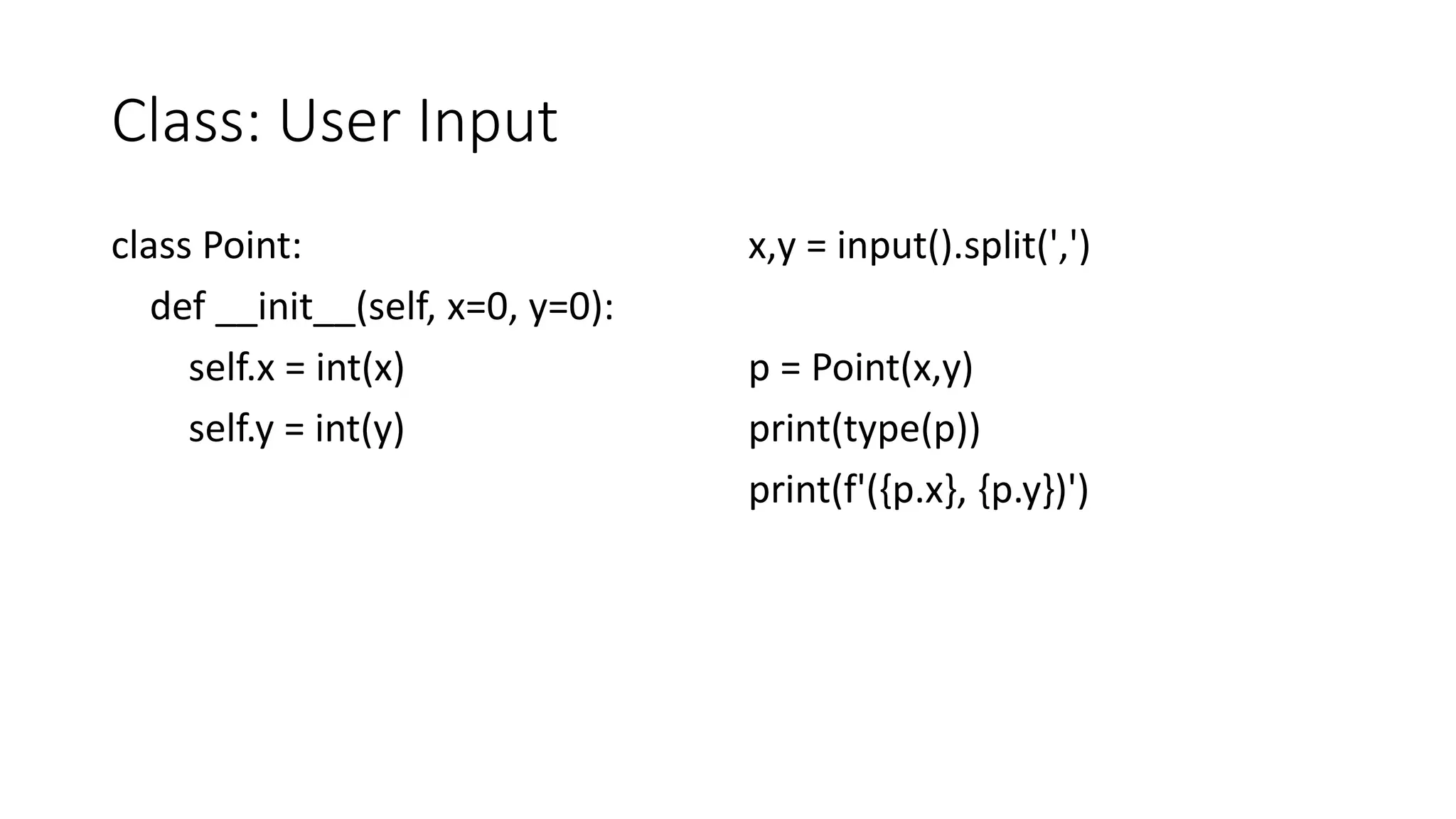
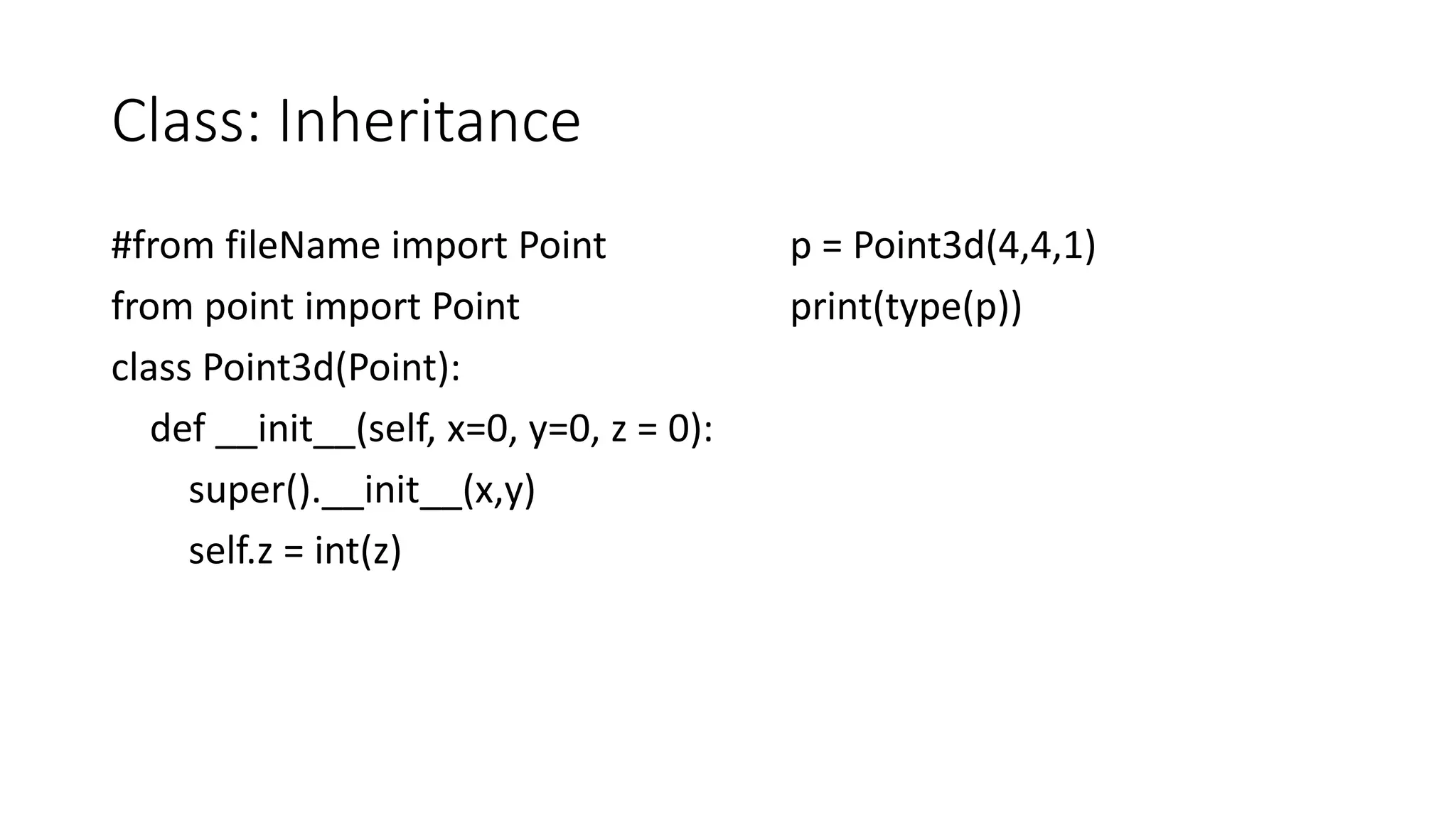
The document discusses object-oriented programming in Python using a Point class as an example. It covers defining a Point class with x and y attributes, initializing points, overloading operators like addition and print, adding methods like calculating distance and slope between points, handling errors, and inheriting from the Point class to create a Point3d class. The goal is to demonstrate key OOP concepts in Python including classes, objects, methods, operator overloading, inheritance and exceptions.










![Magic Methods: Binary Operators
• https://www.python-course.eu/python3_magic_methods.php
• + __add__(self, other)
• - __sub__(self, other)
• * __mul__(self, other)
• // __floordiv__(self, other)
• / __truediv__(self, other)
• % __mod__(self, other)
• ** __pow__(self, other[, modulo])
• << __lshift__(self, other)
• >> __rshift__(self, other)
• & __and__(self, other)
• ^ __xor__(self, other)
• | __or__(self, other)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6pythonoop-180324065316/75/Lecture-6-python-oop-ewurc-12-2048.jpg)










![Class: Inheritance
def __str__(self):
st = super().__str__()
st = st[:-1]
st += f", {self.z})"
return st
p = Point3d(4,4,1)
print(type(p))
print(p)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6pythonoop-180324065316/75/Lecture-6-python-oop-ewurc-24-2048.jpg)