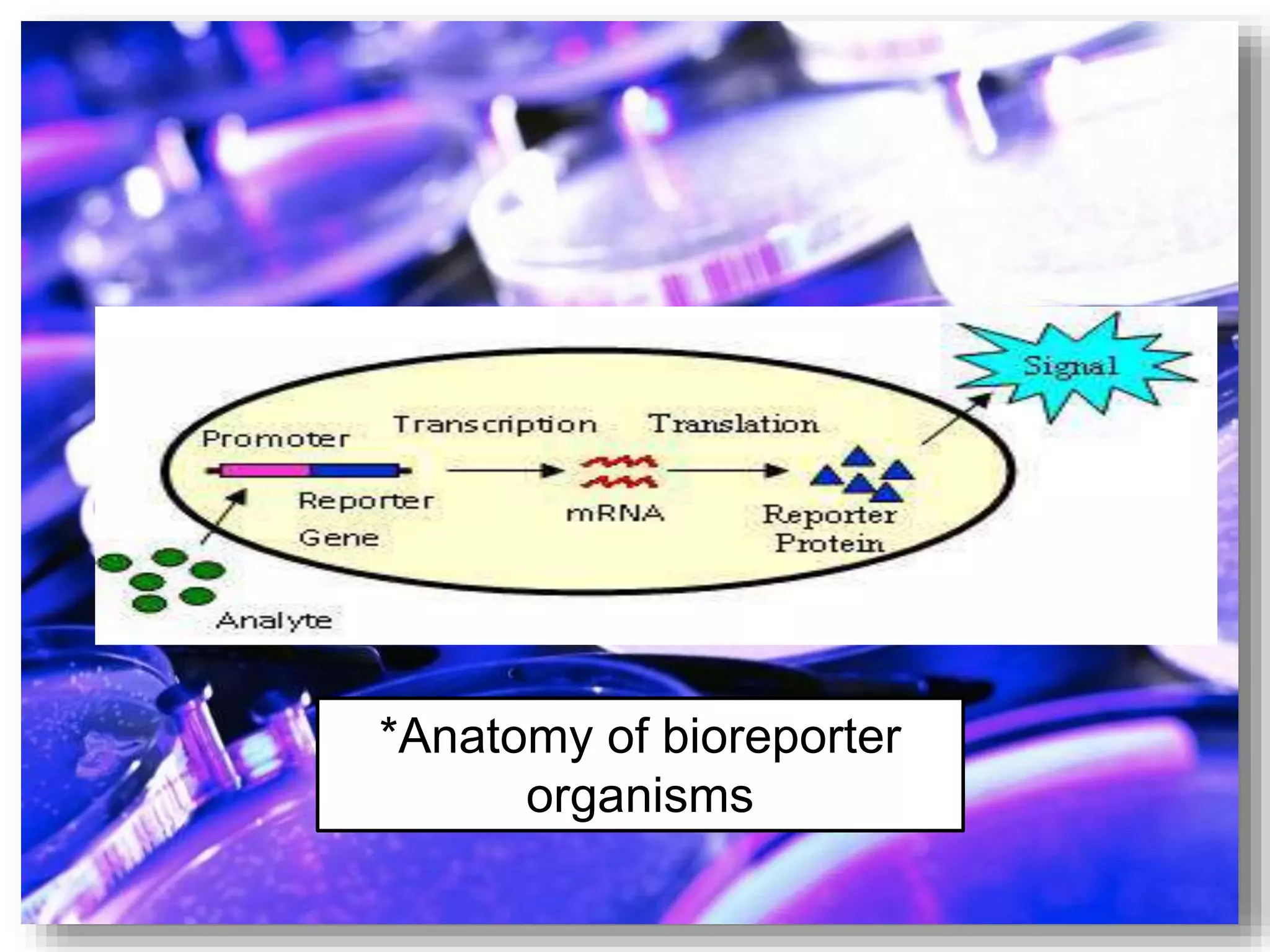
Microbes have many beneficial applications in various industries. They are used to produce foods like yogurt and cheeses through fermentation. In medicine, microbes produce antibiotics and are used in vaccines. Biotechnology uses microbes to produce insulin and enzymes. Agriculture uses bacteria like Bacillus thuringiensis to naturally produce pesticides in genetically engineered crops. The document also discusses how algae, archaea, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses each have distinct characteristics and how they are classified. Environmental applications include using bioreporter microbes that glow in the presence of pollutants to detect contamination.