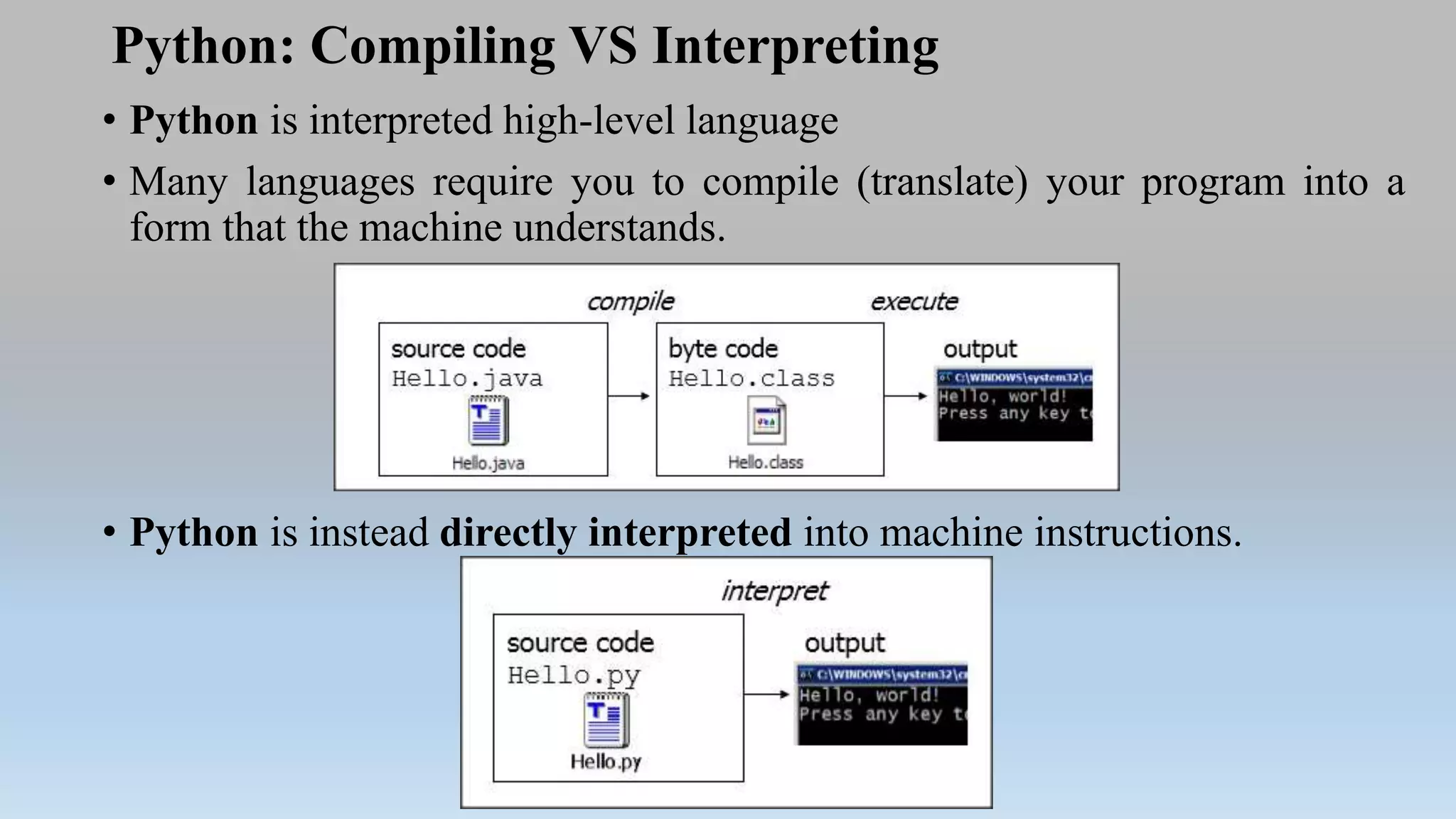
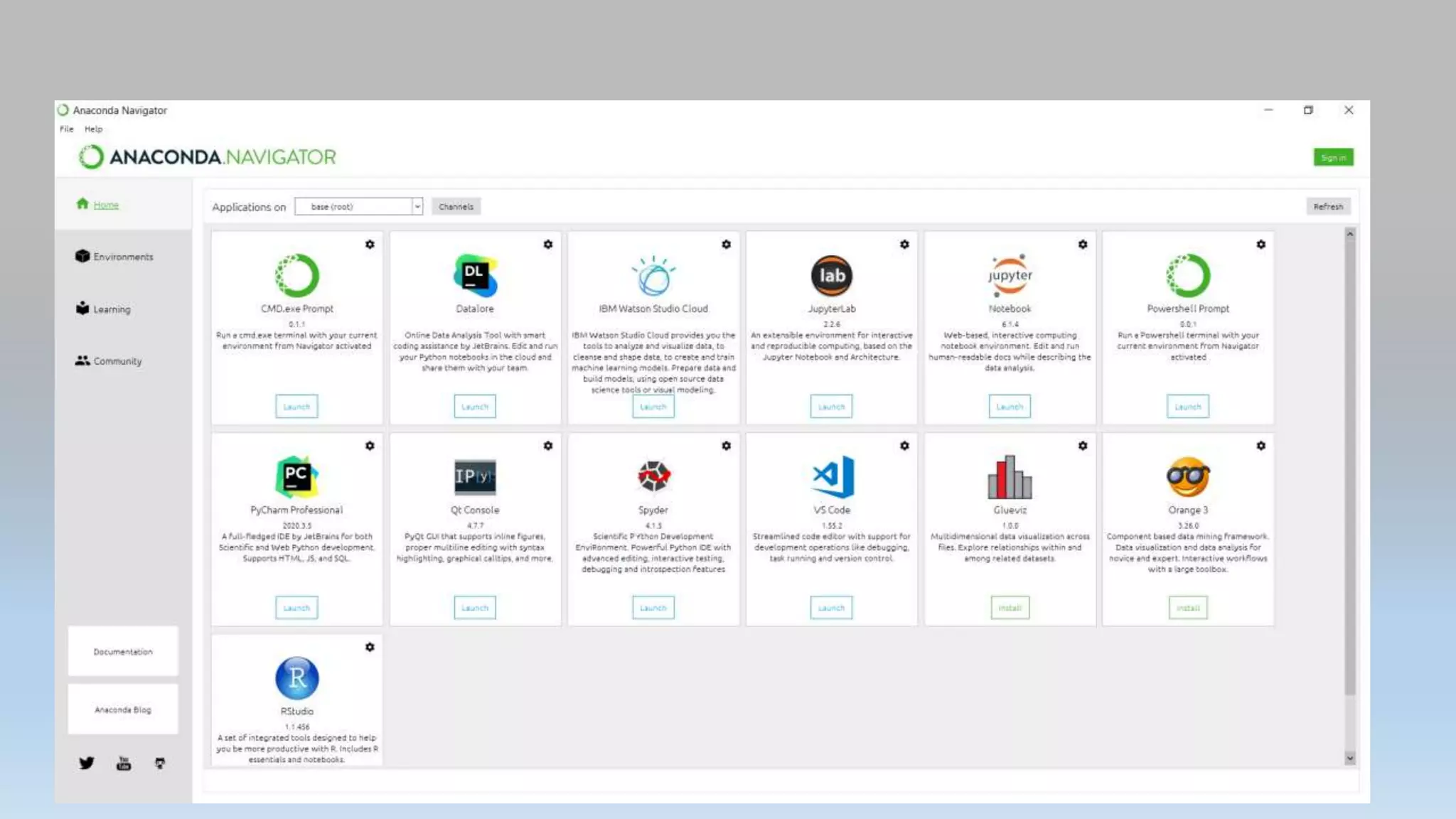
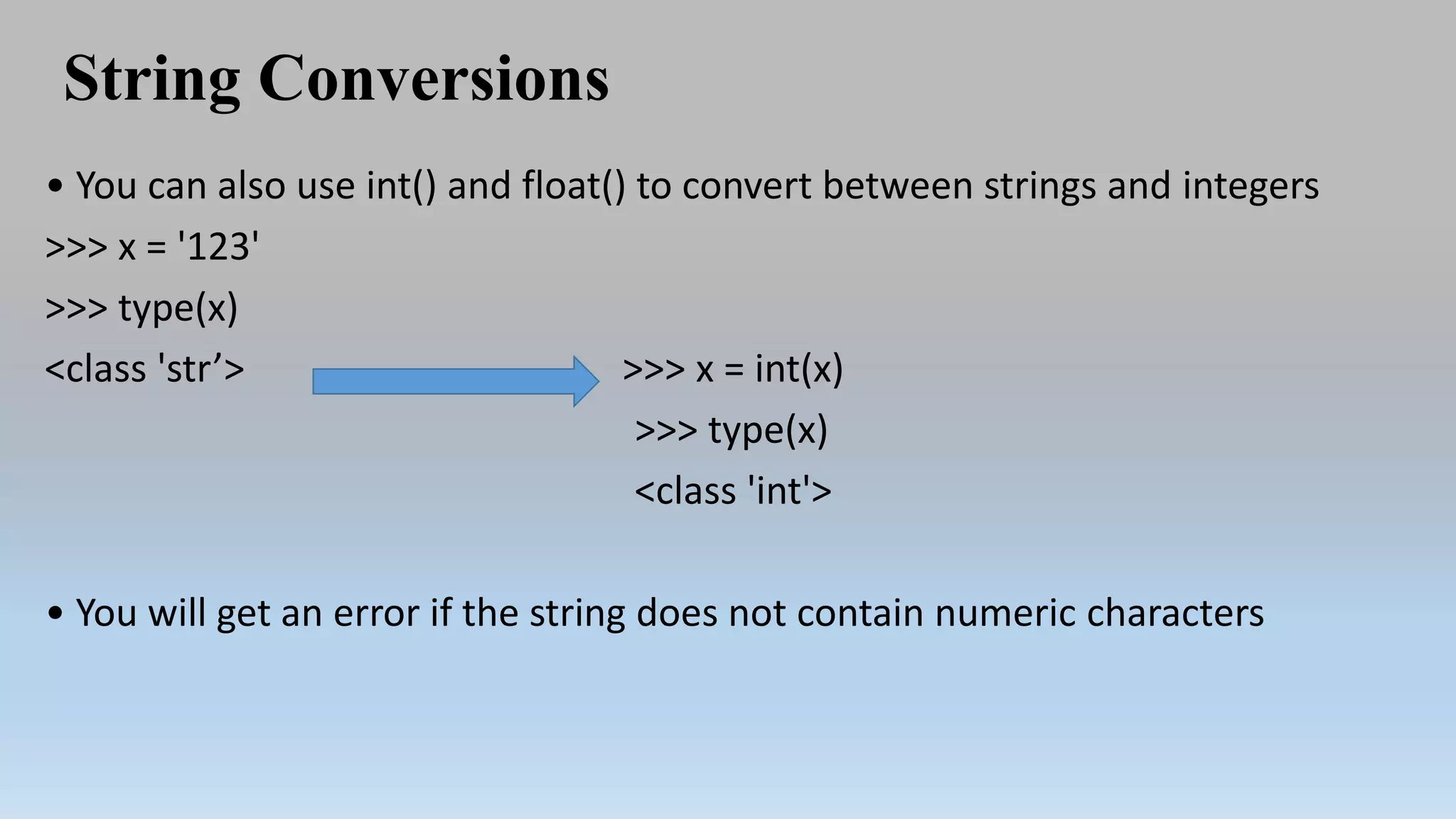
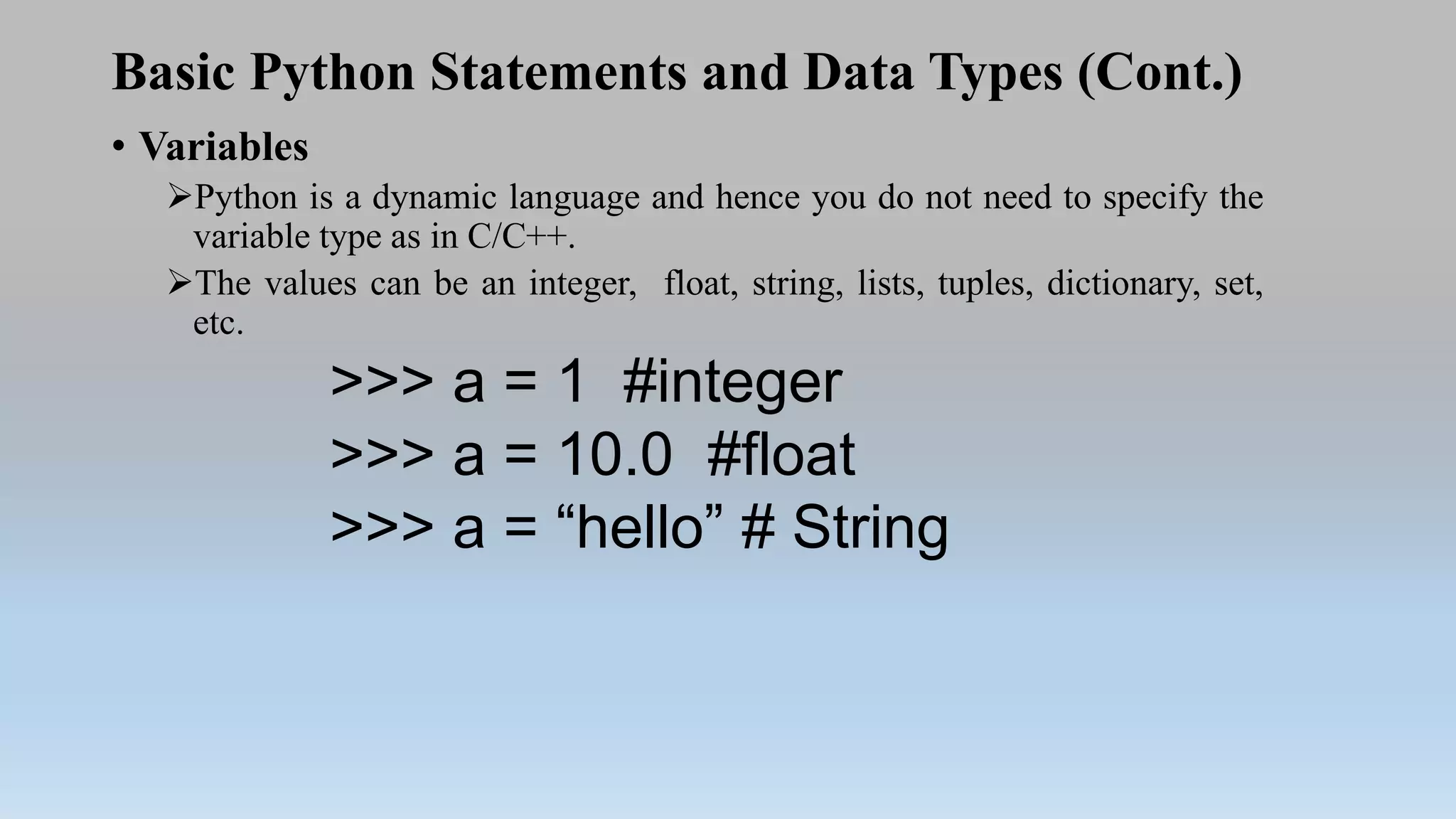
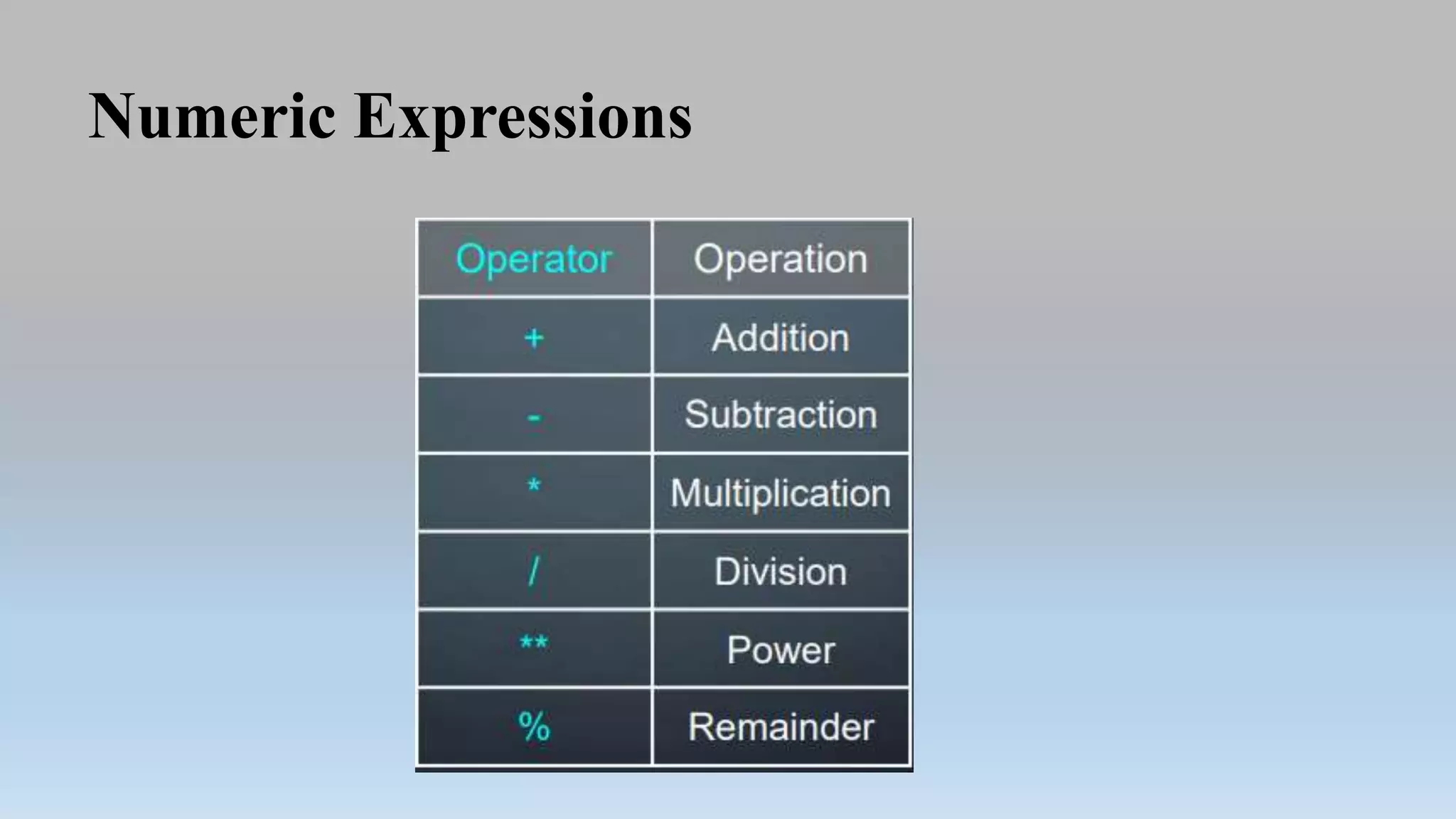
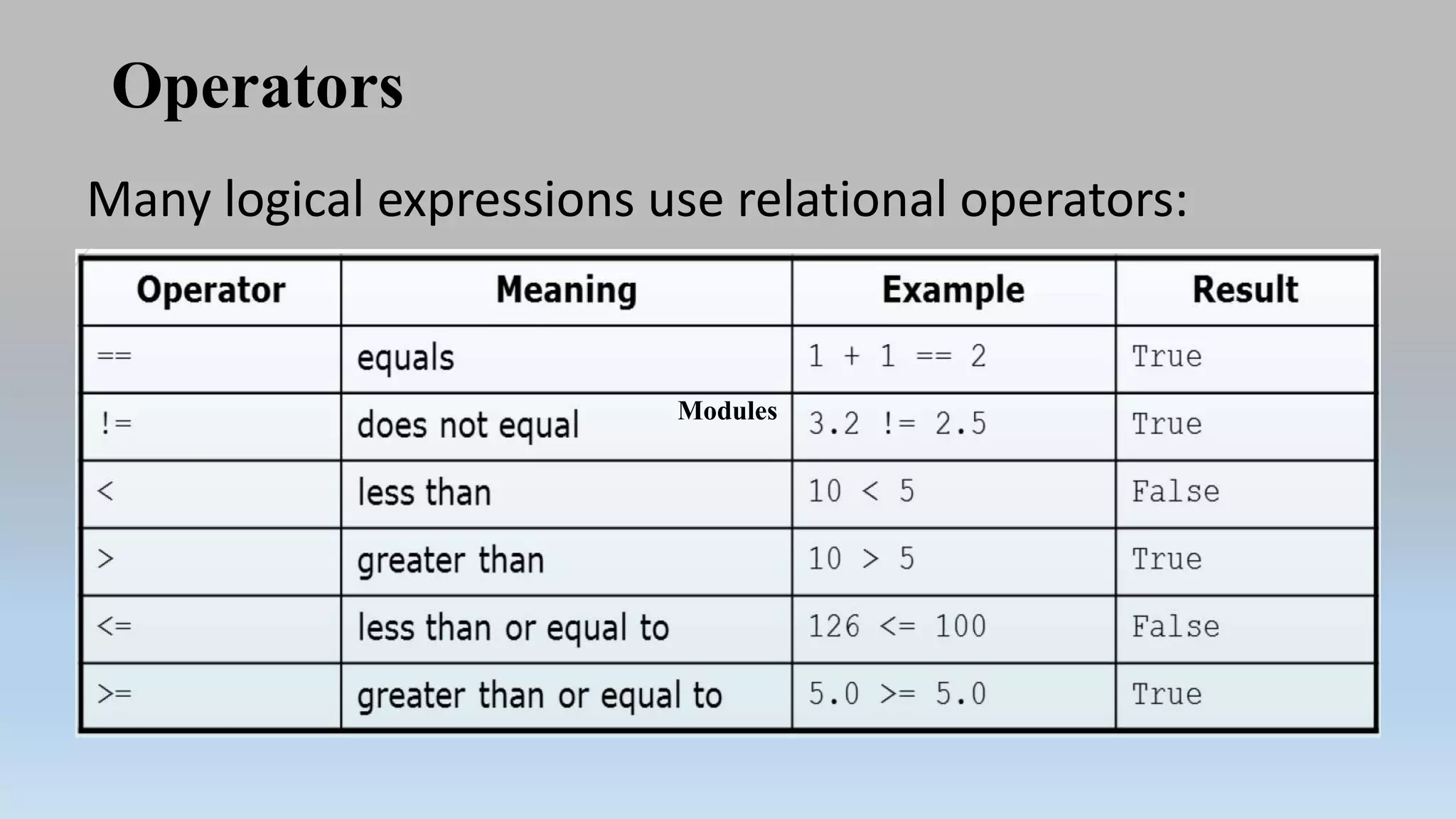
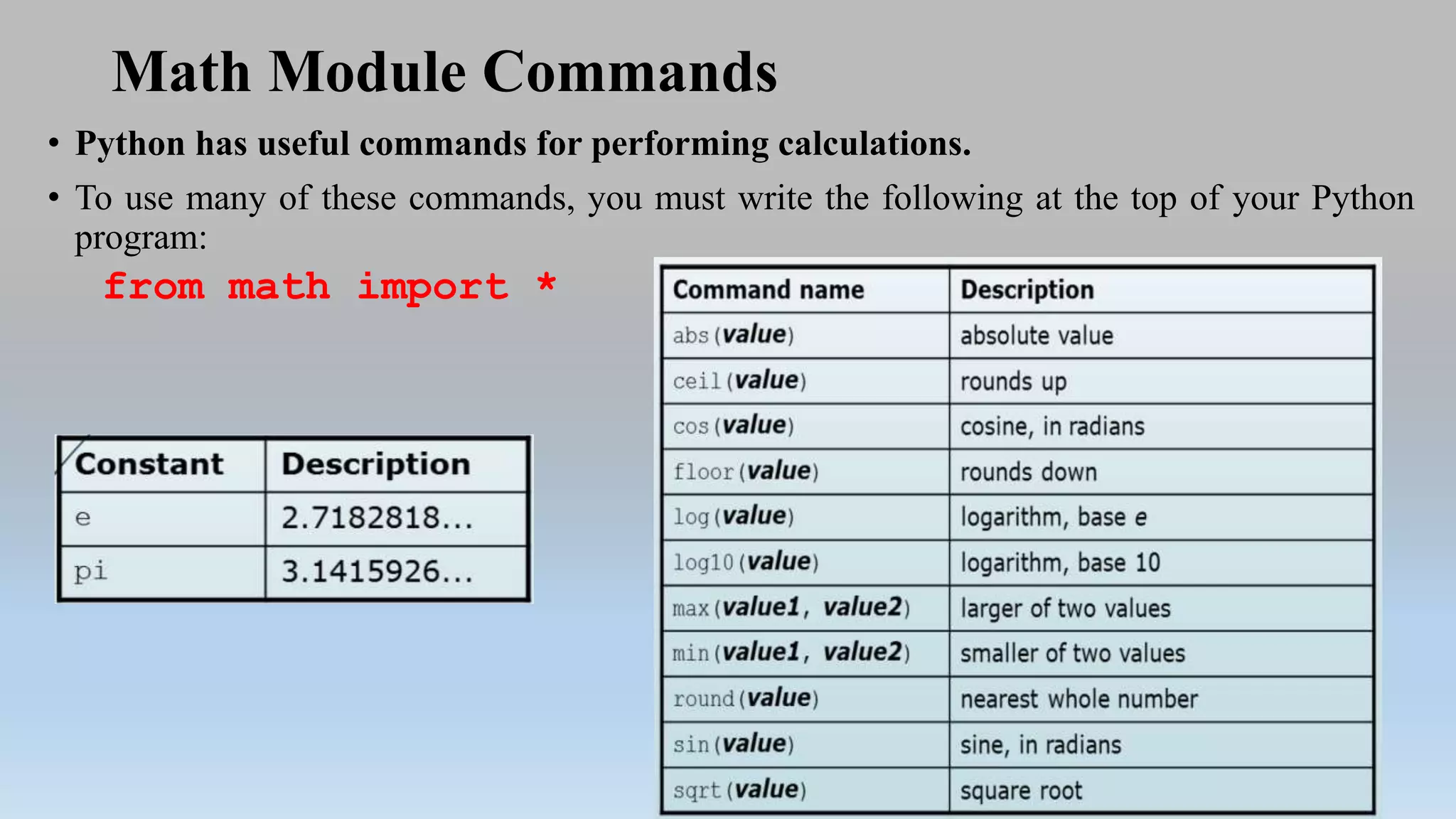
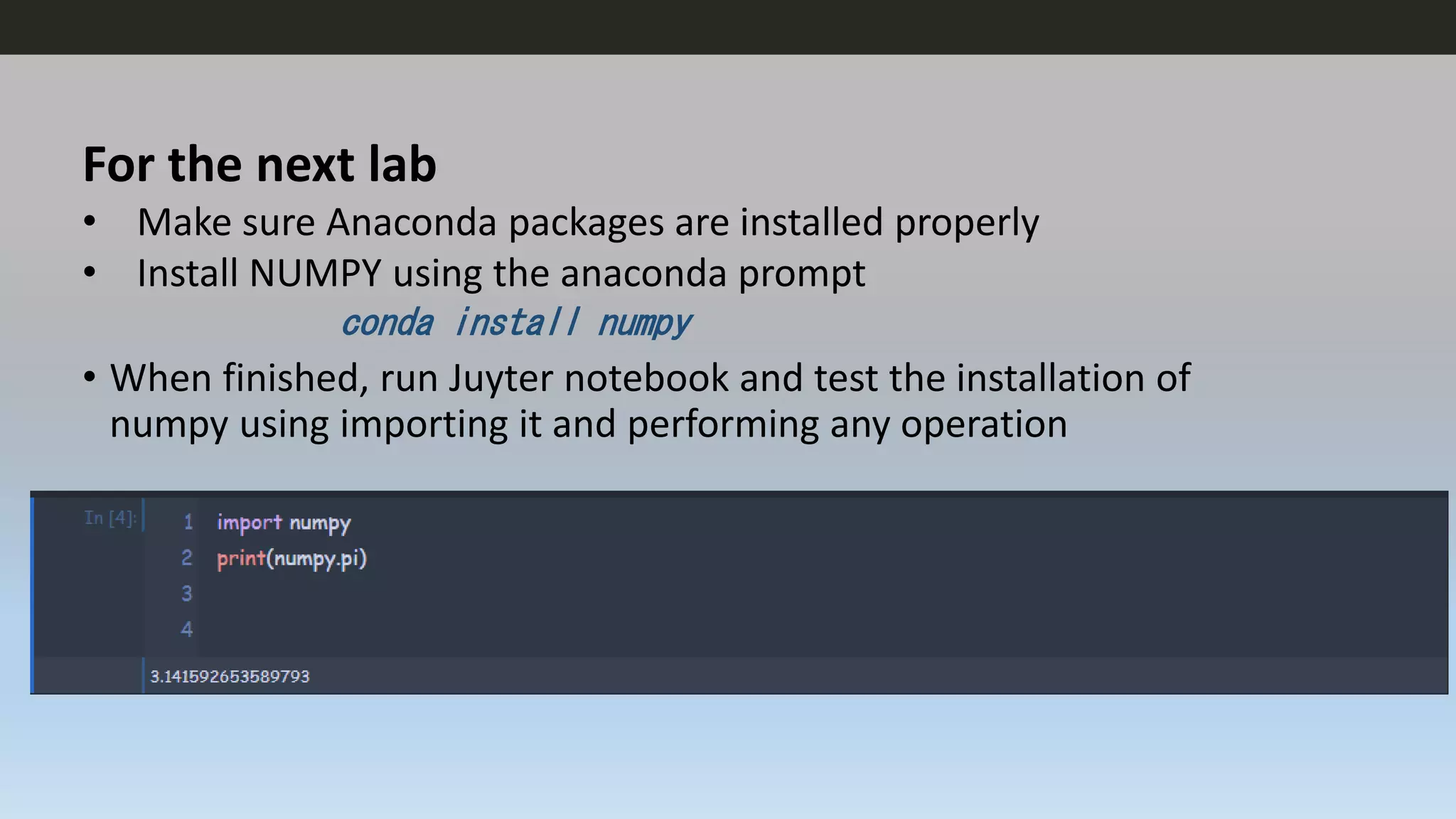
This document provides an introduction to Python programming language. It discusses what Python is, its features, applications, and how it compares to compiled languages in terms of compiling versus interpreting. It also covers installing Python, different Python environments like the Python shell, IDLE, Jupyter Notebook, and Anaconda. Basic Python concepts like variables, data types, operators, functions, modules, and math module commands are explained. The reader is instructed to install NumPy and SciPy using conda for the next lab and test the installations.