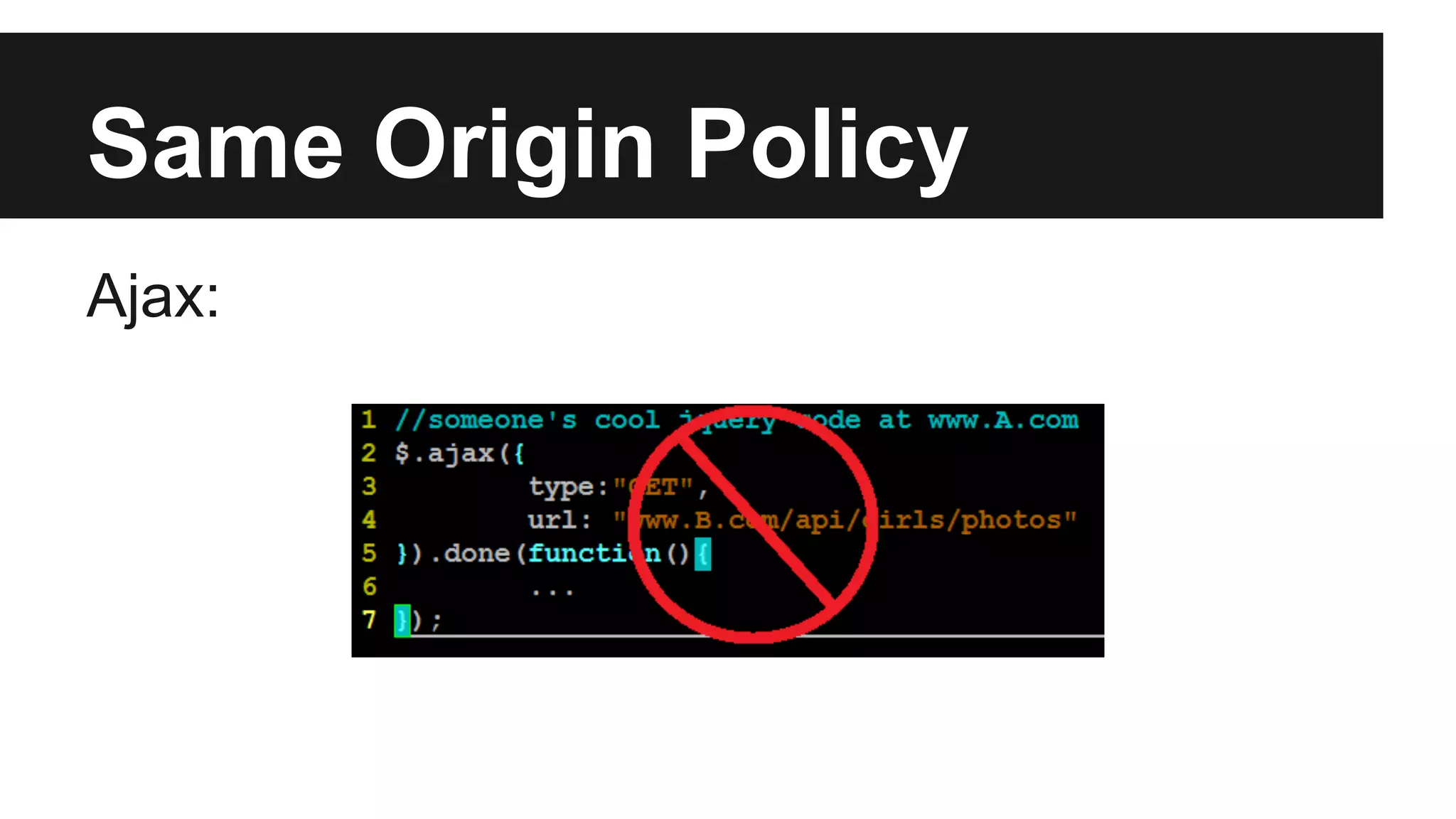
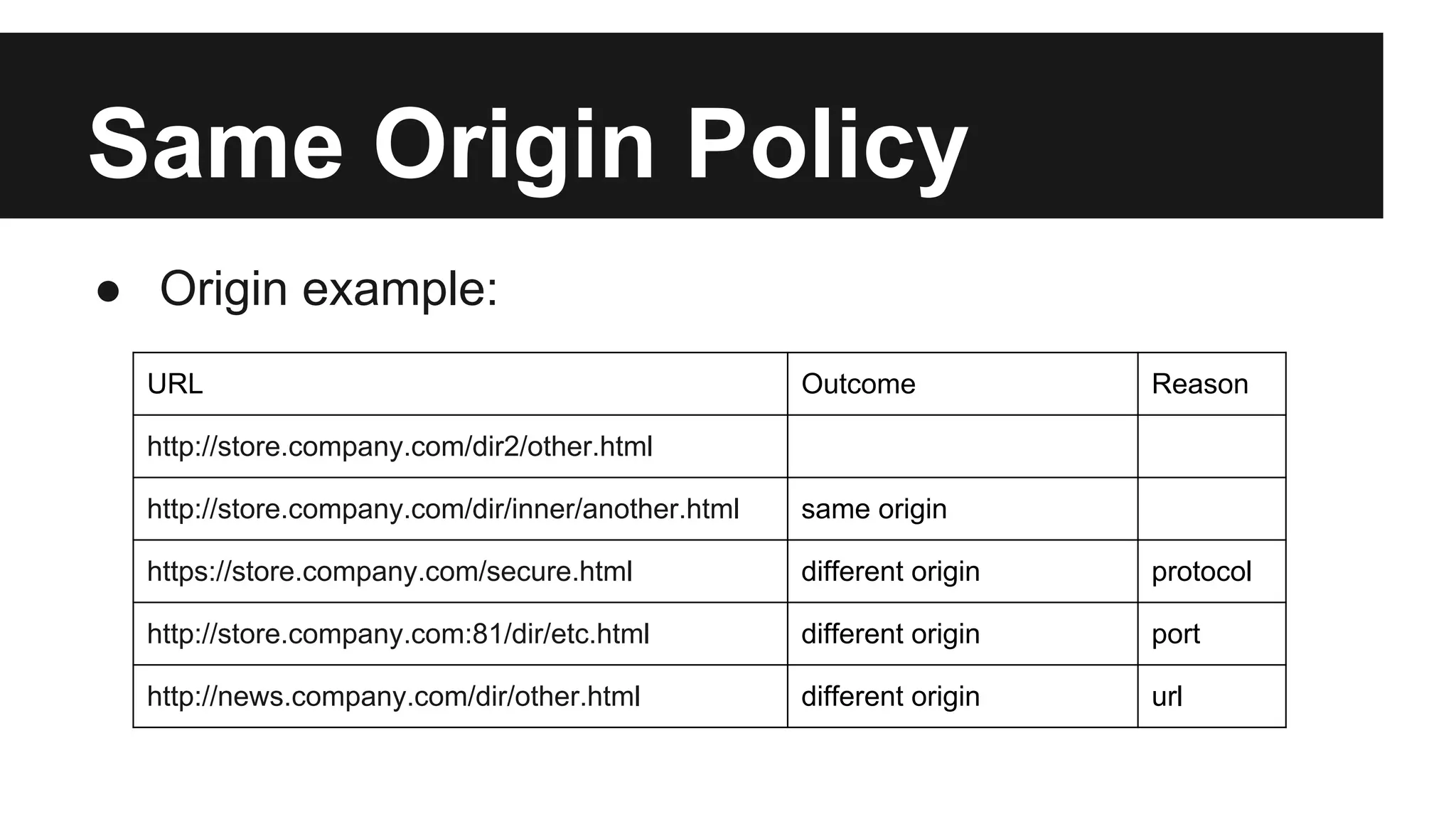
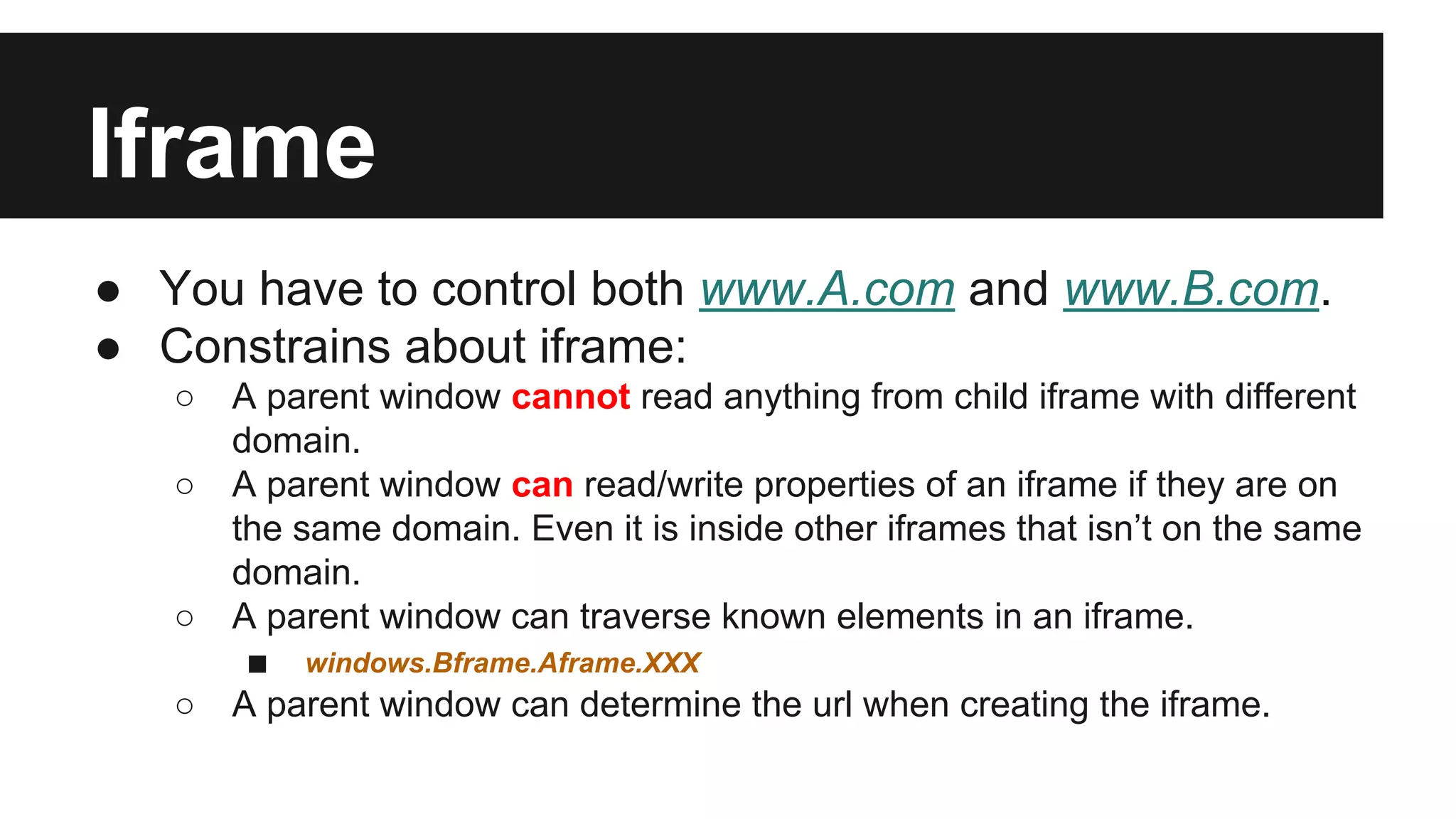
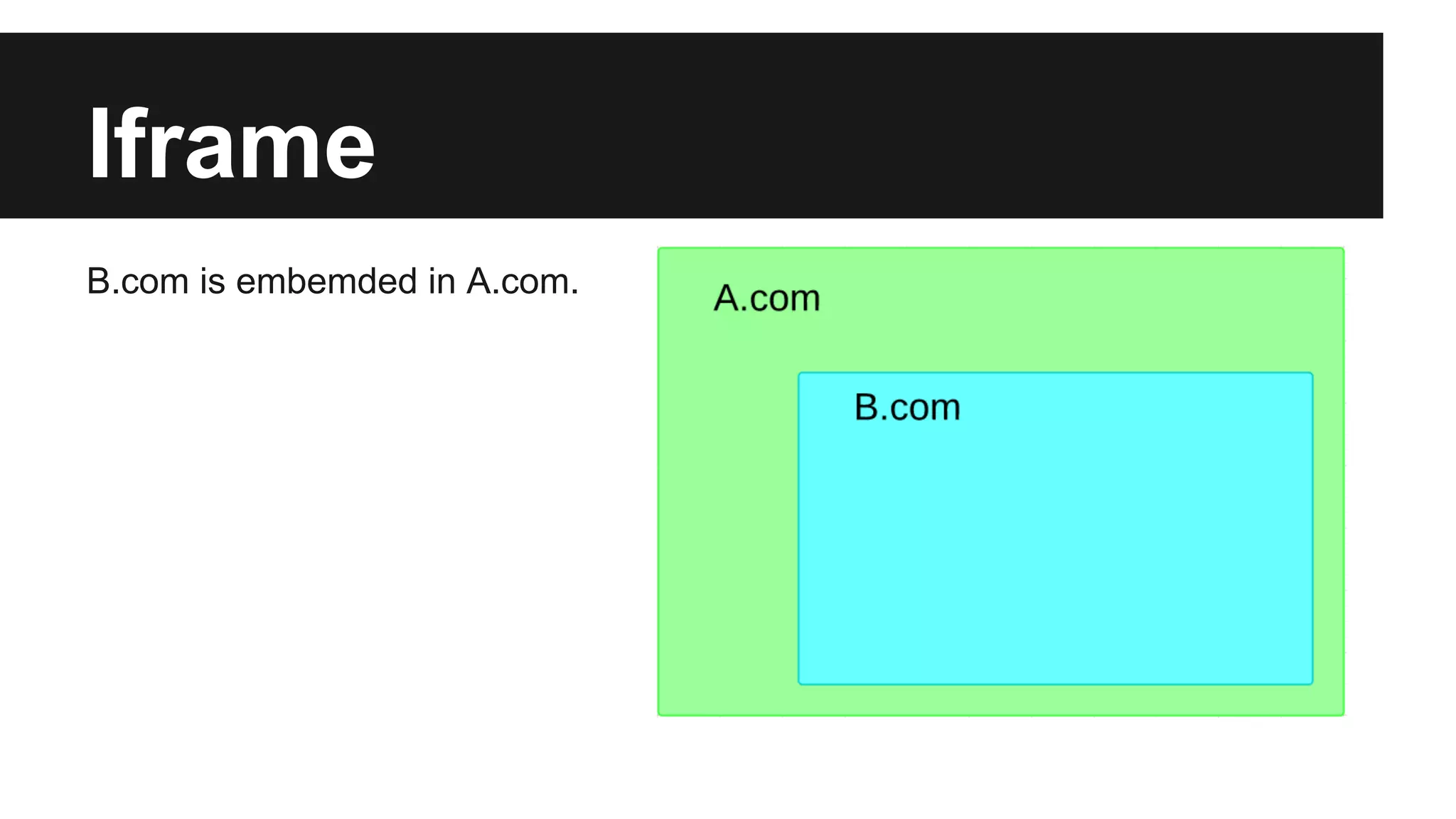
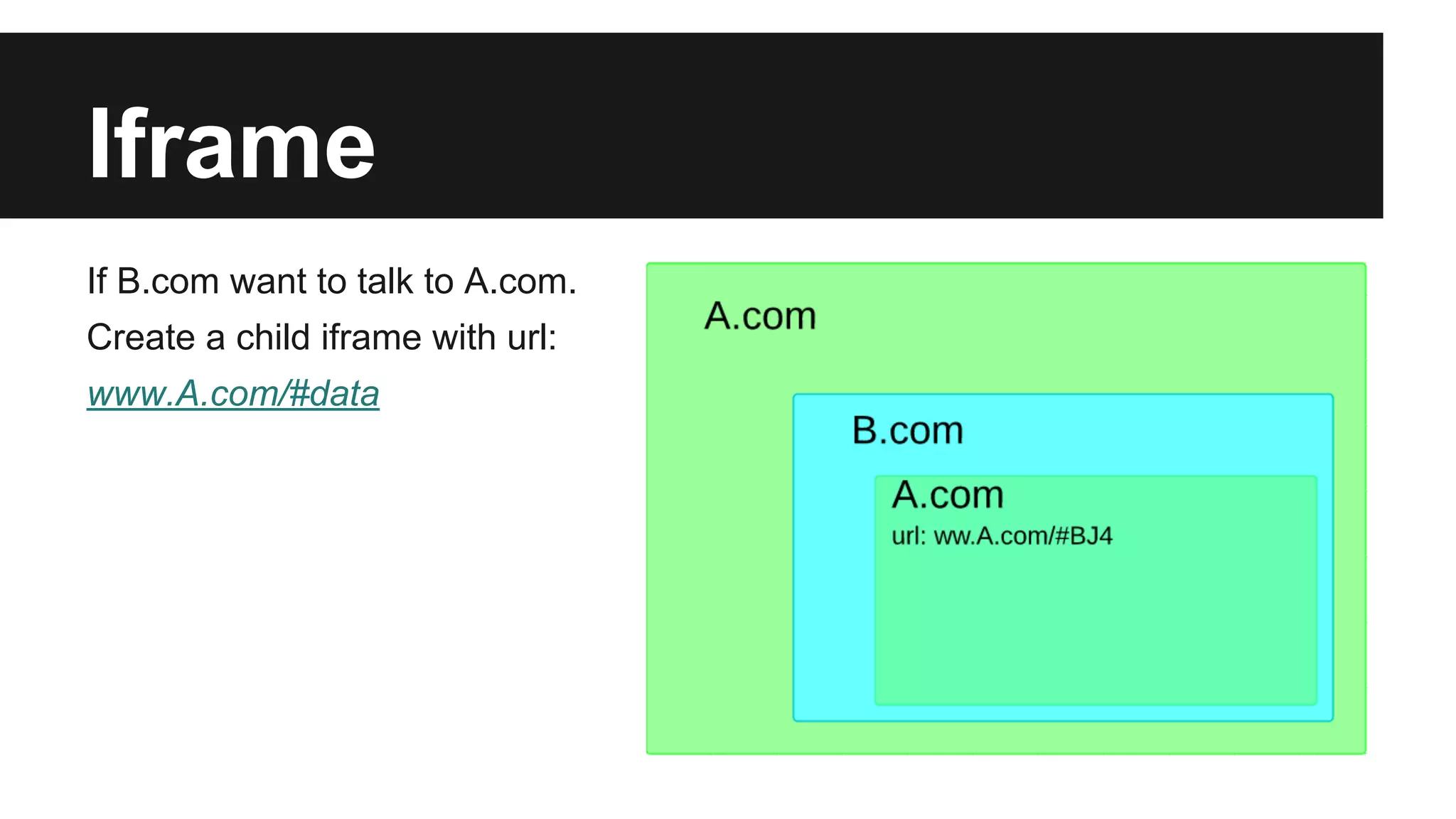
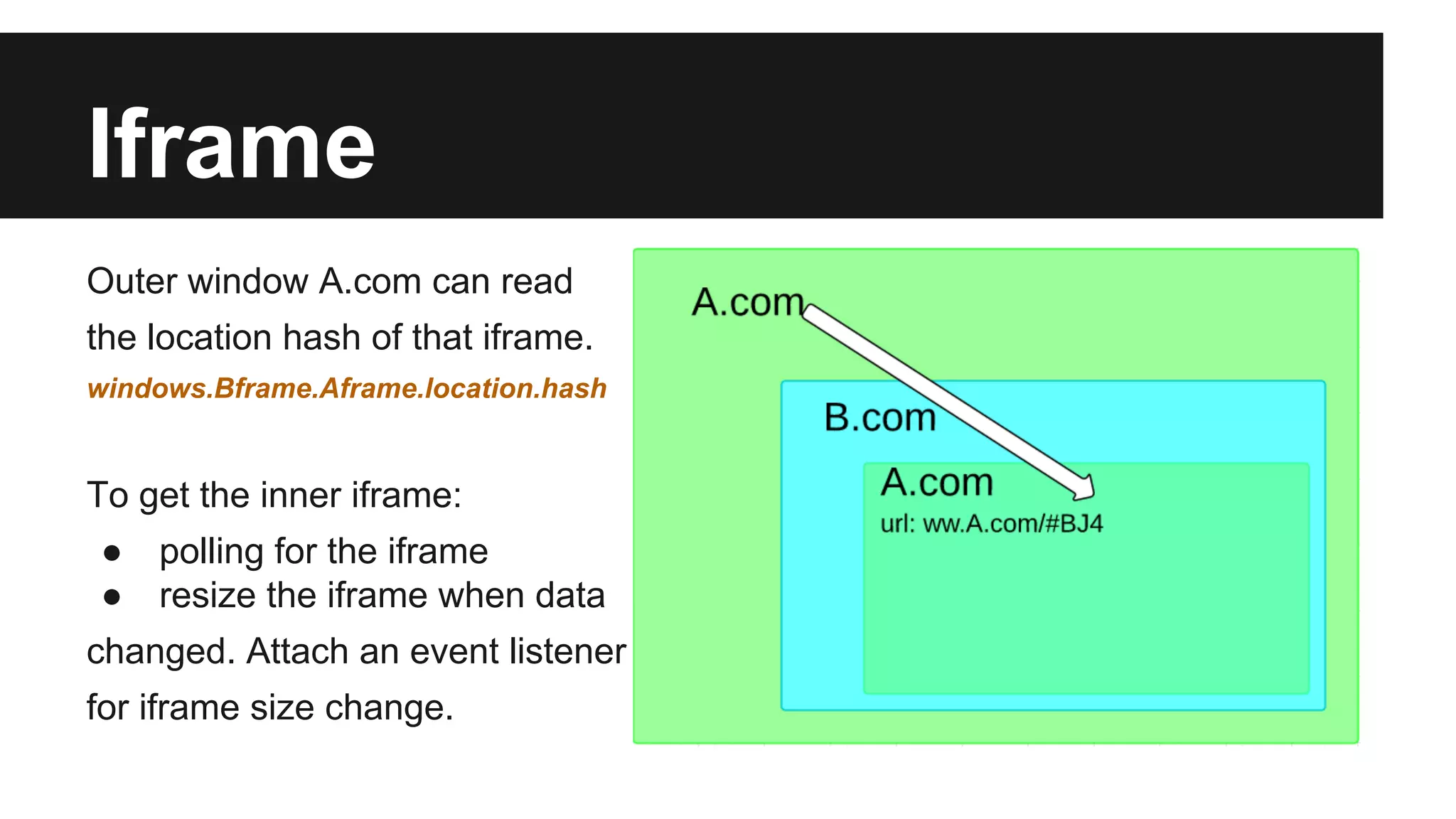
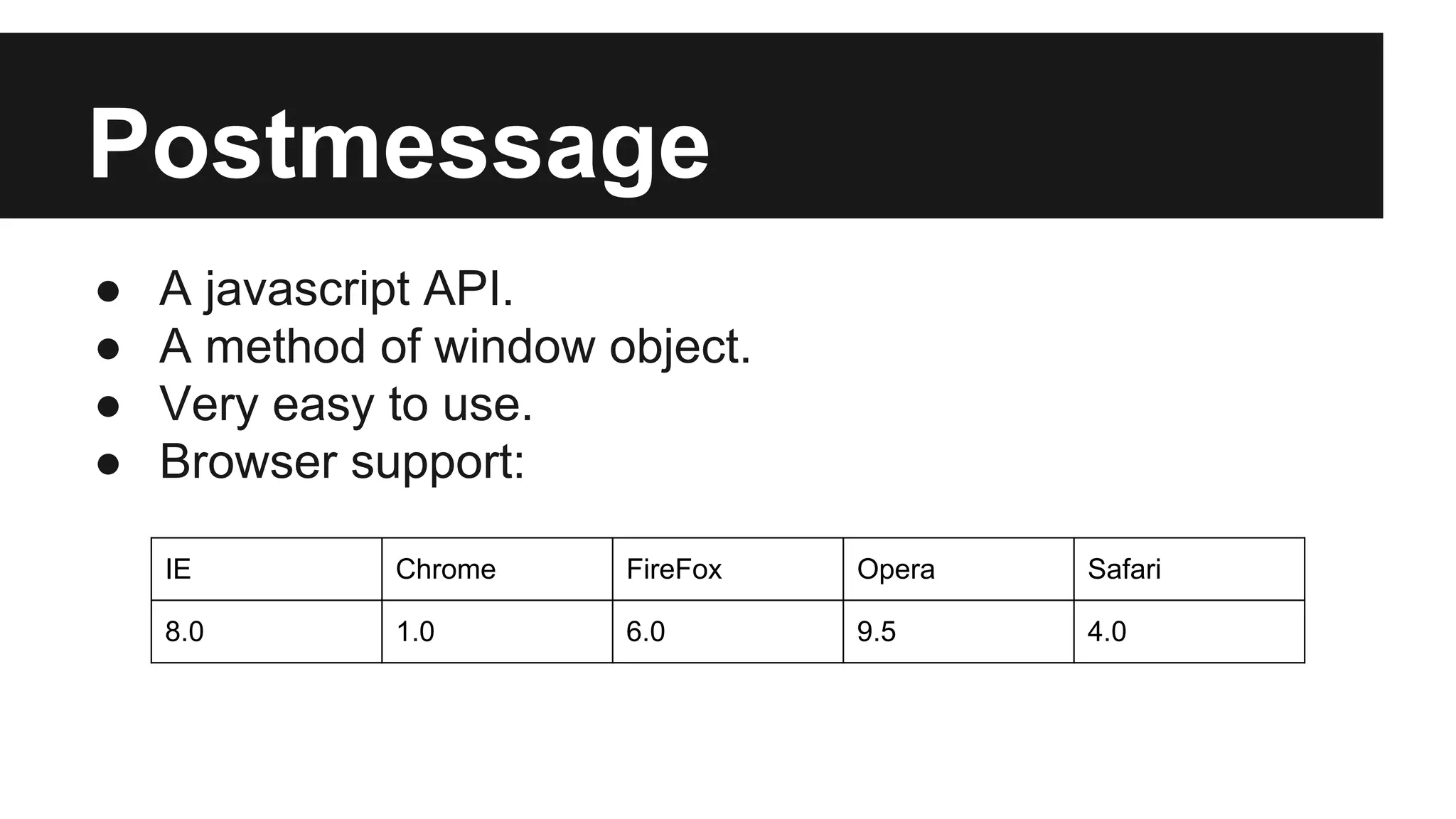
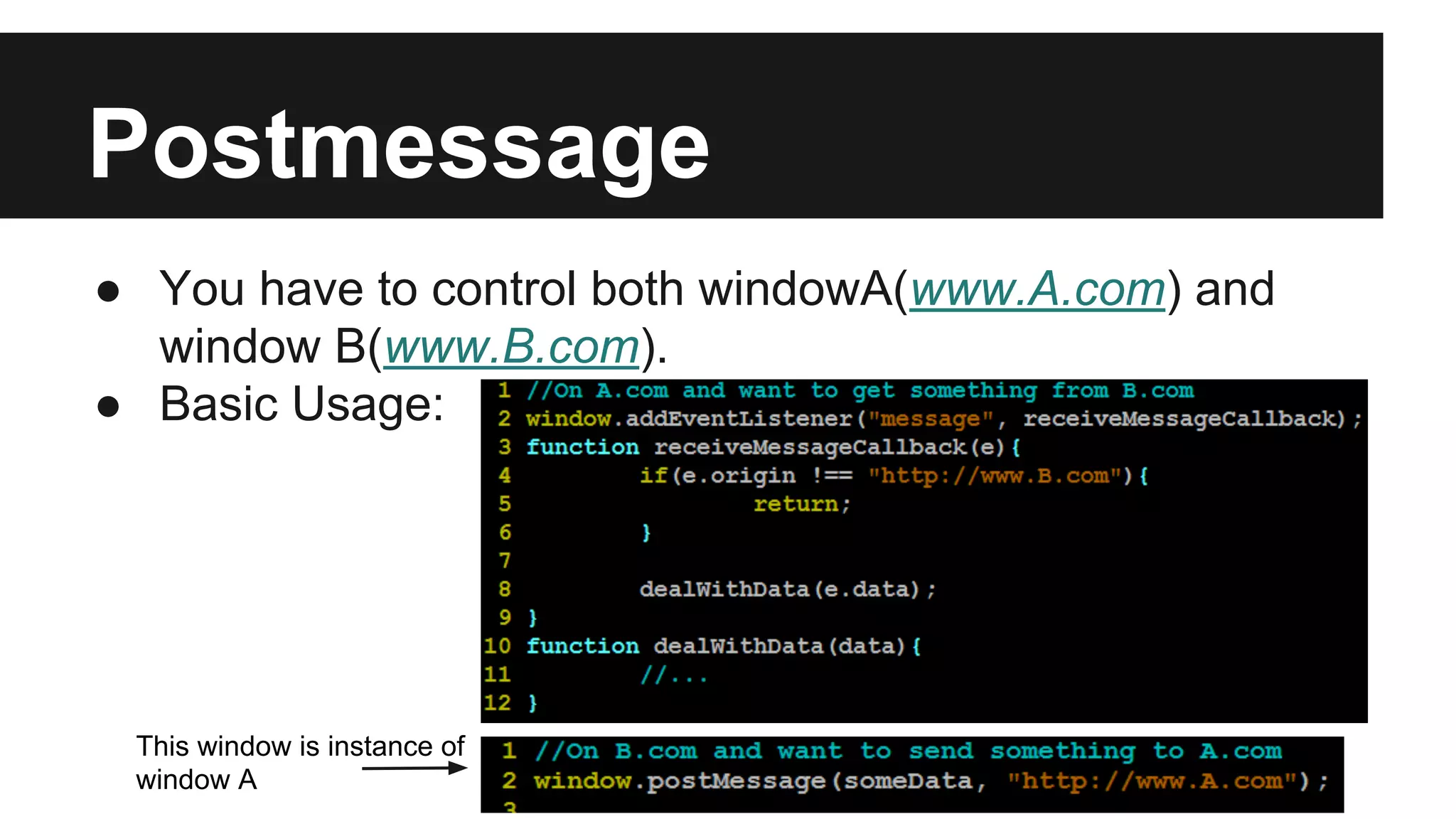
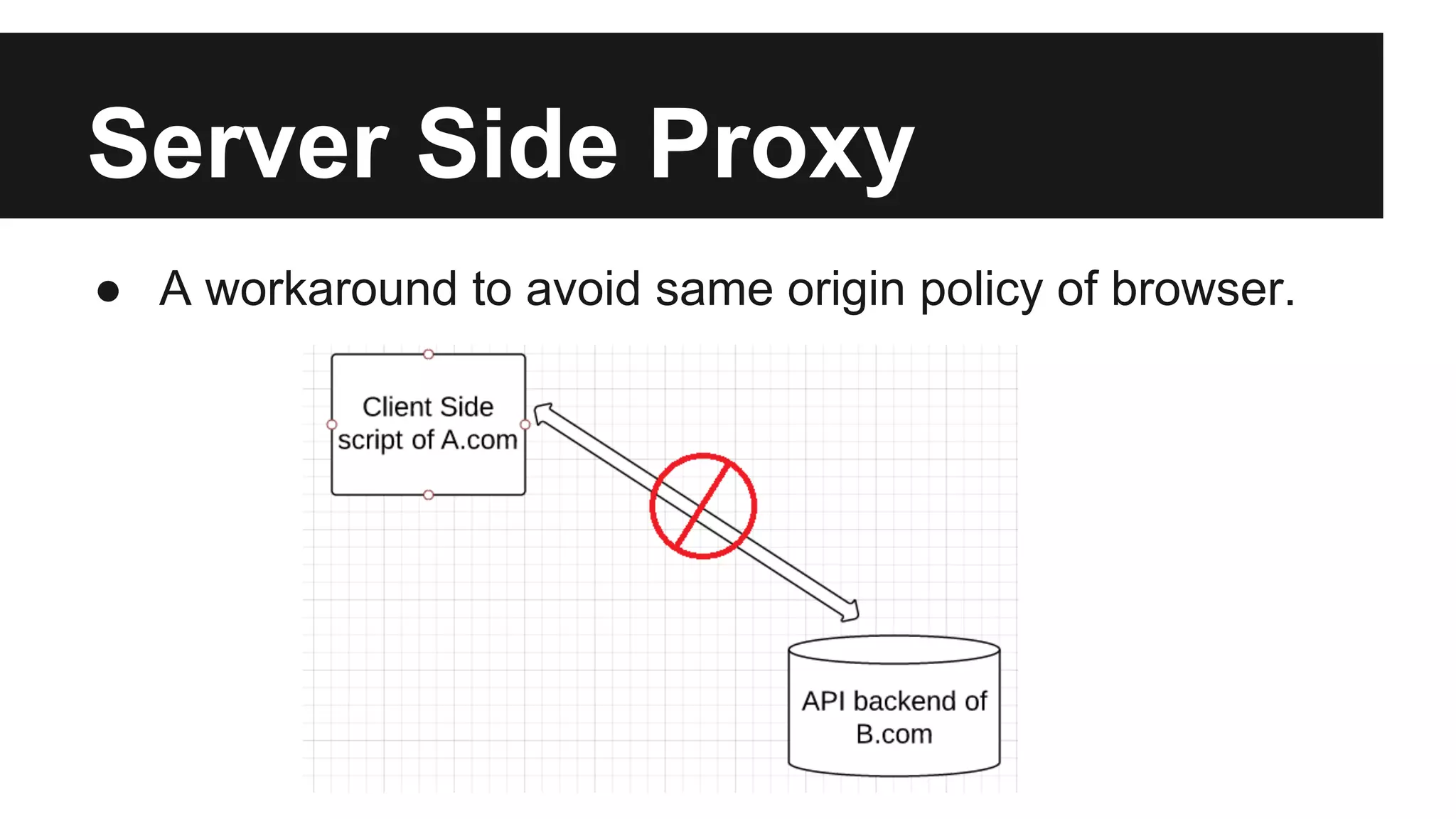
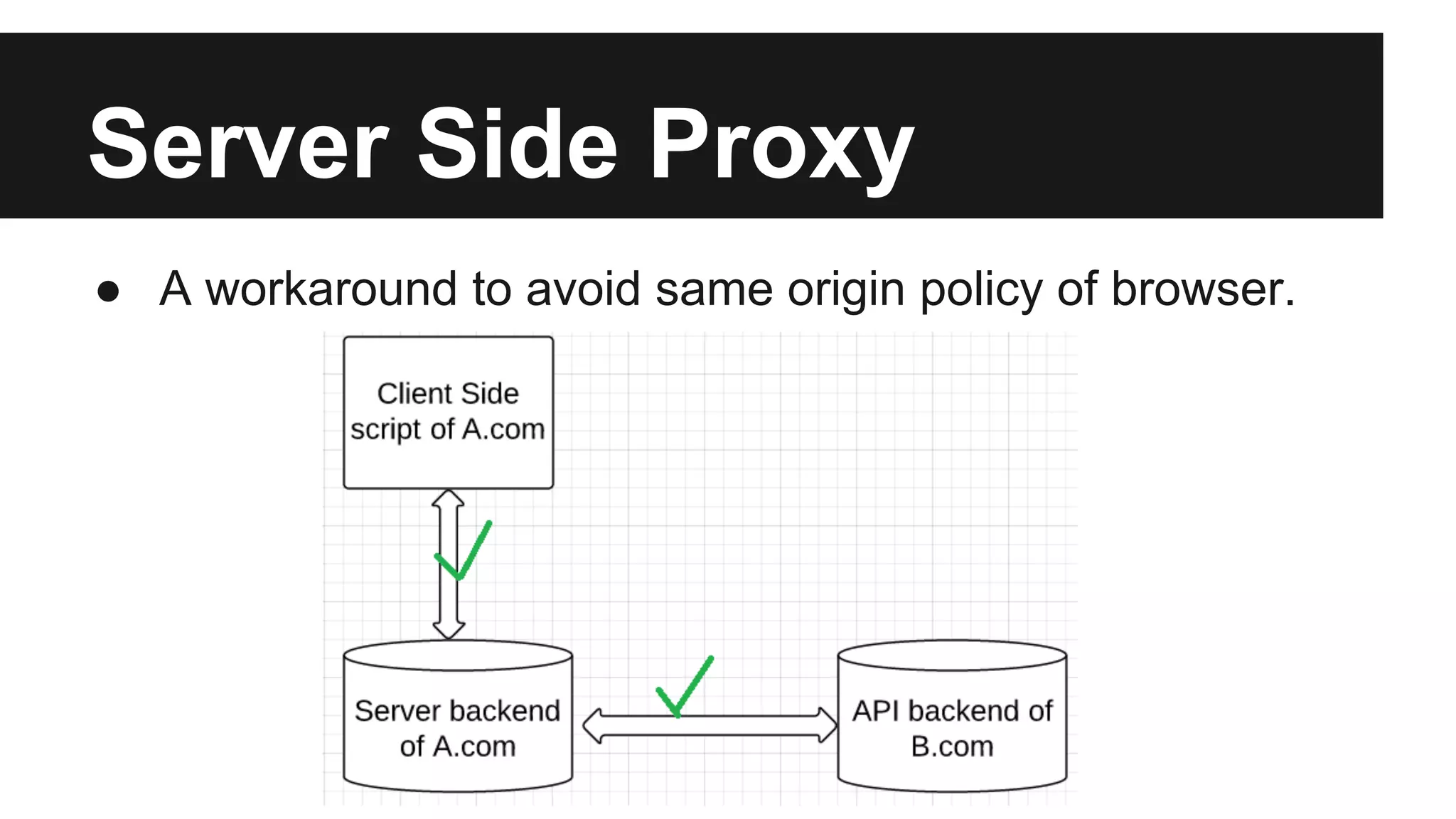
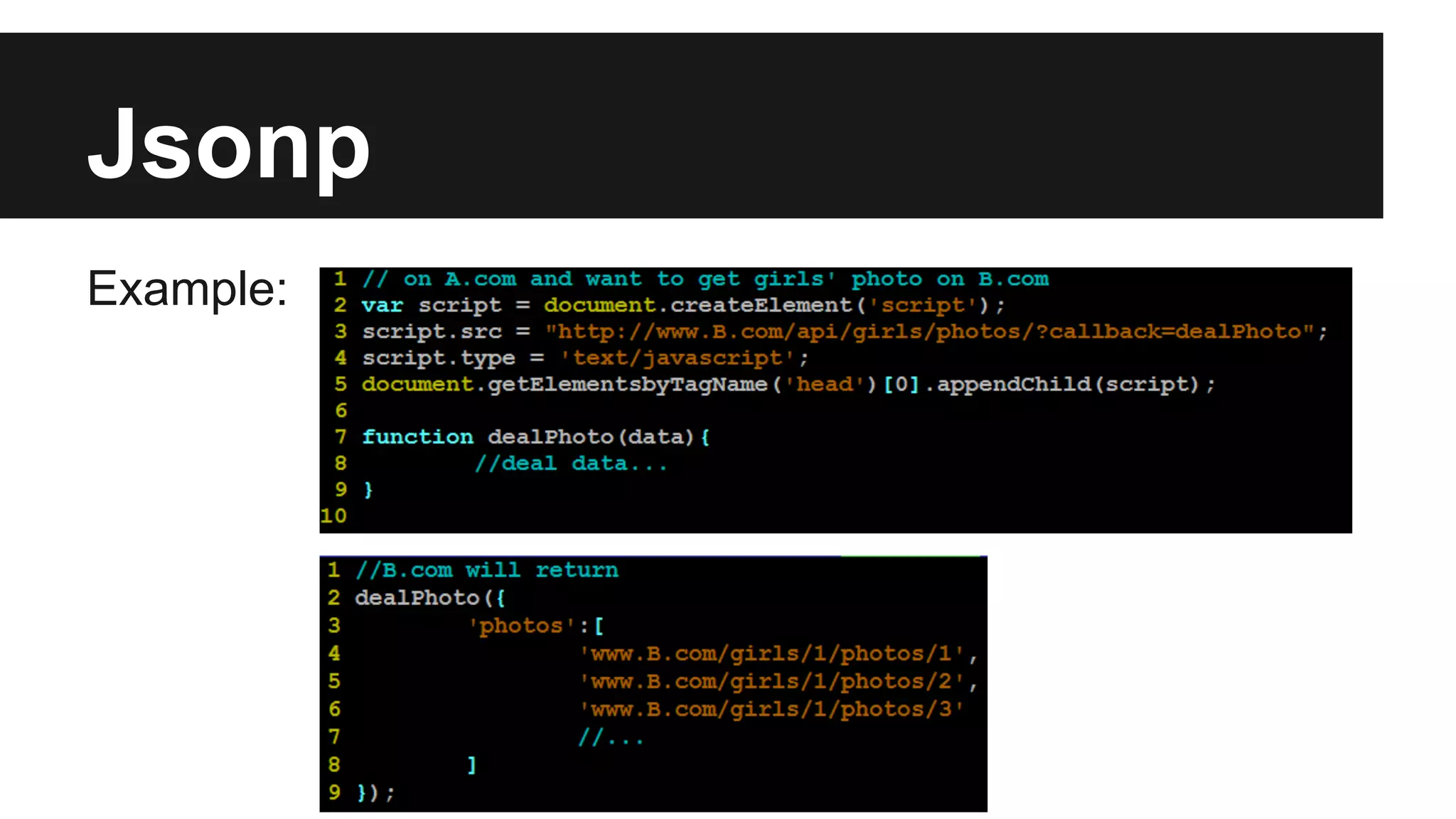
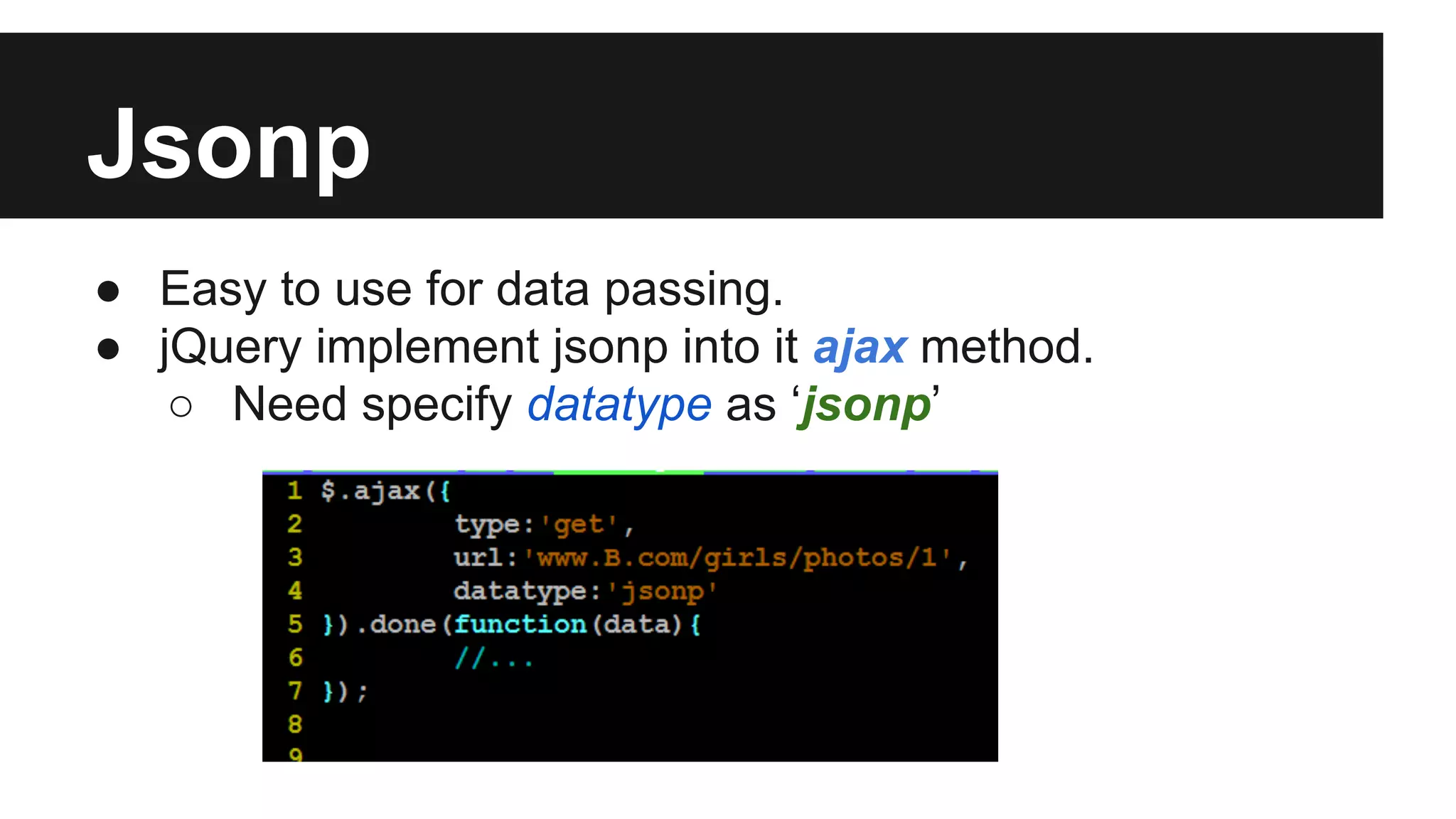
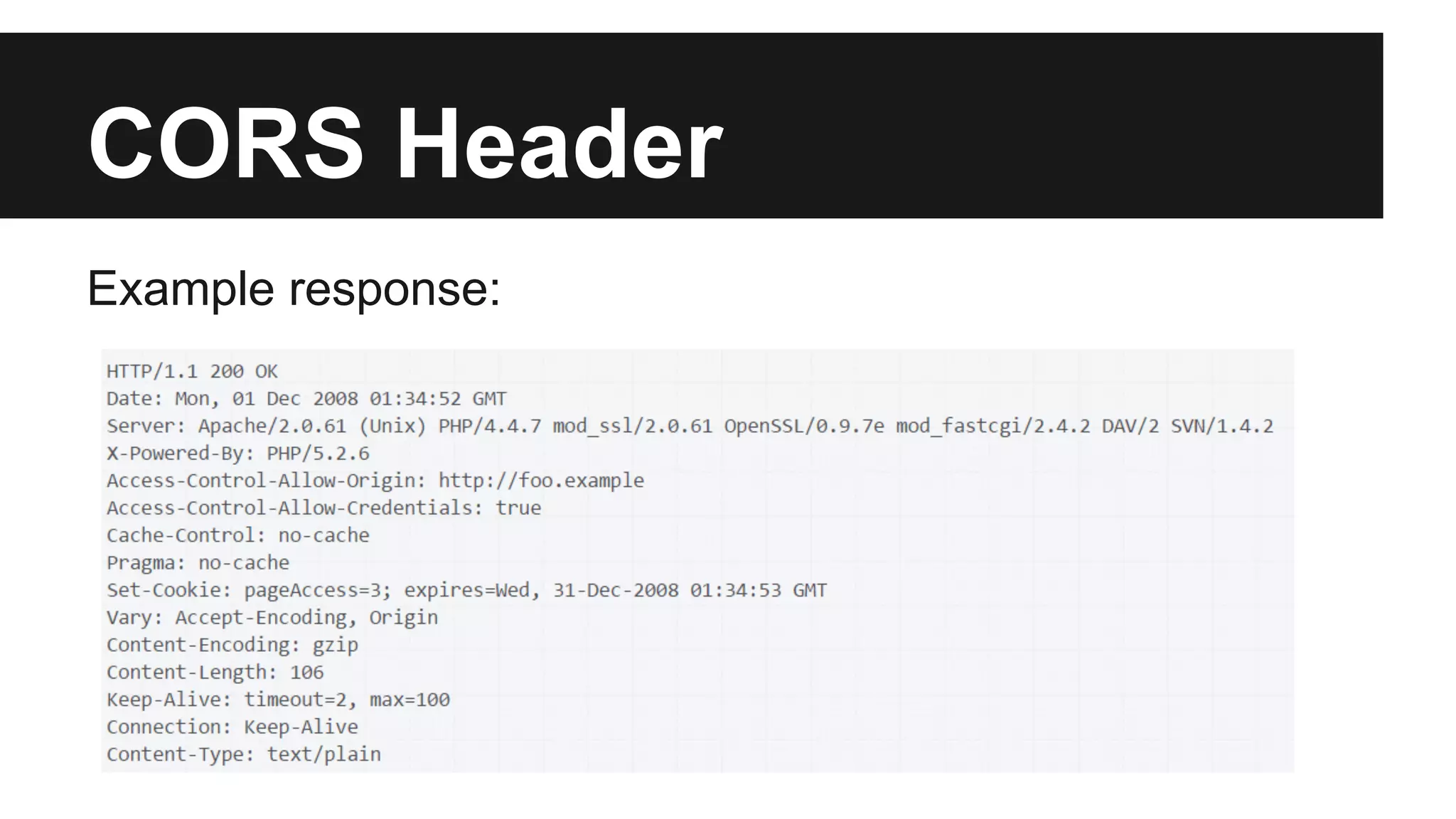
This document discusses methods for enabling cross-domain communication in JavaScript. It begins by explaining the need for cross-domain communication to access third-party APIs and the browser's same-origin policy security restriction. It then describes several approaches for implementing cross-domain communication including using iframes, the postMessage API for cross-window messaging, server-side proxies, JSONP, and the CORS HTTP header for enabling cross-origin requests directly in JavaScript.