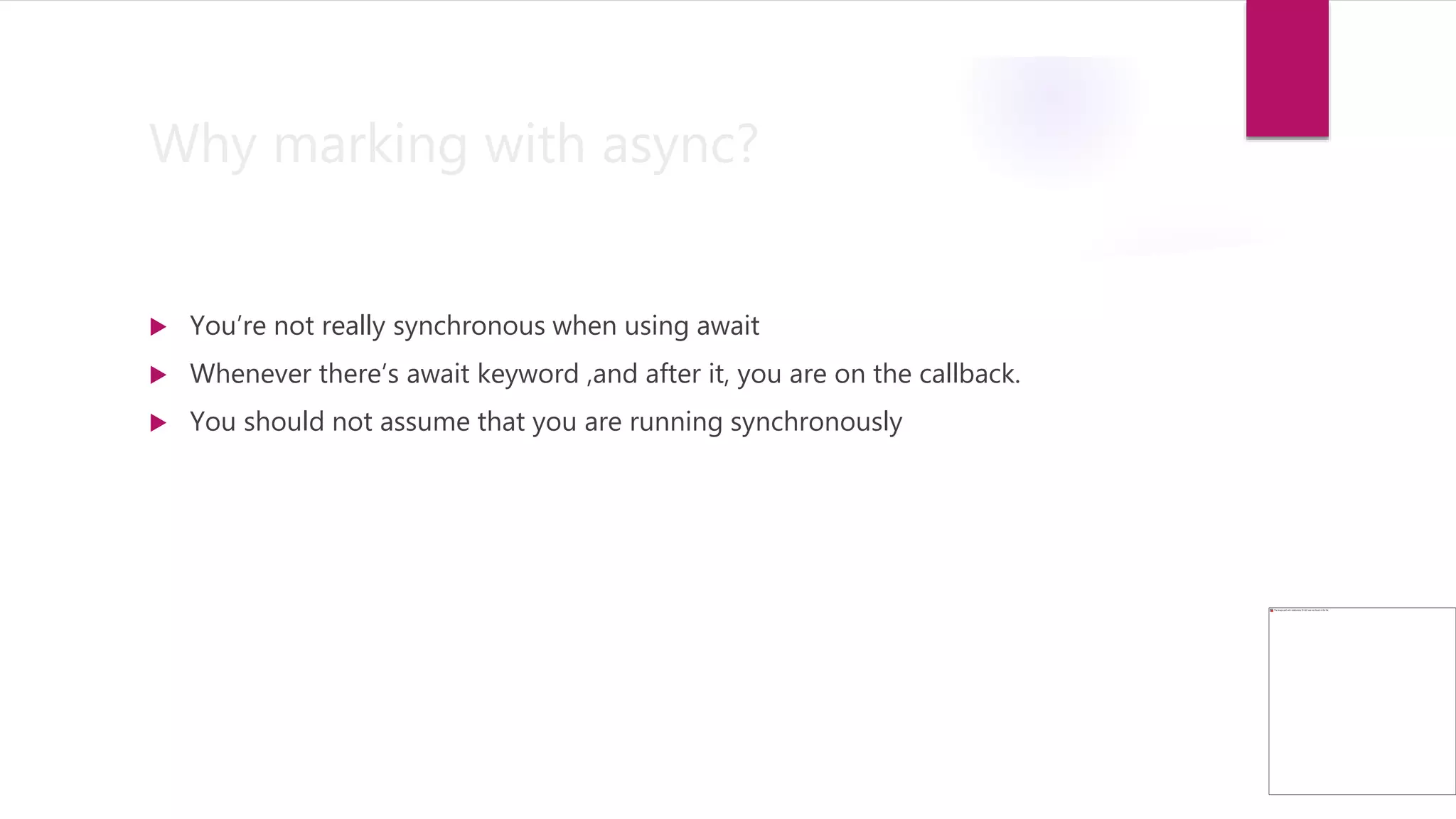
The document discusses async/await in JavaScript. It explains that async/await allows writing asynchronous code that looks synchronous by using the await keyword to "turn" a promise into its resolved value. Async functions always return promises, even though code below await reads synchronously. Async/await simplifies code by avoiding callback nesting and is supported in modern browsers.