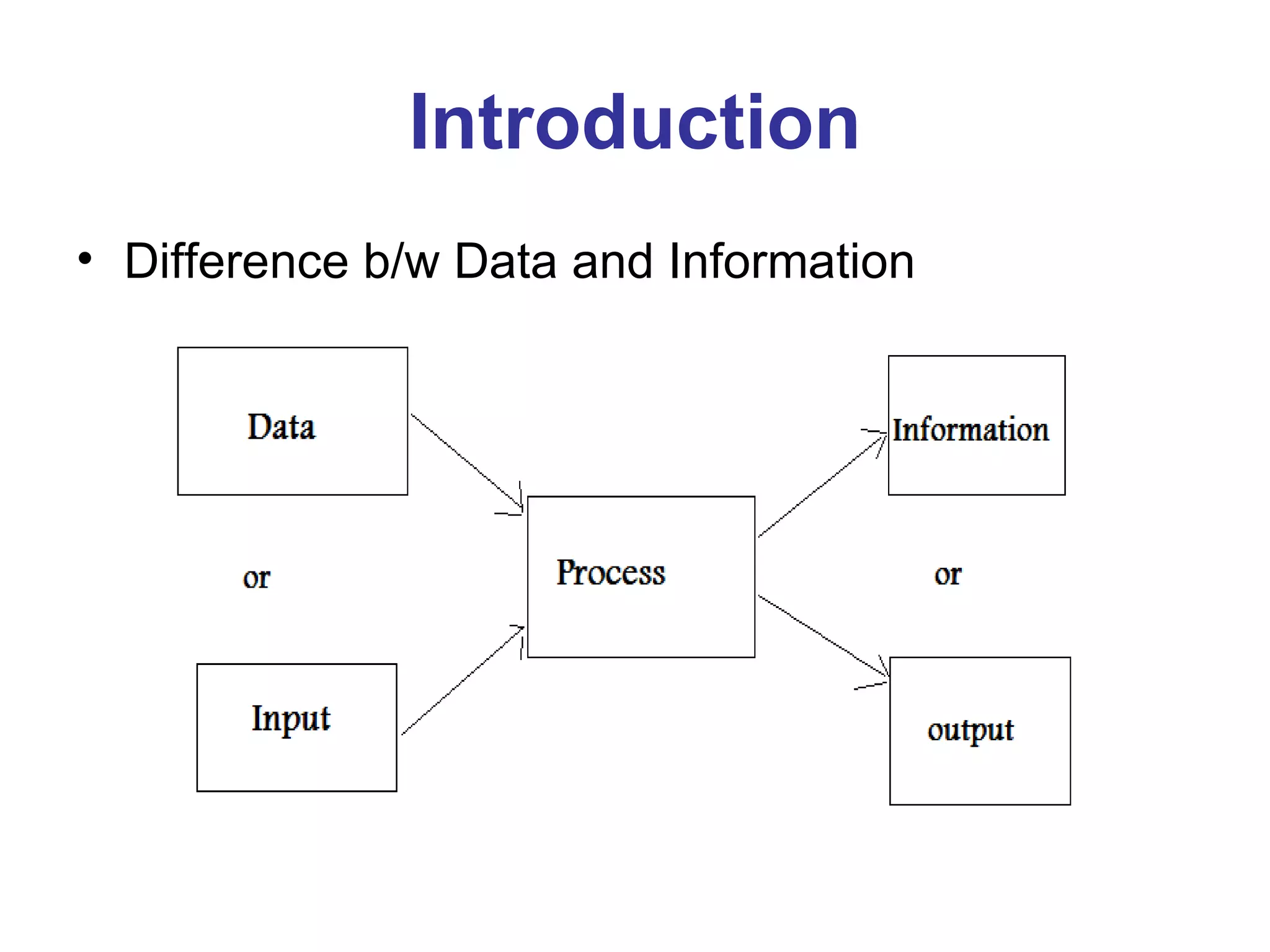
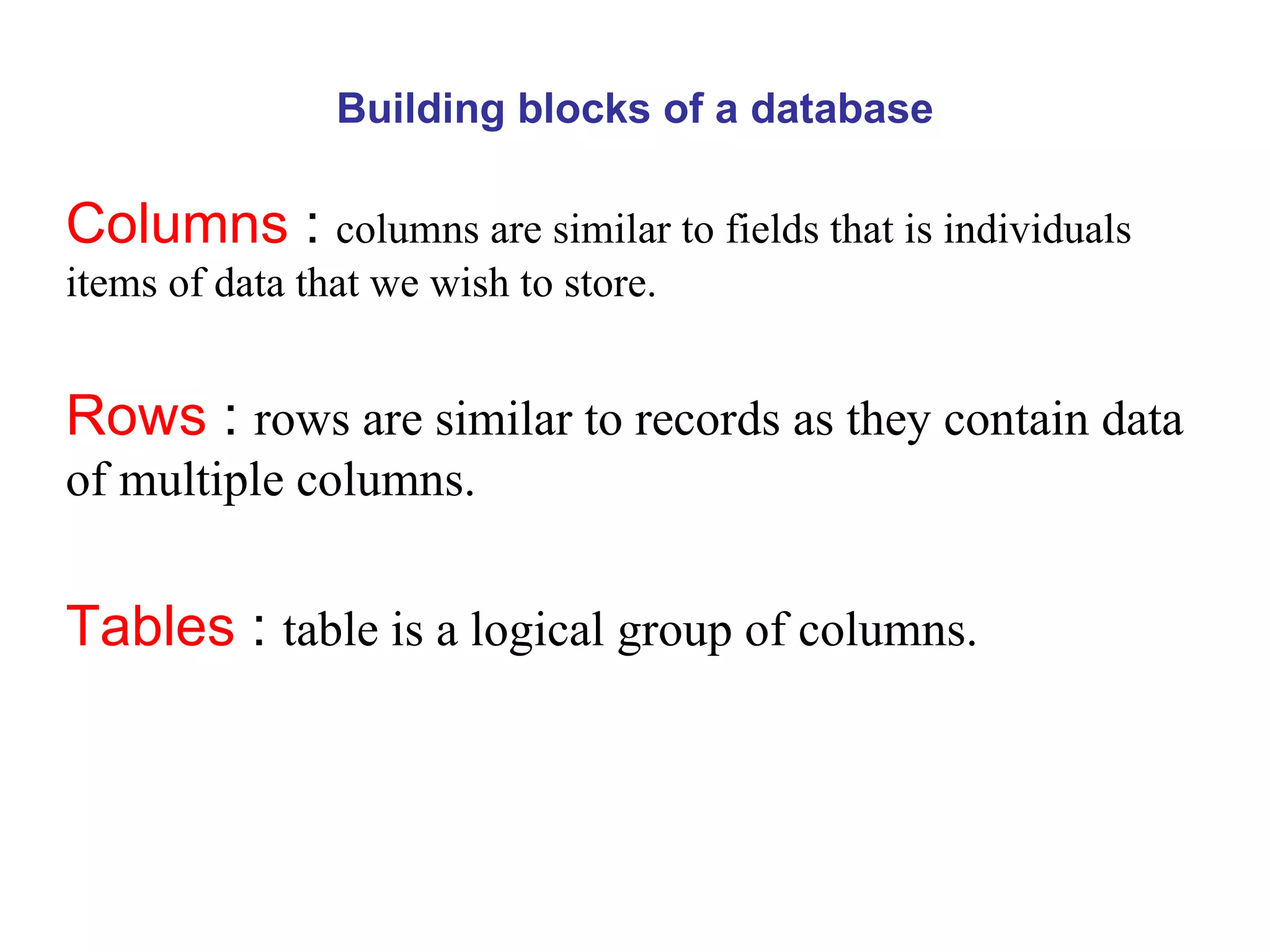
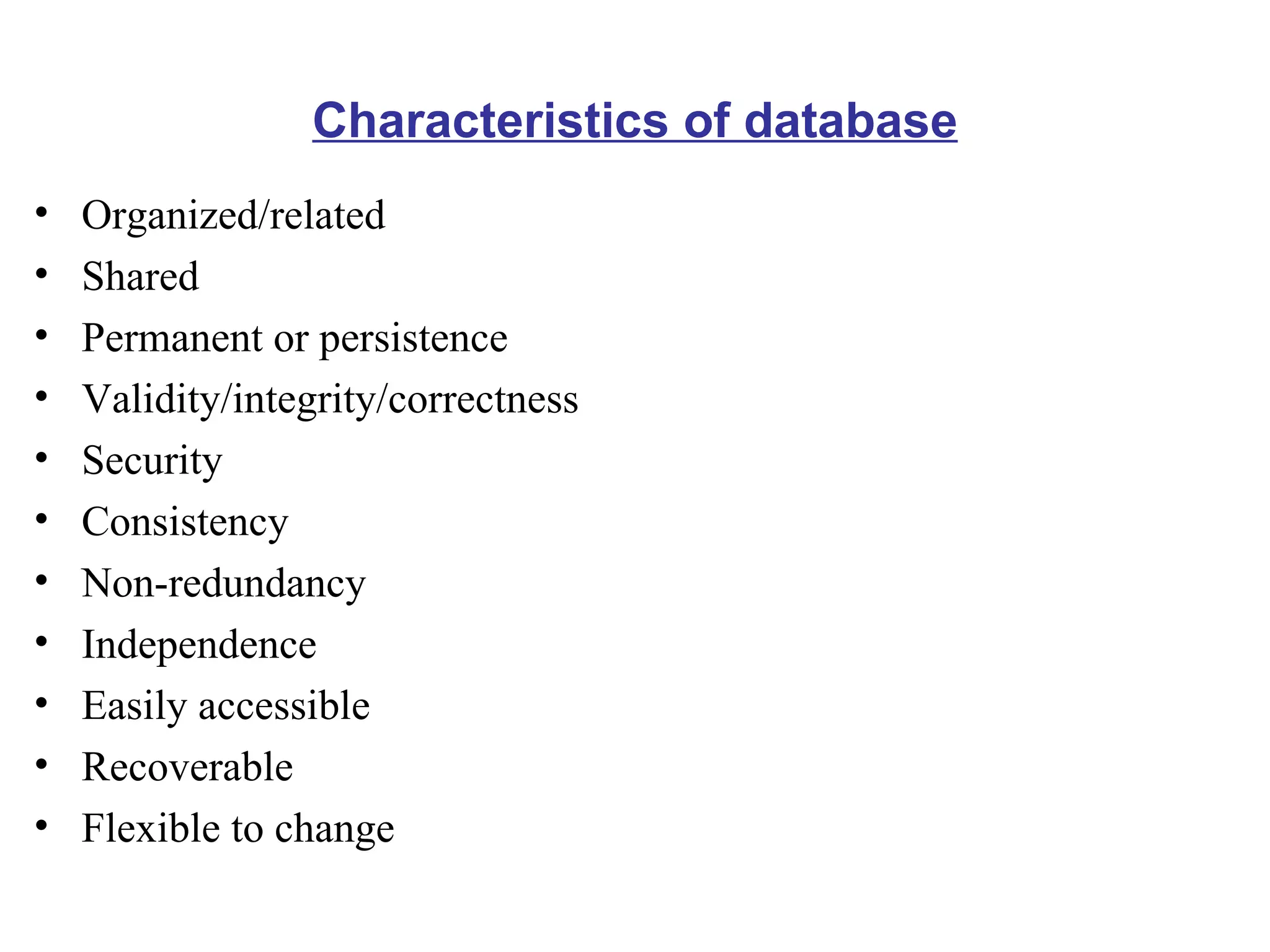
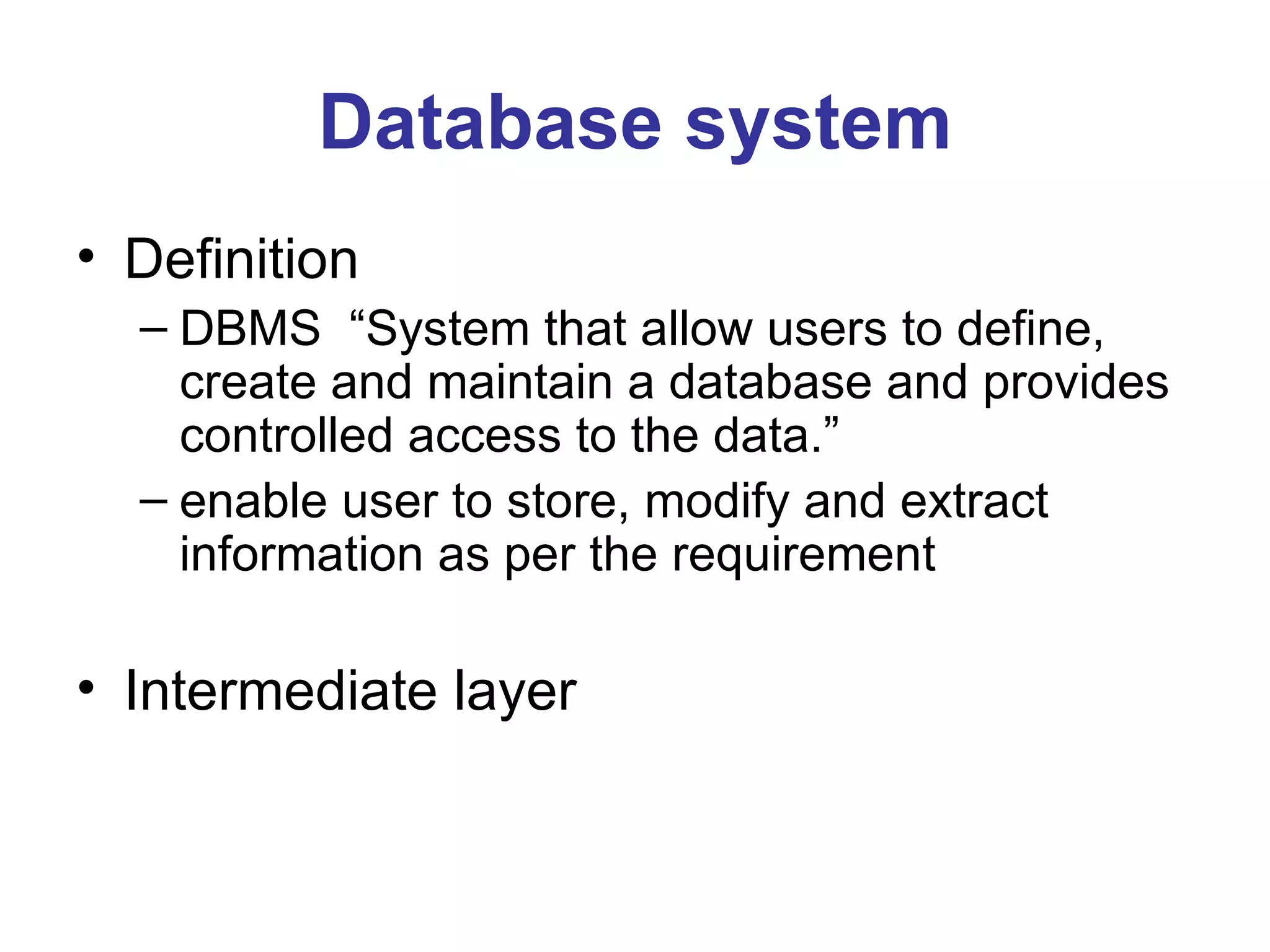
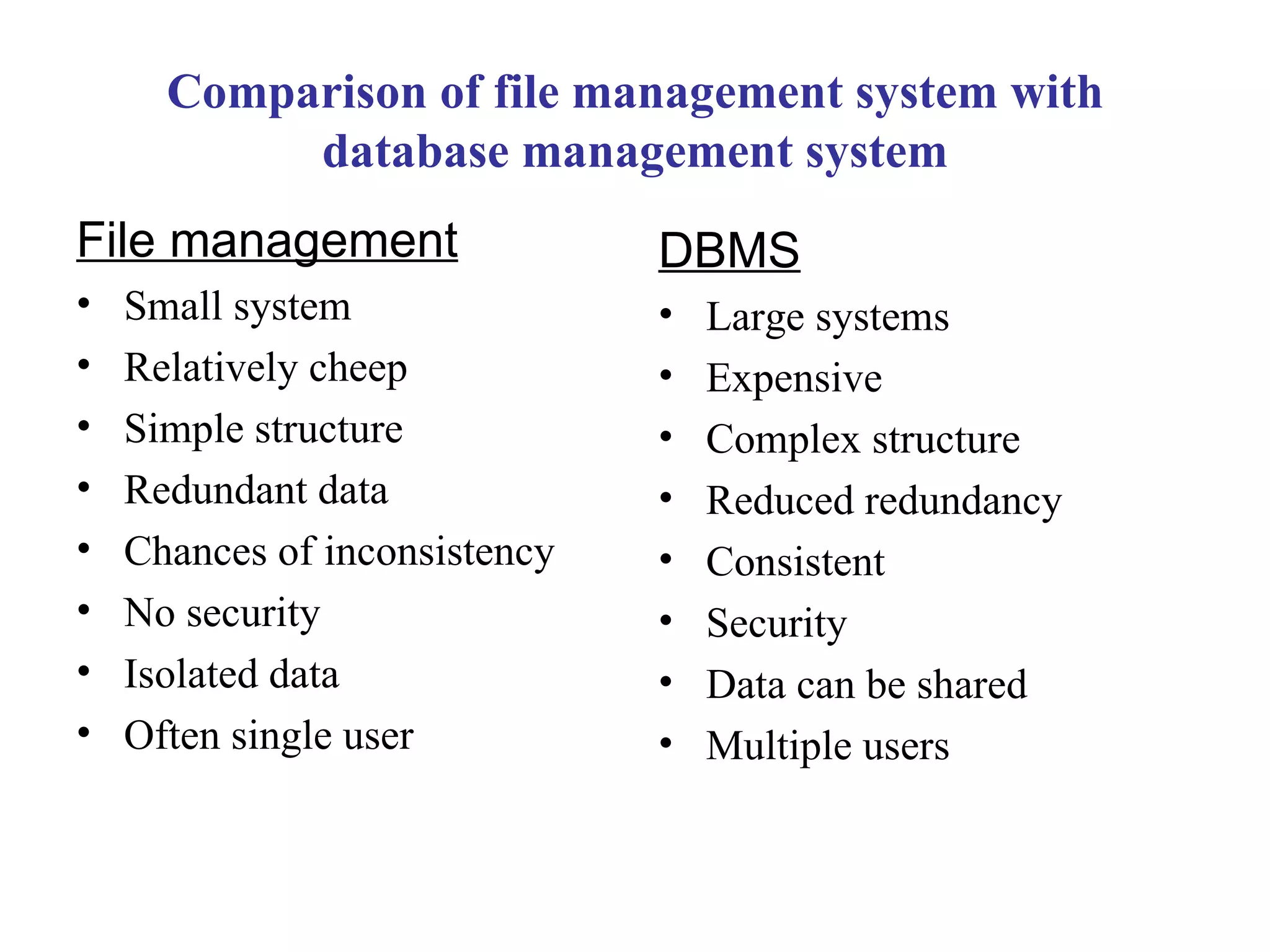
The document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS). It discusses how a DBMS organizes related information into tables with rows and columns to create a database. It also describes common database operations like insertion, updation, deletion, and retrieval. Additionally, it outlines the key components of a DBMS including hardware, software, data, users, and procedures. The document highlights advantages like data sharing and integrity as well as disadvantages such as complexity and costs of a DBMS compared to traditional file management systems.