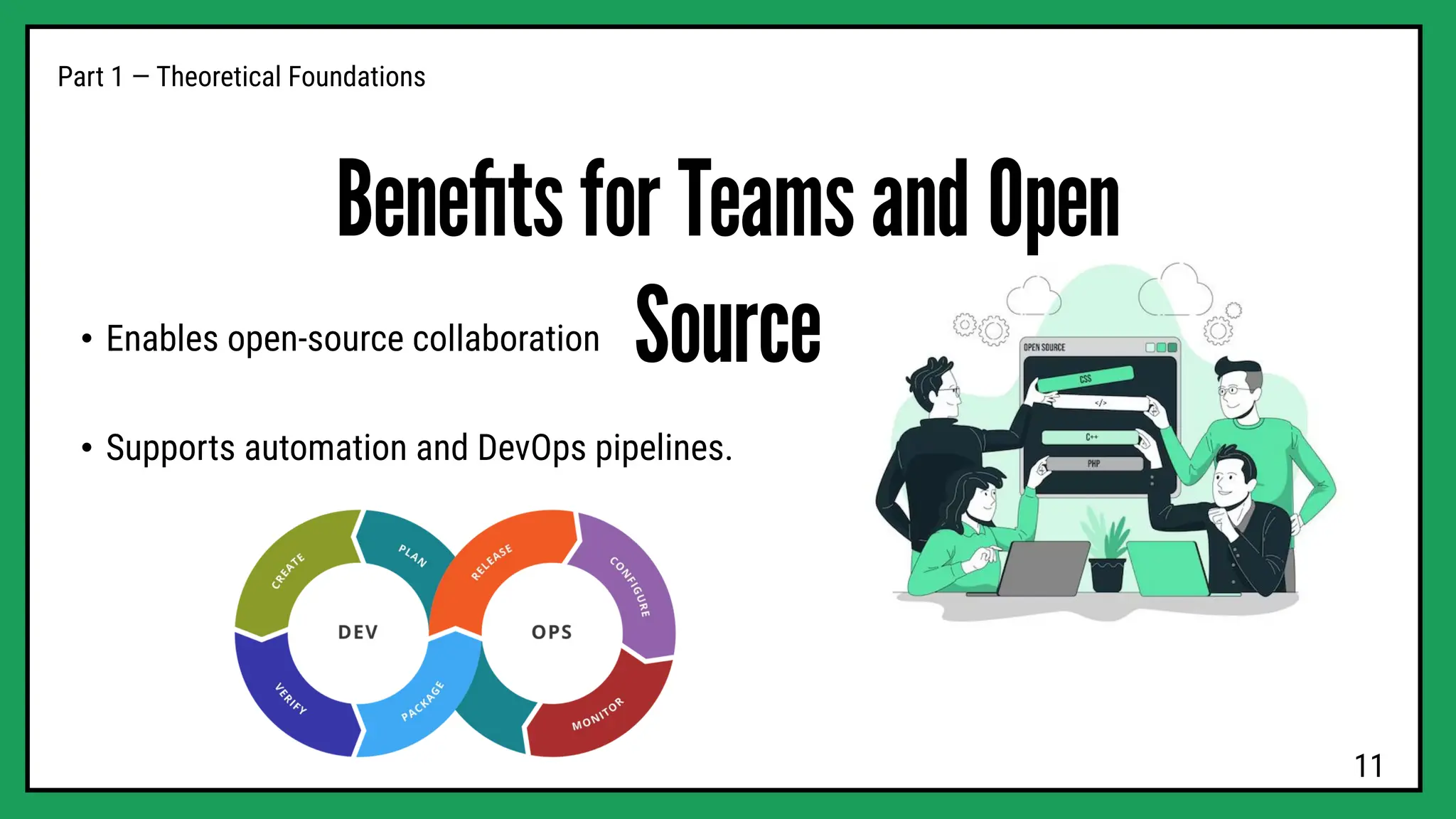
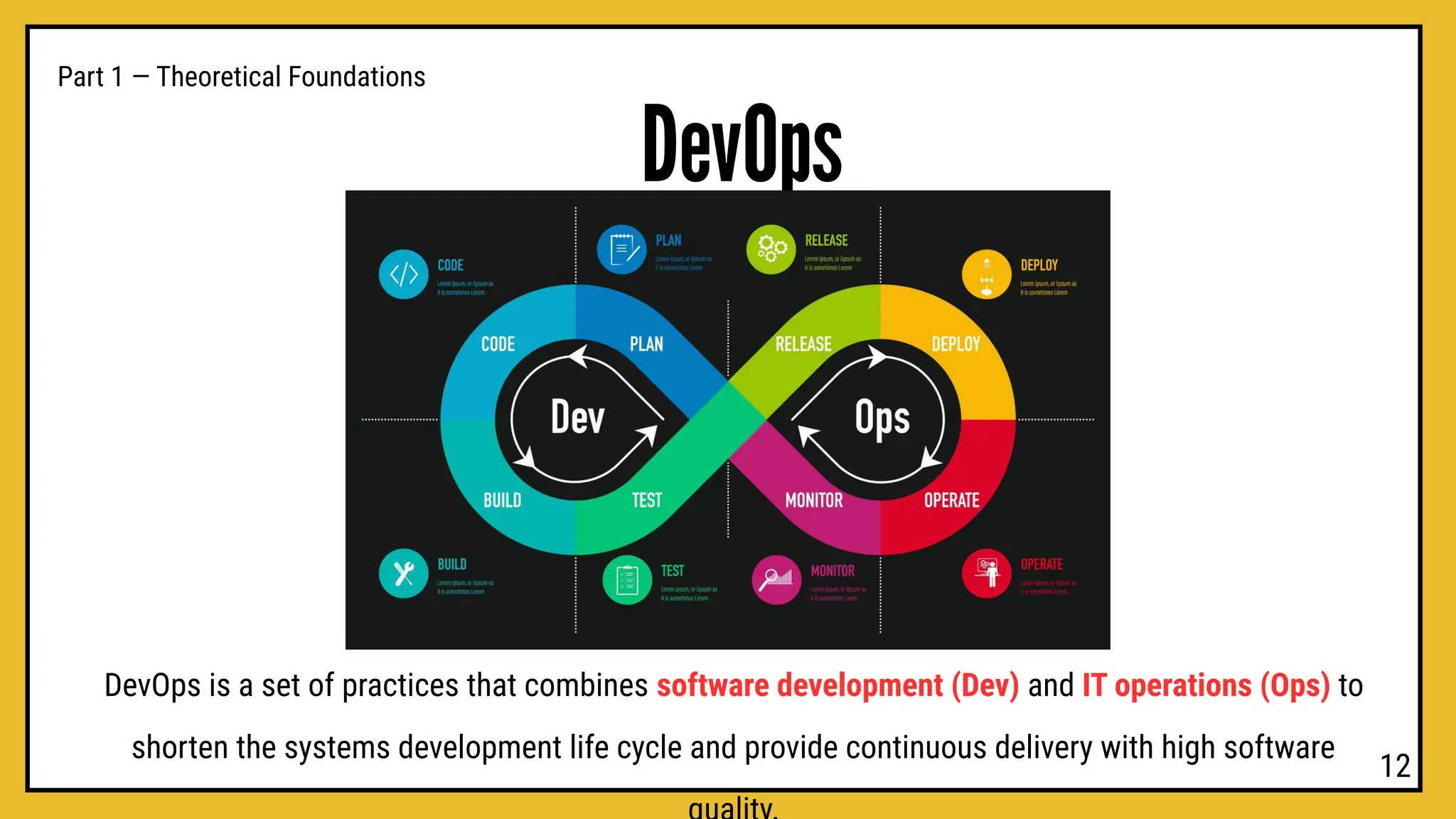
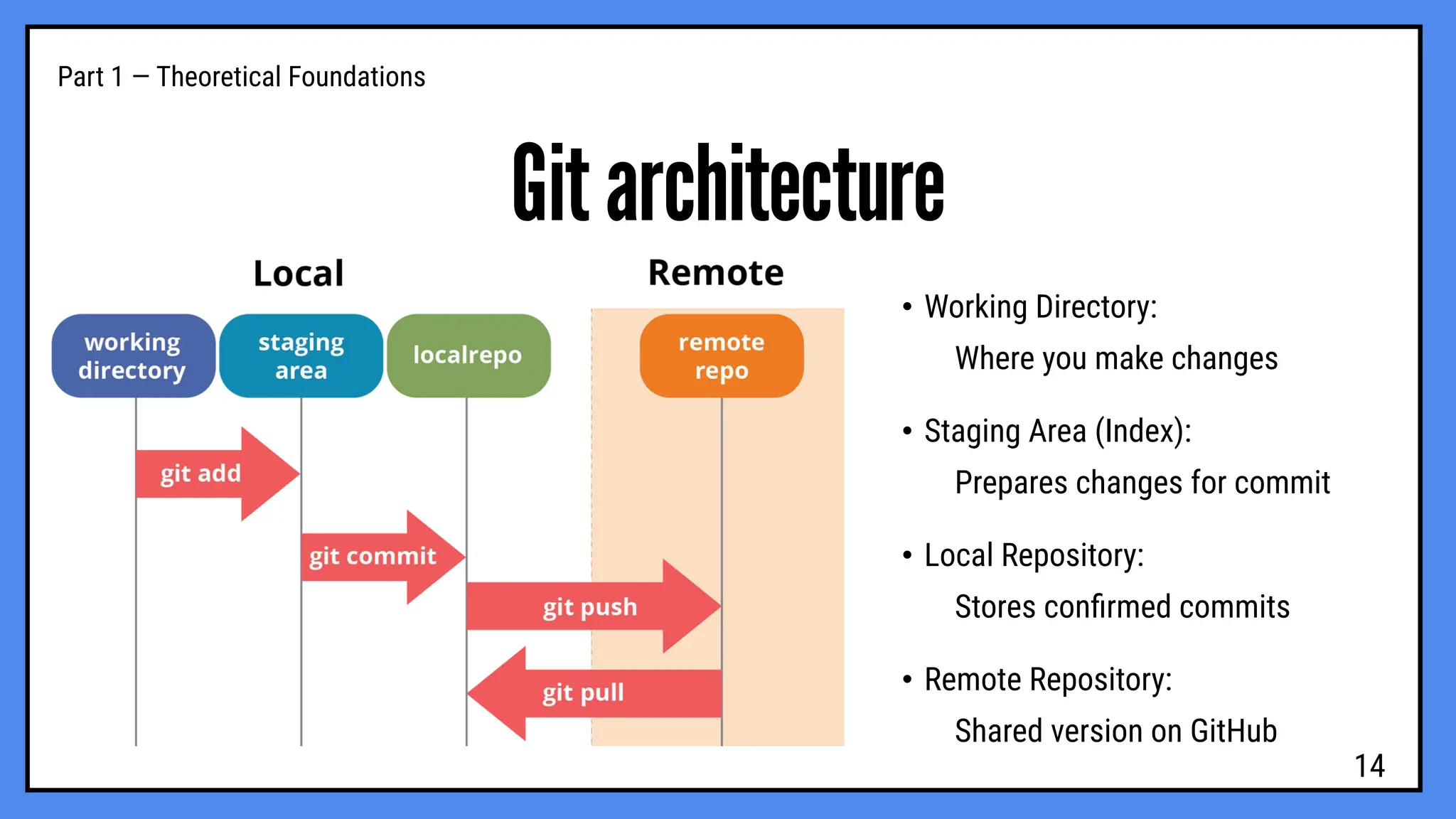
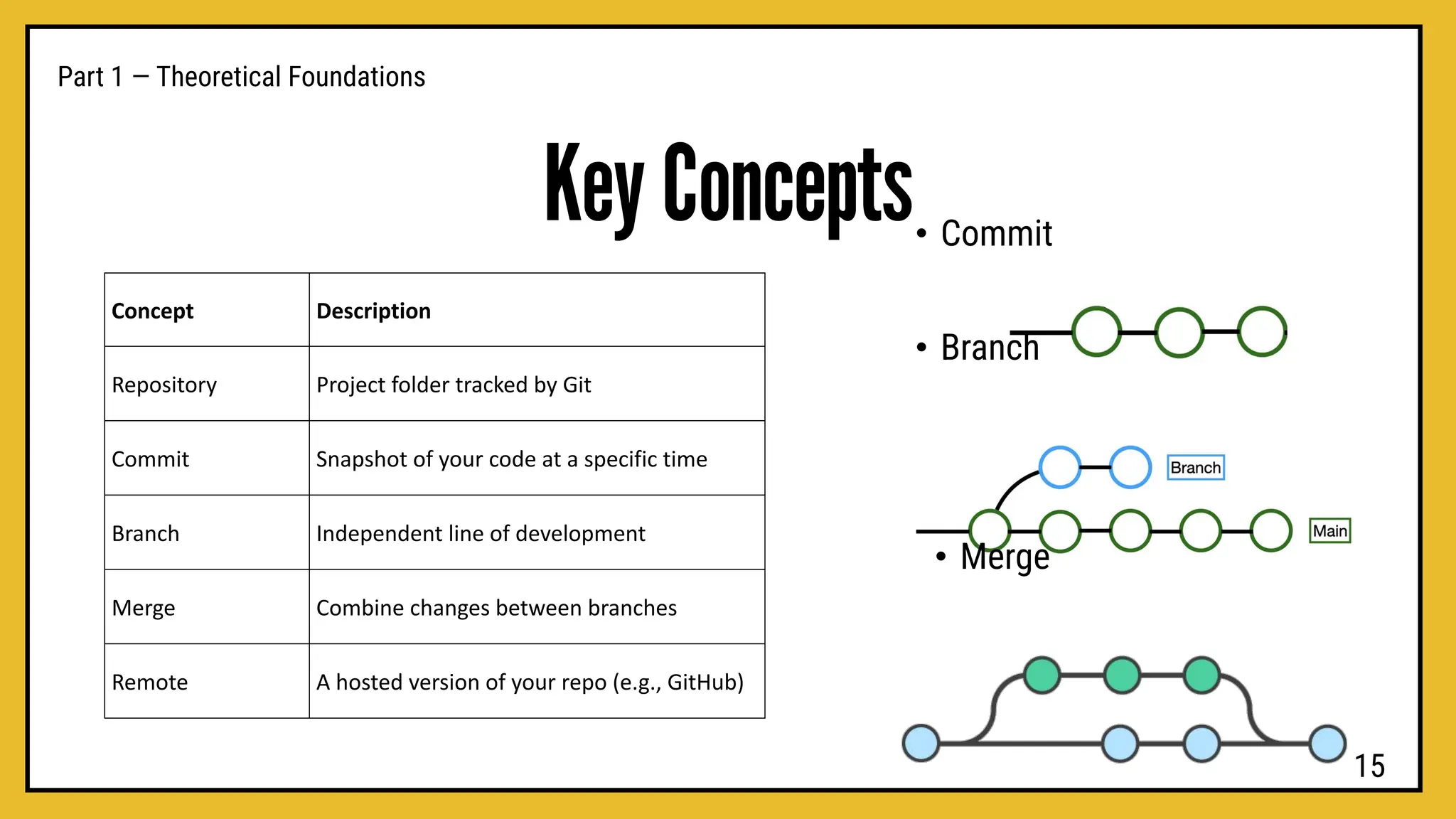
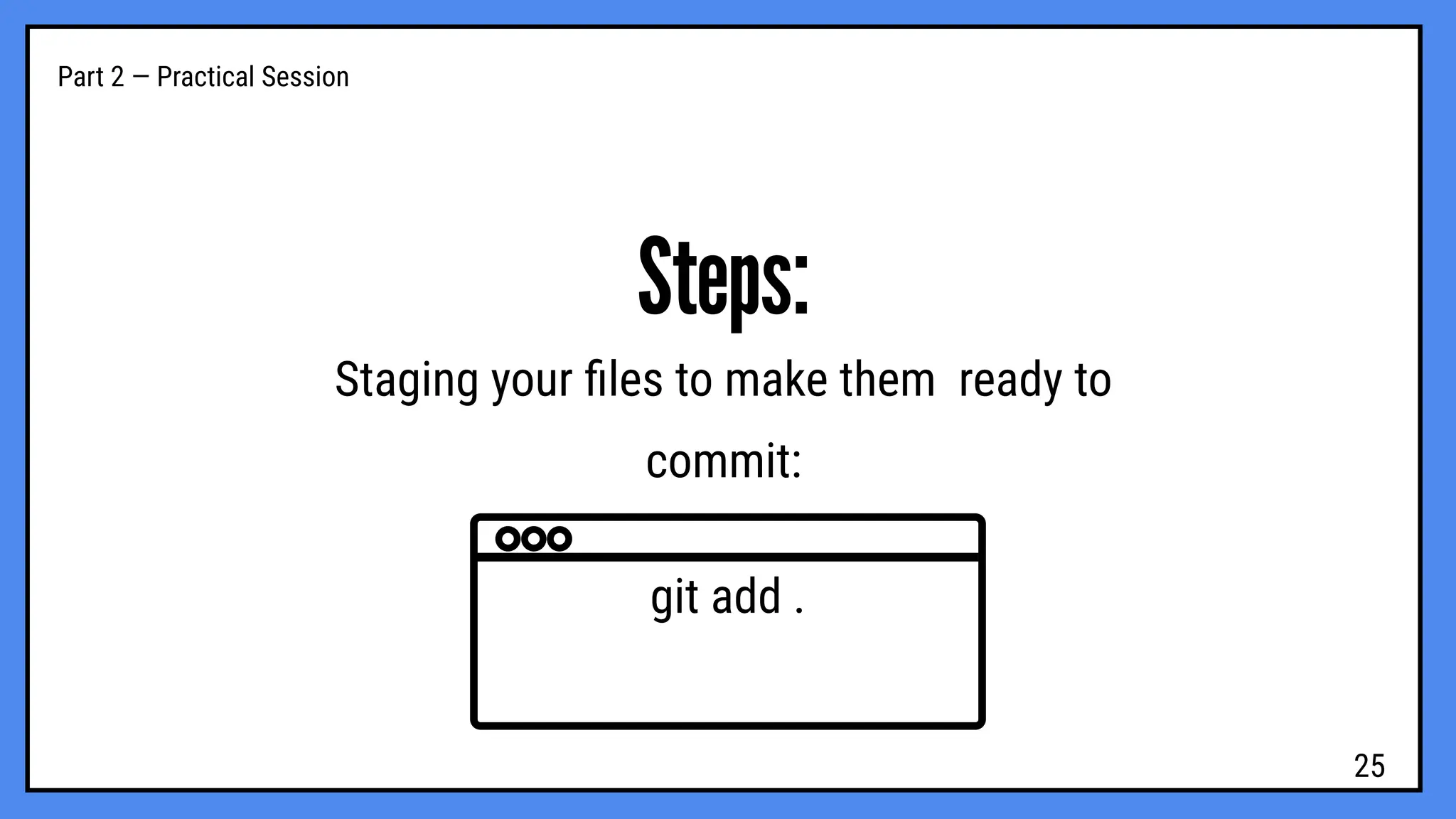
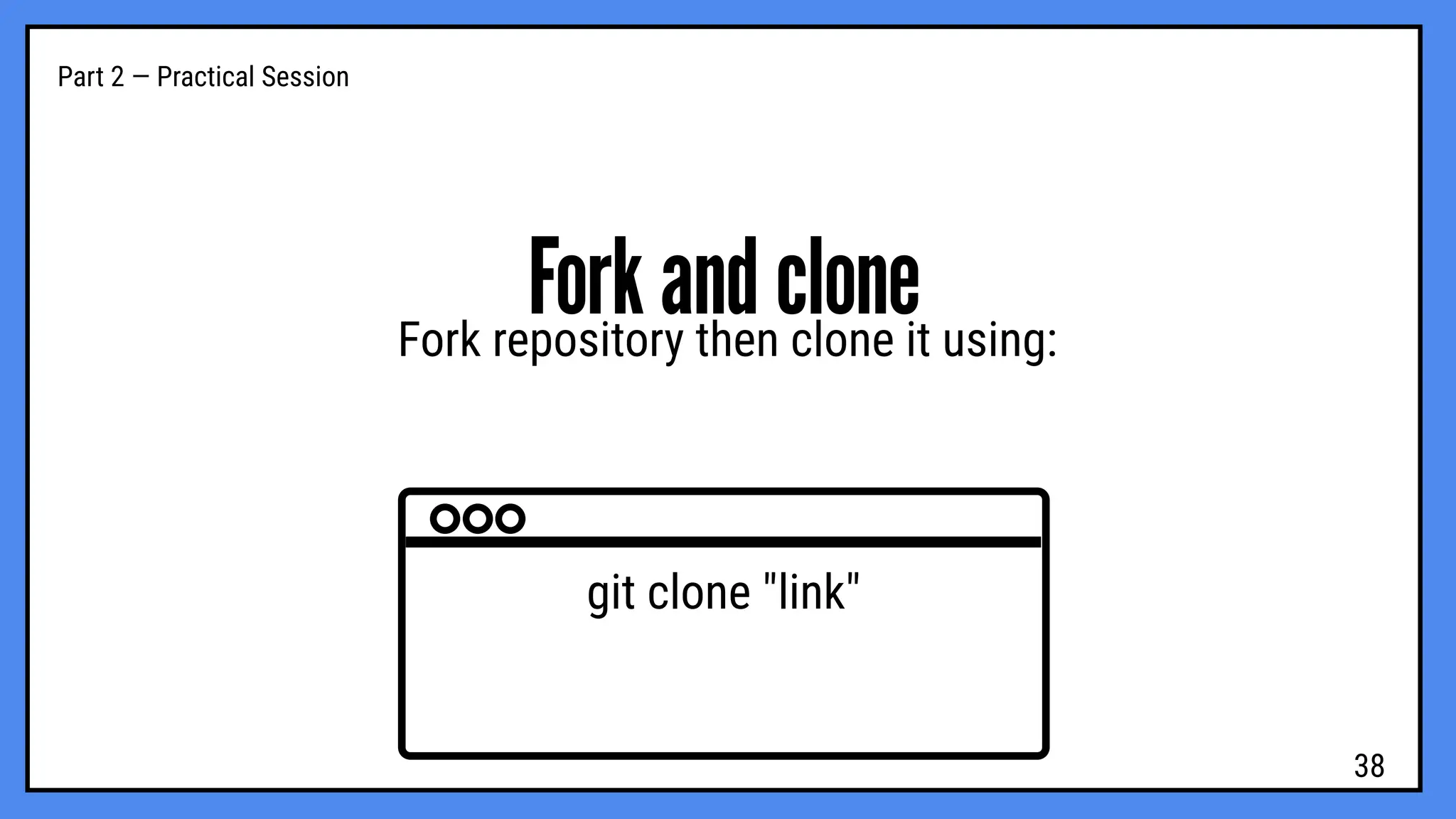
hands-on workshop to learn how developers use Git and GitHub to manage projects, collaborate efficiently, and keep track of every change in their code.
We’ll cover the basics of version control, repositories, commits, branches, and pull requests — everything you need to start working like a pro in real-world development projects.