This document provides an overview of several Matlab commands for input/output:
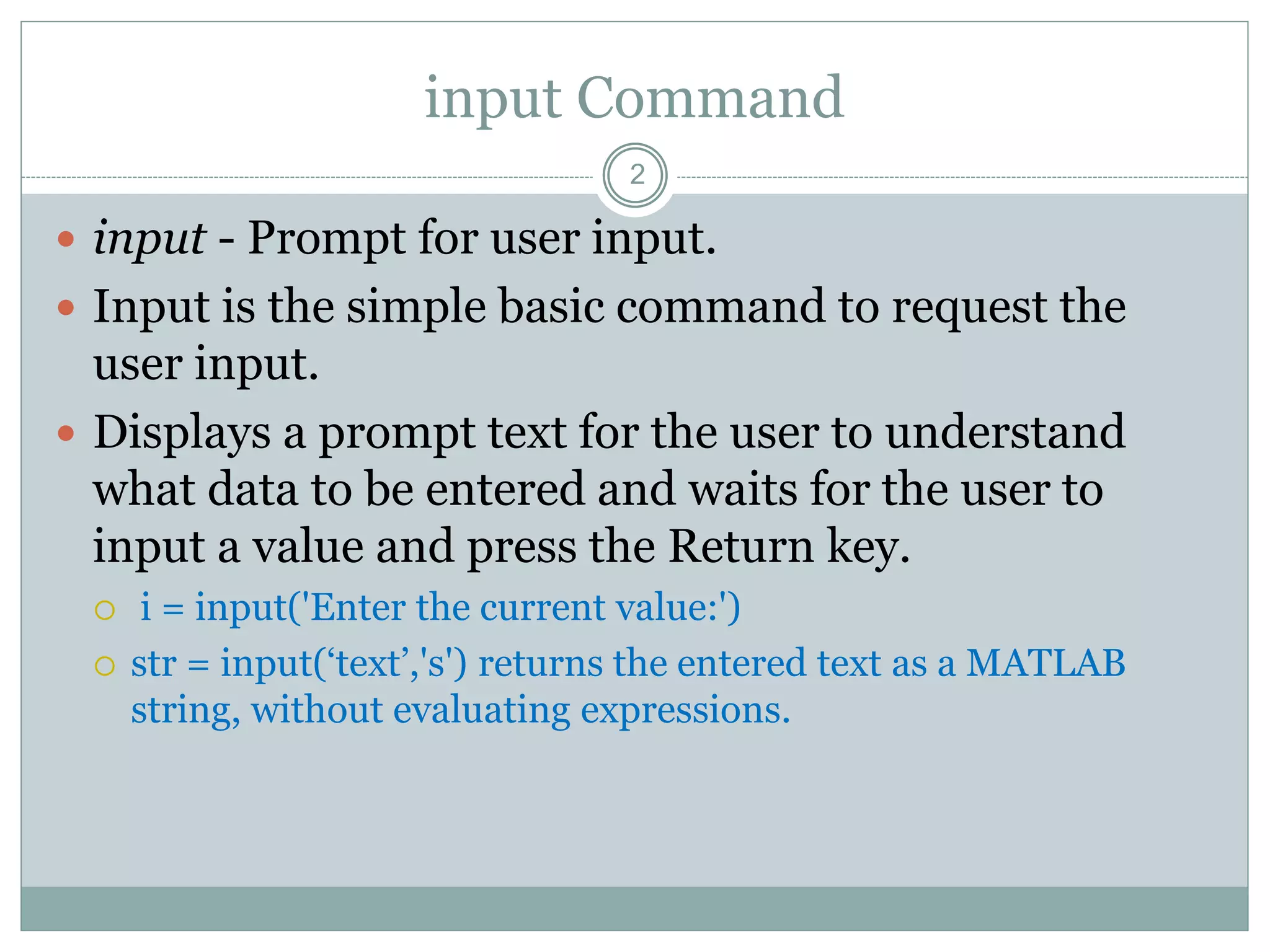
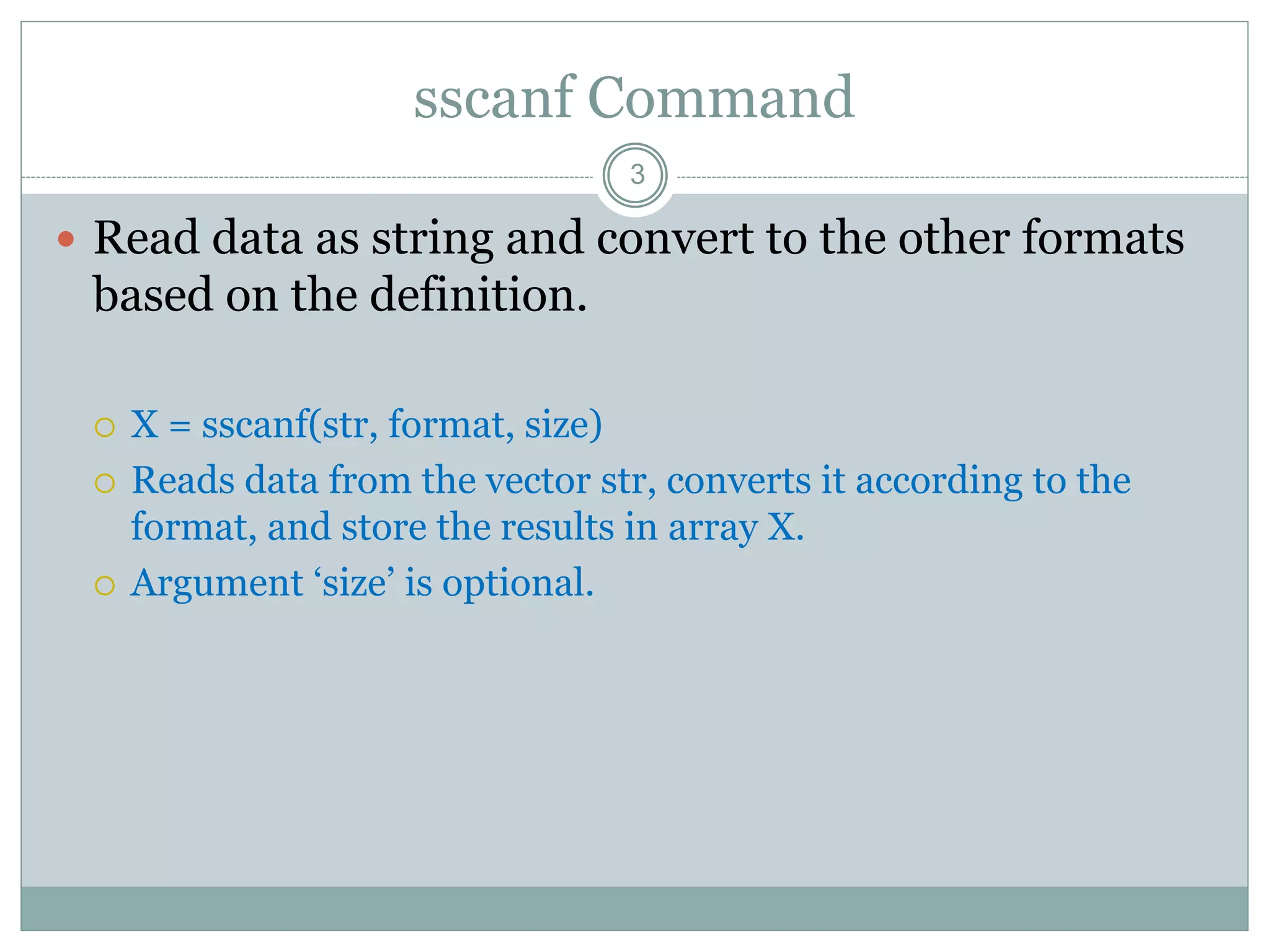
1) The input command prompts the user to enter a value and stores it in a variable. The sscanf command reads data as a string and converts it to other formats.
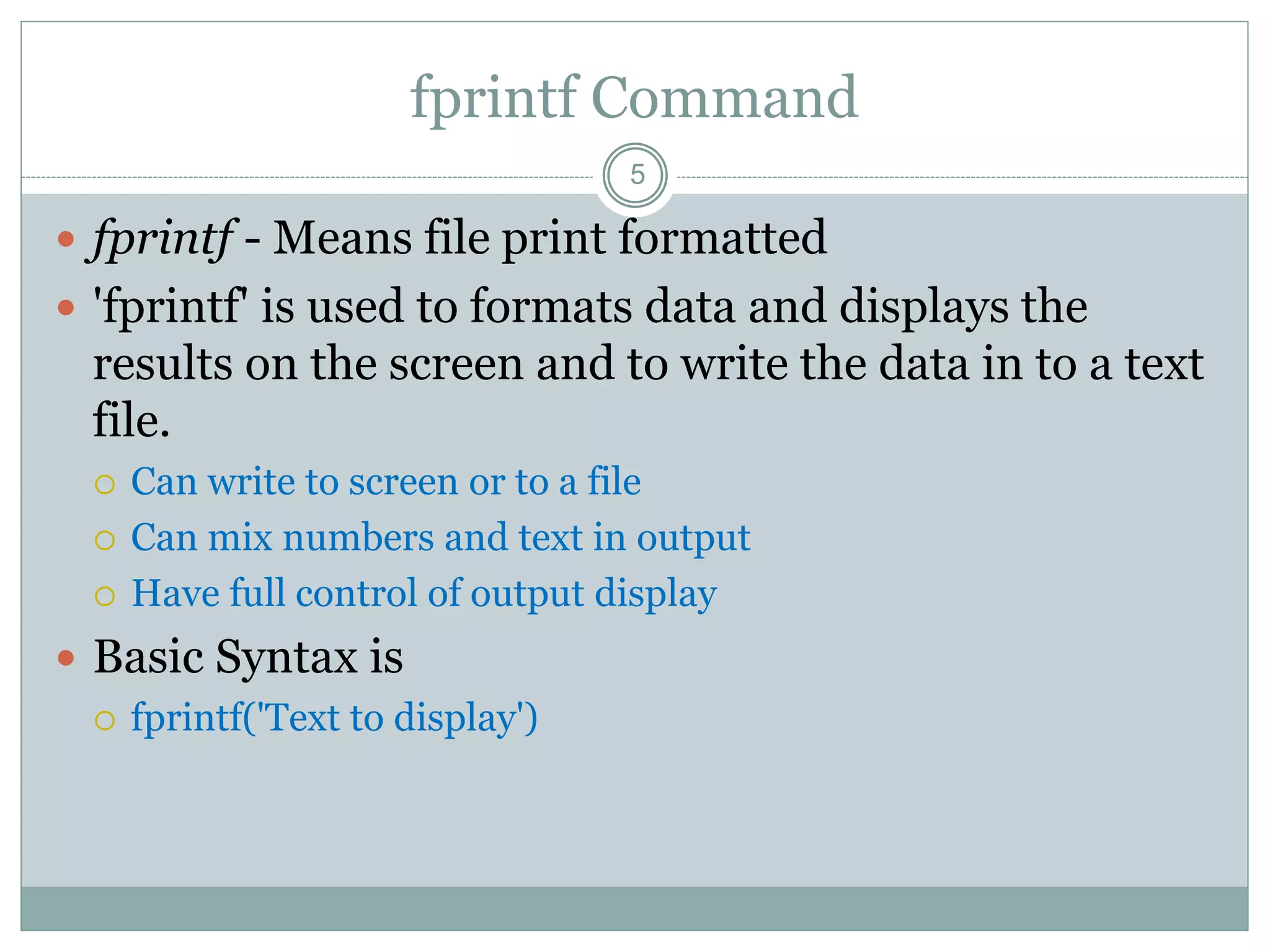
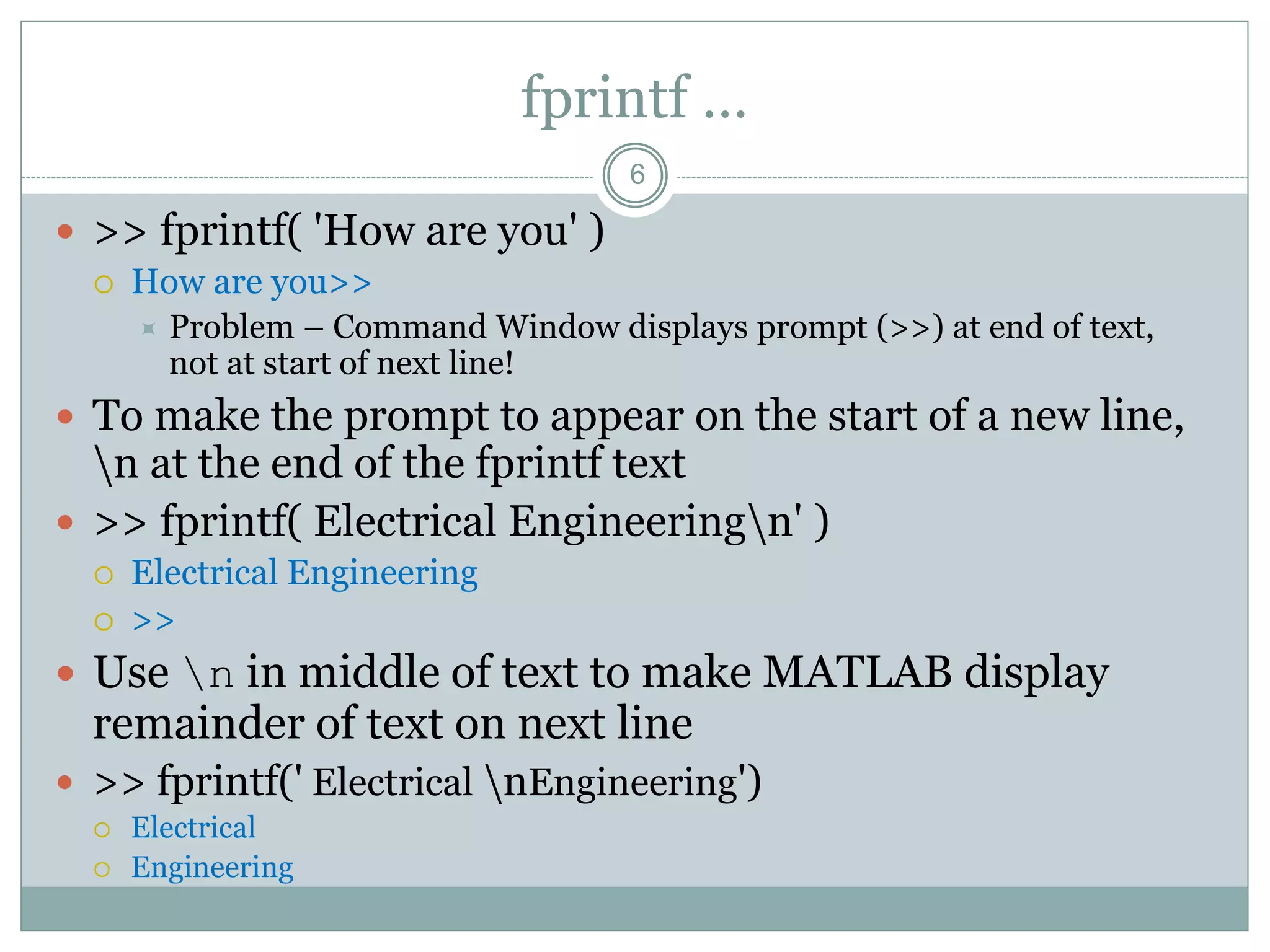
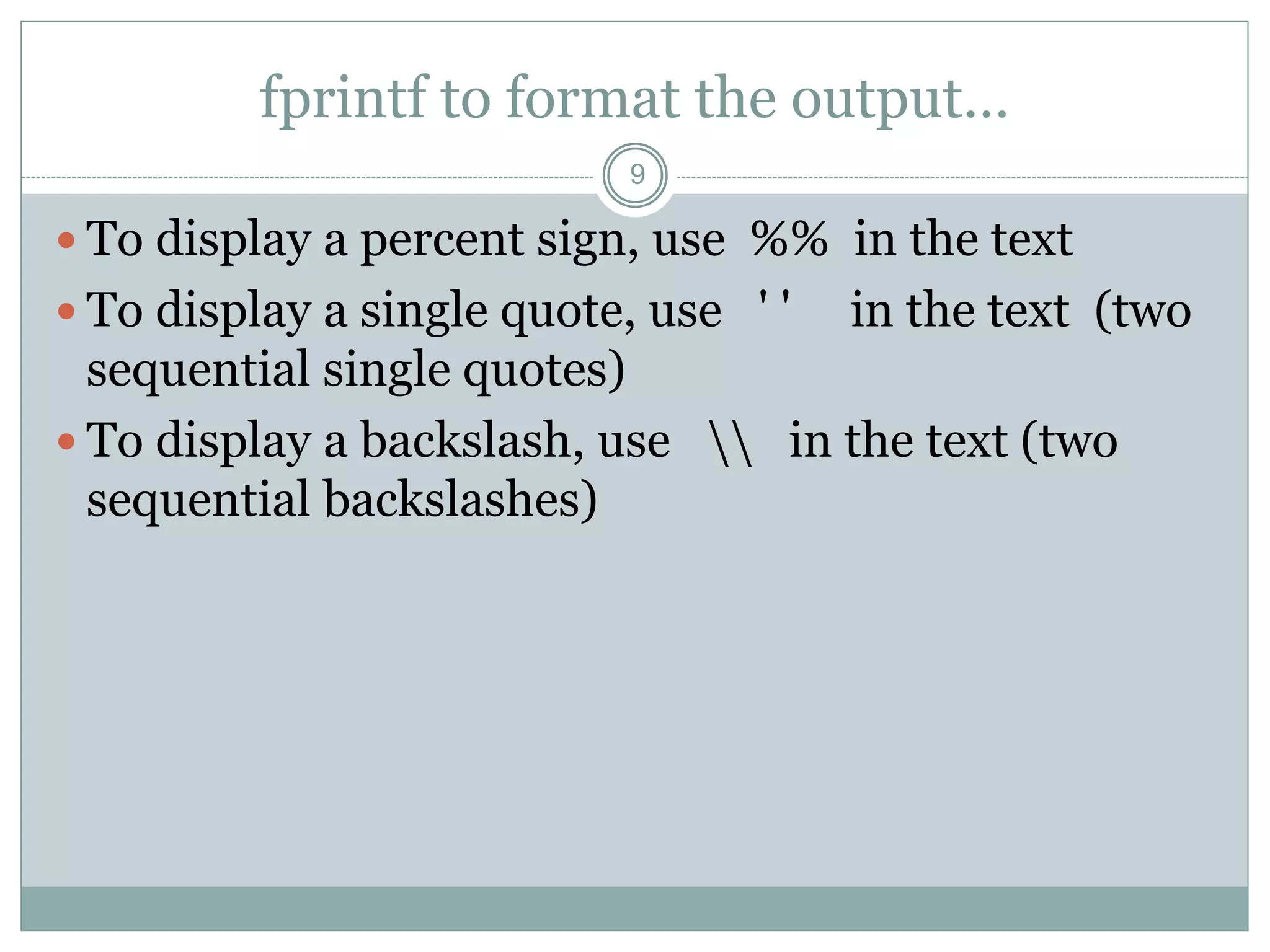
2) The disp command displays variable values or text without variable names. The fprintf command formats and displays data on screen or writes it to a file with control over formatting.
3) The fprintf command uses formatting operators like %d, %f, and %s to control the display of different data types when combined with conversion characters.