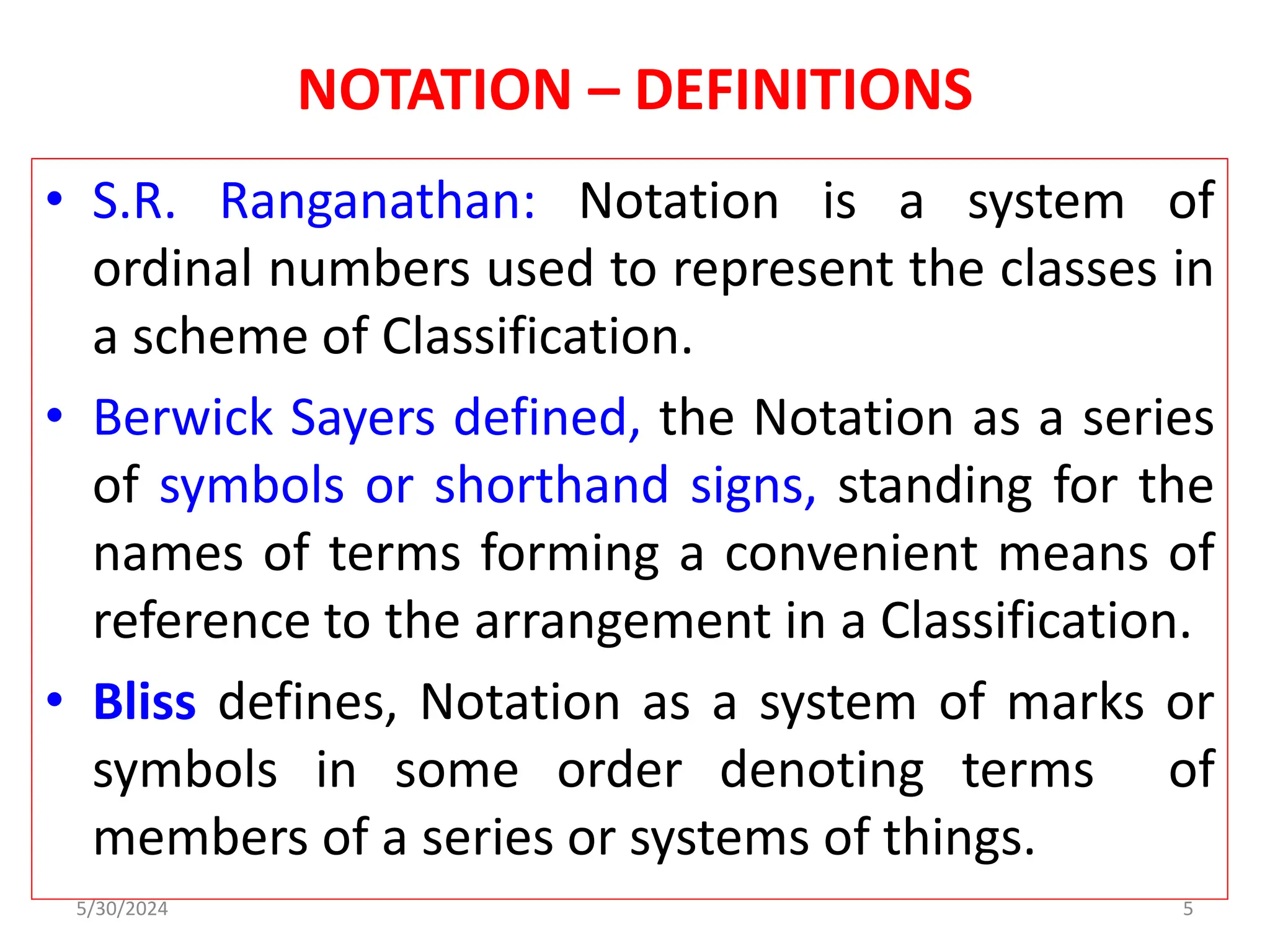
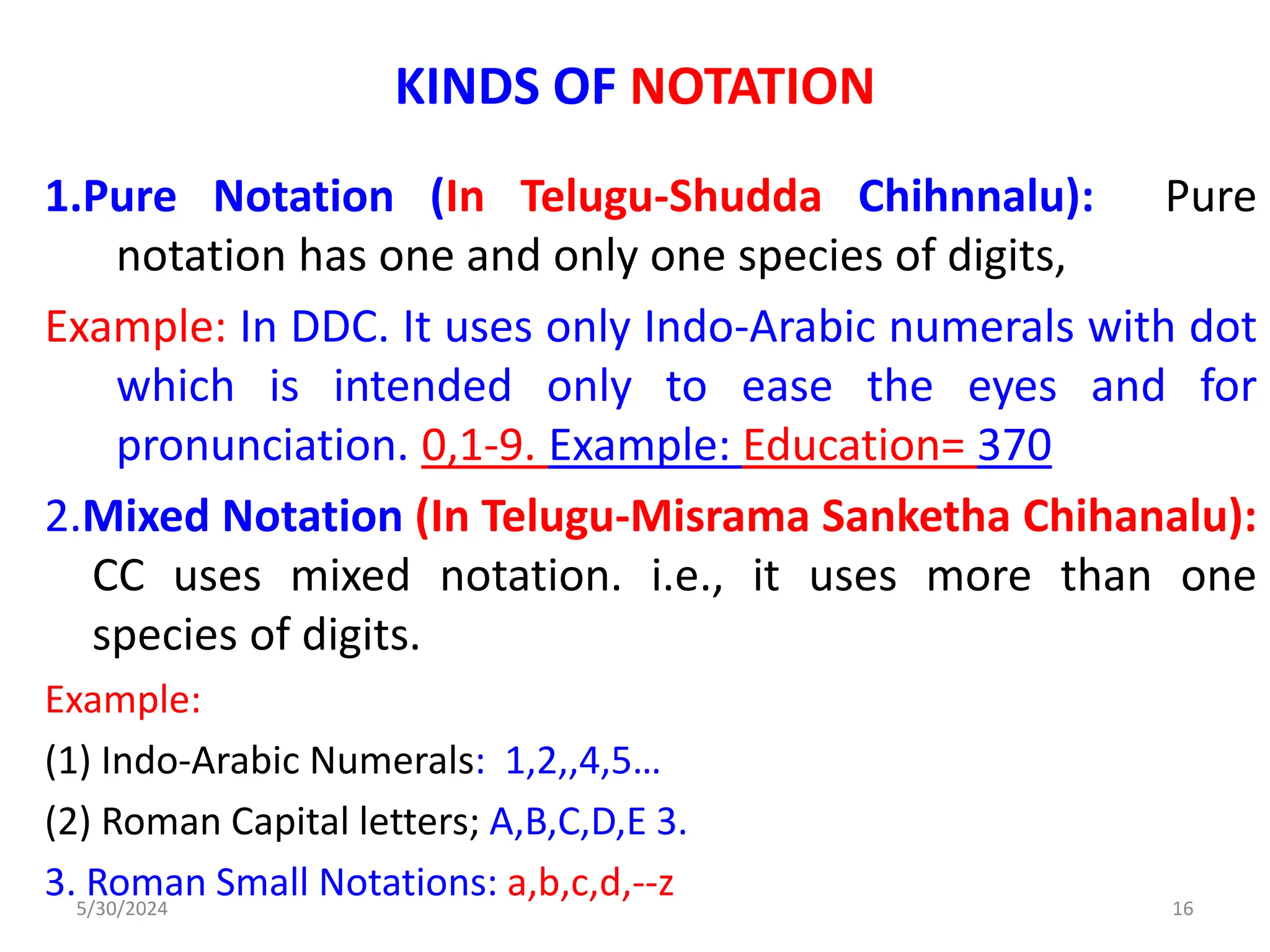
This document discusses the notation system, devices, and mnemonics used in library classification, particularly focusing on their definitions, purpose, and qualities. It highlights the advantages of mnemonics in classification schemes and details the structure and assignment of call numbers for books in libraries. The document emphasizes the importance of notational systems in organizing and simplifying access to information within library science.


































![CC: Formula of Book Number:
[L][F][Y][A].[V]-[S];[C]:[Cr]
Where
• L = Language of the book
• F = Form in which the book is written e.g. index, list,
picture, graph.
• Y = Year of publication of the book
• A = Accession part of the book number. It is given when
more than one books of the same subject published in
the same year are acquired in the library
• V = Volume the number is given when a multivolume
book is acquired in the library
5/30/2024 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/libraryclassification-notation-240530145927-bfde0288/75/Library-Classification-NOTATION-Notationspt-39-2048.jpg)