This document summarizes Abram Hindle's presentation on C Perl, Inline::C, XS, and Perl guts. The presentation covers how to use Inline::C to write Perl subroutines in C, the basic data types and functions for manipulating scalars, arrays, and hashes from C using the Perl API, and how to integrate C code into Perl using XS. It provides examples for Inline::C and discusses where to find documentation and help.


![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
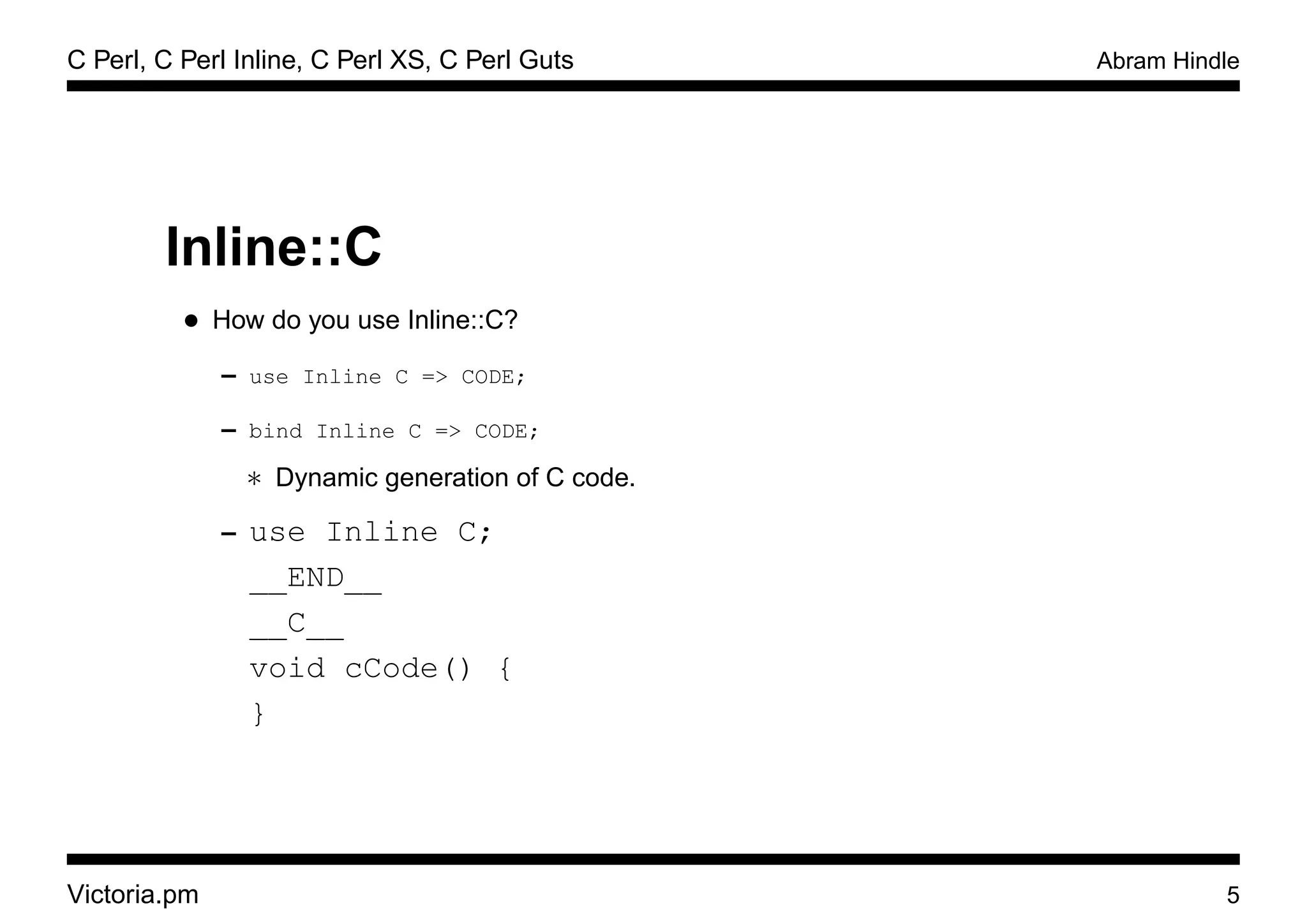
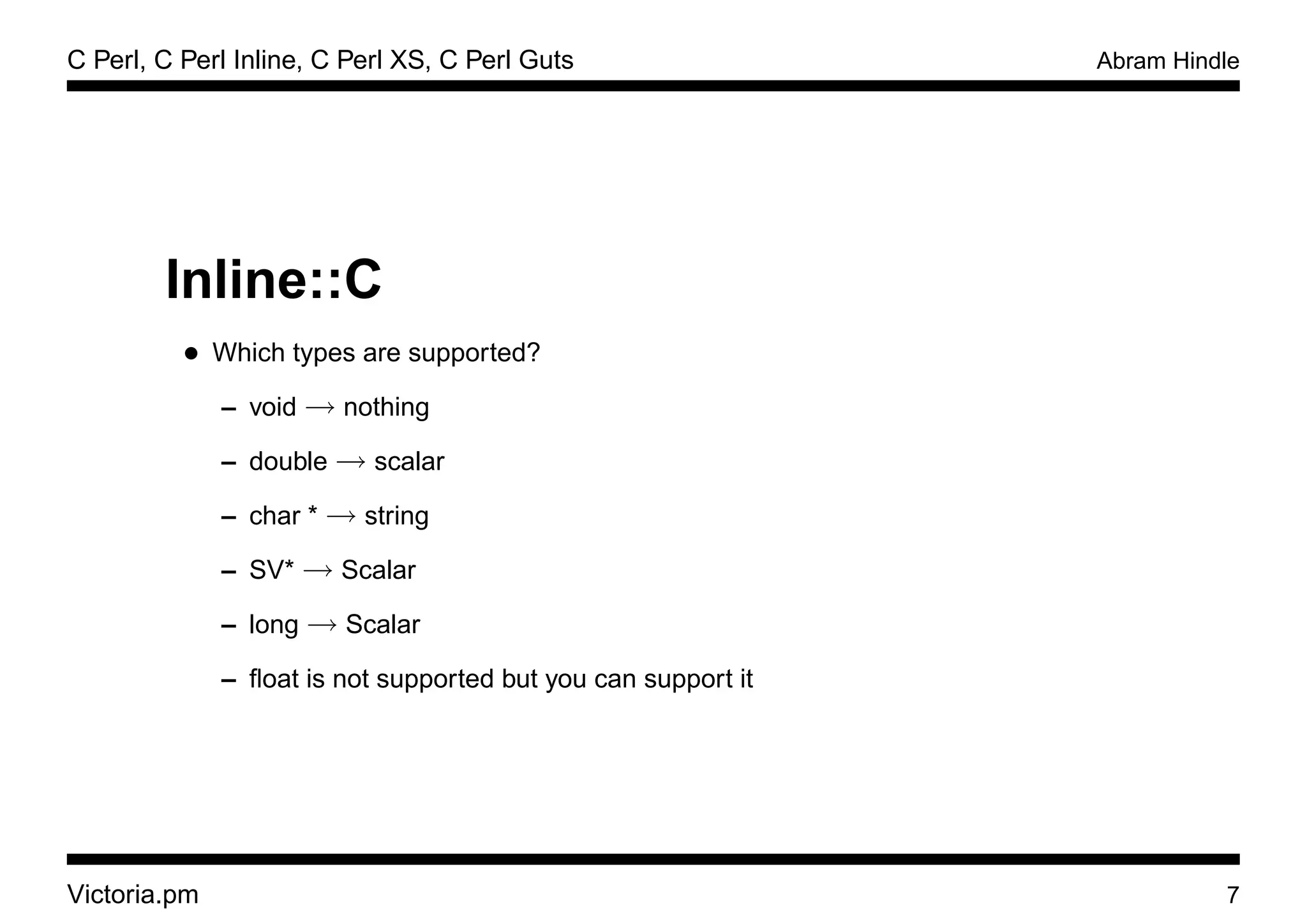
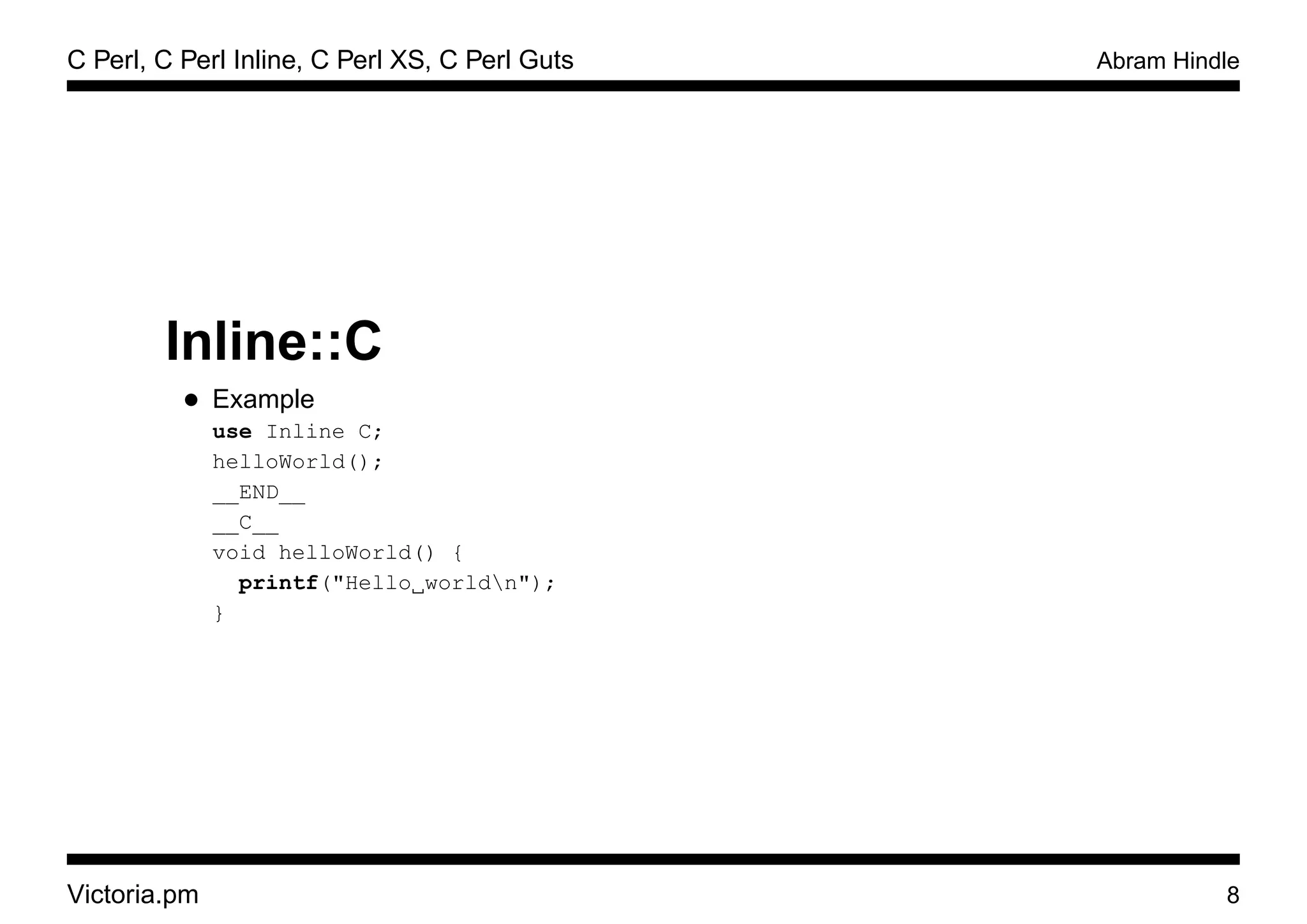
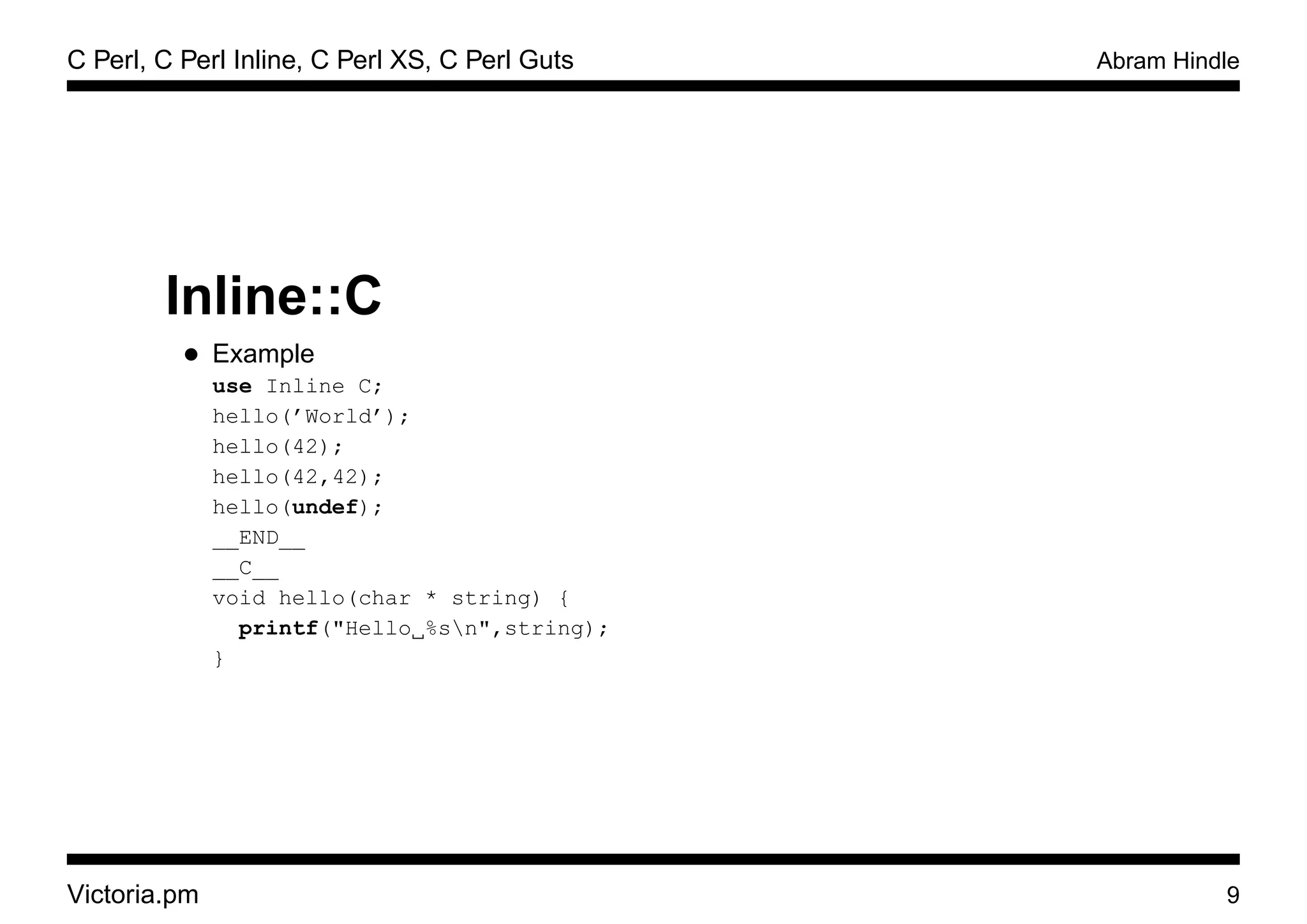
Inline::C
• What is it?
– Write Perl Subroutines in C [1]
– Compile and Link C into Perl
– Embed subroutines into perl scripts and modules
– Automatically Wrap functions based on prototypes.
Victoria.pm 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-4-2048.jpg)



![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
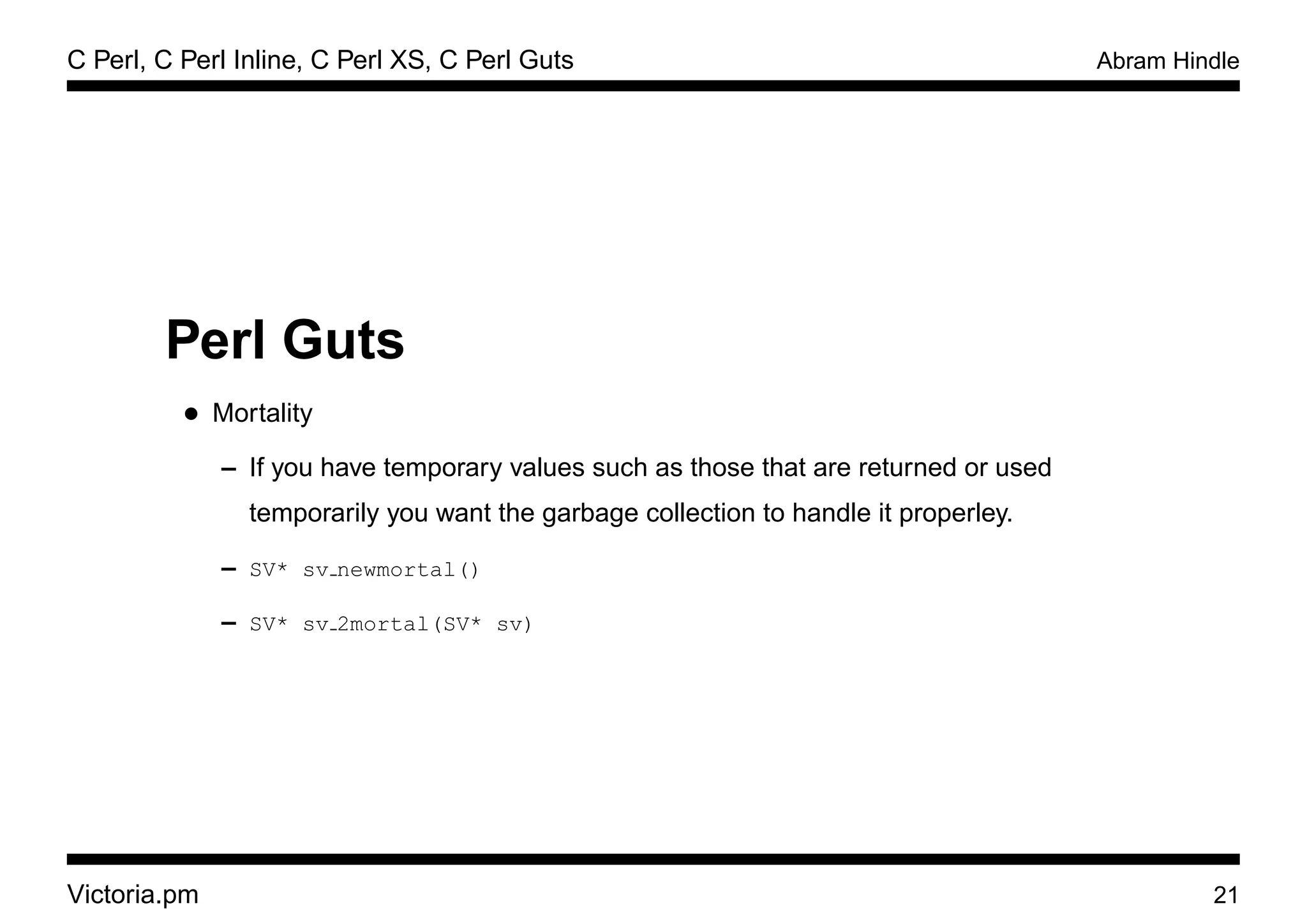
Perl Guts
• Types in C [5]
– SV - Scalar Value
– AV - Array Value
– HV - Hash Value
– IV - Integer Value *
– UV - Unsigned Value *
– NV - Double Value *
– PV - String Value *
– * return values
Victoria.pm 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-12-2048.jpg)
![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Convert Scalars [5] ( these are macros )
– int SvIV(SV*)
– unsigned int SvUV(SV*)
– double SvNV(SV*)
– char * SvPV(SV*, STRLEN len)
∗ puts length in len, i is the buffer in SV*
– char * SvPV nolen(SV*)
Victoria.pm 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-13-2048.jpg)
![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Set scalars [5] ( these are macros )
– void sv setiv(SV*, IV);
– void sv setuv(SV*, UV);
– void sv setnv(SV*, double);
– void sv setpv(SV*, const char*);
– void sv setpvn(SV*, const char*, int)
Victoria.pm 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-14-2048.jpg)
![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Create scalars [5] ( these are macros )
– SV* newSViv(IV);
– SV* newSVuv(UV);
– SV* newSVnv(double);
– SV* newSVpv(const char*, int);
– SV* newSVpvn(const char*, int);
– SV* newSVpvf(const char*, ...);
– SV* newSVsv(SV*);
Victoria.pm 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-15-2048.jpg)
![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Arrays [5]
– Make an array
∗ create - AV* newAV();
∗ create - AV* av make(I32 num, SV **ptr);
– Operations
∗ push - void av push(AV*, SV*);
∗ pop - SV* av pop(AV*);
∗ shift - SV* av shift(AV*);
∗ unshift - void av unshift(AV*, I32 num);
Victoria.pm 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-16-2048.jpg)
![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Arrays [5]
– length - I32 av len(AV*);
– fetch - SV** av fetch(AV*, I32 key, I32 lval);
– store - SV** av store(AV*, I32 key, SV* val);
– clear - void av clear(AV*);
– destroy - void av undef(AV*);
– expand - void av extend(AV*, I32 key);
Victoria.pm 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-17-2048.jpg)


![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
Perl Guts
• Package Vars [5]
– SV* get sv("package::varname", TRUE);
– AV* get av("package::varname", TRUE);
– HV* get hv("package::varname", TRUE);
Victoria.pm 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-20-2048.jpg)

![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
XS
• Into the fire: [4] - Some of this is ripped from the perlxstut
– h2xs -A -n PackageName
– Edit PackageName.xs
– perl Makefile.PL
– make
– Make a test script in the PackageName directory
– make install – only do this if your test script has problems finding
PackageName
Victoria.pm 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-23-2048.jpg)





![C Perl, C Perl Inline, C Perl XS, C Perl Guts Abram Hindle
References
[1] I NGERSON , B. Inline::c - write perl subroutines in c.
[2] I NGERSON , B., AND WATKISS , N. Inline - write perl subroutines in other
programming languages.
[3] M AC E ACHERN , D., AND O RWANT, J. perlembed - how to embed perl in your c
program.
[4] O KAMOTO, J. perlxstut - tutorial for writing xsubs.
[5] P ORTERS , P. . perlguts - introduction to the perl api.
[6] R OEHRICH , D., O KAMOTO, J., AND S TUHL , B. perlapi - autogenerated
documentation for the perl public api.
[7] R OEHRICH , D., AND P ORTERS , T. P. perlxs - xs language reference manual.
Victoria.pm 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2620571/75/March2004-CPerlRun-29-2048.jpg)