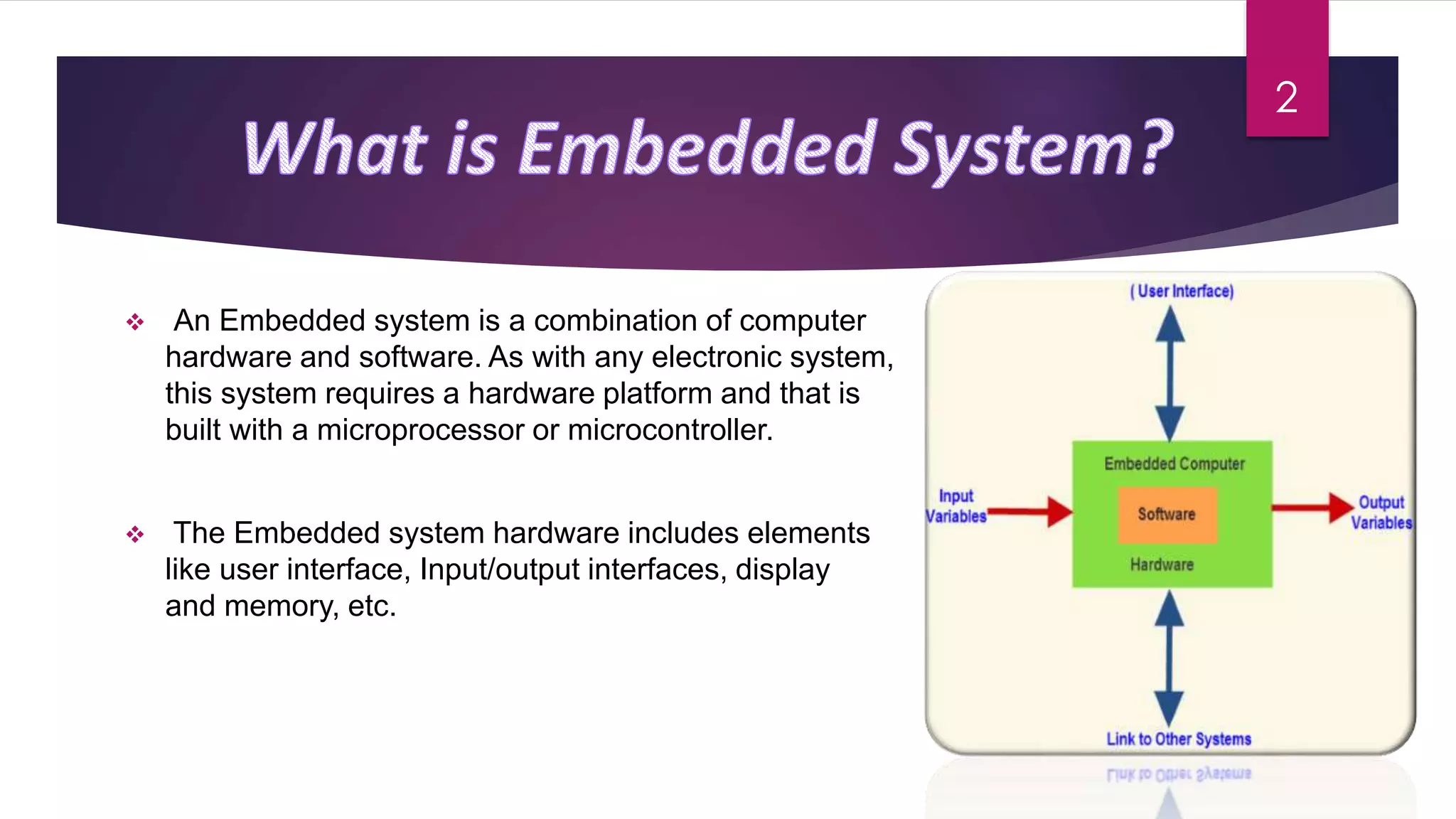
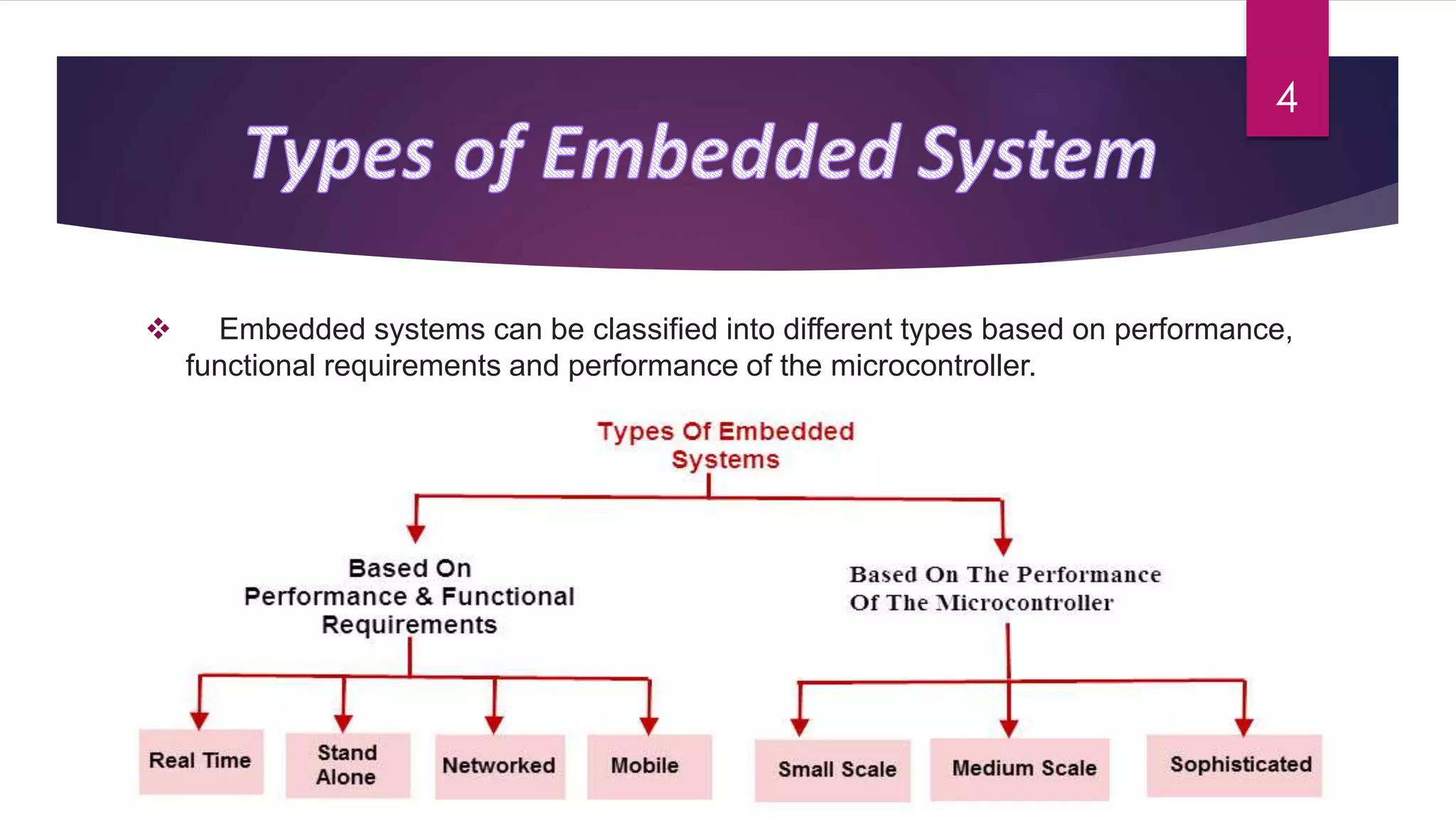
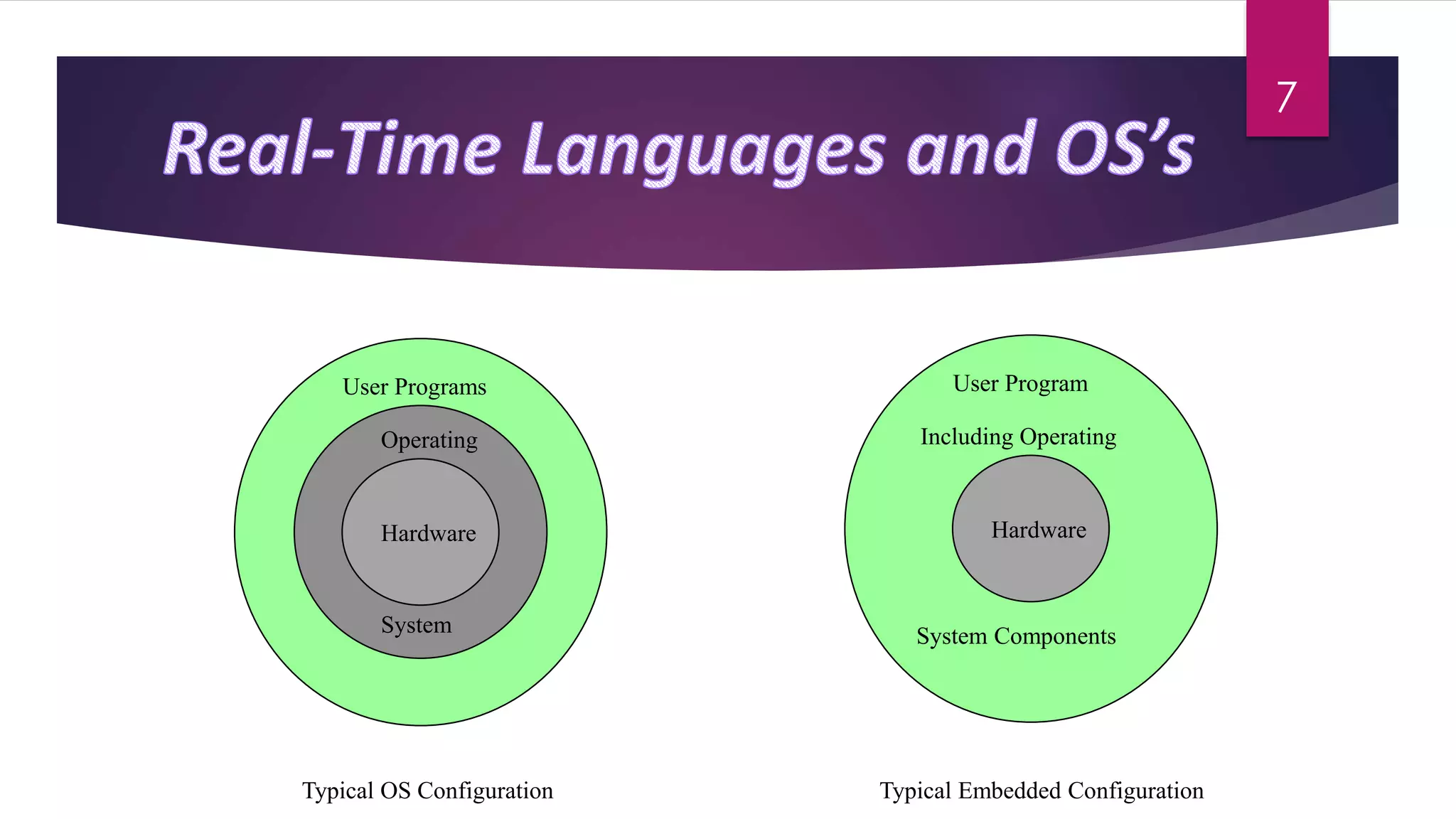
Embedded systems combine computer hardware and software to perform specific tasks. They have limited memory and CPU power compared to desktop systems. Programming embedded systems requires considering the real-time nature and differences in hardware between systems. Embedded systems can be classified based on their performance, requirements, and microcontroller performance. Common applications of embedded systems include automobiles, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. A variety of languages are used for different scales of embedded systems.