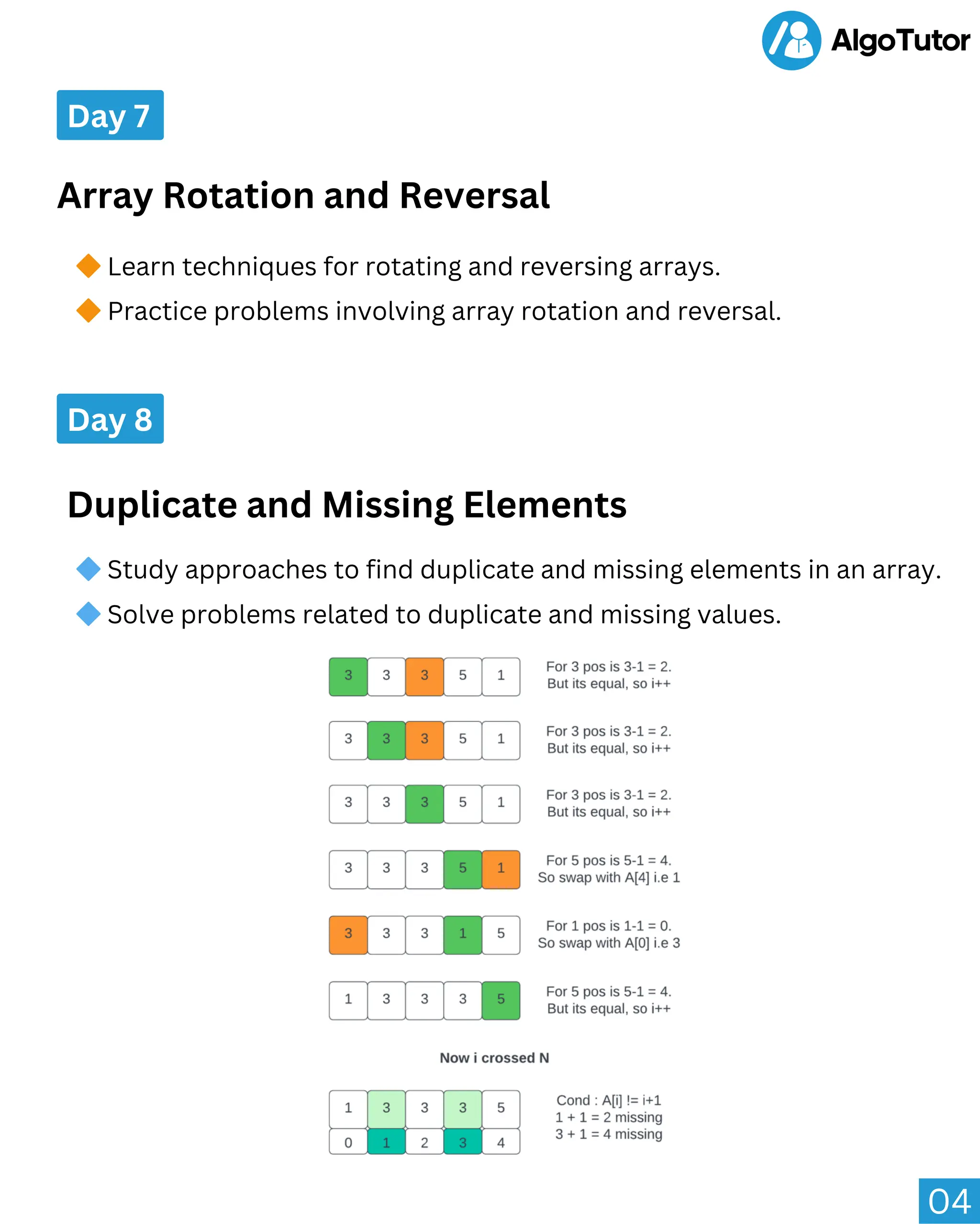
This document outlines a 10-day curriculum on array concepts and problems. Over the 10 days, students will learn about array fundamentals like indexing and operations; traversal and searching algorithms; sorting algorithms; dynamic arrays; subarrays and subsequences; rotation and reversal; duplicate and missing elements; frequency counting and prefix sums; and advanced problems. Each day covers 1-2 core topics through explanations and practice problems.


![Practice
06
Given an m x n integer matrix matrix, if an element is 0,
set its entire row and column to 0's.
01. Set Matrix Zeroes
Input: matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
Example 1:
Important Practice Questions
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
Output: [[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-8-2048.jpg)
![07
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target,
return indices of the two numbers such that they add up
to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one
solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
Output: [1,2]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
Output: [0,1]
02. Two Sum
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-9-2048.jpg)
![08
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the
price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock.
You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any
time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on
the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
03. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-10-2048.jpg)
![09
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price
of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day
to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the
future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this
transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
04. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-11-2048.jpg)
![10
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or
blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color
are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and
blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color
red, white, and blue, respectively.
You must solve this problem without using the library's
sort function.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
Output: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,0,1]
Output: [0,1,2]
05. Sort Colors
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-12-2048.jpg)
![11
Given an integer array nums of length n where all the
integers of nums are in the range [1, n] and each integer
appears once or twice, return an array of all the integers
that appears twice.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and
uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: []
06. Find All Duplicates in an Array
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-13-2048.jpg)
![12
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets
[nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i != k, and j != k,
and nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.
Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate
triplets.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1,1]
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: nums = [0,0,0]
Output: [[0,0,0]]
07. 3Sum
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-14-2048.jpg)
![13
Given an array nums of n integers, return an array of all
the unique quadruplets [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c],
nums[d]] such that:
0 <= a, b, c, d < n
a, b, c, and d are distinct.
nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
Output: [[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8
Output: [[2,2,2,2]]
08. 4Sum
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-15-2048.jpg)
![Practice
14
You are given an m x n integer matrix matrix with the
following two properties:
Each row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
The first integer of each row is greater than the last
integer of the previous row.
Given an integer target, return true if target is in matrix or
false otherwise.
You must write a solution in O(log(m * n)) time complexity.
09. Search a 2D Matrix
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3
Output: true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-16-2048.jpg)
![15
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the
length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1]
Output: 9
10. Longest Consecutive Sequence
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-17-2048.jpg)
![16
A peak element is an element that is strictly greater than
its neighbors.
Given a 0-indexed integer array nums, find a peak
element, and return its index. If the array contains
multiple peaks, return the index to any of the peaks.
You may imagine that nums[-1] = nums[n] = -∞. In other
words, an element is always considered to be strictly
greater than a neighbor that is outside the array.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(log n) time.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,1,3,5,6,4]
Output: 5
11. Find Peak Element
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-18-2048.jpg)
![17
You are given a sorted array consisting of only integers
where every element appears exactly twice, except for
one element which appears exactly once.
Return the single element that appears only once.
Your solution must run in O(log n) time and O(1) space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2,3,3,4,4,8,8]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,3,7,7,10,11,11]
Output: 10
12. Single Element in a Sorted Array
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-19-2048.jpg)
![18
Suppose an array of length n sorted in ascending order is
rotated between 1 and n times. For example, the array
nums = [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become:
[4,5,6,7,0,1,2] if it was rotated 4 times.
[0,1,2,4,5,6,7] if it was rotated 7 times.
Notice that rotating an array [a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-1]] 1
time results in the array [a[n-1], a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-2]].
Given the sorted rotated array nums of unique elements,
return the minimum element of this array.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(log n) time.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2]
Output: 1
13. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted
Array
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-20-2048.jpg)
![19
There is an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing
order (not necessarily with distinct values).
Before being passed to your function, nums is rotated at
an unknown pivot index k (0 <= k < nums.length) such that
the resulting array is [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1],
nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]] (0-indexed). For example,
[0,1,2,4,4,4,5,6,6,7] might be rotated at pivot index 5 and
become [4,5,6,6,7,0,1,2,4,4].
Given the array nums after the rotation and an integer
target, return true if target is in nums, or false if it is not in
nums.
You must decrease the overall operation steps as much
as possible.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: true
14. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-21-2048.jpg)
![20
There is an integer array nums sorted in ascending order
(with distinct values).
Prior to being passed to your function, nums is possibly
rotated at an unknown pivot index k (1 <= k < nums.length)
such that the resulting array is [nums[k], nums[k+1], ...,
nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]] (0-indexed).
For example, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might be rotated at pivot
index 3 and become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2].
Given the array nums after the possible rotation and an
integer target, return the index of target if it is in nums, or
-1 if it is not in nums.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime
complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
15. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-22-2048.jpg)
![21
Given an array of integers nums sorted in non-decreasing
order, find the starting and ending position of a given
target value.
If target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime
complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
Output: [3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
Output: [-1,-1]
16. Find First and Last Position of
Element in Sorted Array
Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-23-2048.jpg)
![Practice
22
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value
target in an m x n integer matrix matrix. This matrix has
the following properties:
Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left
to right.
Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top
to bottom.
17. Search a 2D Matrix II
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],
[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
Output: true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-24-2048.jpg)
![Practice
23
A peak element in a 2D grid is an element that is strictly
greater than all of its adjacent neighbors to the left, right,
top, and bottom.
Given a 0-indexed m x n matrix mat where no two
adjacent cells are equal, find any peak element mat[i][j]
and return the length 2 array [i,j].
You may assume that the entire matrix is surrounded by
an outer perimeter with the value -1 in each cell.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(m log(n)) or
O(n log(m)) time.
18. Find a Peak Element II
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[1,4],[3,2]]
Output: [0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-25-2048.jpg)
![Practice
24
Given a sorted array of distinct integers and a target
value, return the index if the target is found.
If not, return the index where it would be if it were
inserted in order.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime
complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 5
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,3,5,6], target = 2
Output: 1
19. Search Insert Position](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-26-2048.jpg)
![Practice
25
Given an array of integers nums which is sorted in
ascending order, and an integer target, write a function to
search target in nums. If target exists, then return its
index. Otherwise, return -1.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime
complexity.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
Output: 4
Explanation: 9 exists in nums and its index is 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2
Output: -1
Explanation: 2 does not exist in nums so return -1
20. Binary Search](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1703302314238-231224134731-15dd404a/75/Master-the-arrays-and-algorithms-using-Algotutor-27-2048.jpg)
