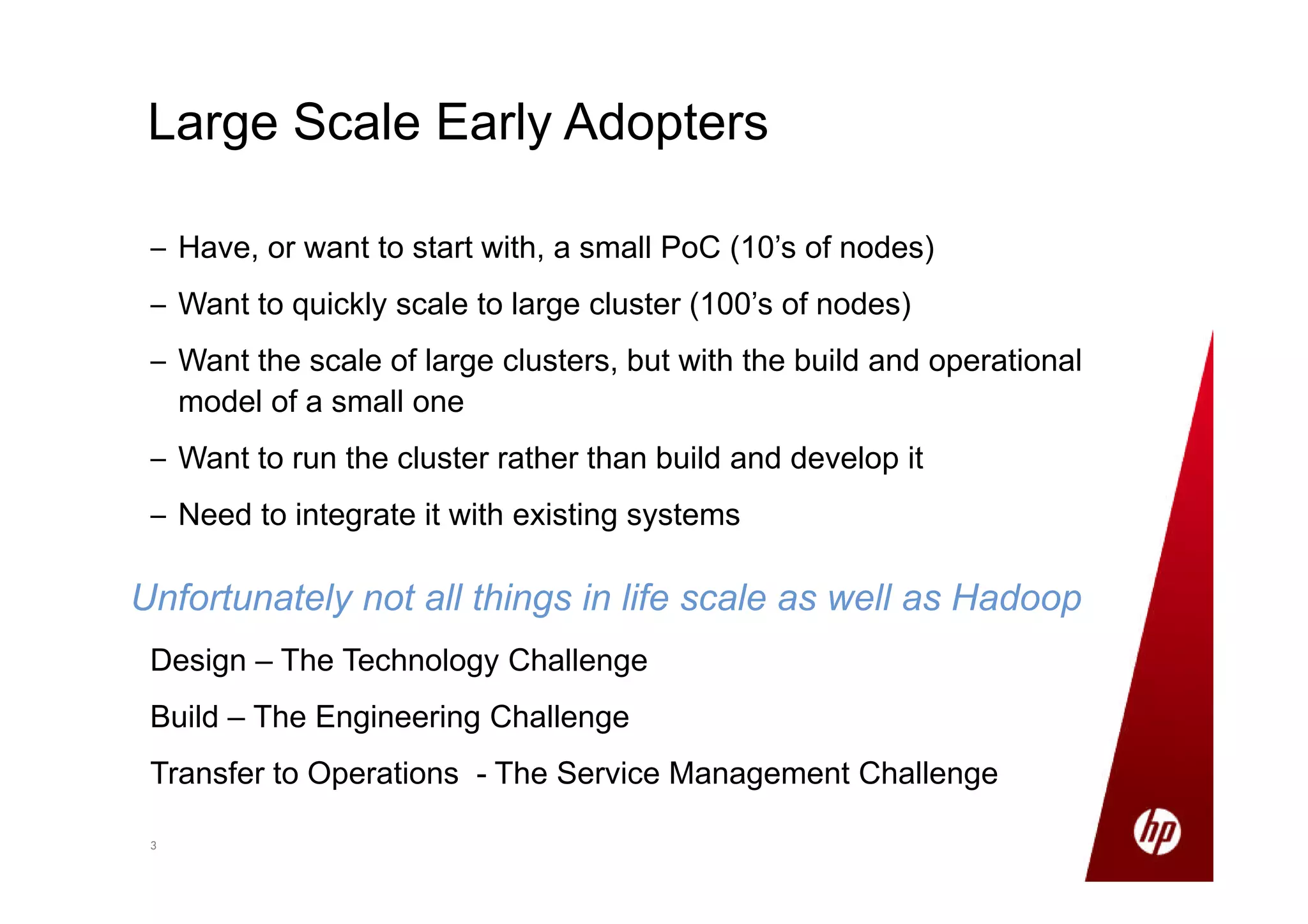
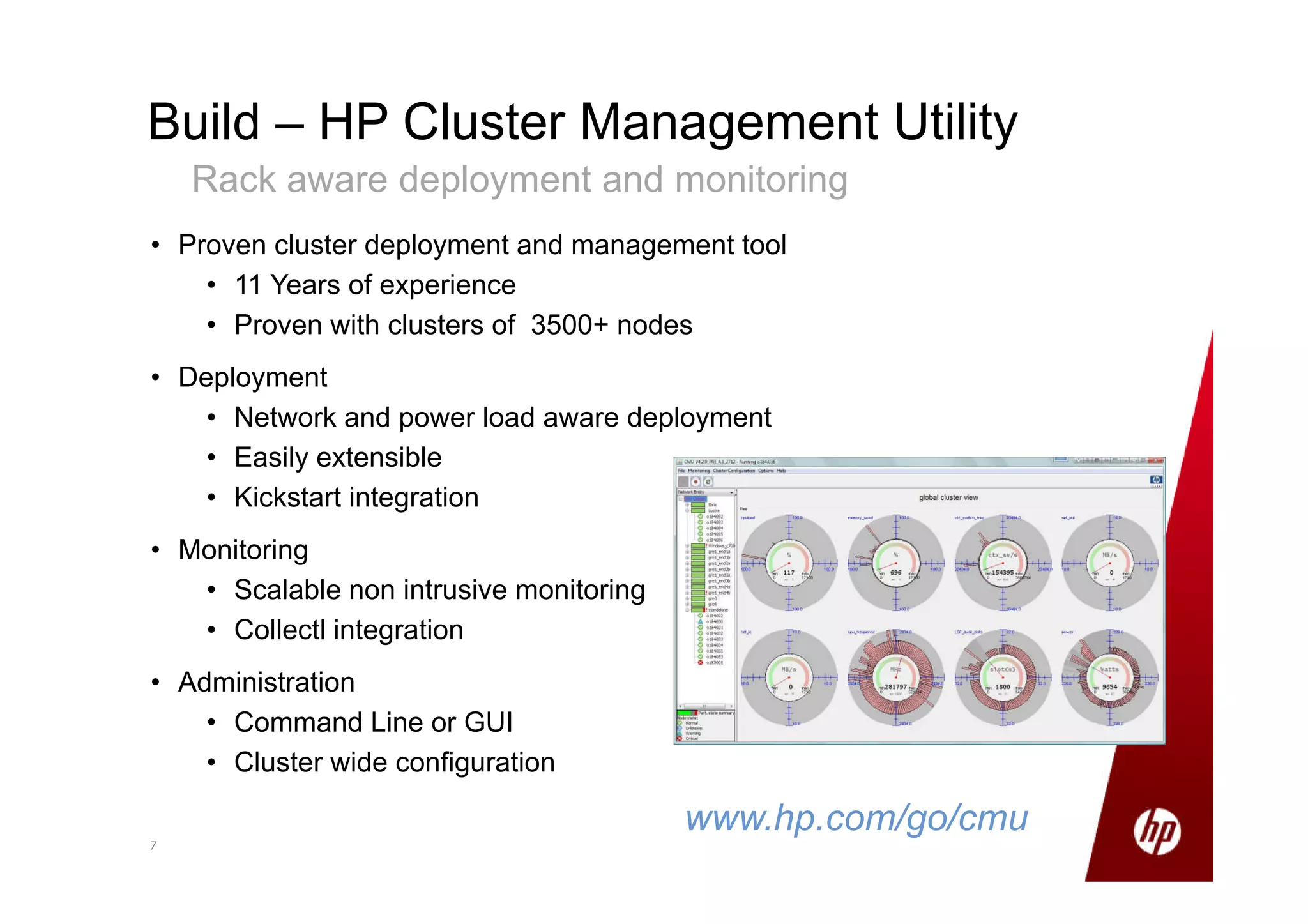
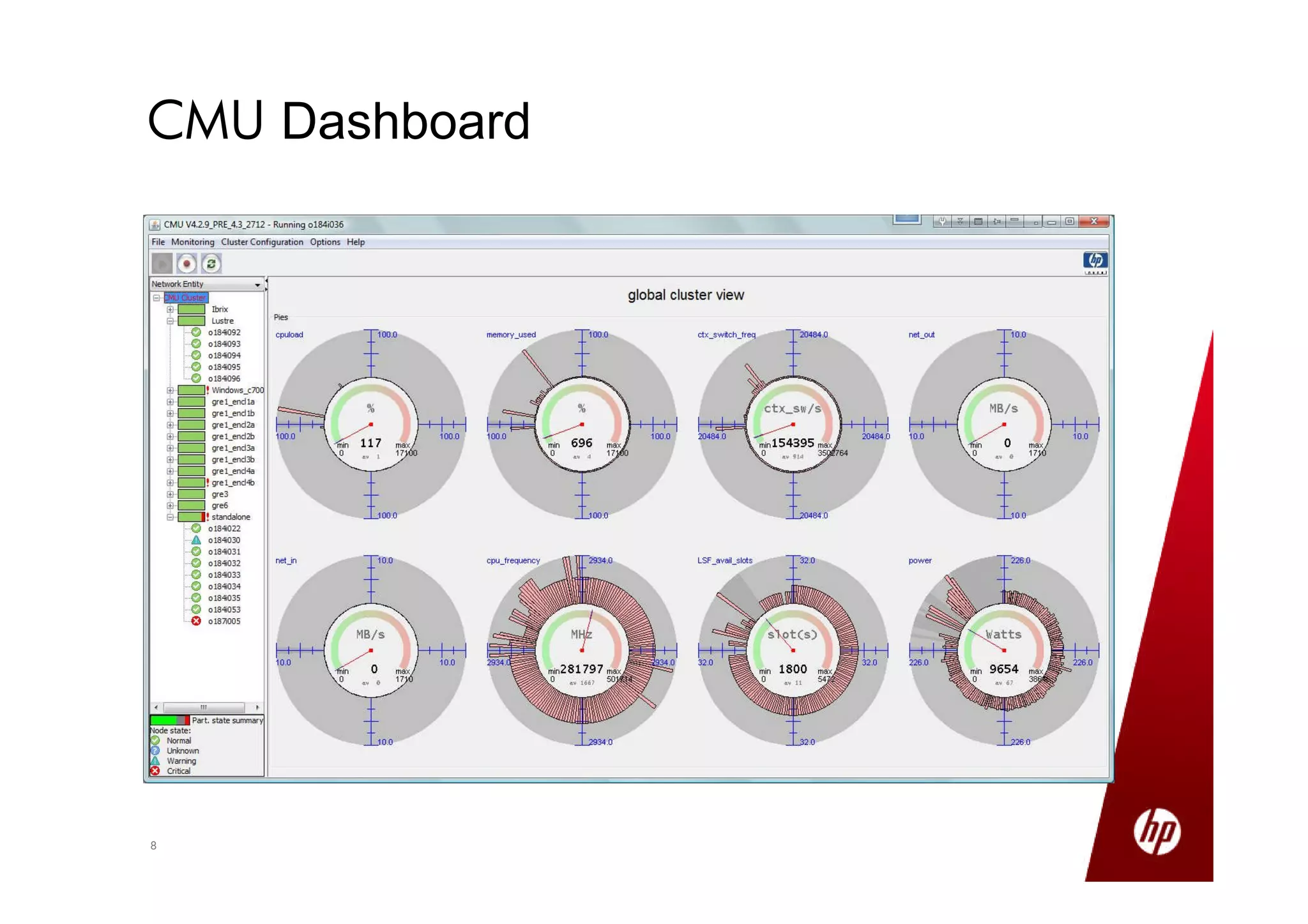
Small production clusters can be built and run by a few skilled people and are a natural extension of conventional IT, while large clusters require more pioneers and a large development staff to deal with the challenges of scale. For those wanting to start small but scale large, it is important to select the right server configuration and network setup, build the cluster consistently in a factory setting if possible, and treat core nodes as more important than data nodes when monitoring cluster health and operations. Not all aspects of IT scale as well as Hadoop, so the operational model must be designed to support large clusters.