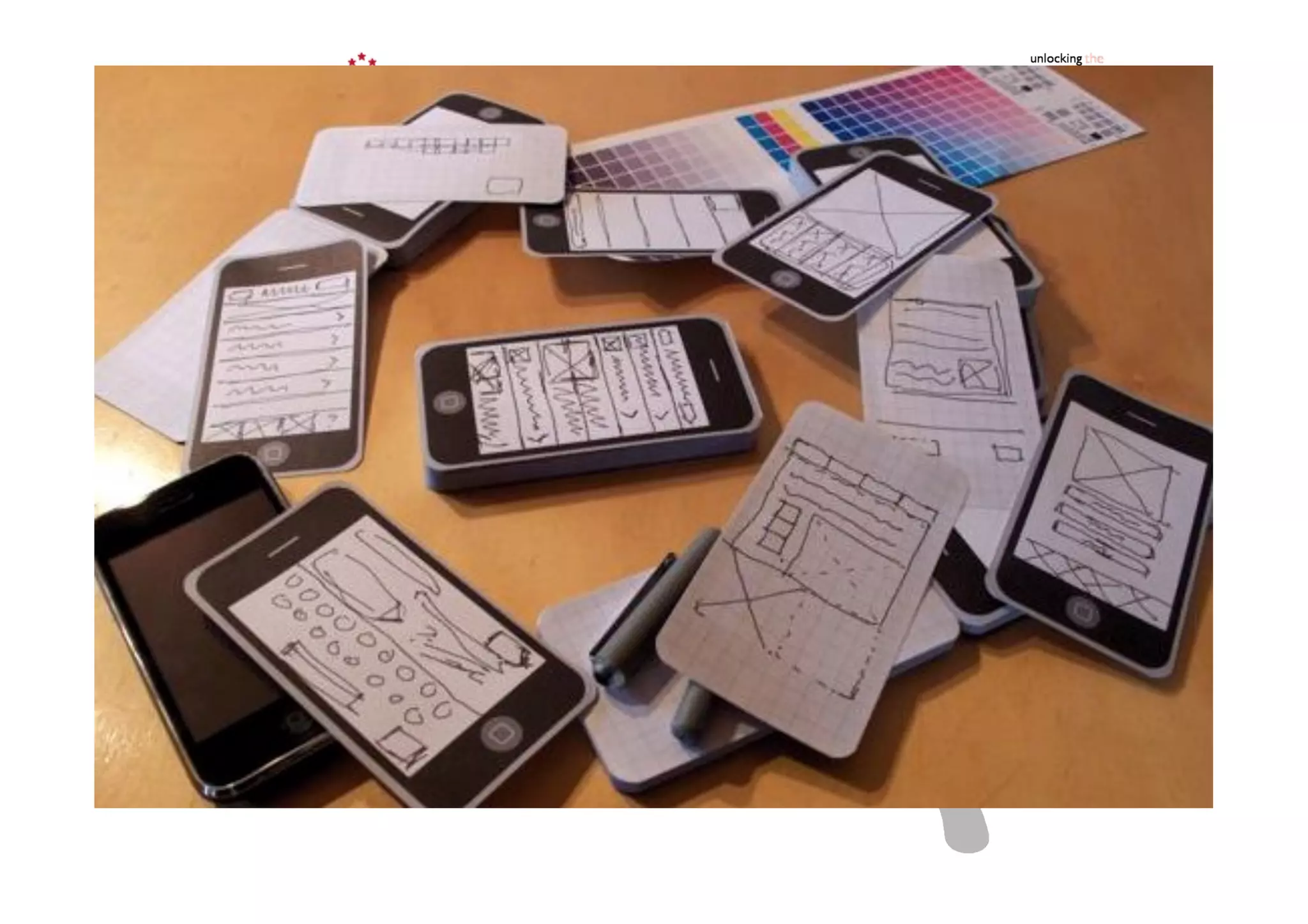
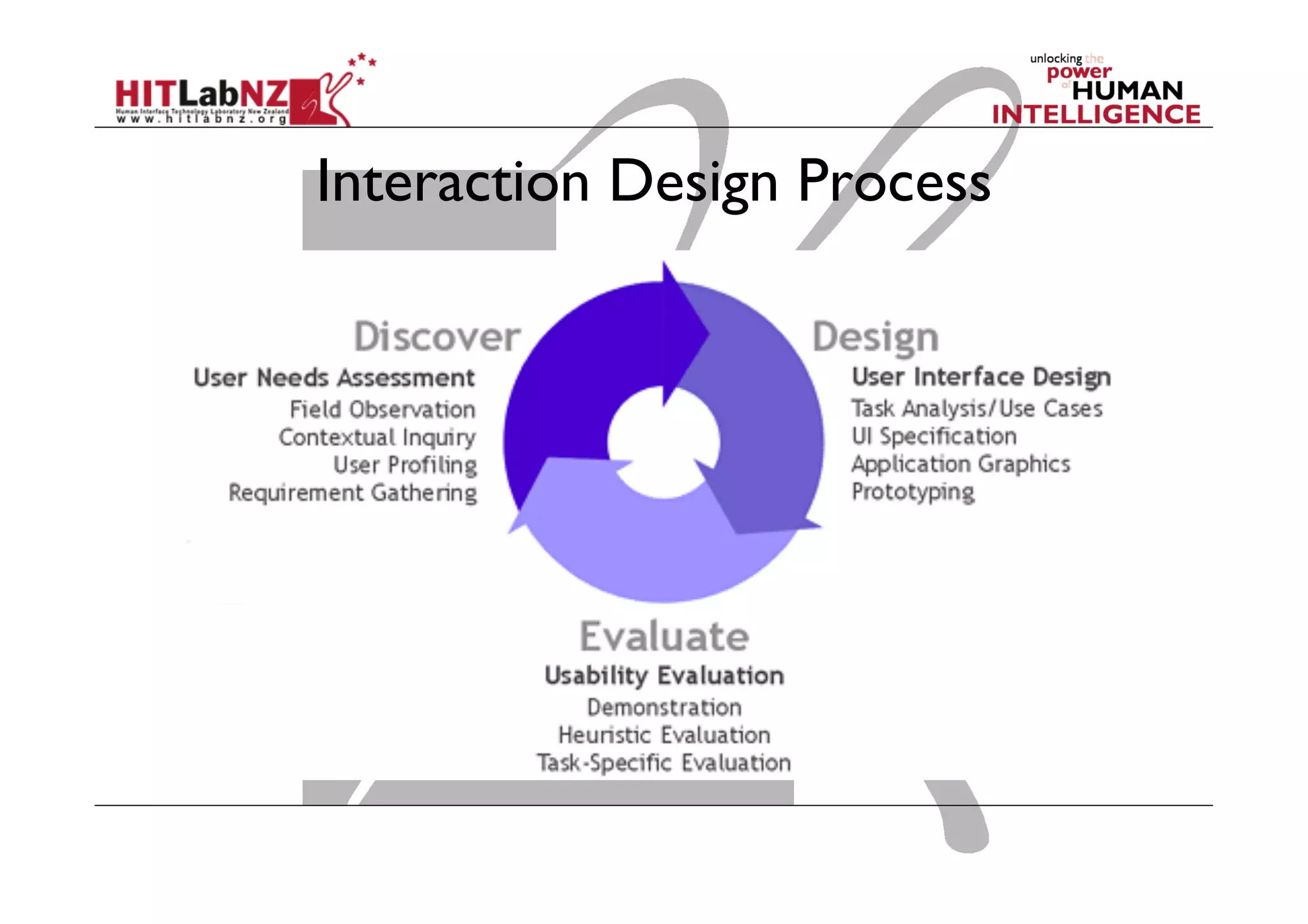
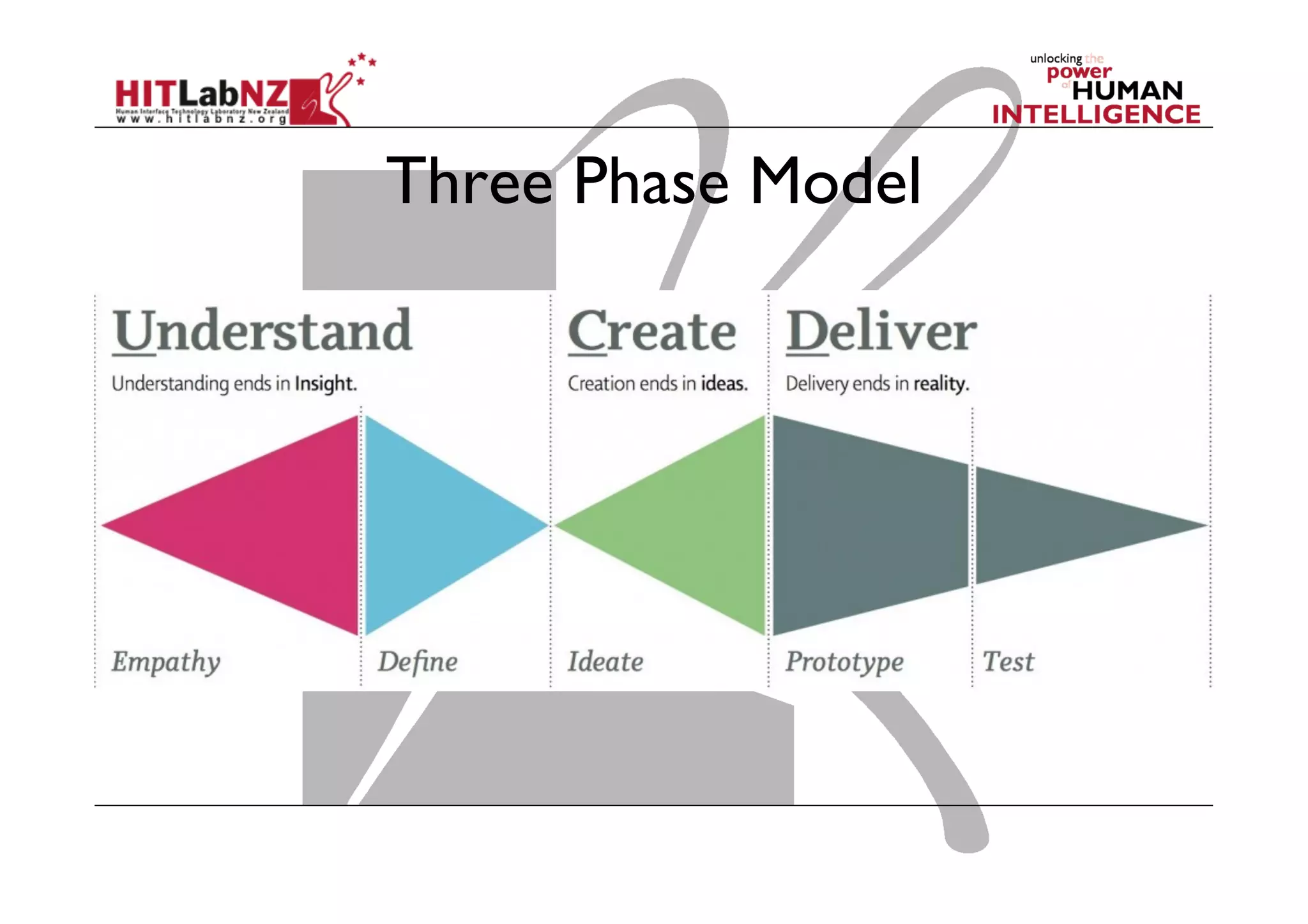
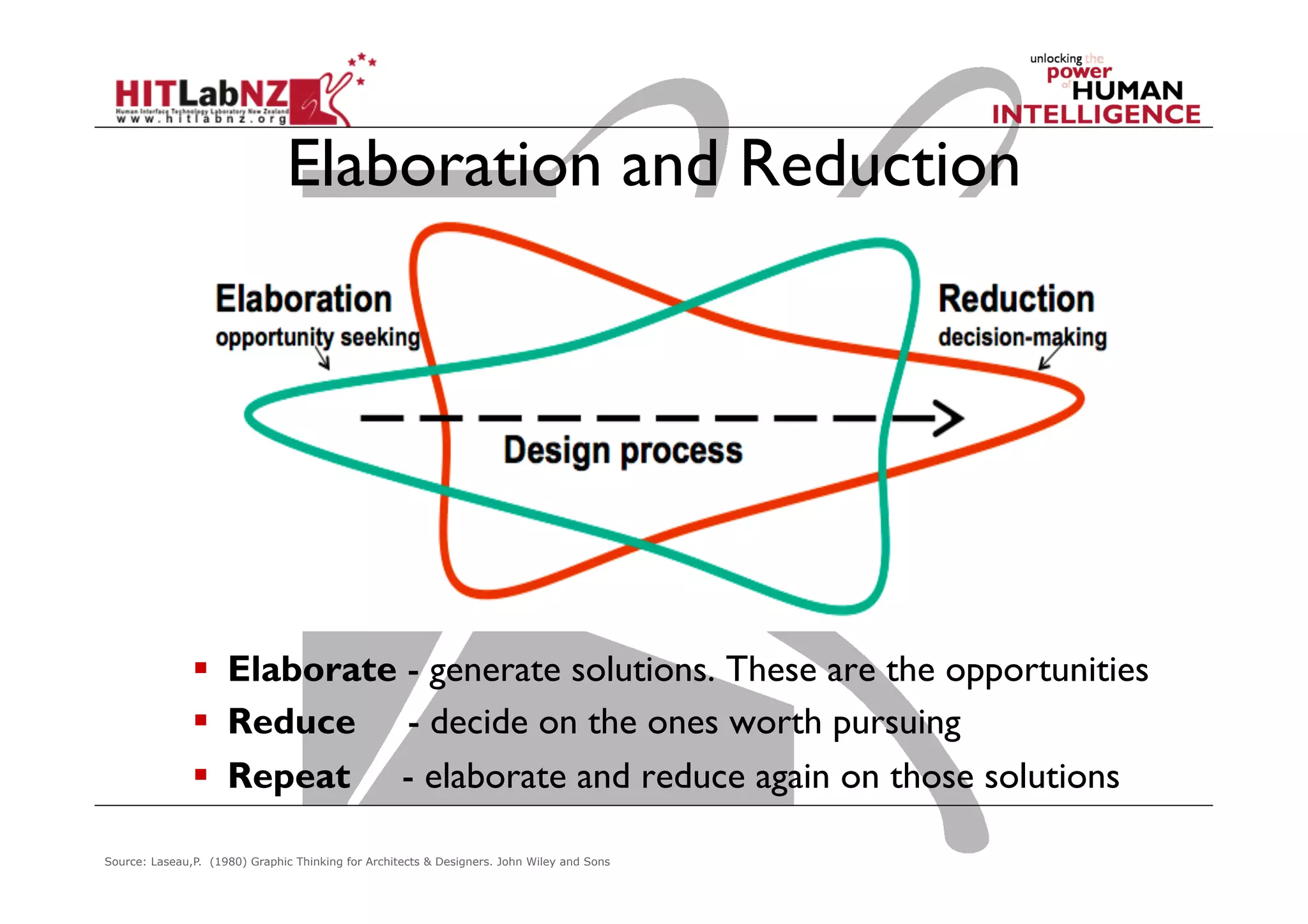
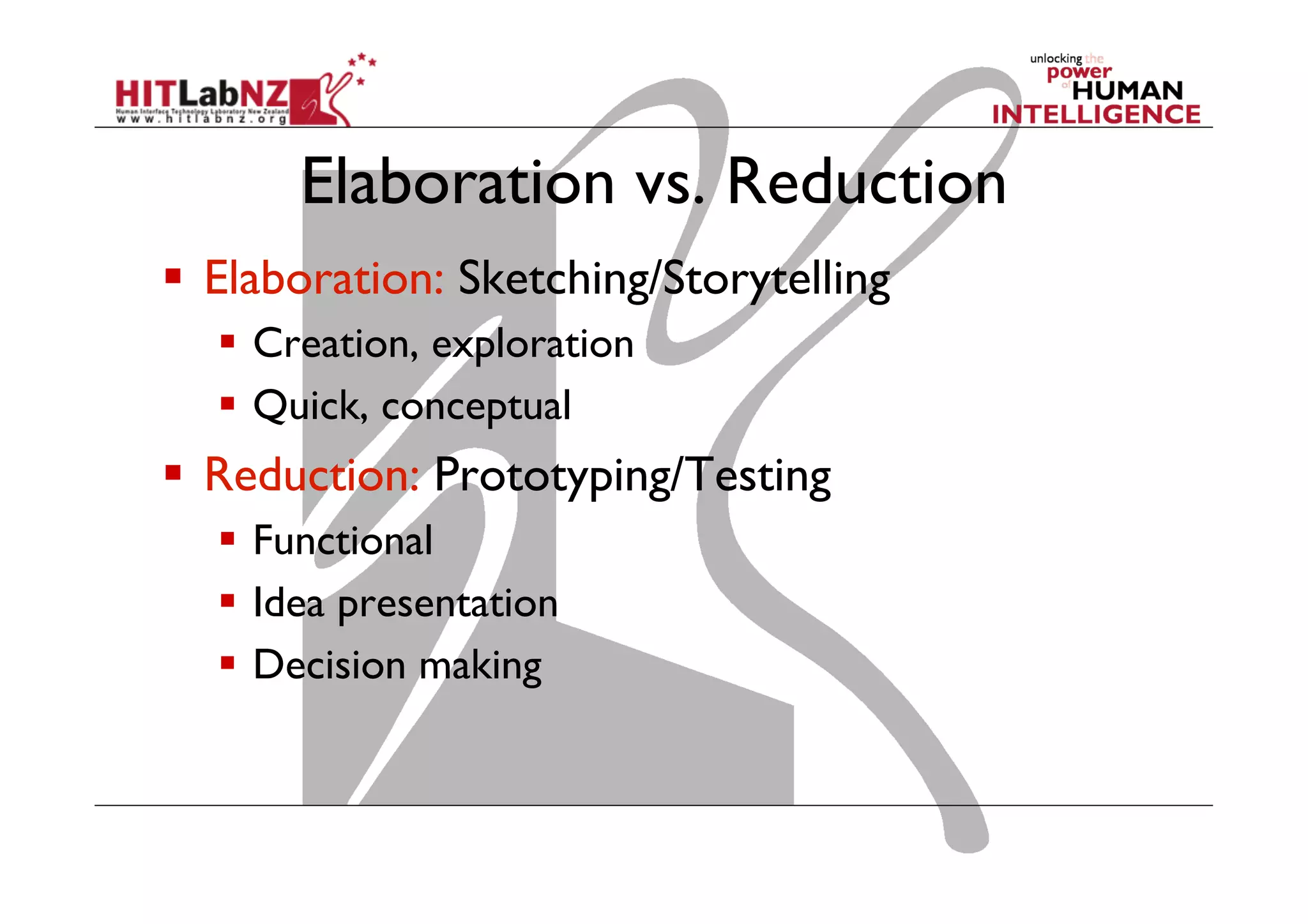
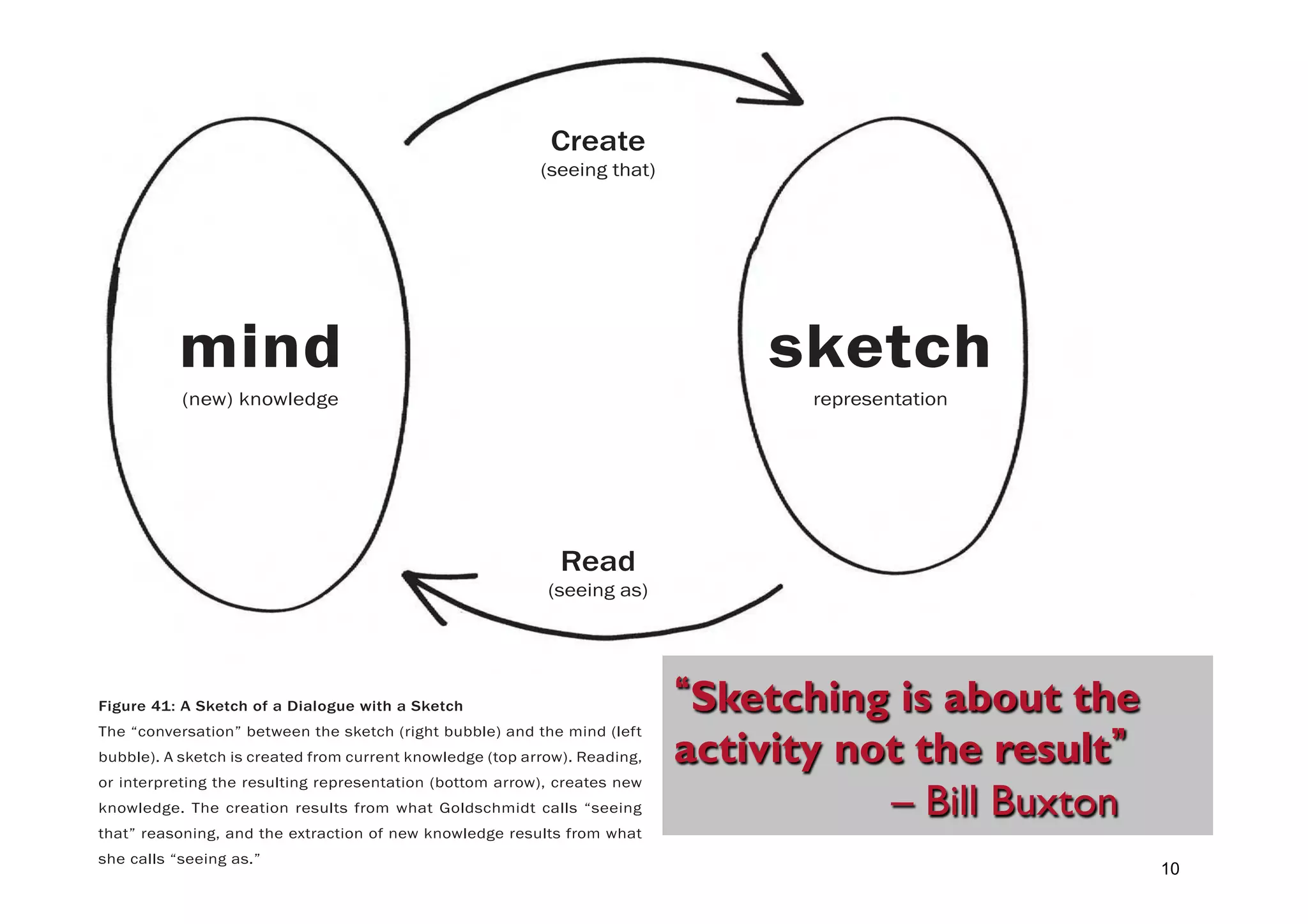
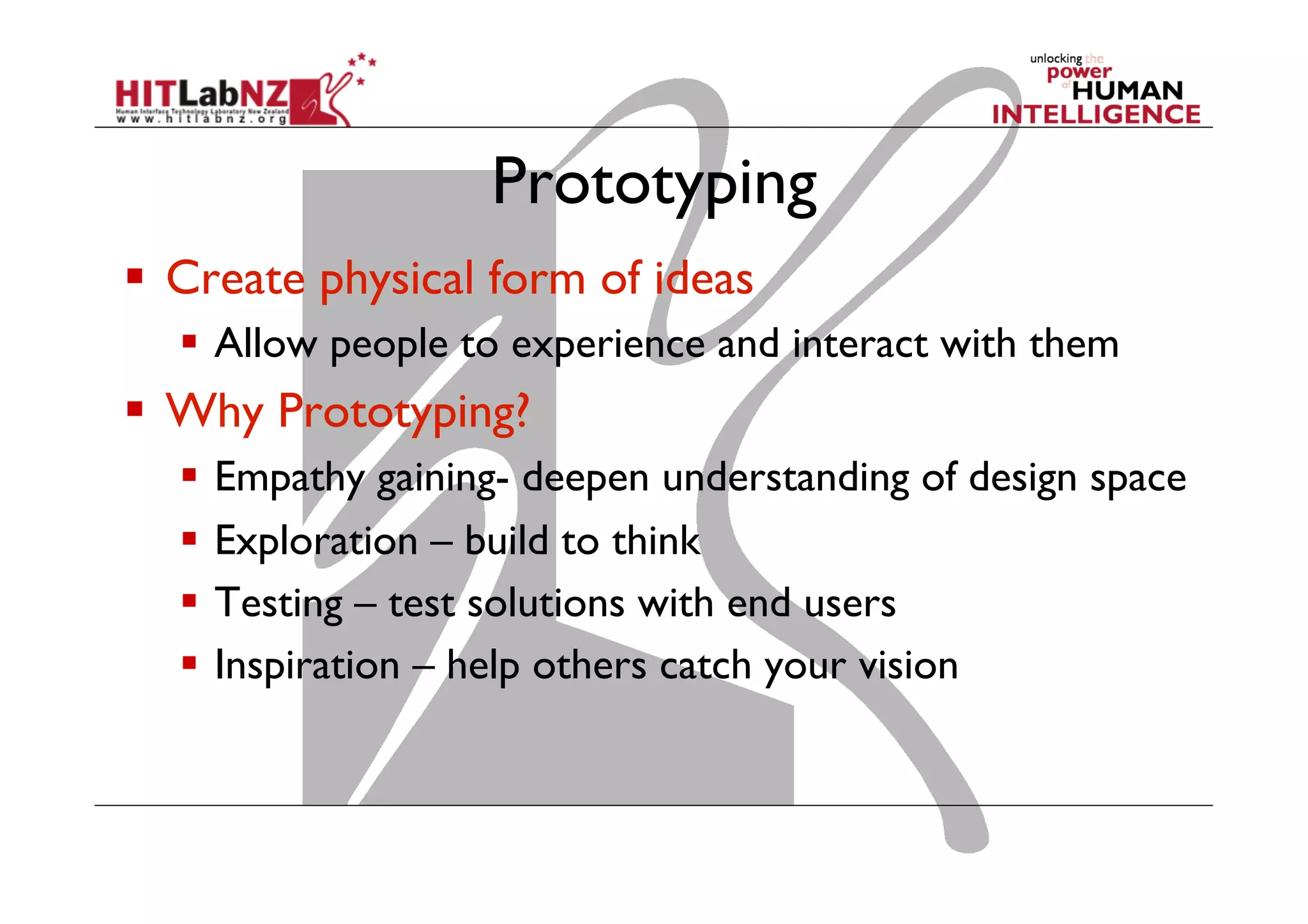
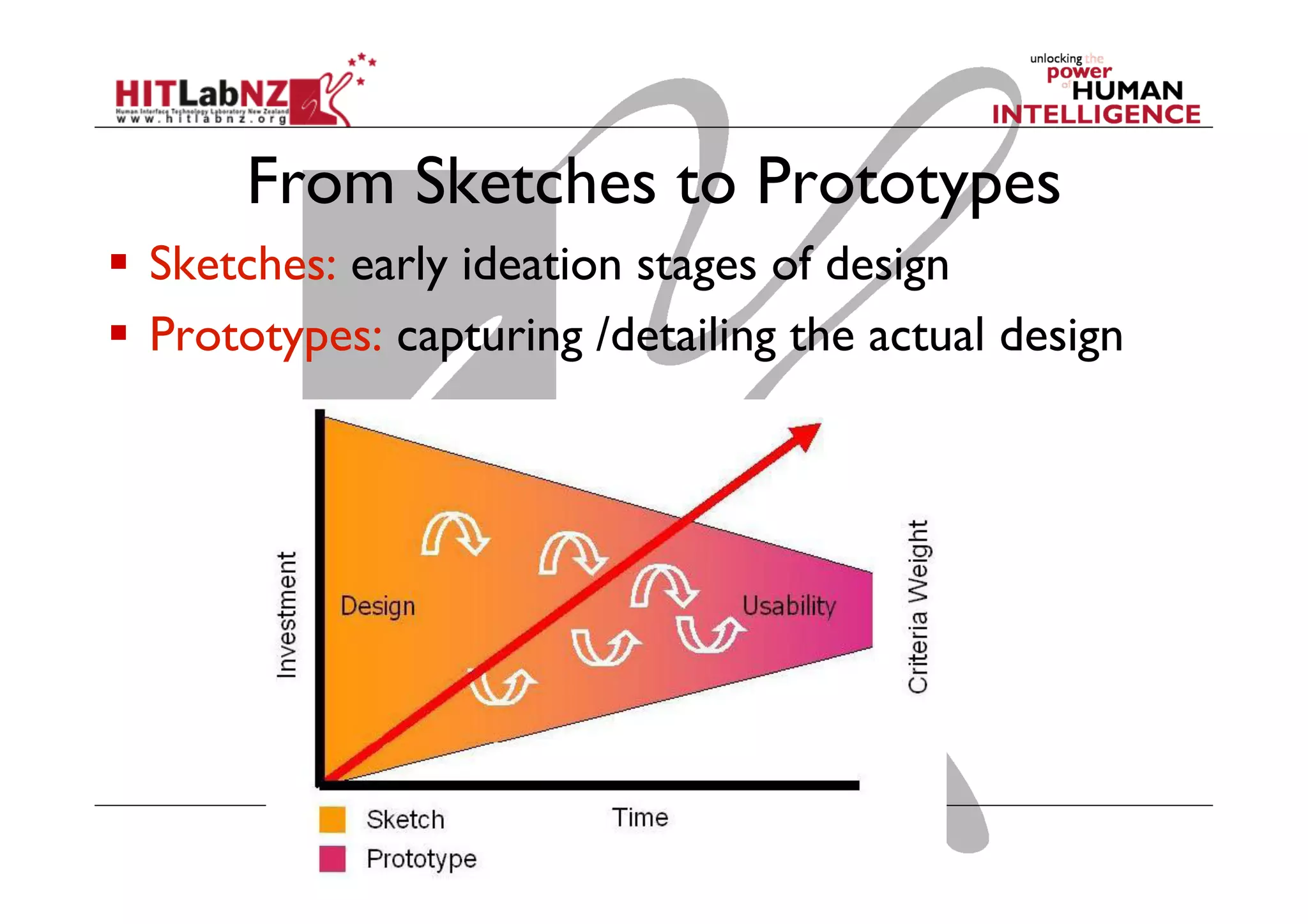
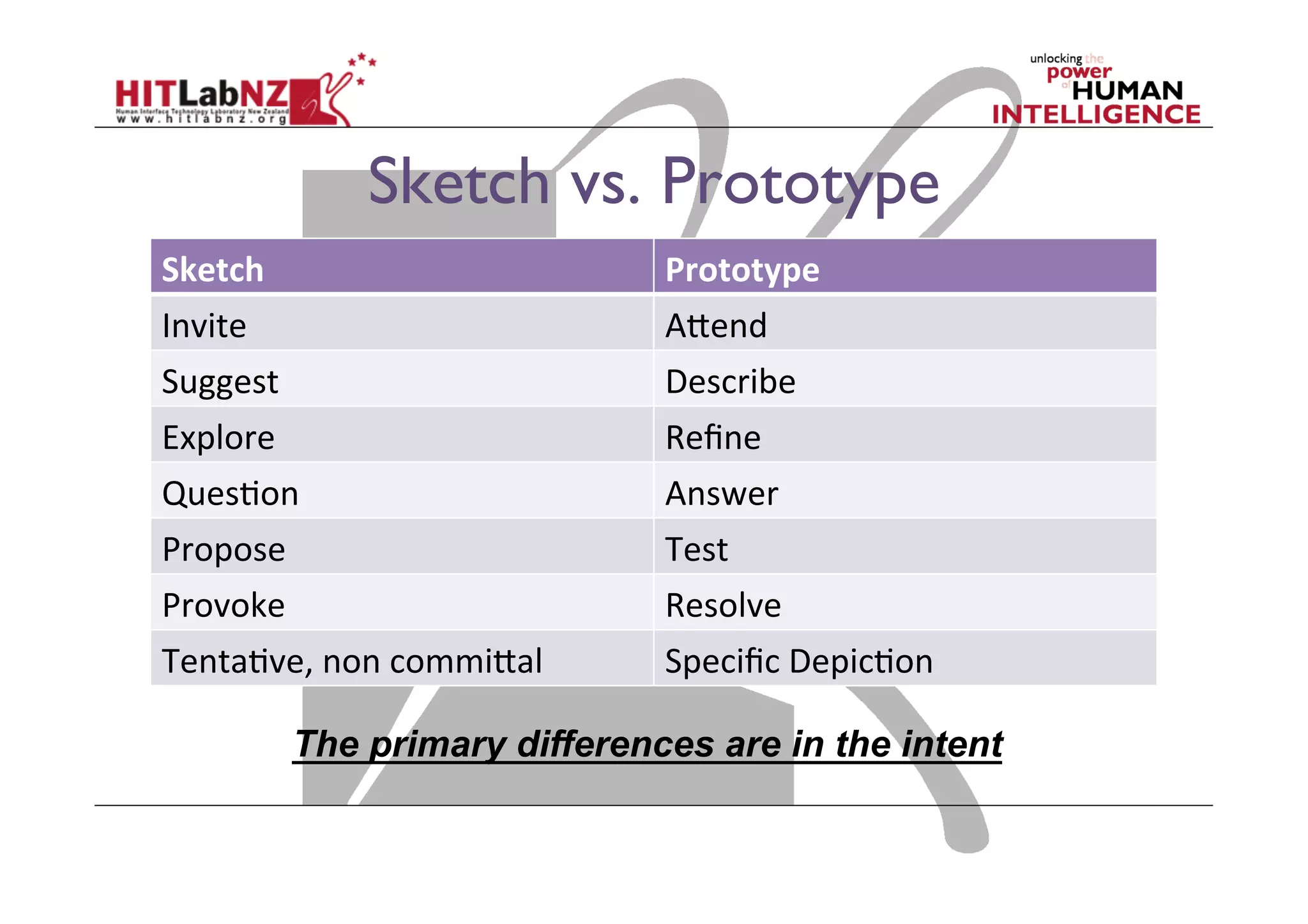
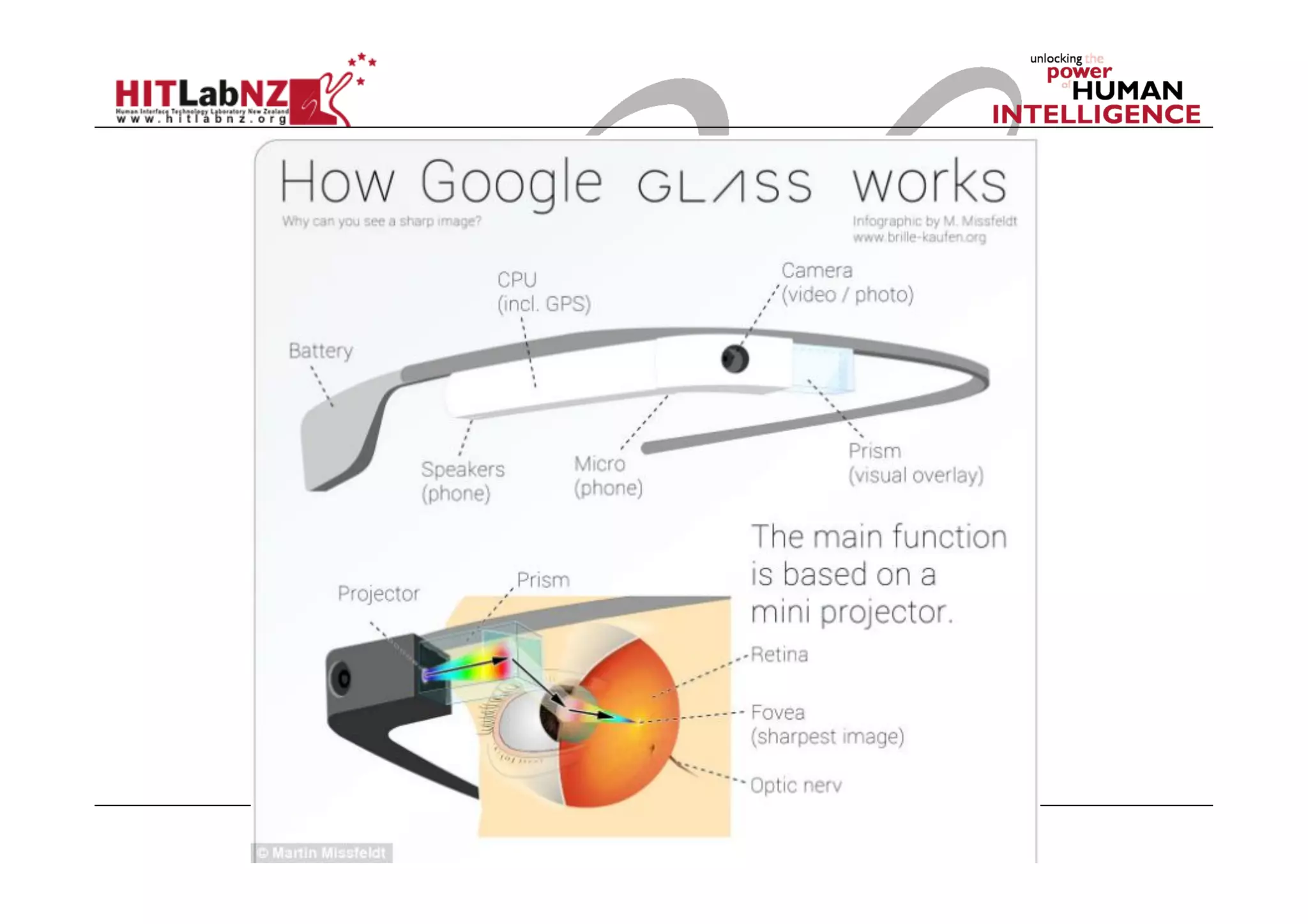
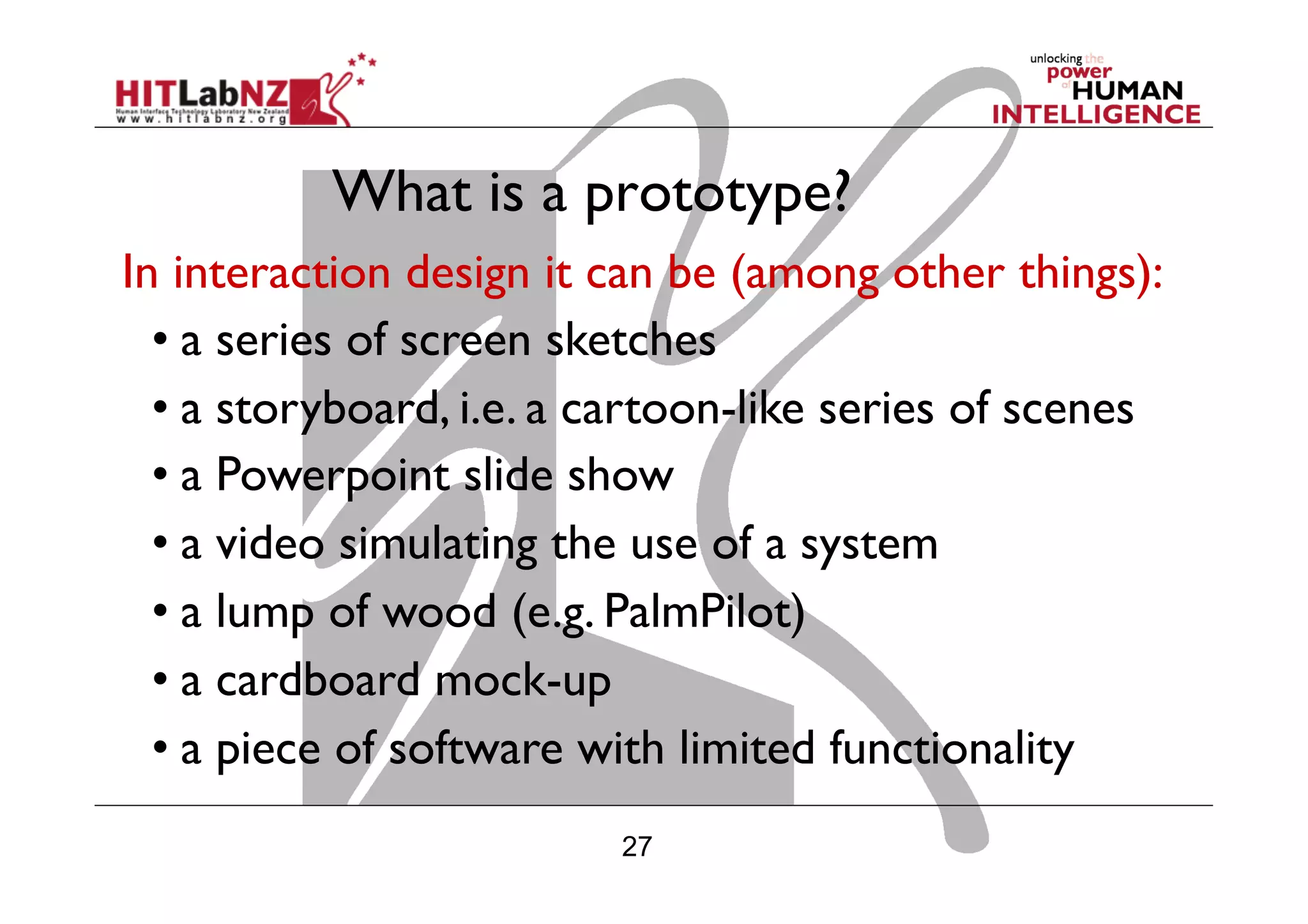
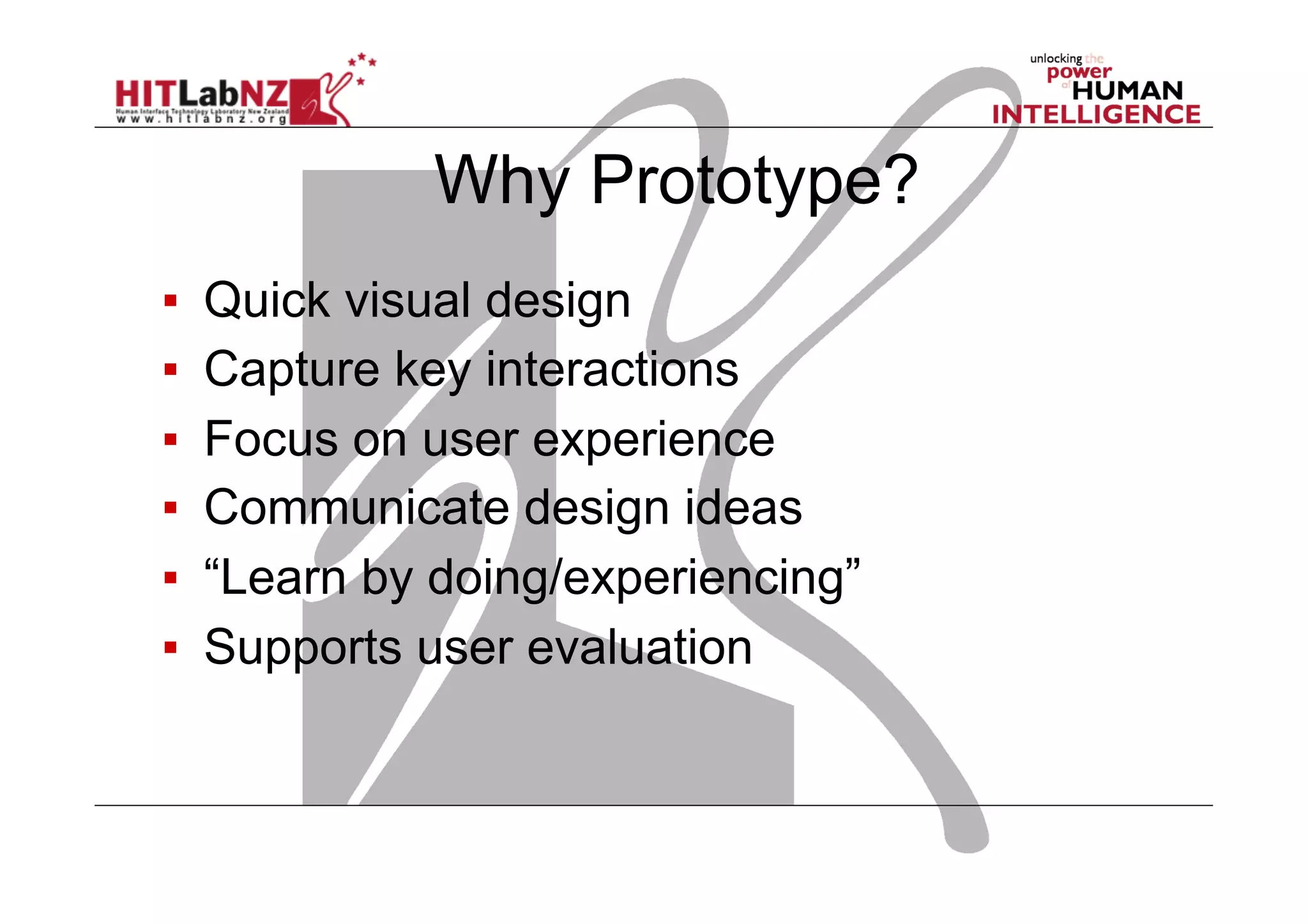
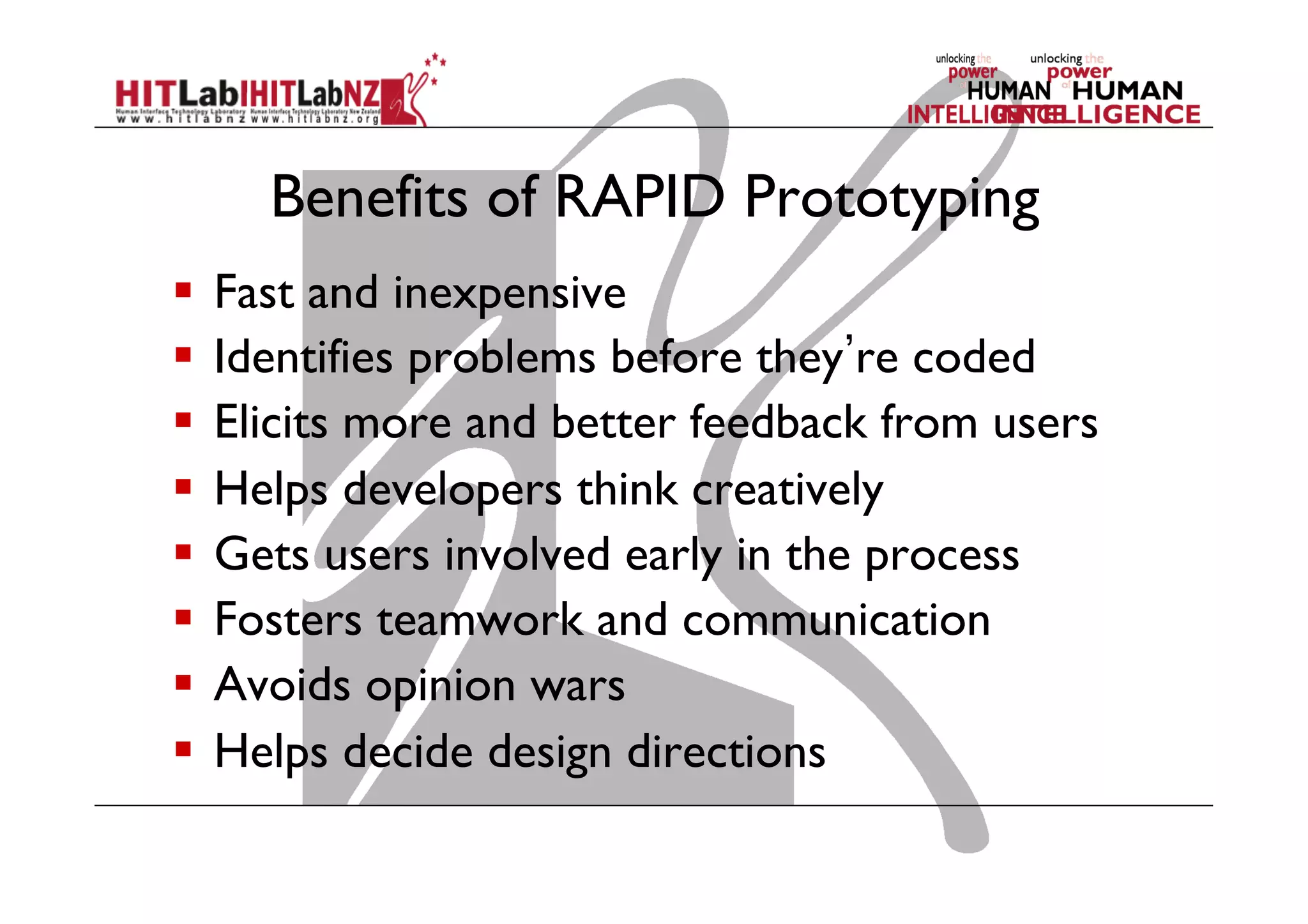
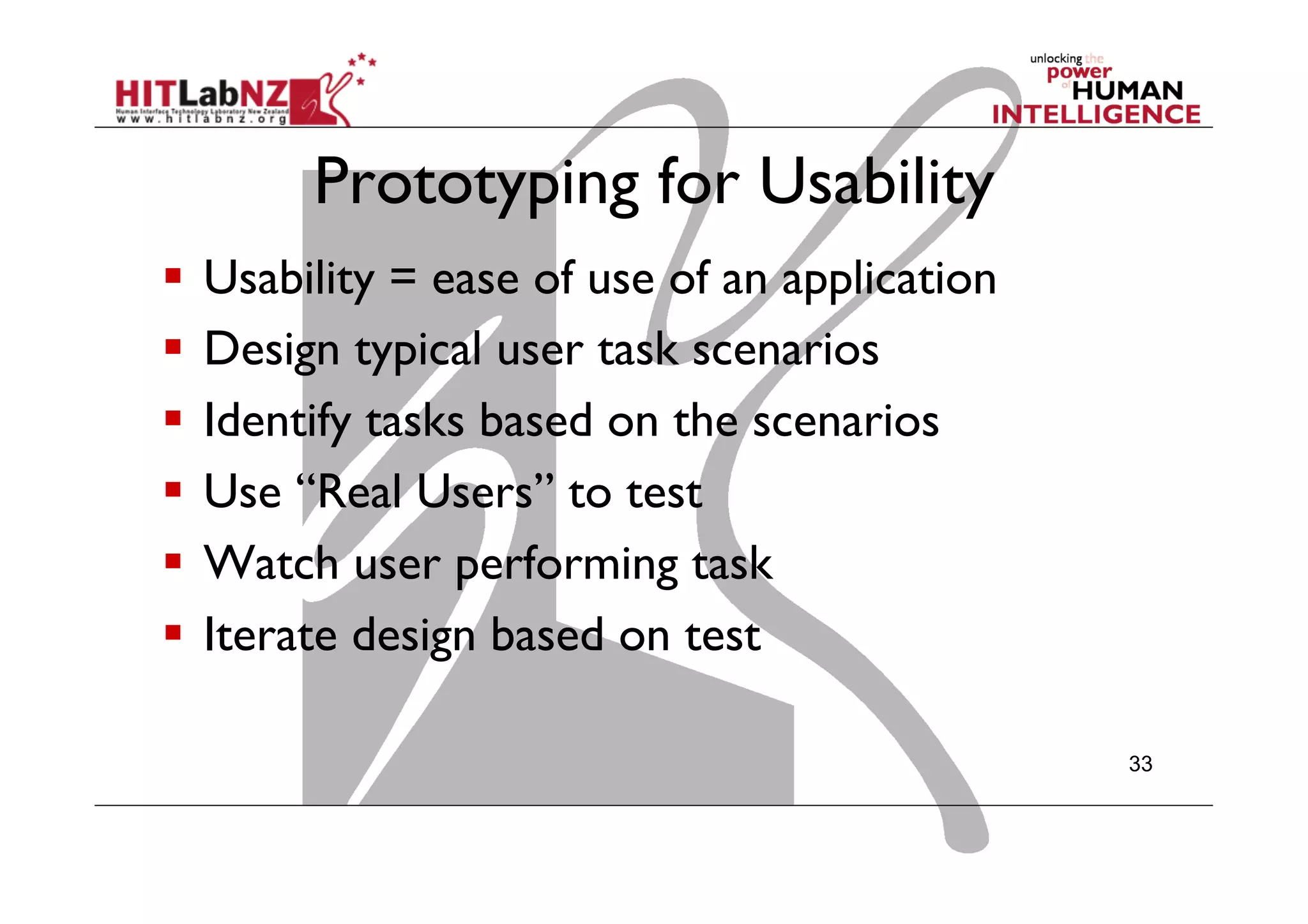
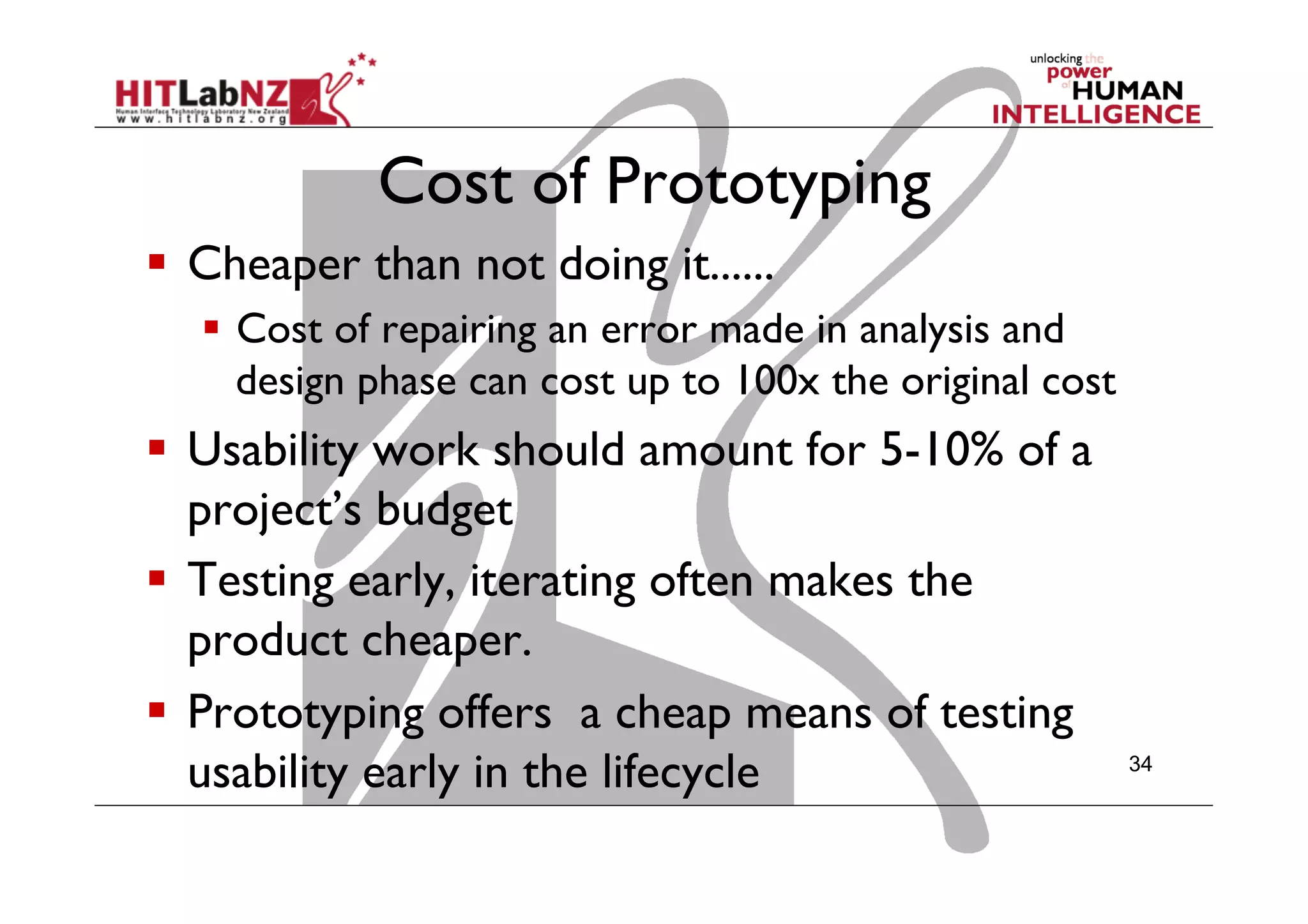
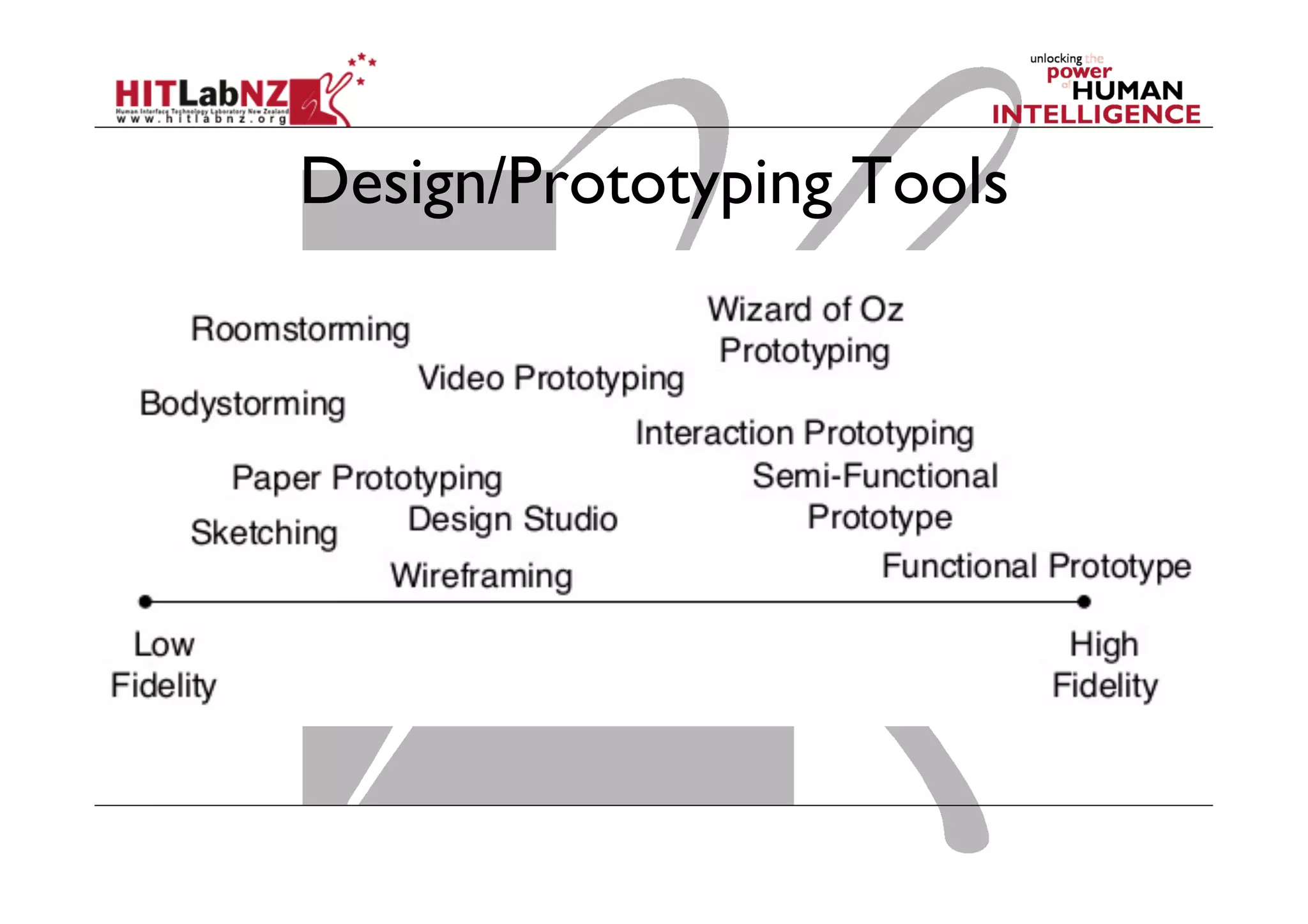
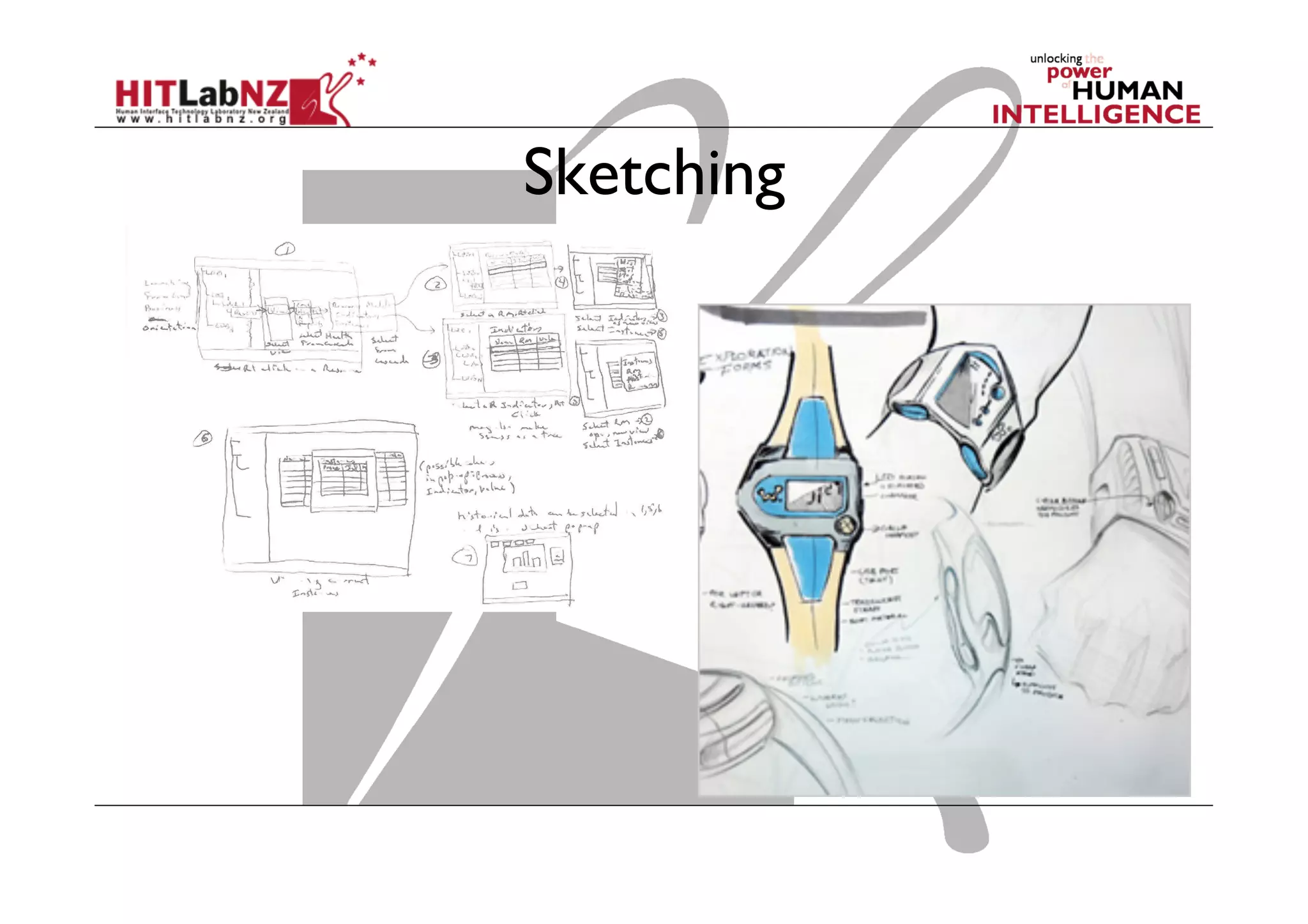
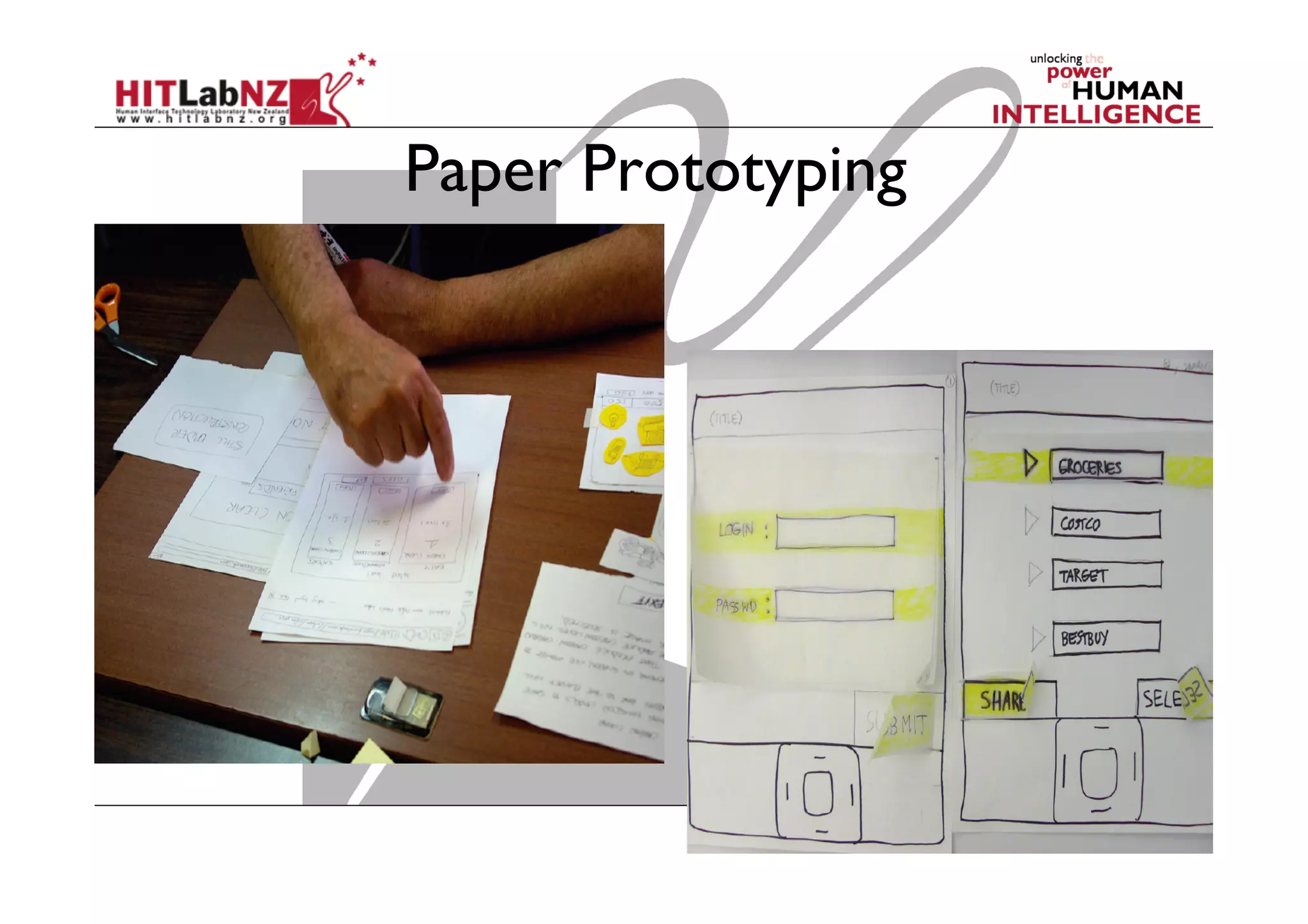
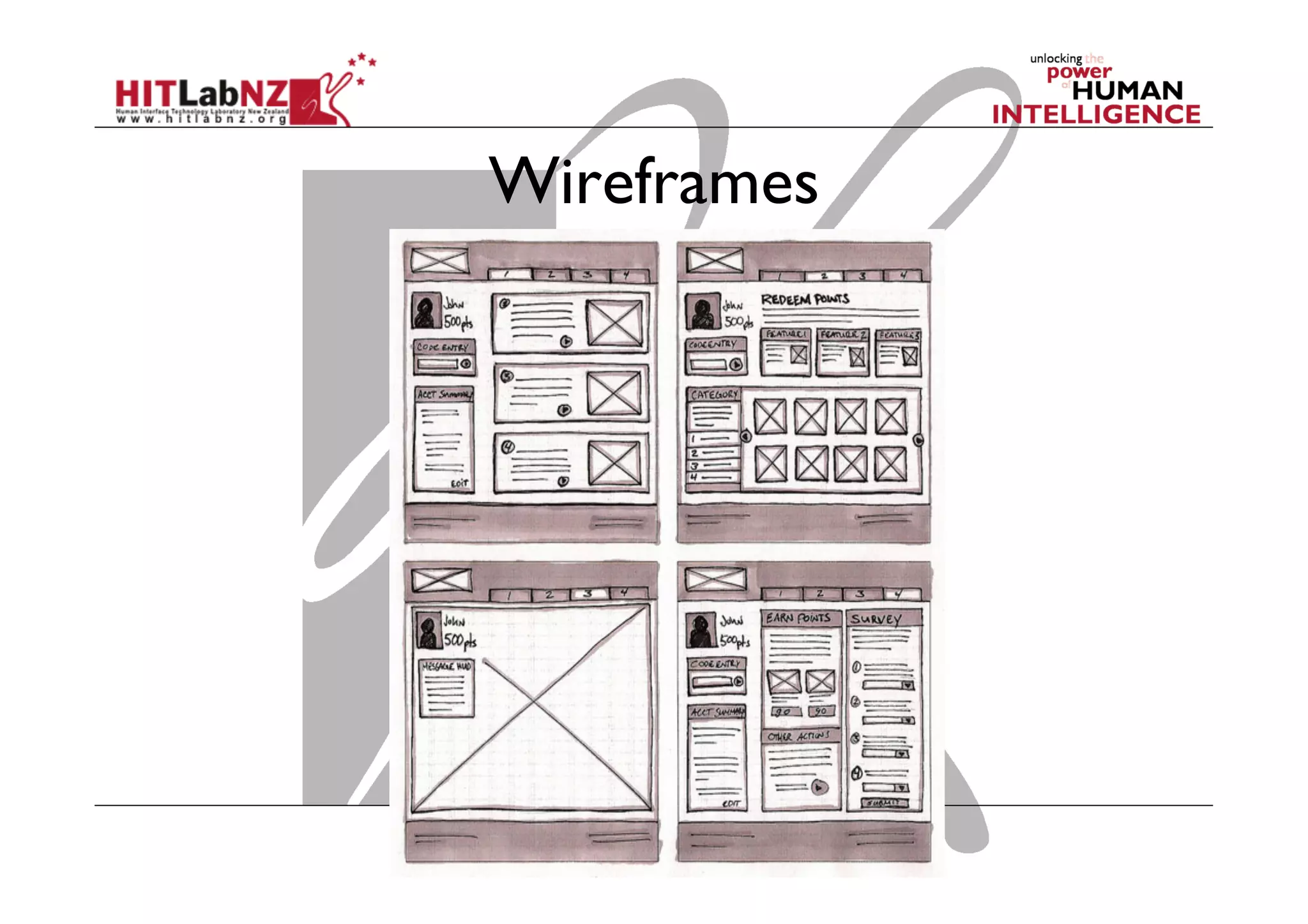
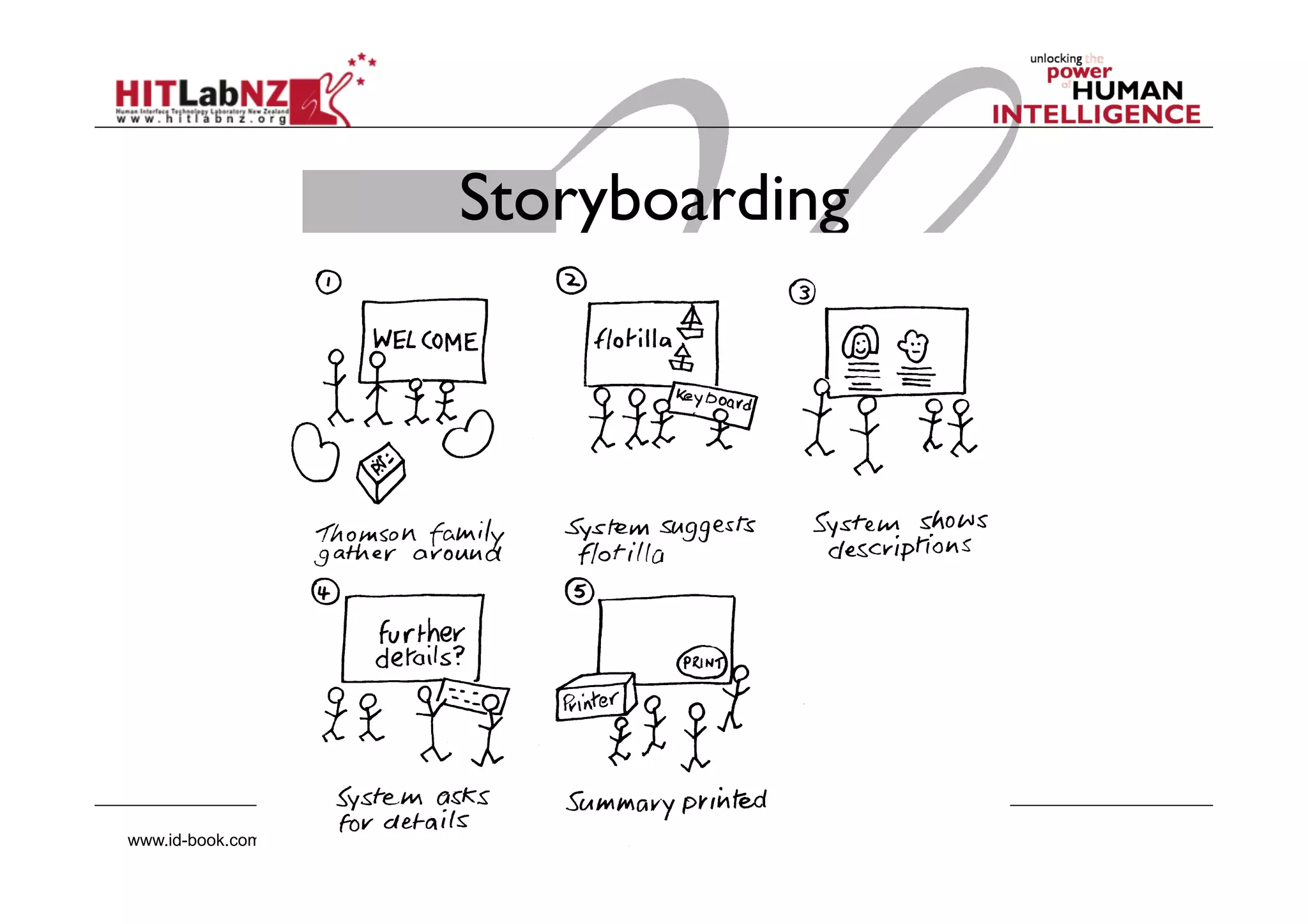
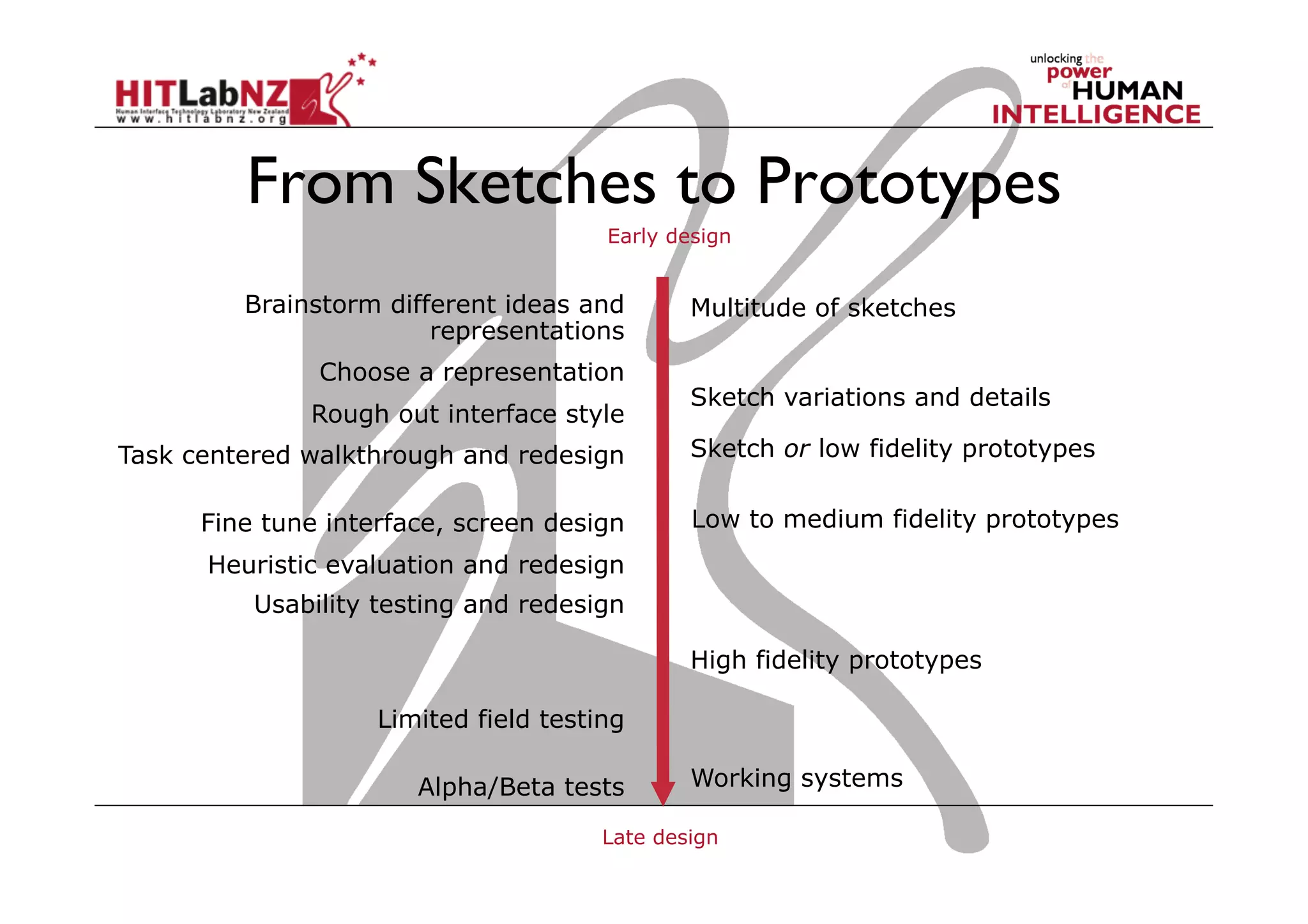
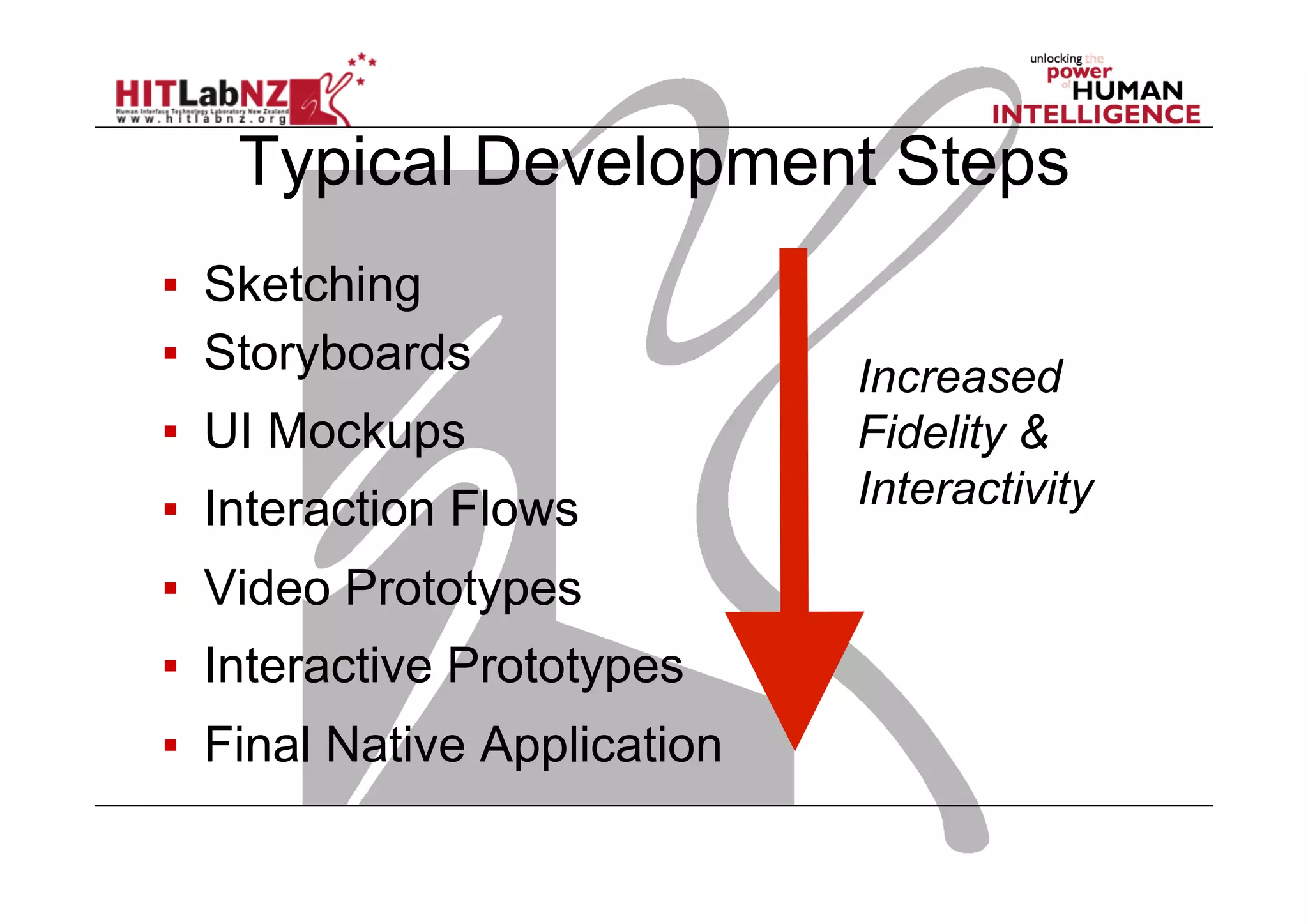
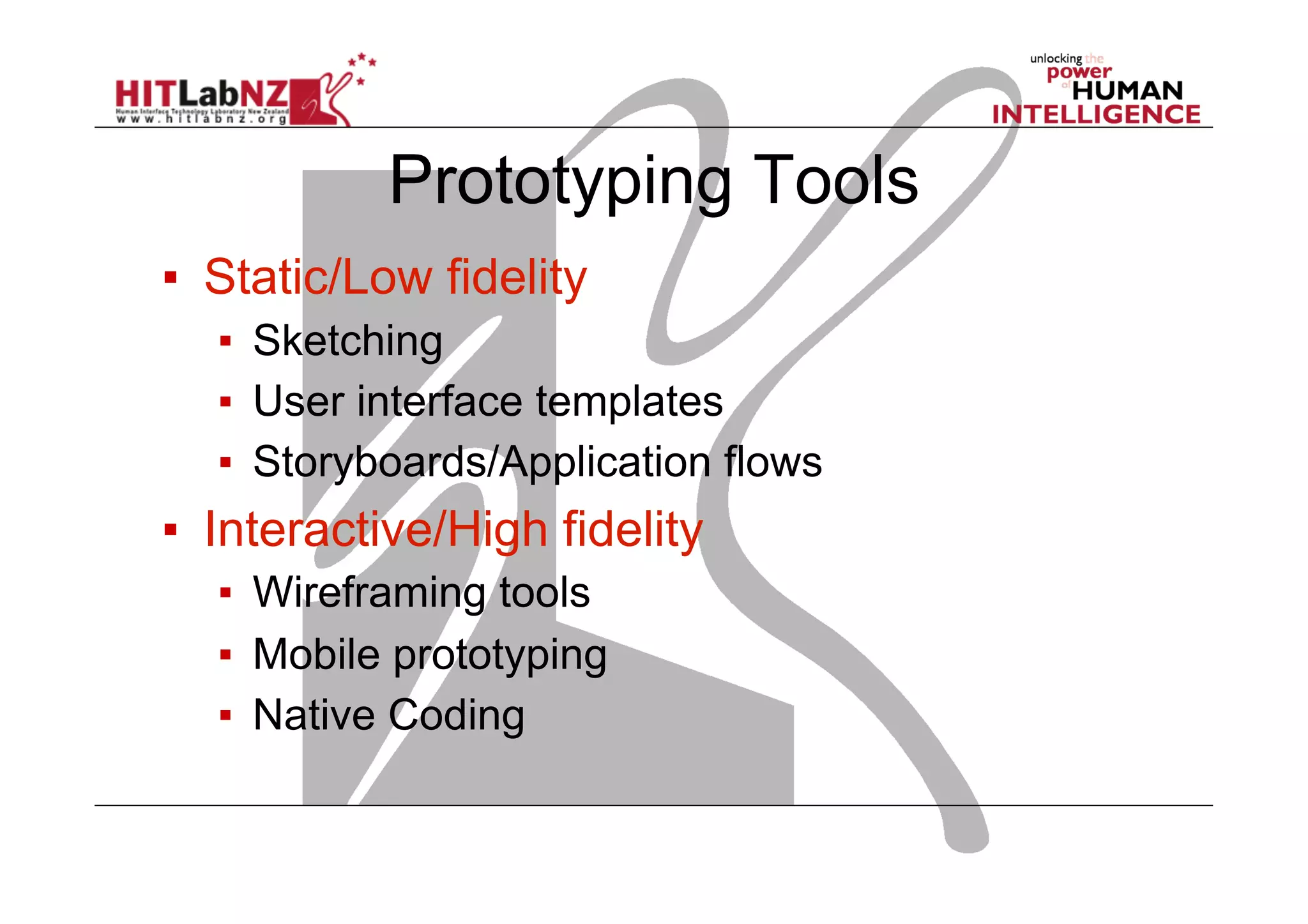
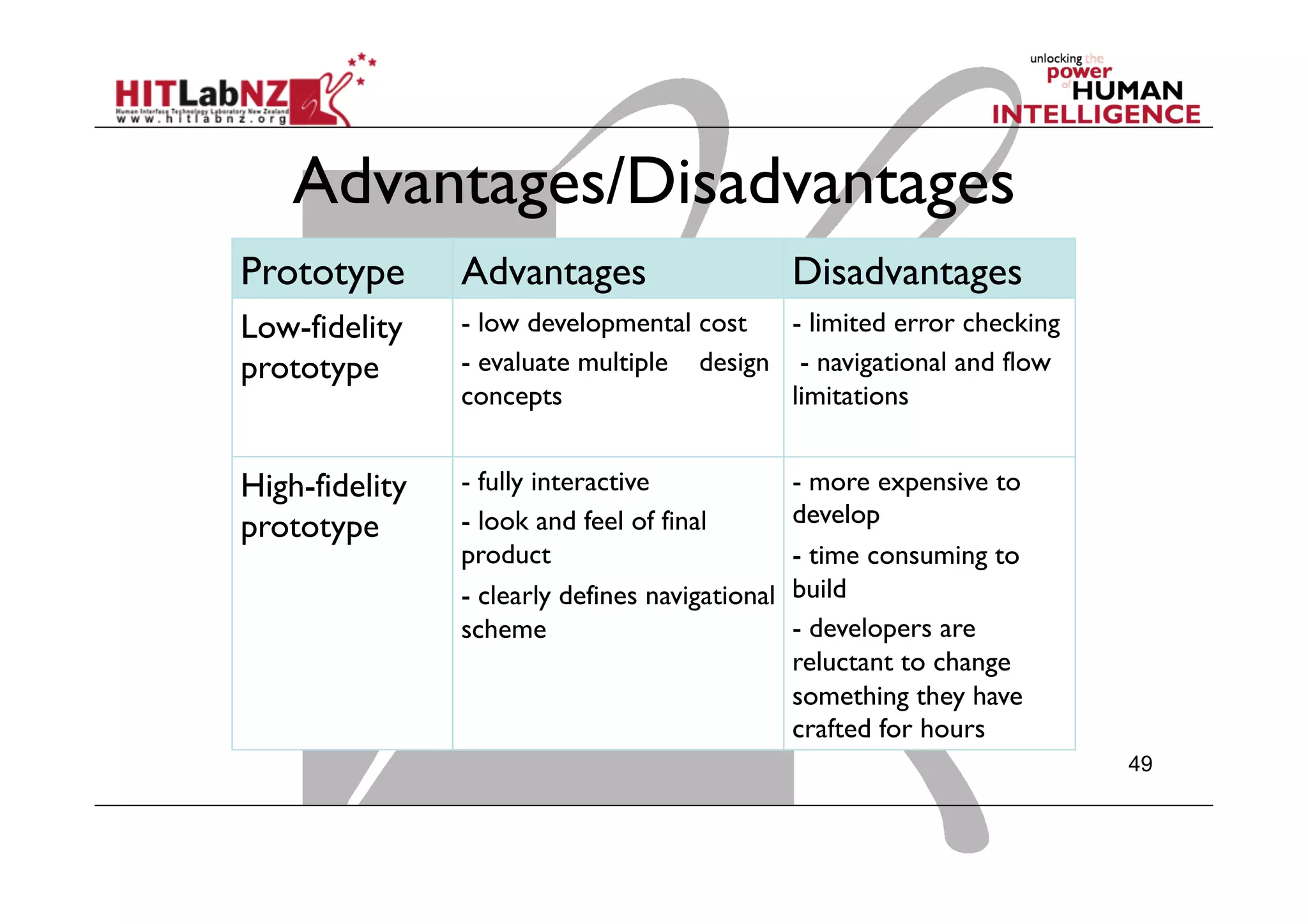
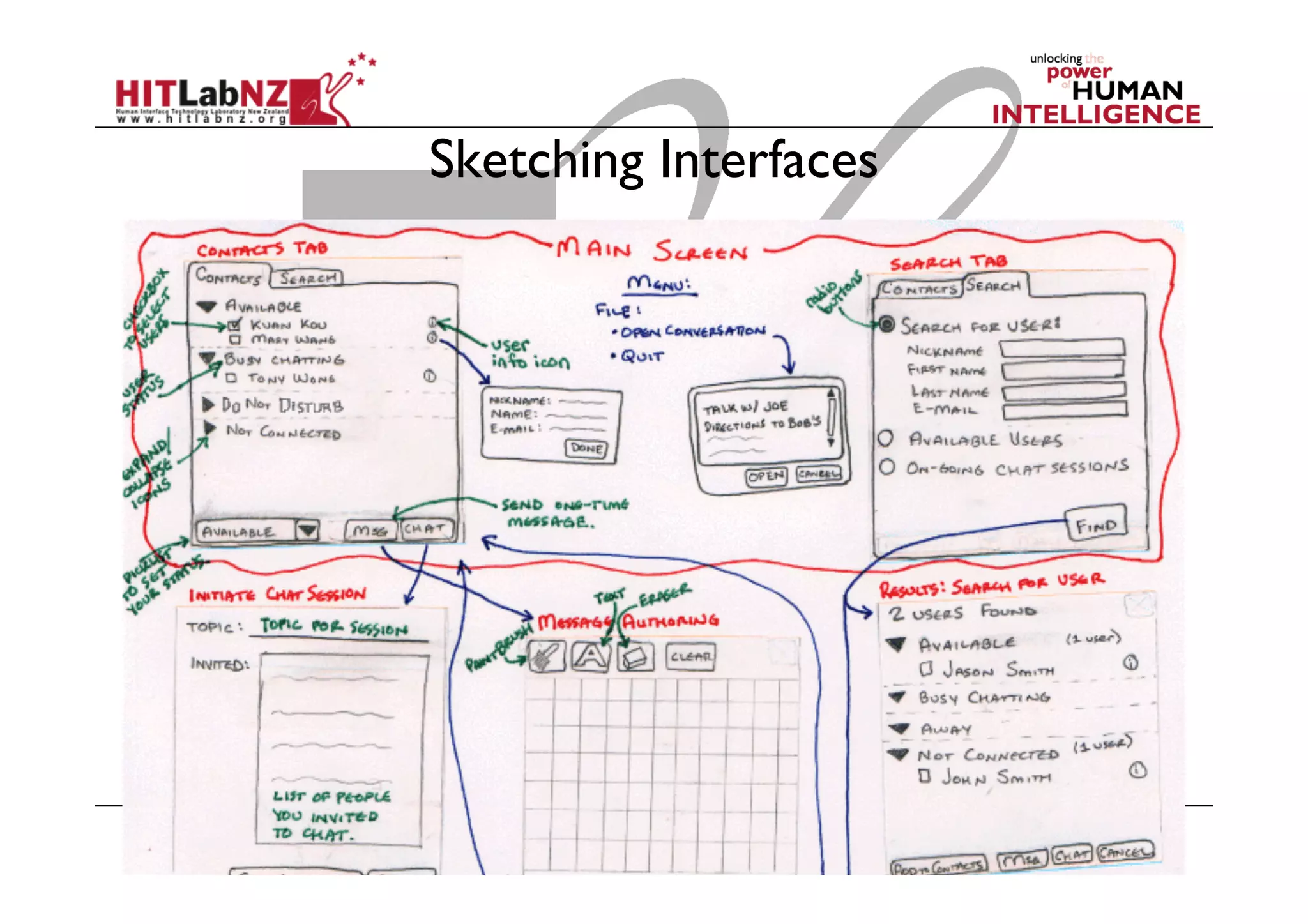
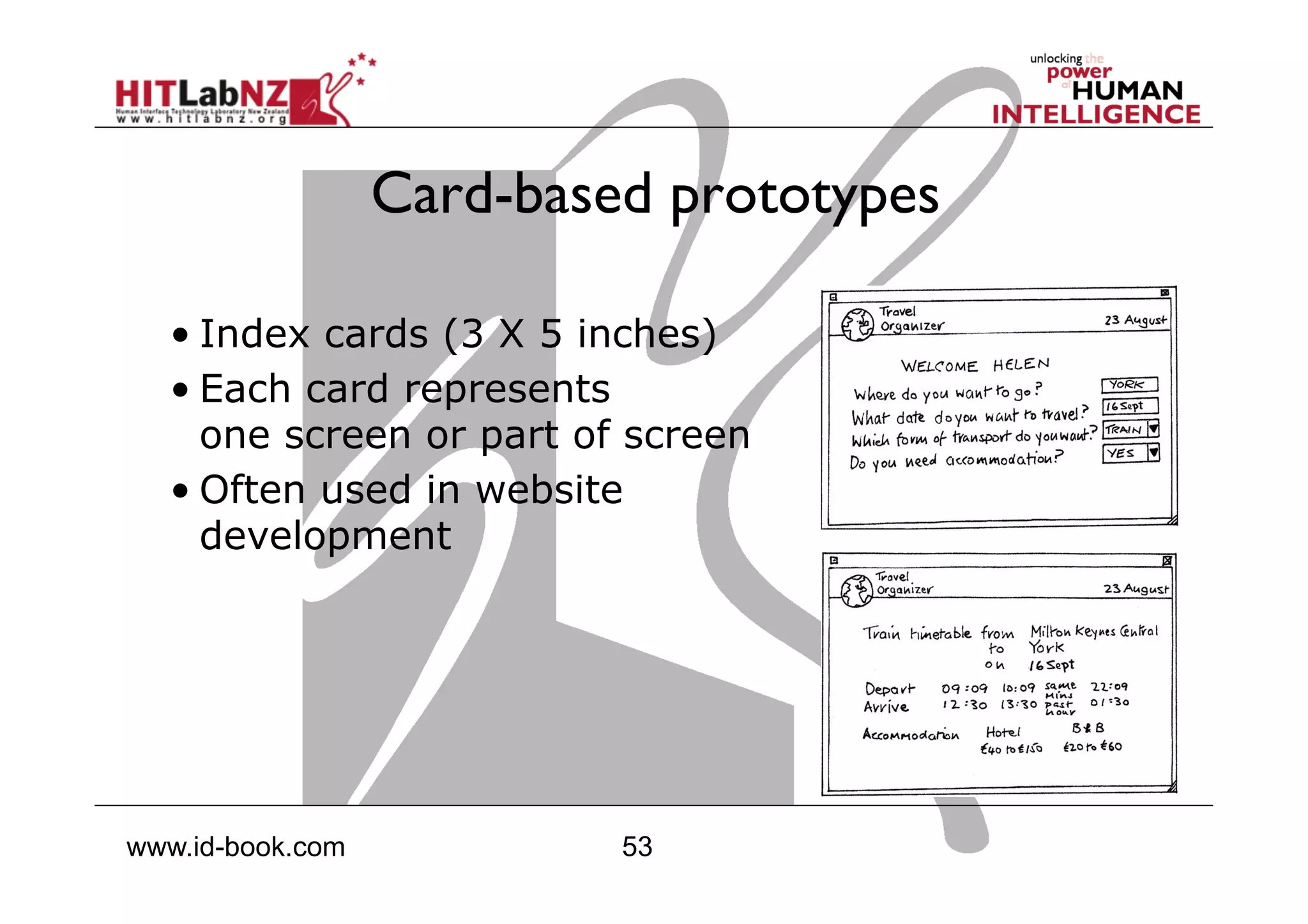
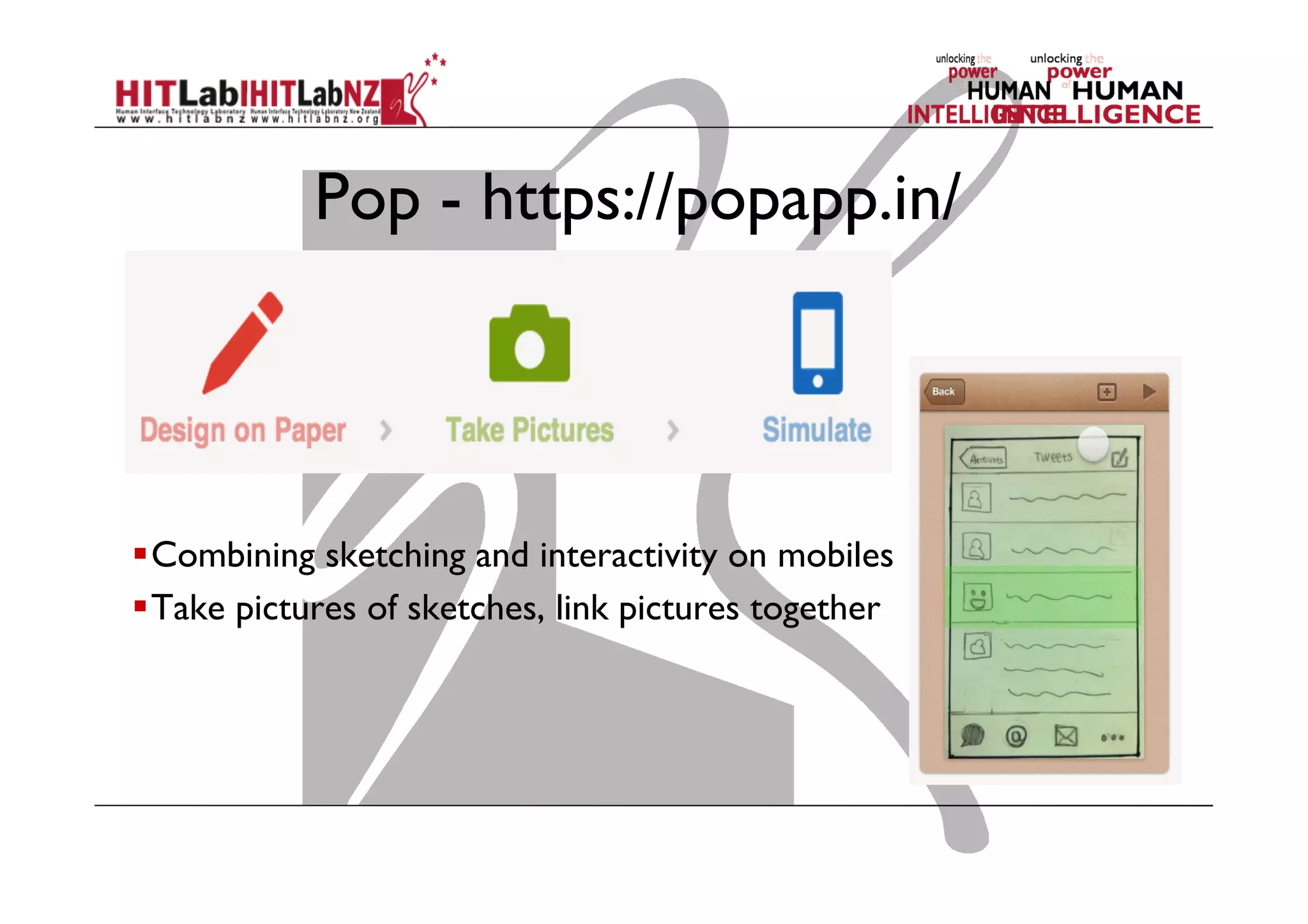
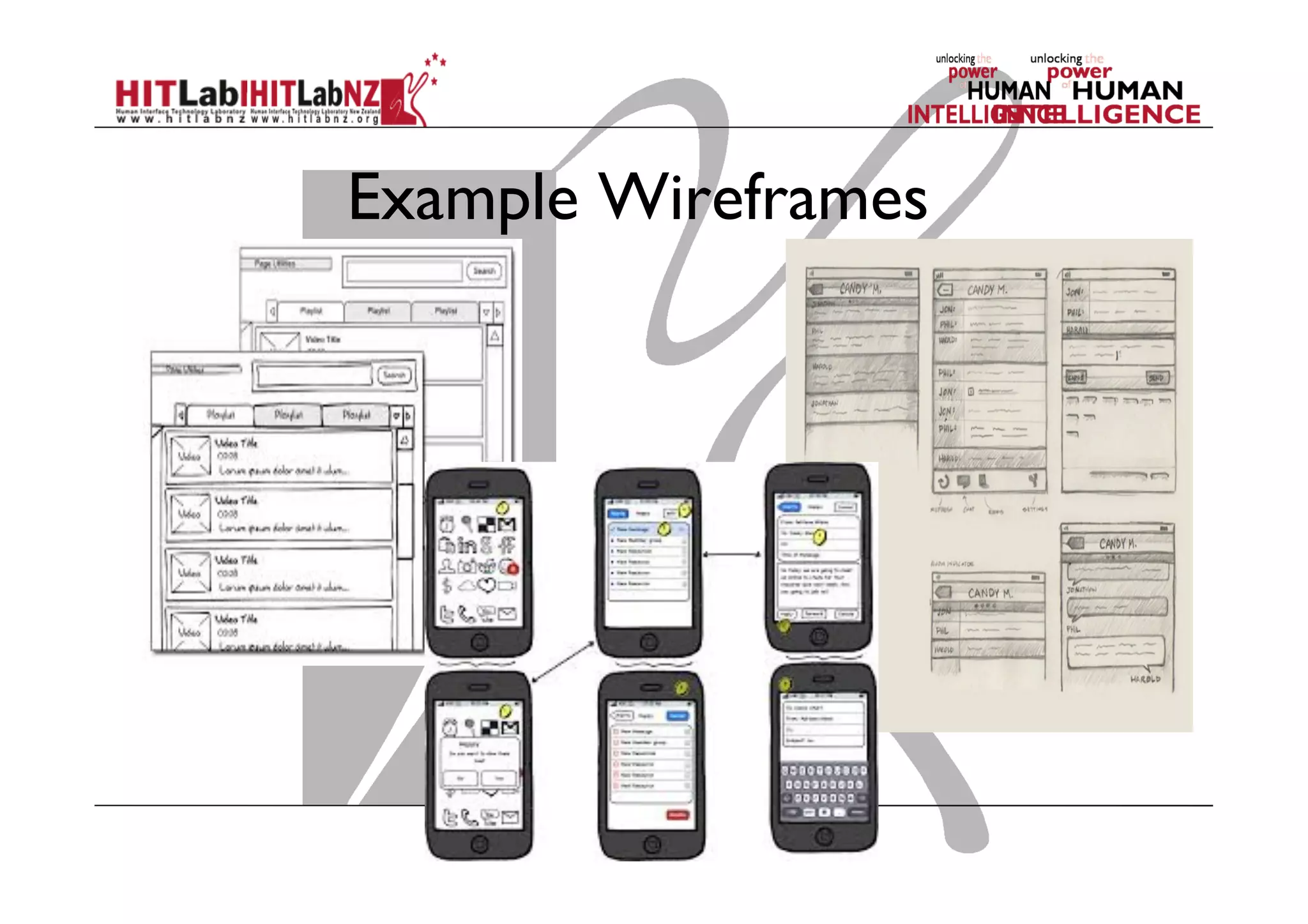
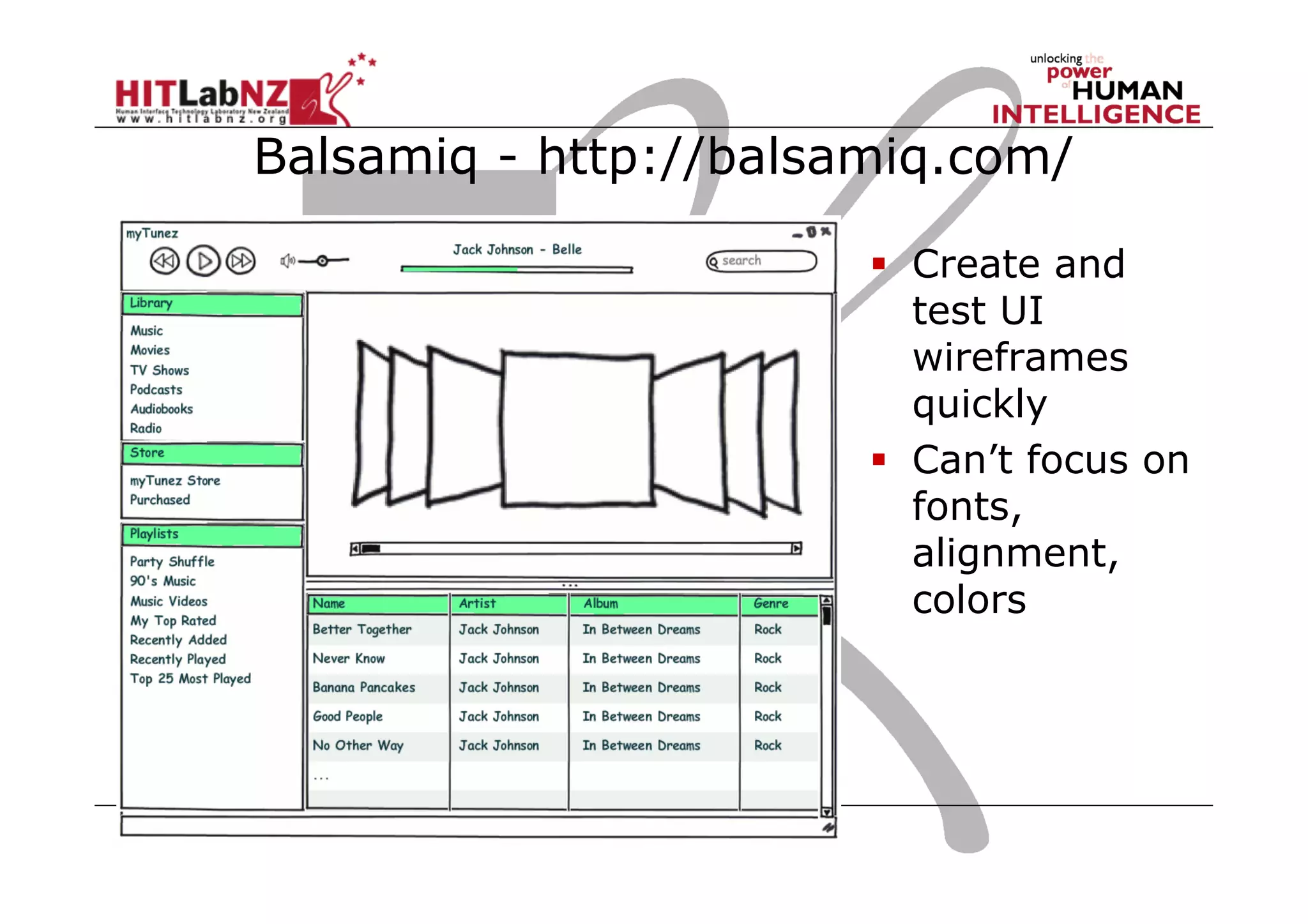
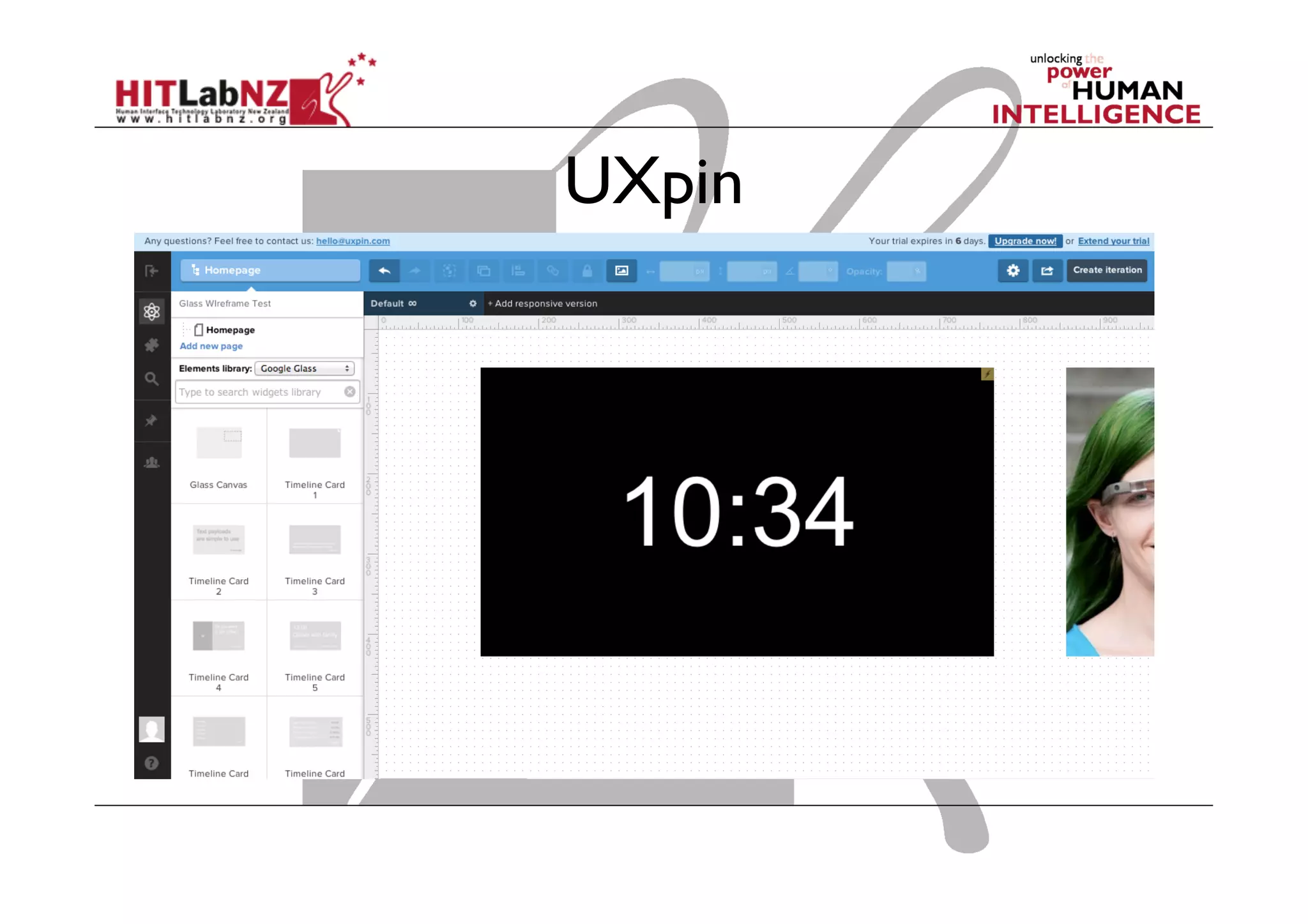
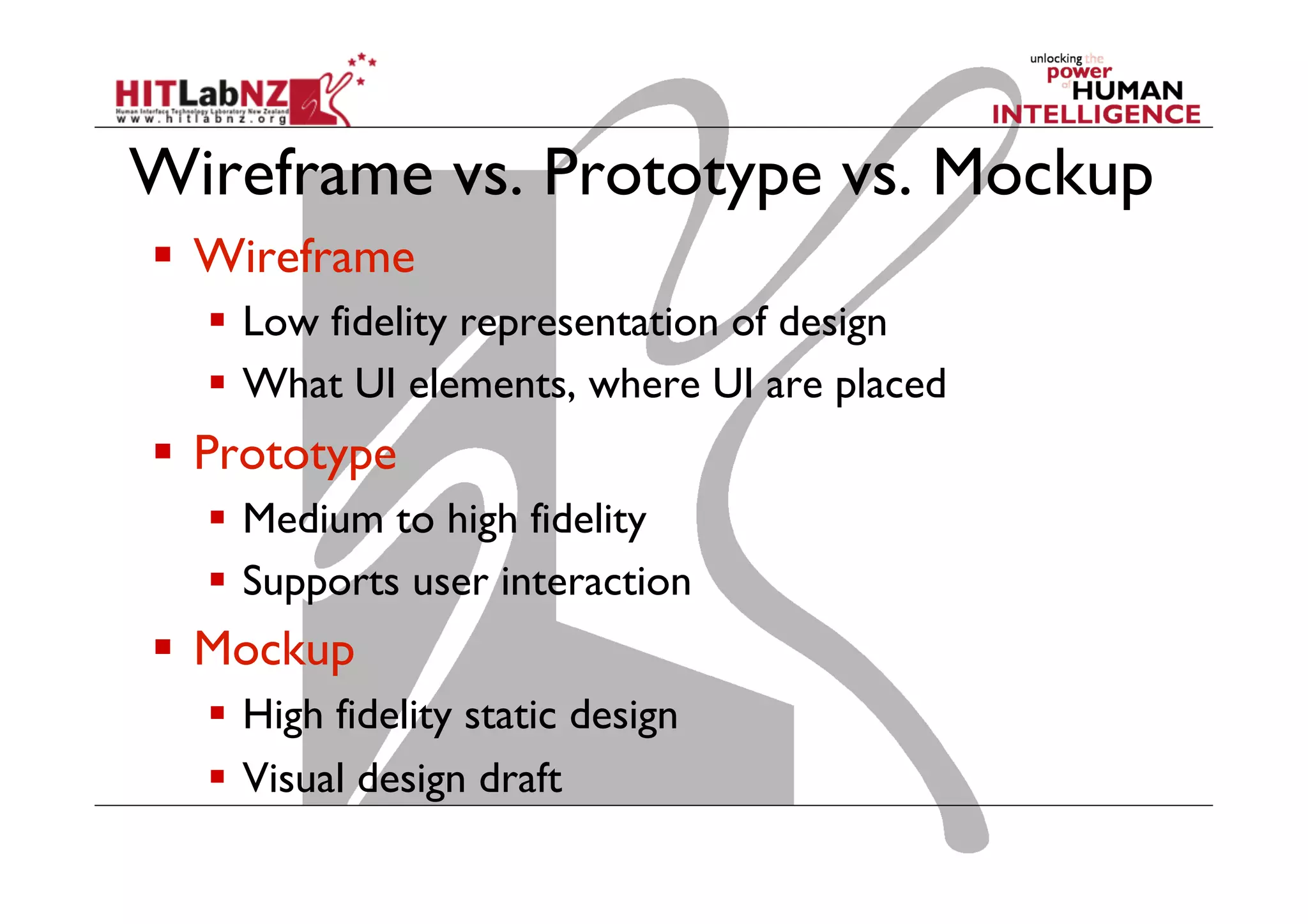
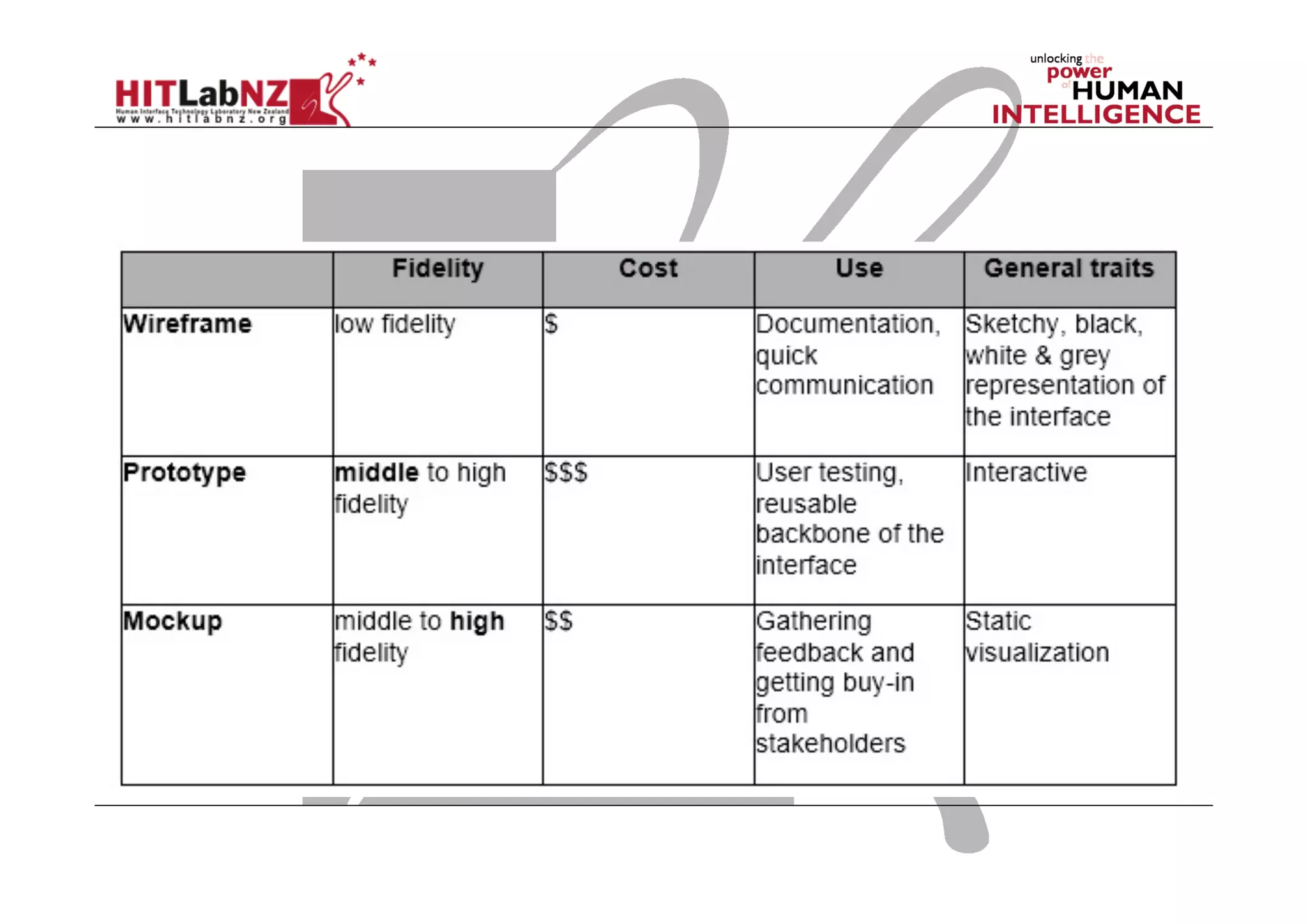
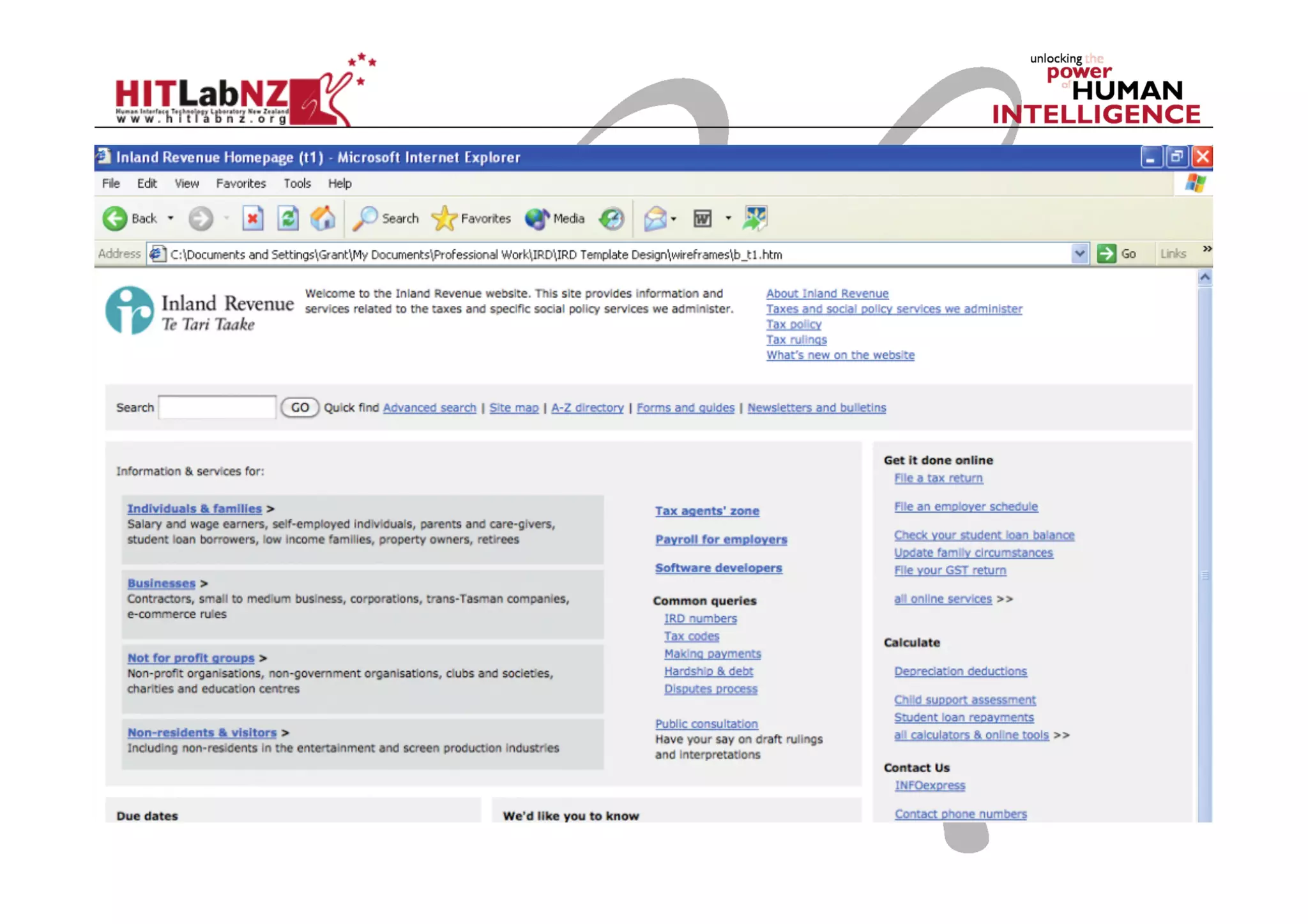
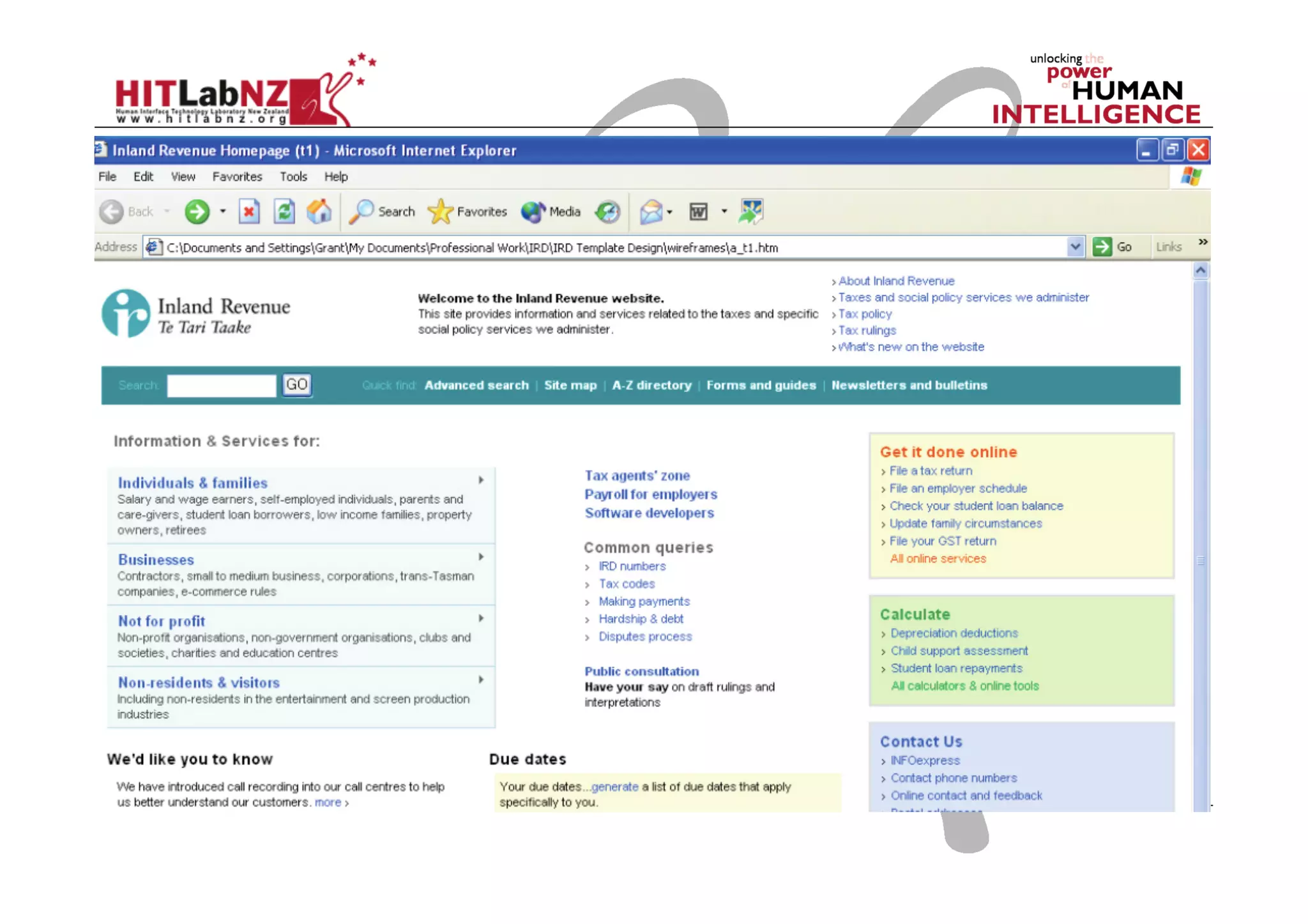
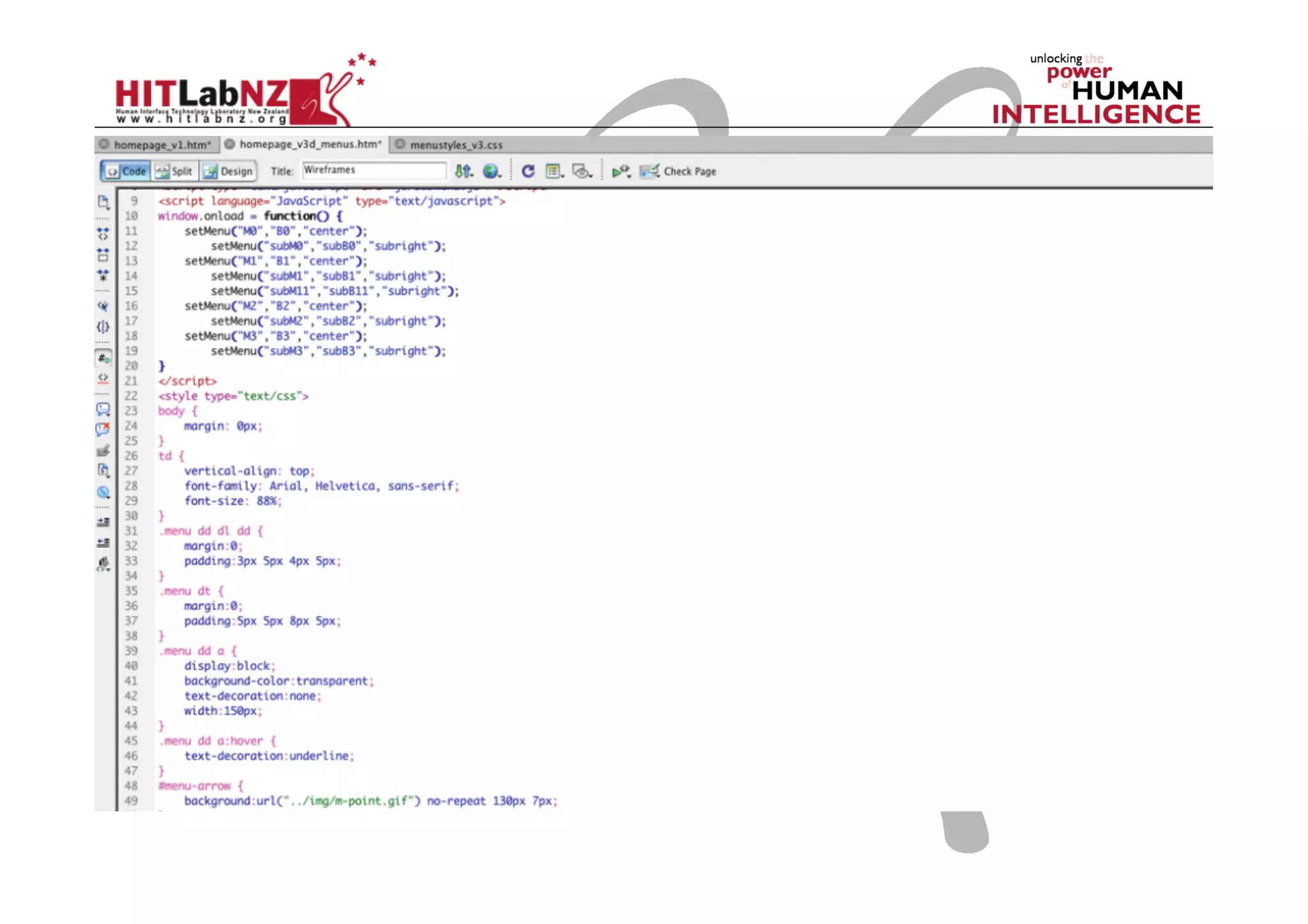
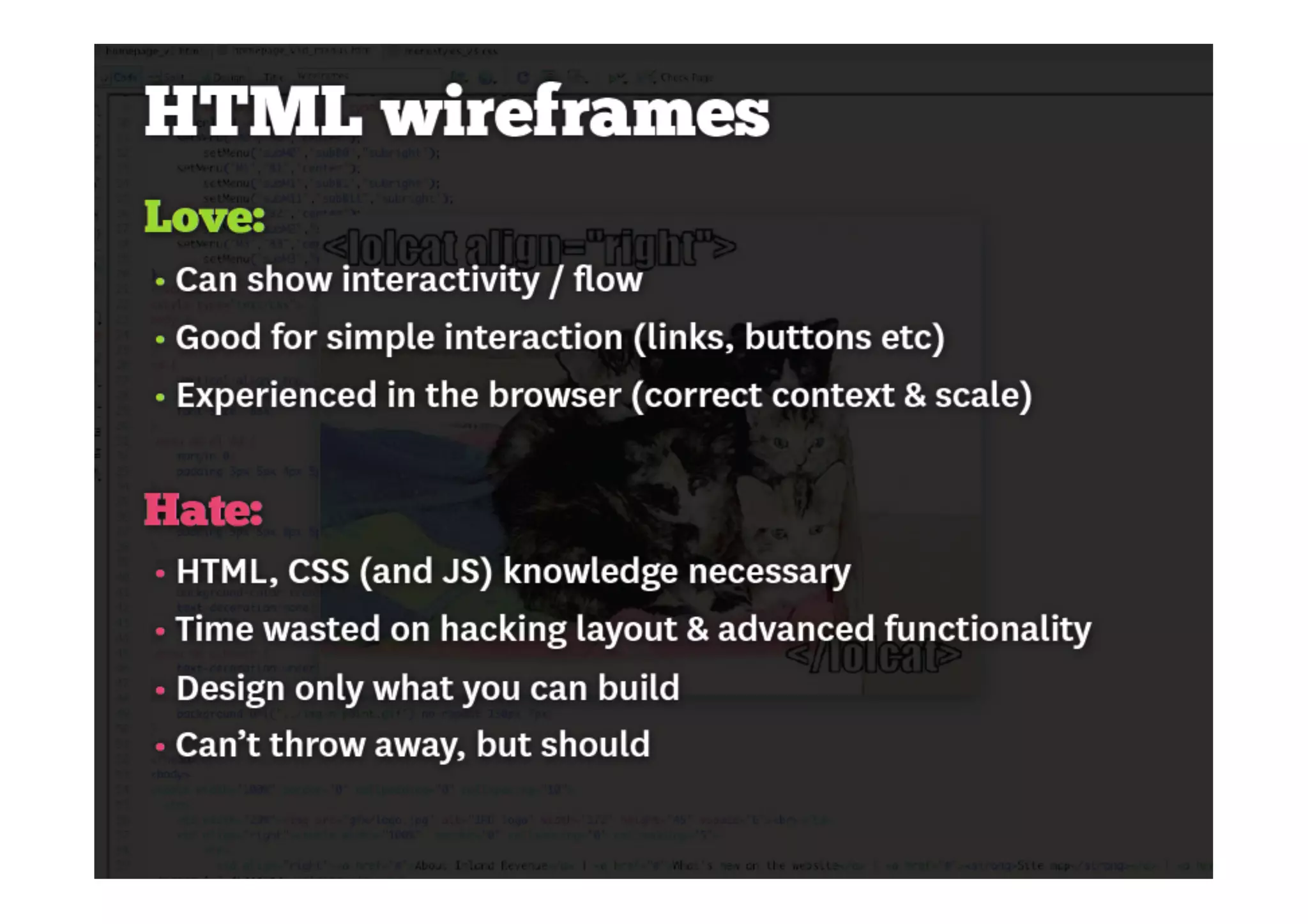
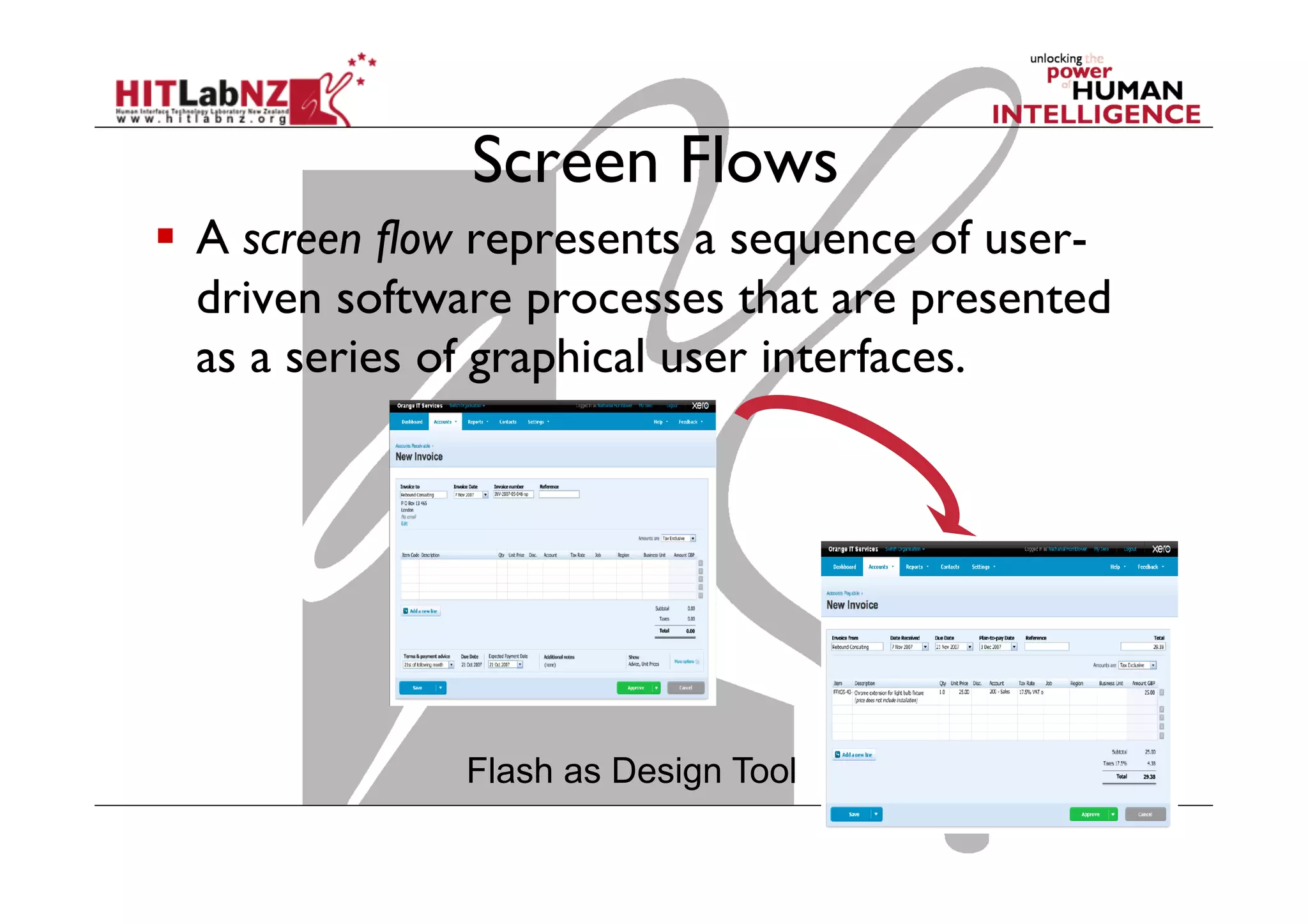
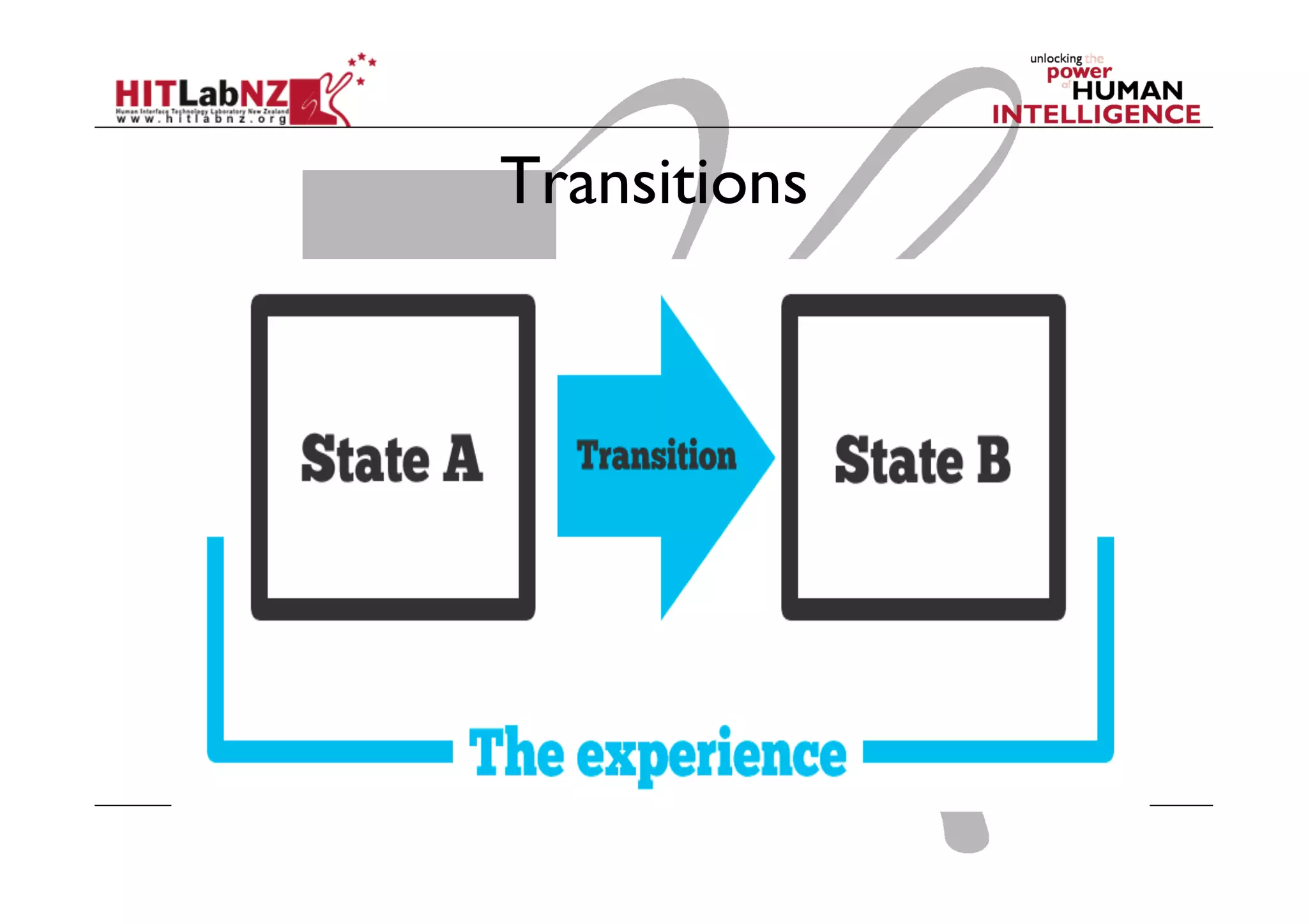
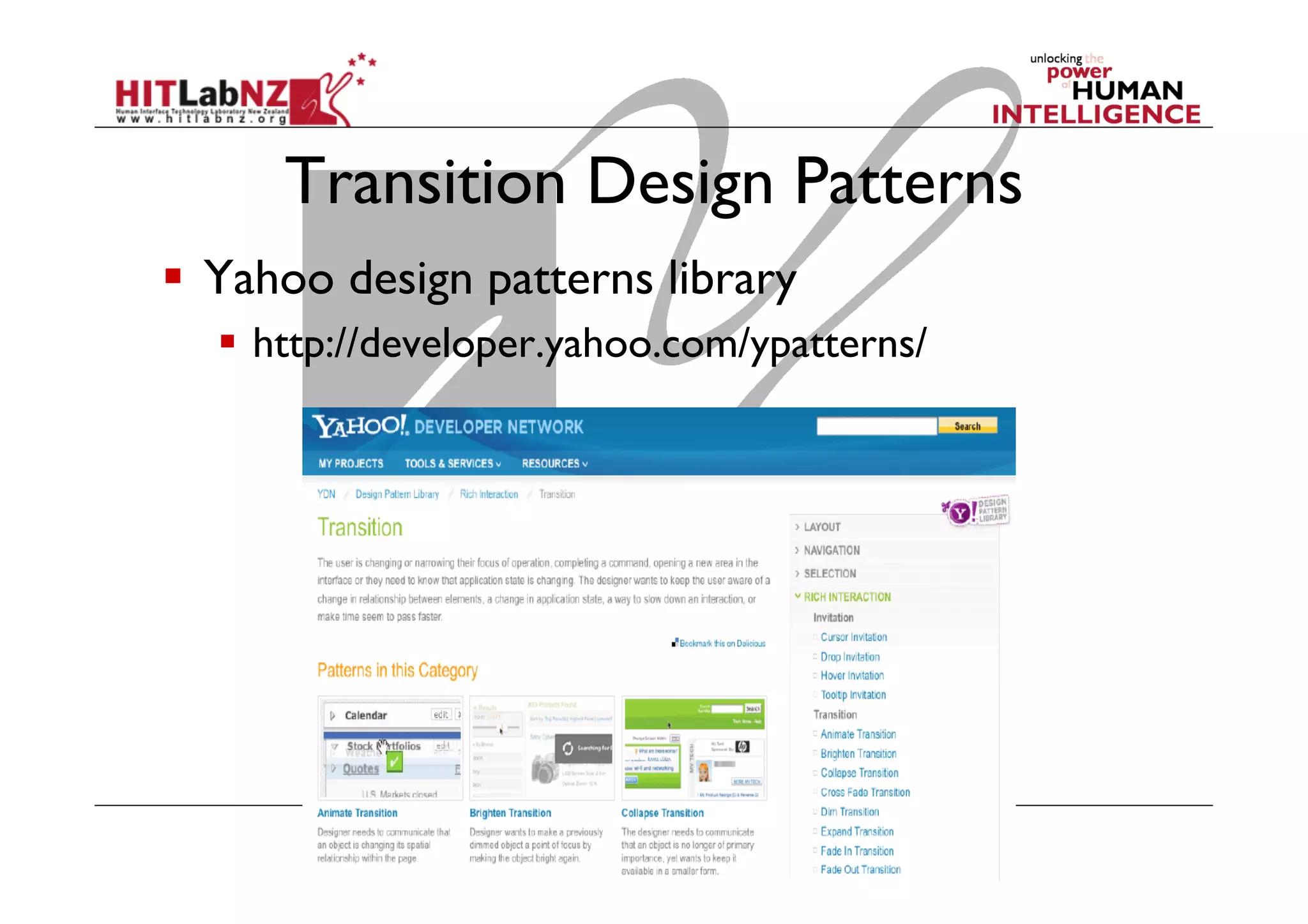
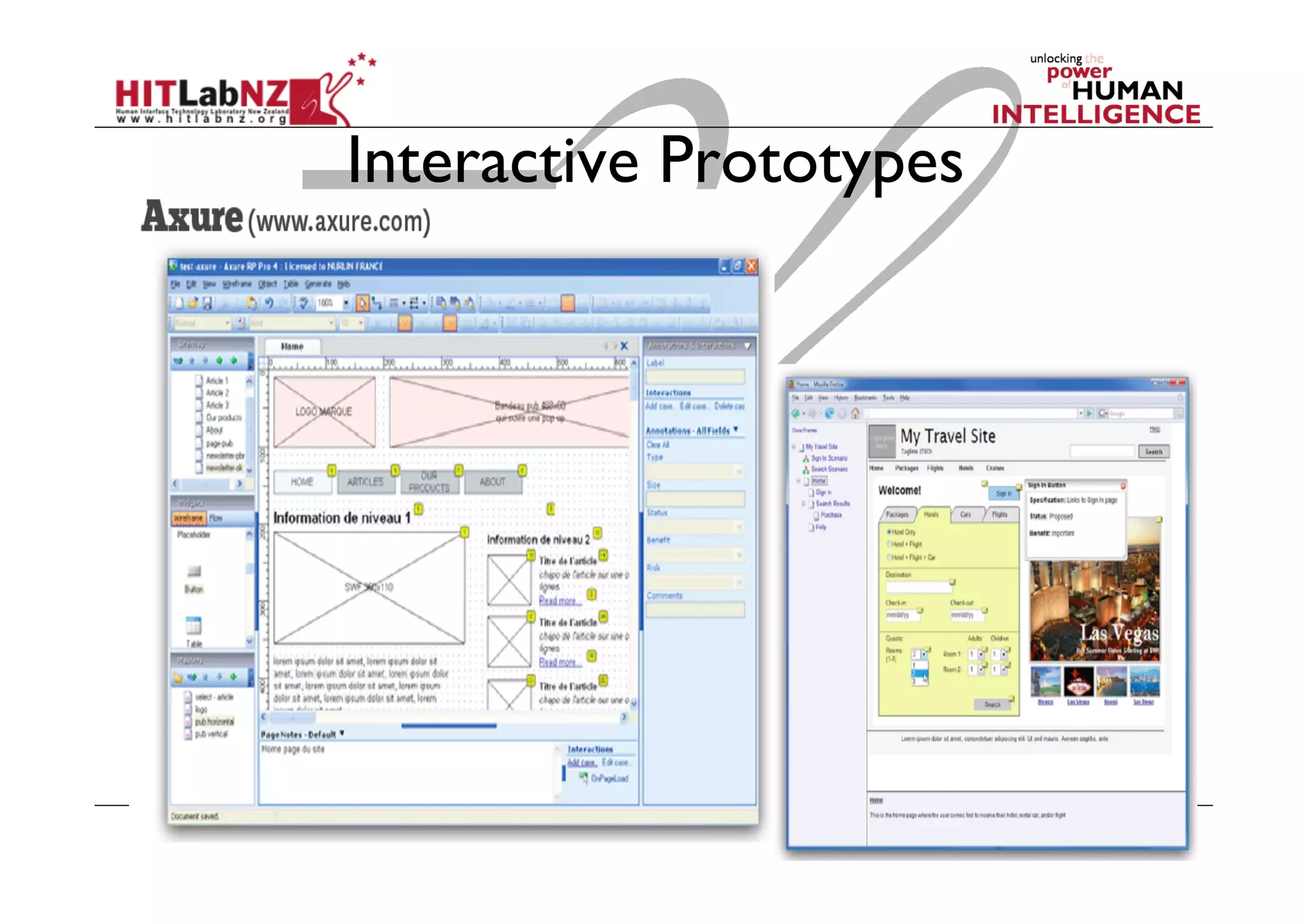
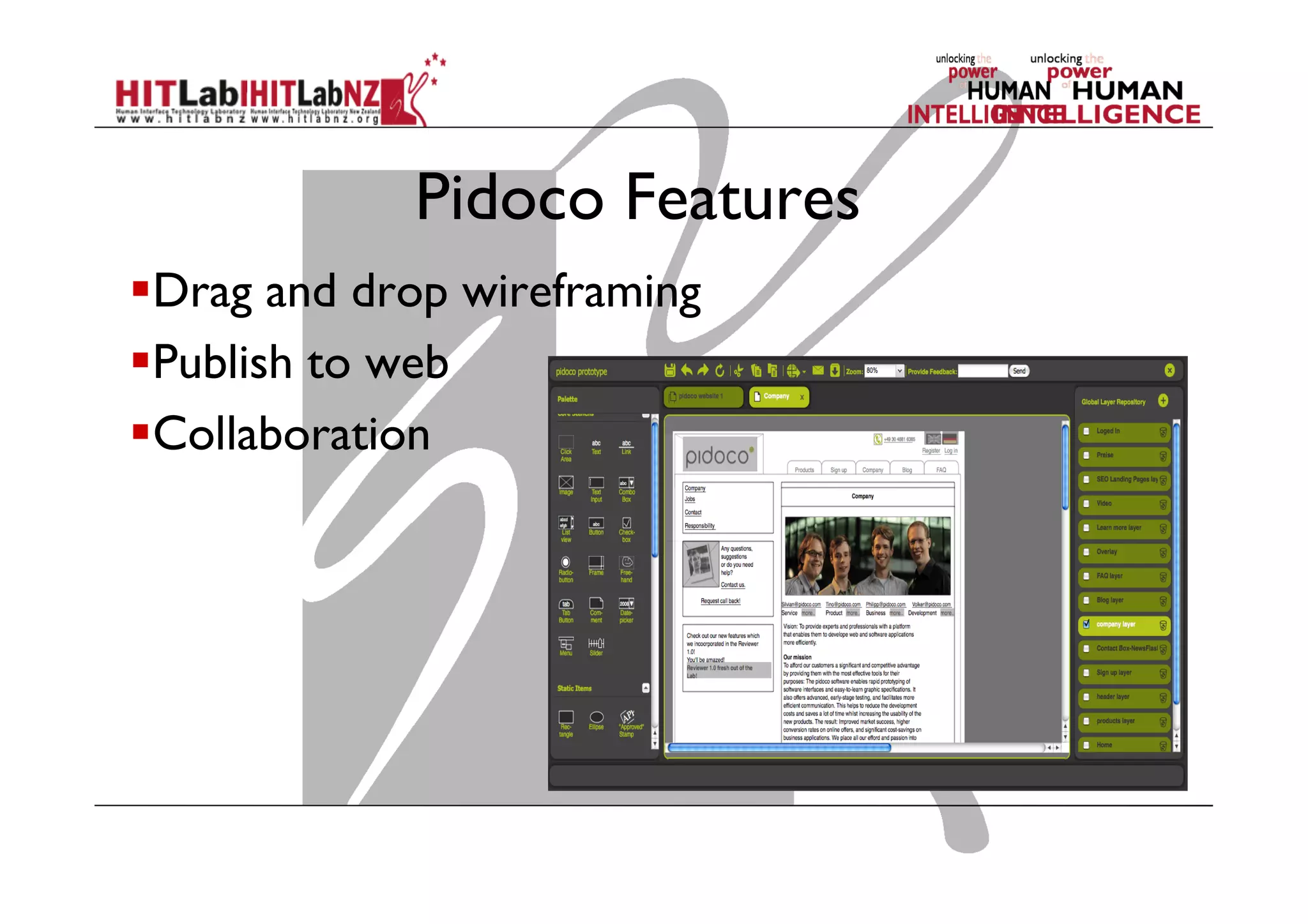
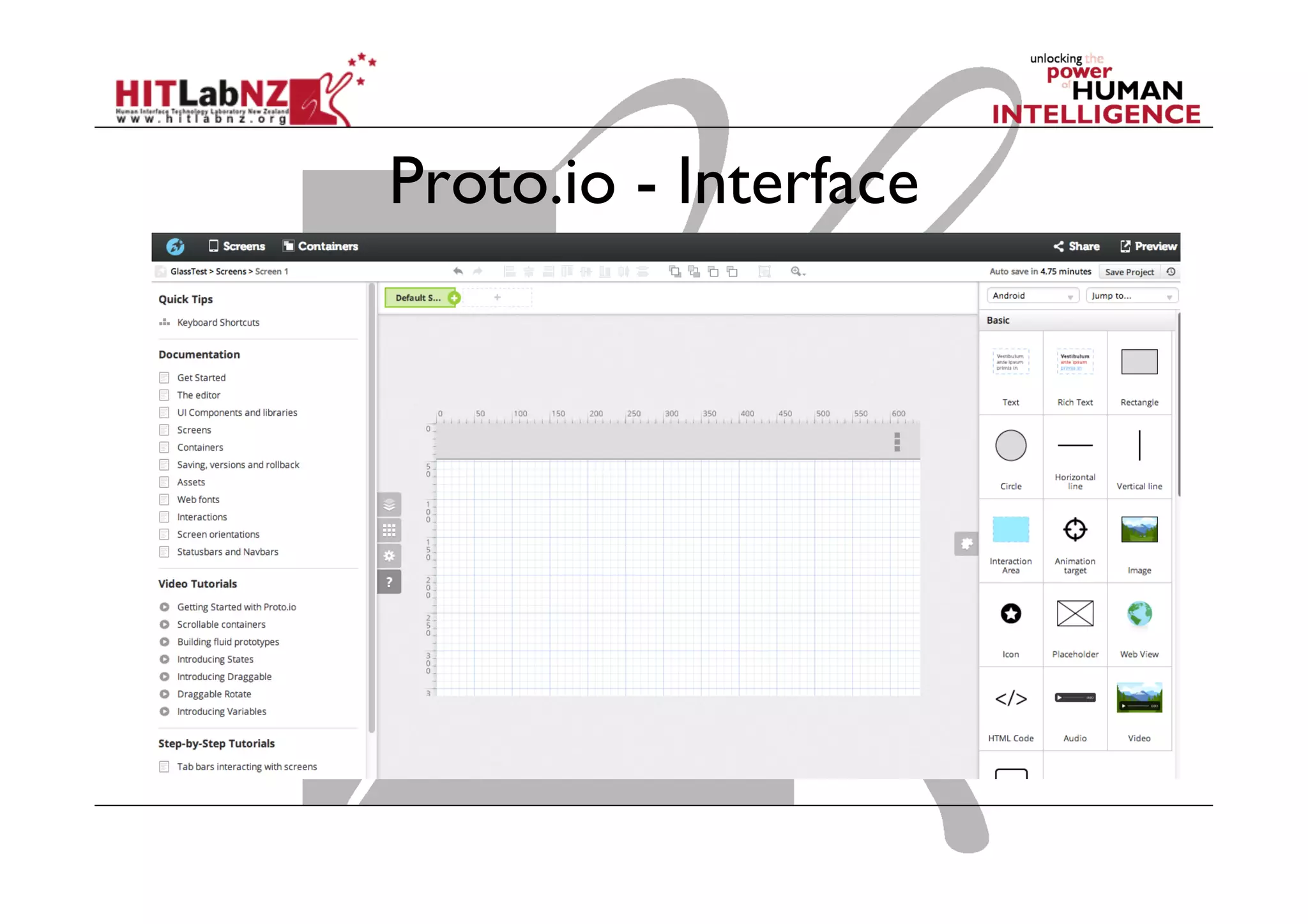
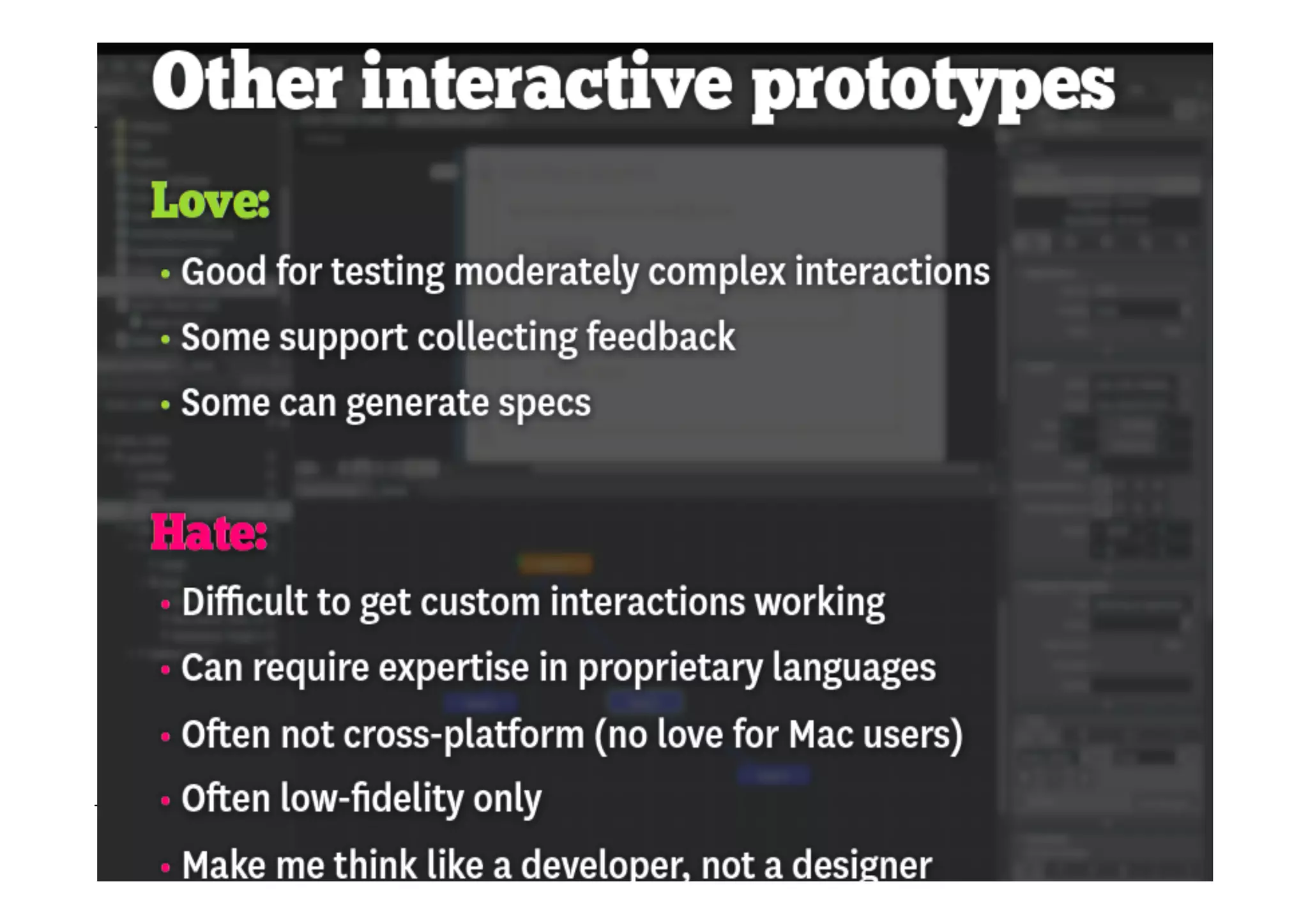
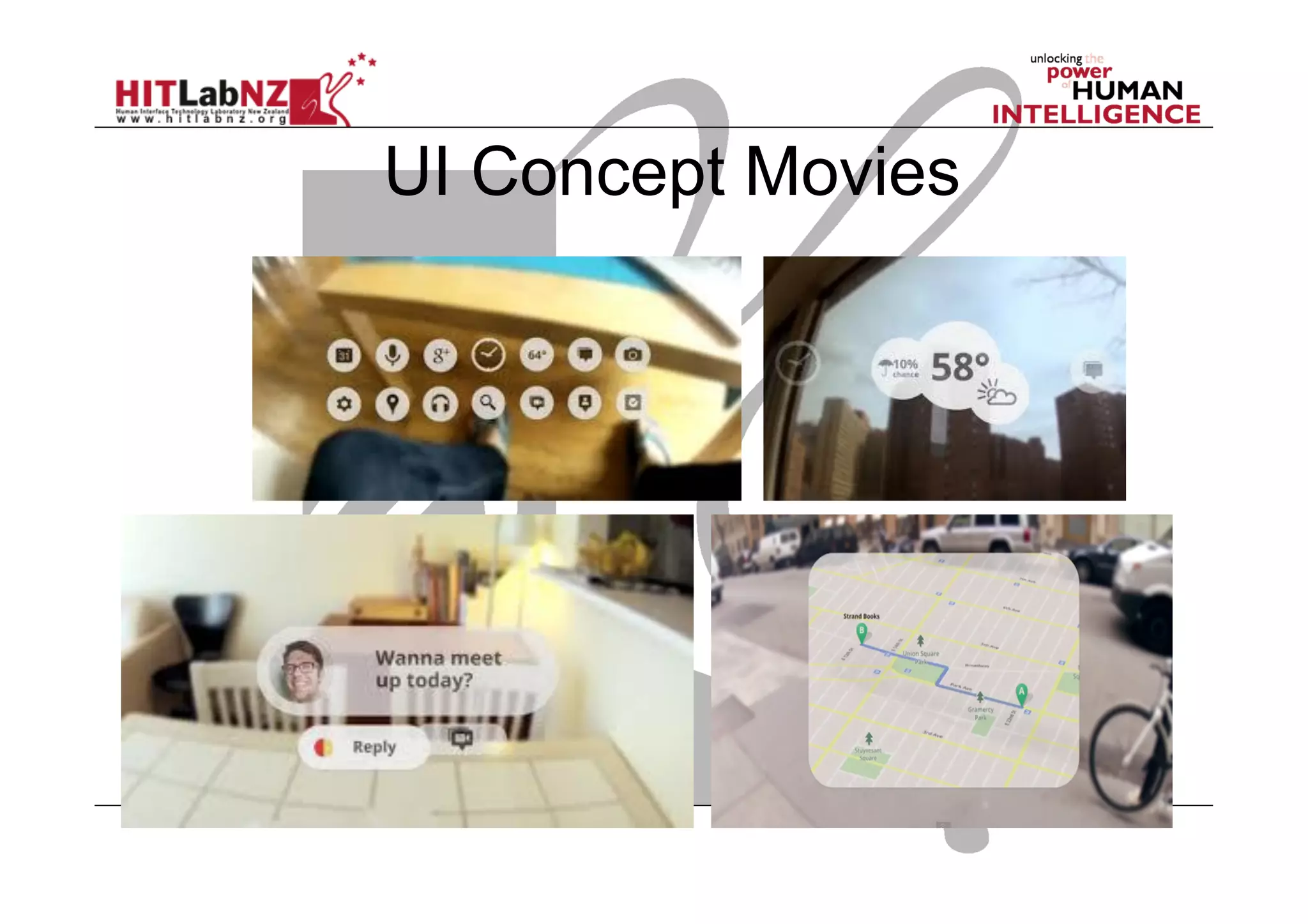
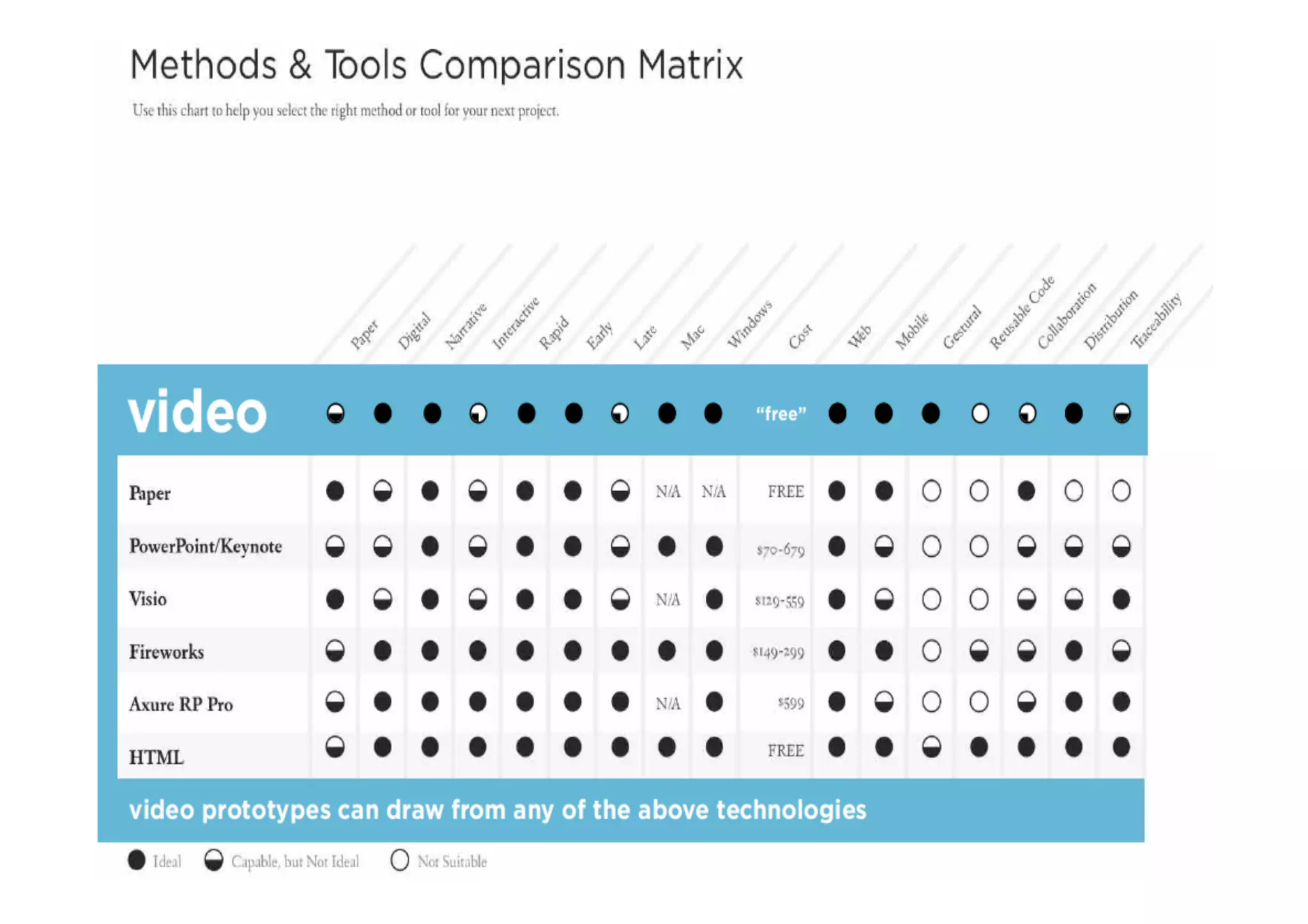
This document outlines the fundamentals of prototyping in interaction design, detailing key processes such as elaboration and reduction, which help in generating and refining design solutions. It discusses the significance of sketching and various prototyping tools, emphasizing their roles in user engagement, idea testing, and enhancing usability. The document also highlights the benefits, methods, and types of prototypes—including low and high fidelity, along with practical tips for effective design and development.