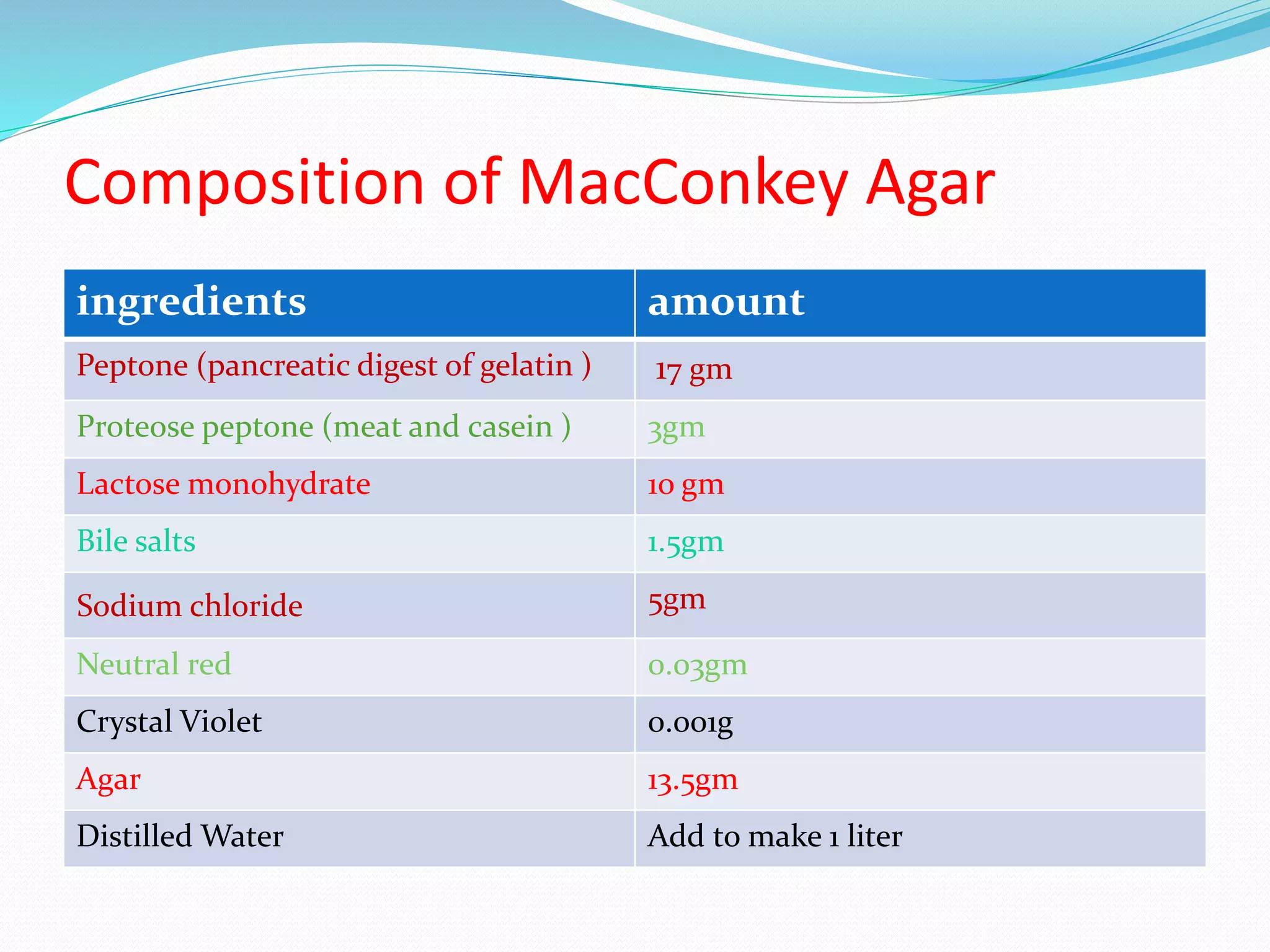
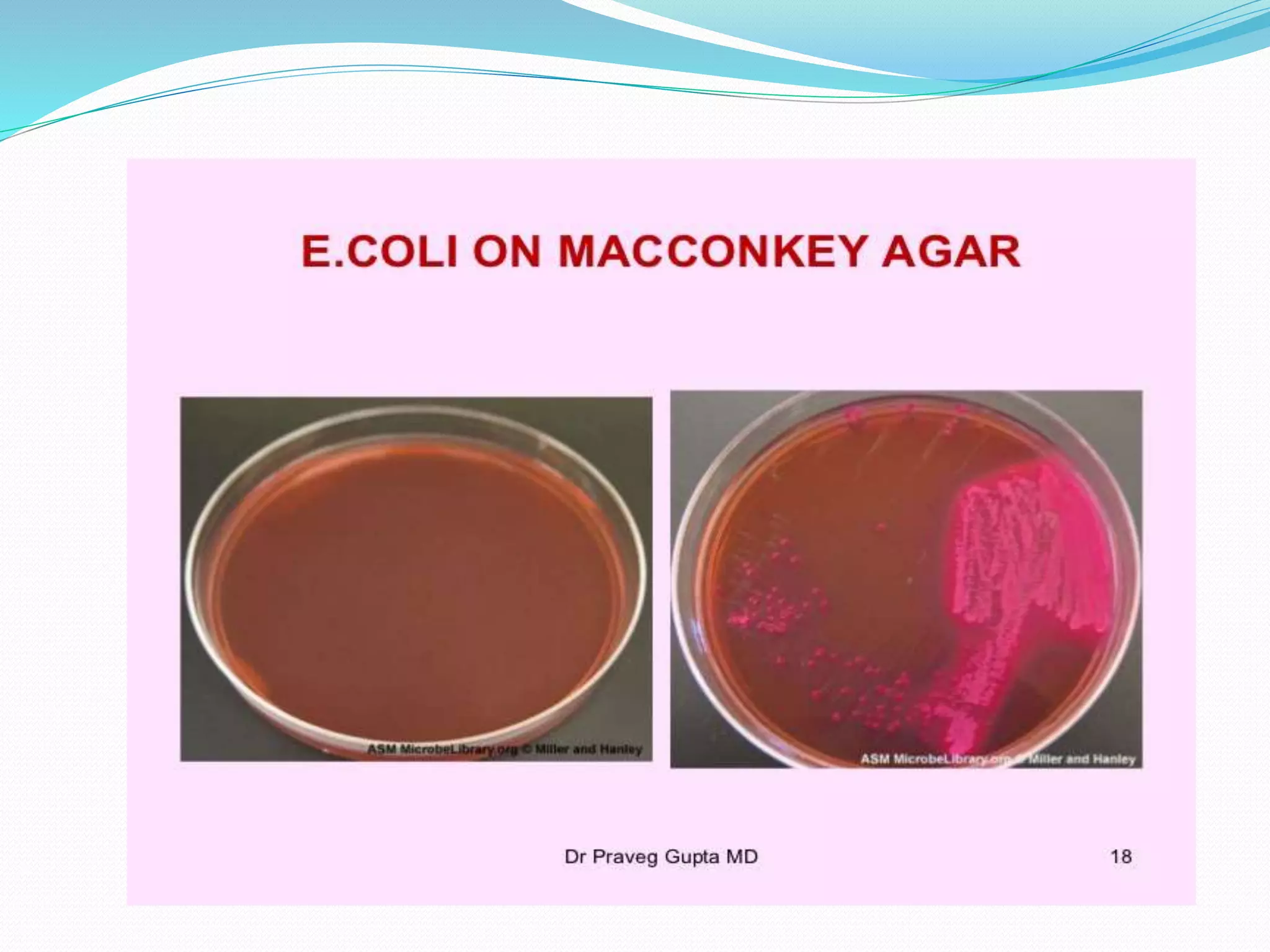
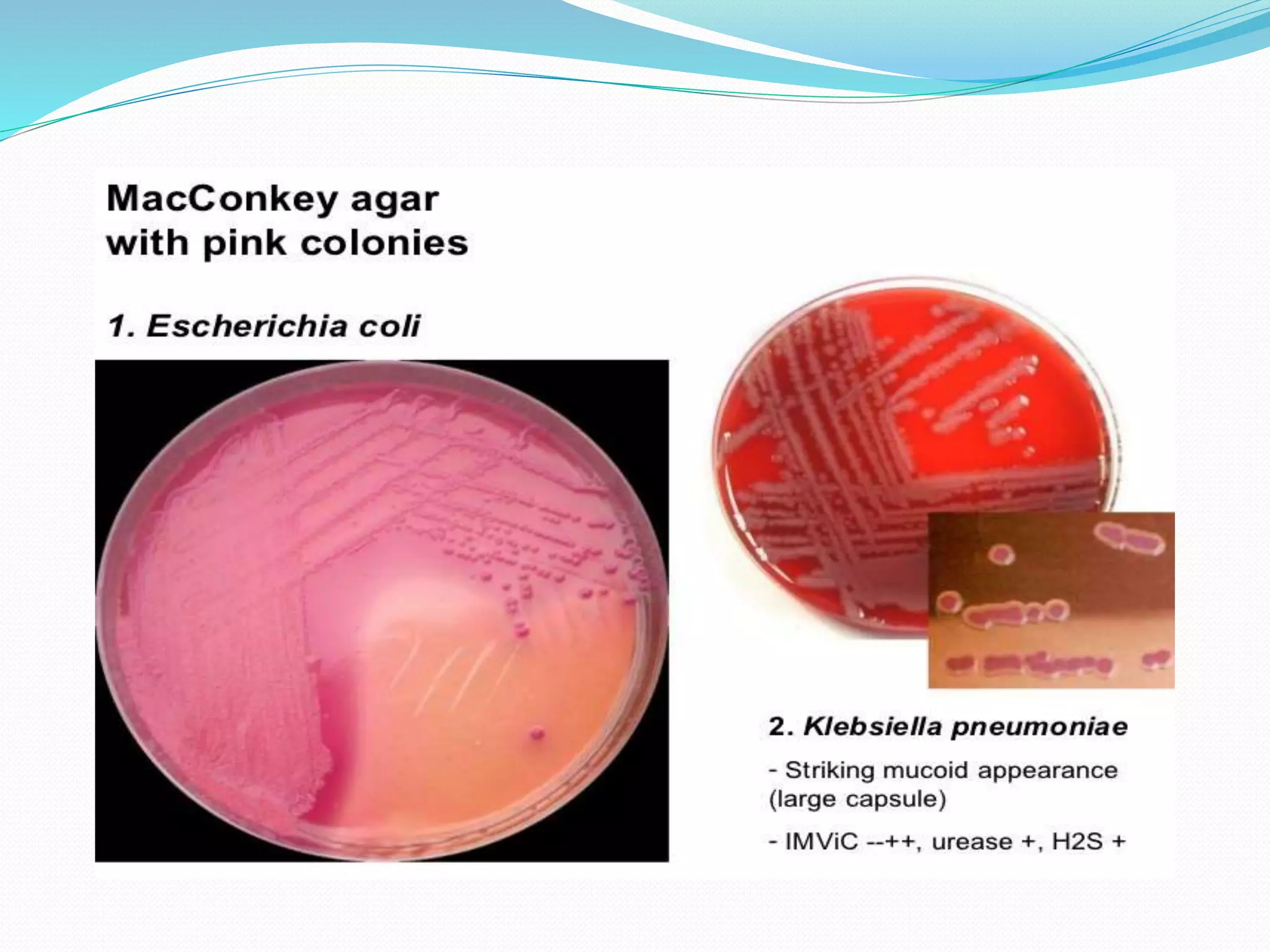
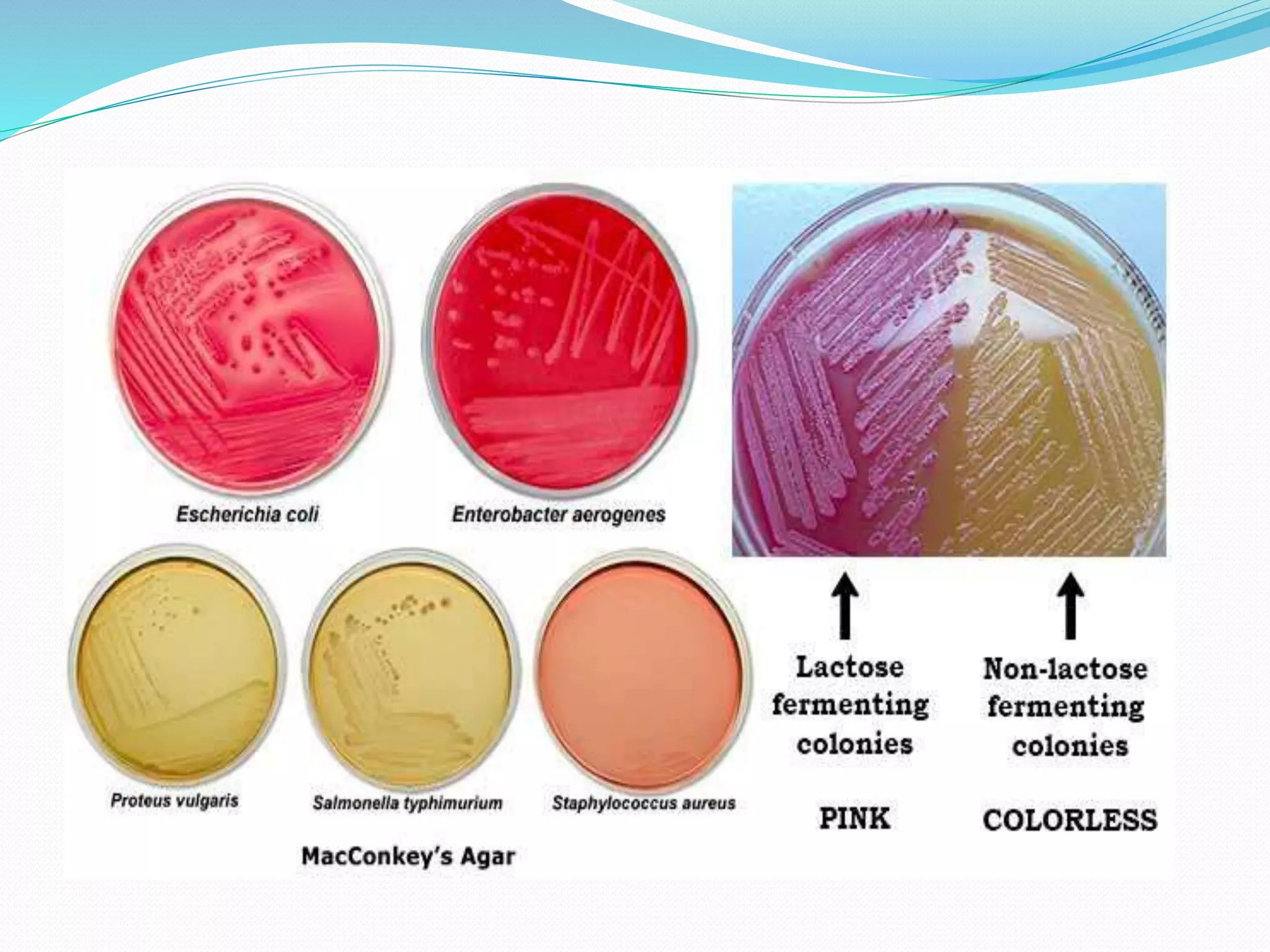
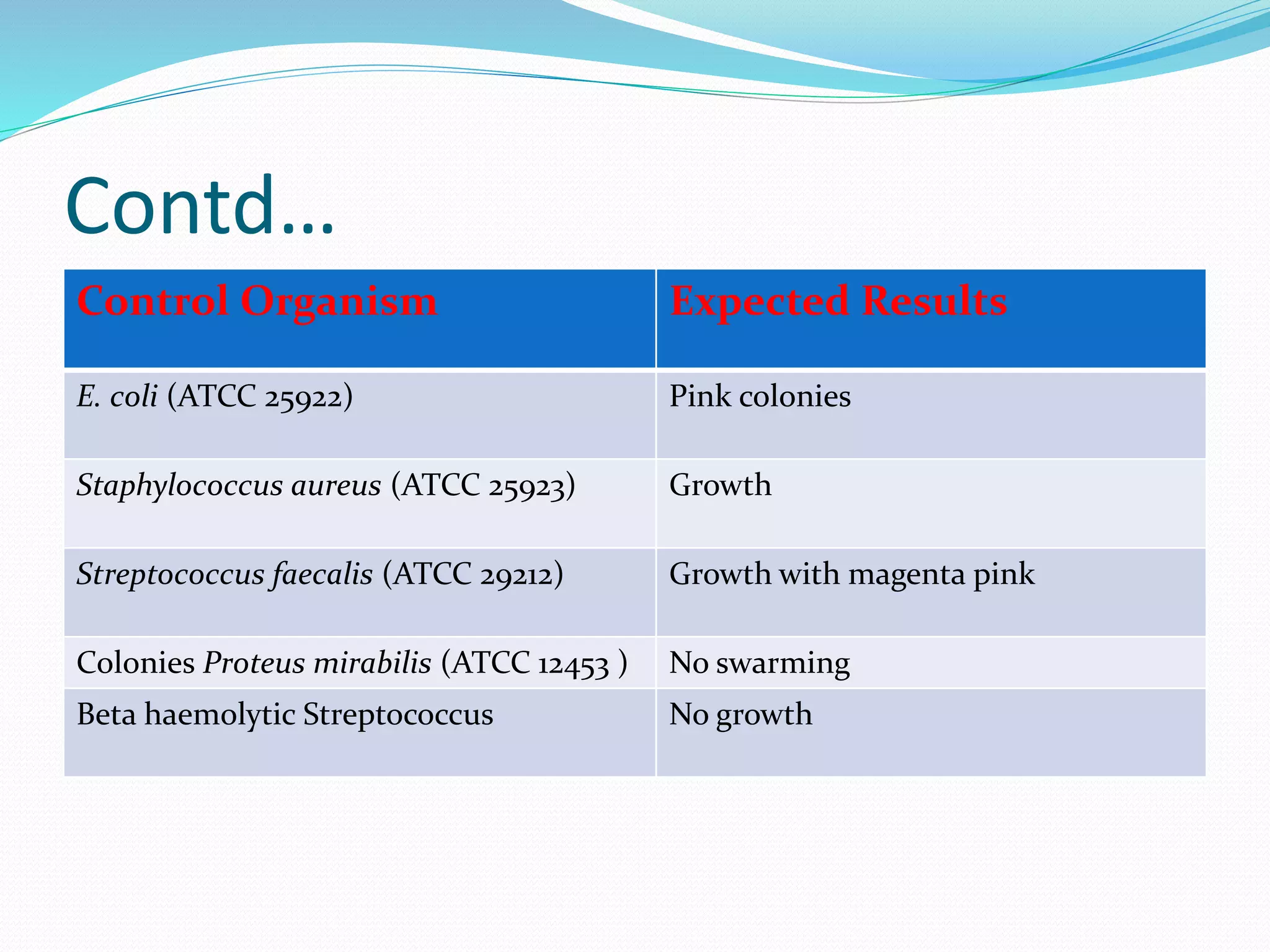
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential medium used to isolate and differentiate gram-negative enteric bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella. It contains lactose and bile salts which allow lactose-fermenting bacteria to grow as red or pink colonies due to acid production, while lactose-nonfermenters form colorless colonies. MacConkey agar is widely used to detect intestinal pathogens in food, water and clinical samples. Quality control involves testing for growth of E. coli and no growth of beta hemolytic Streptococcus.