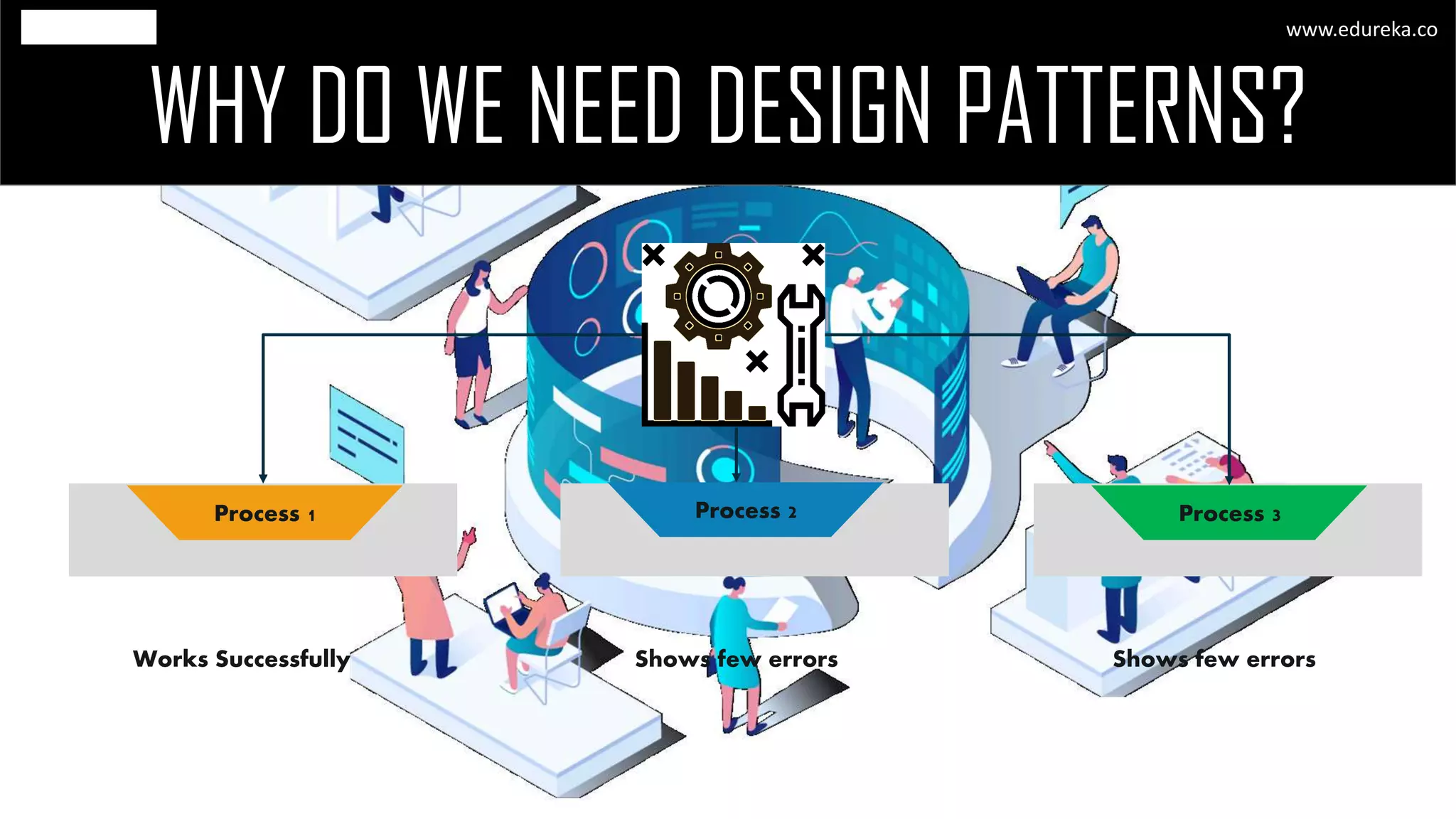
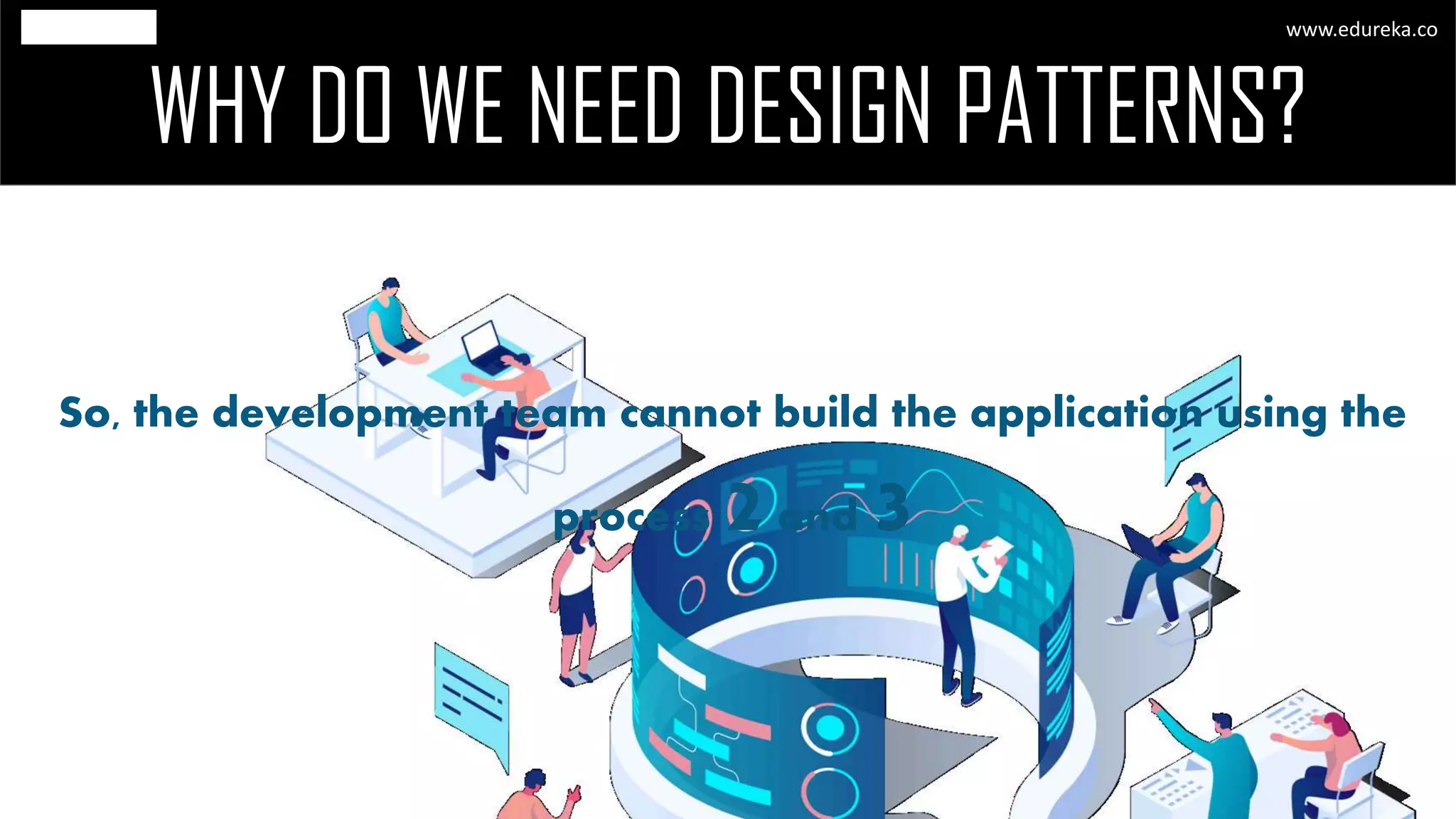
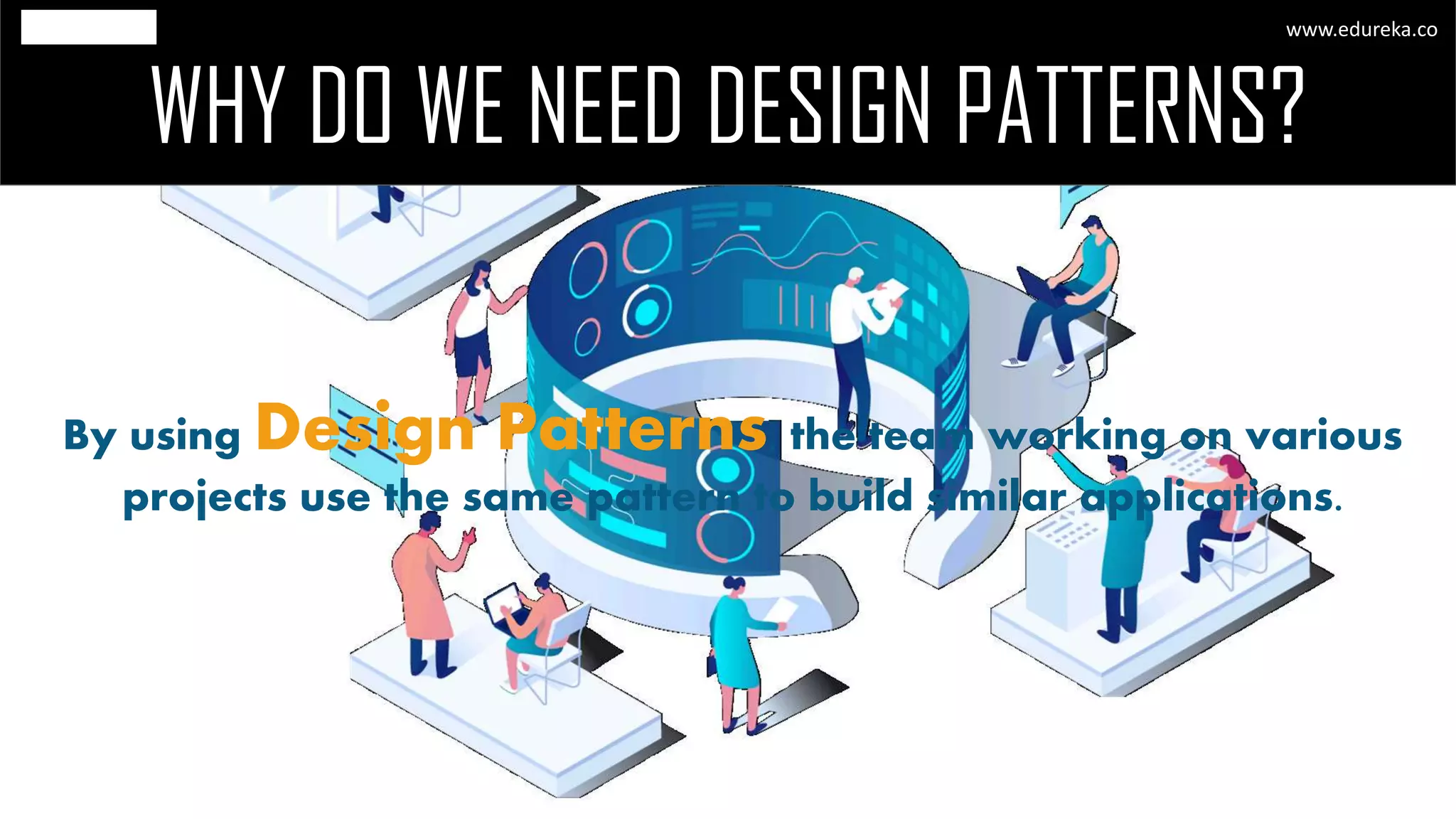
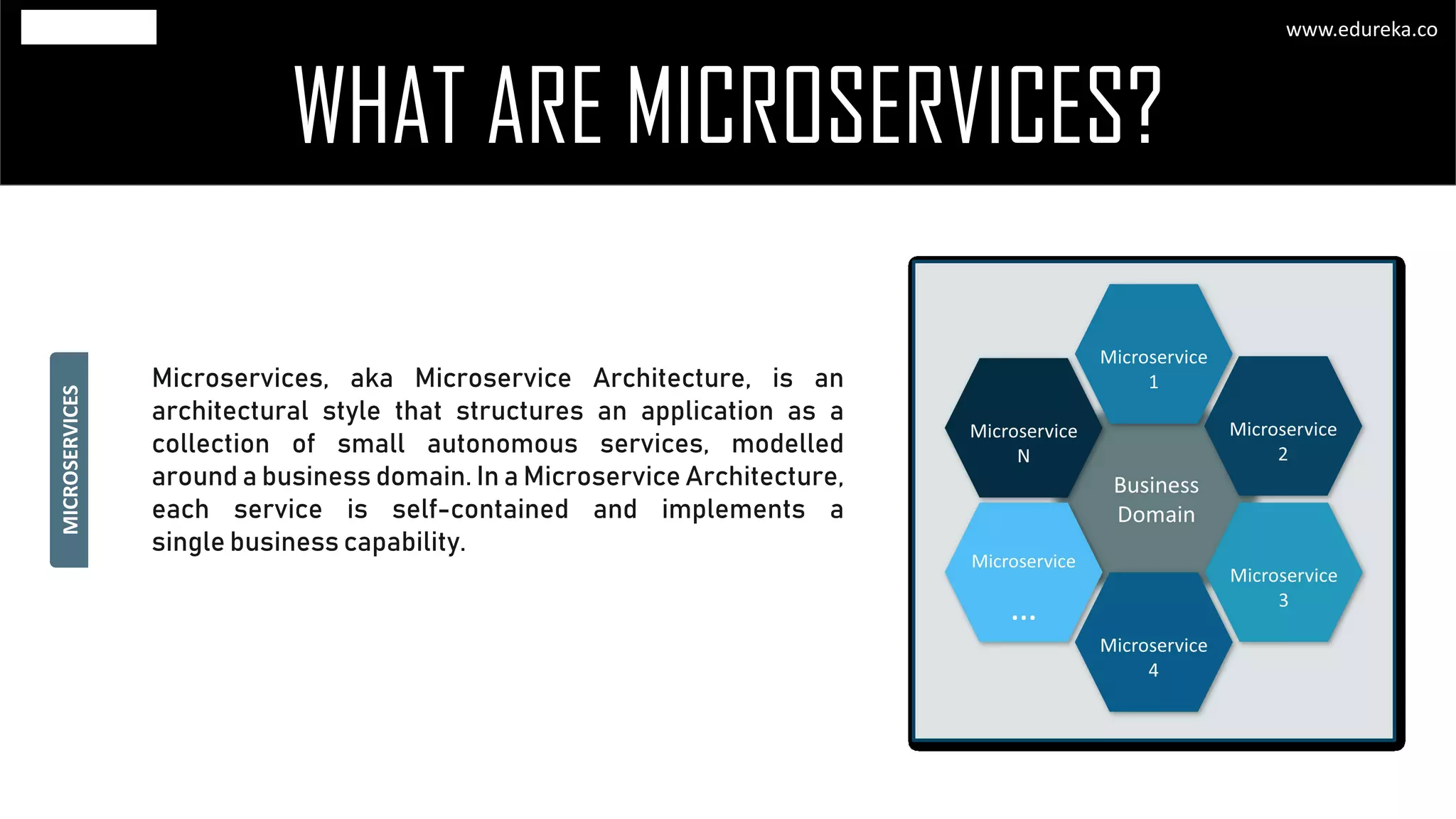
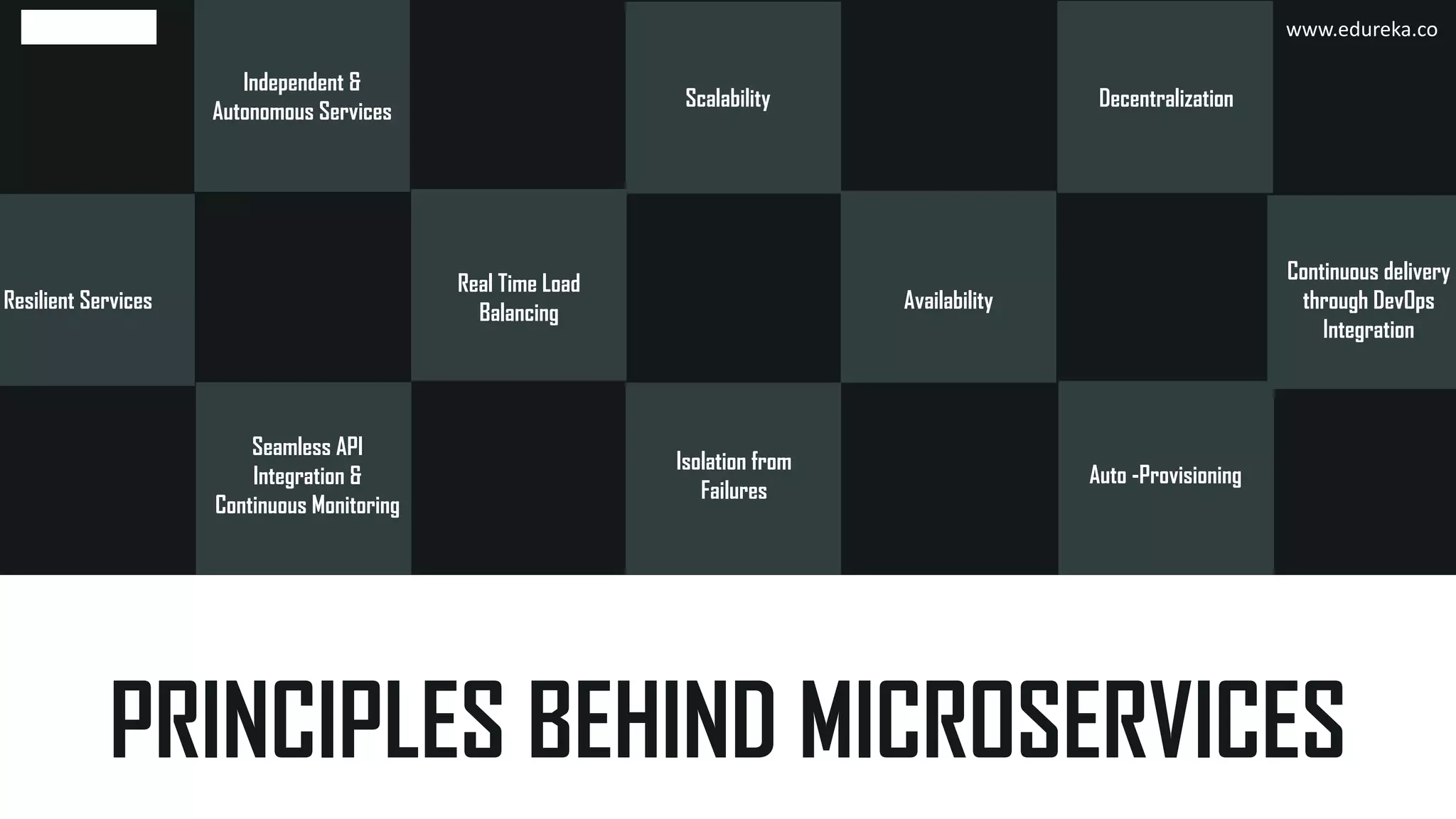
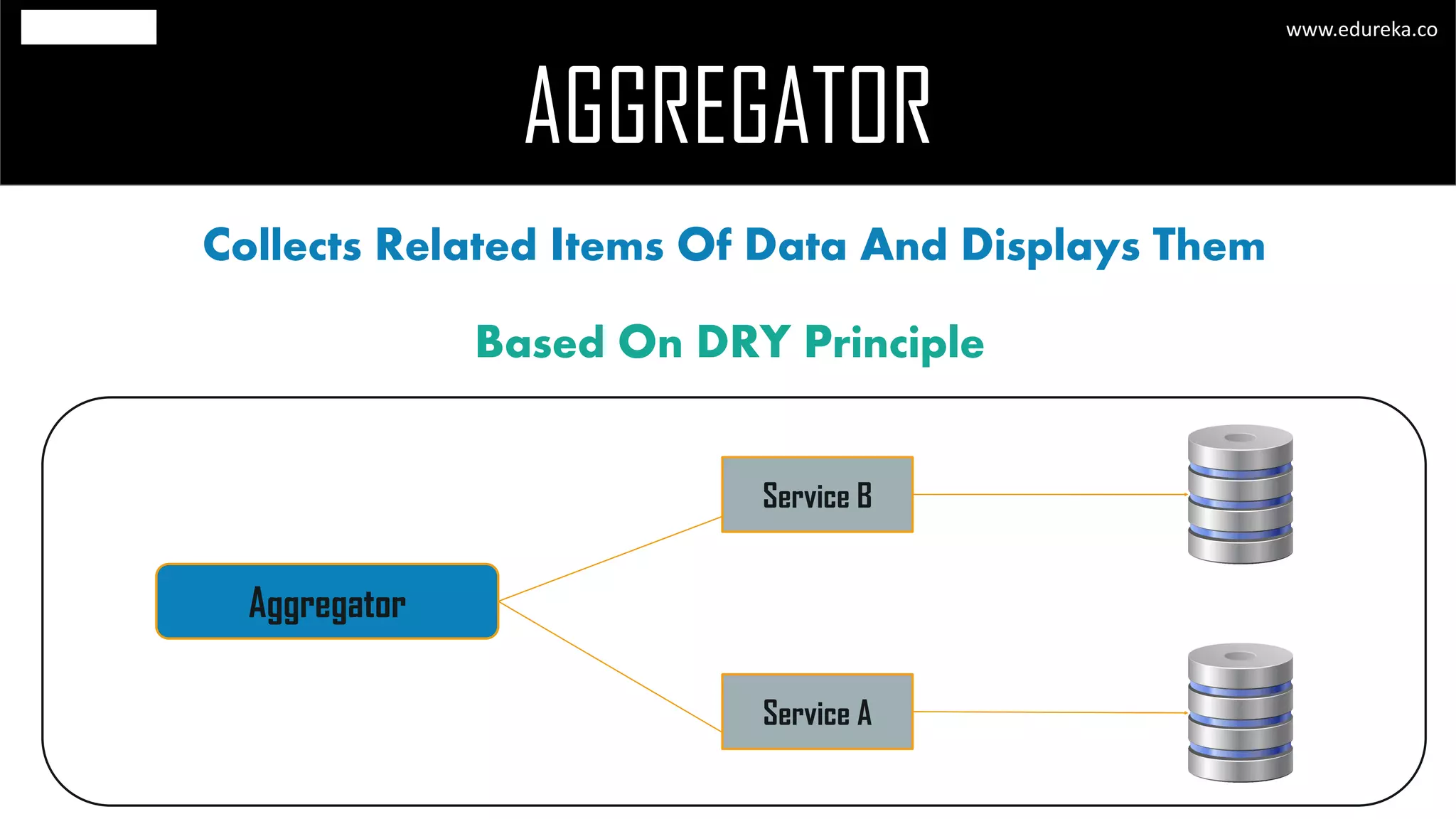
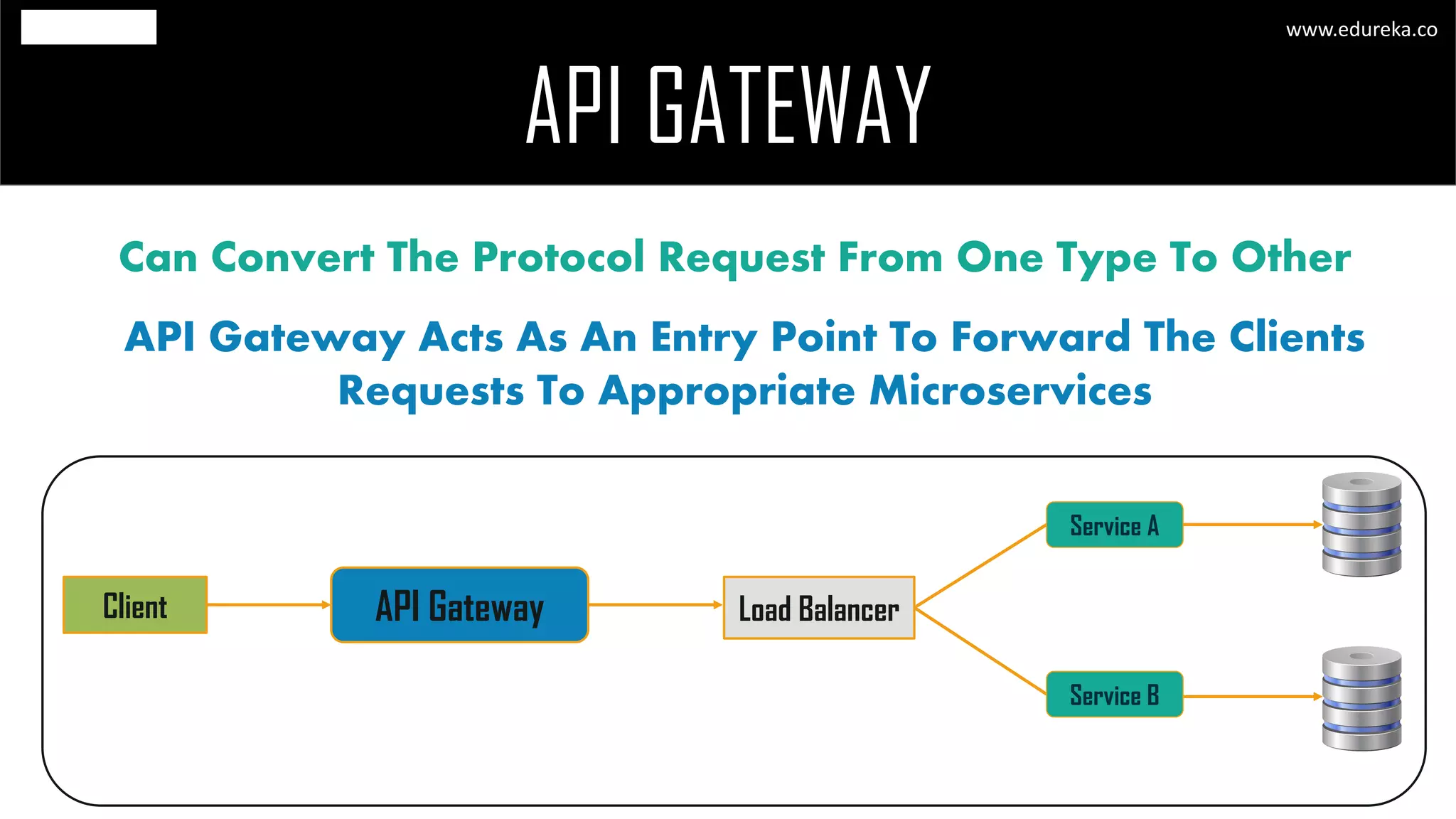
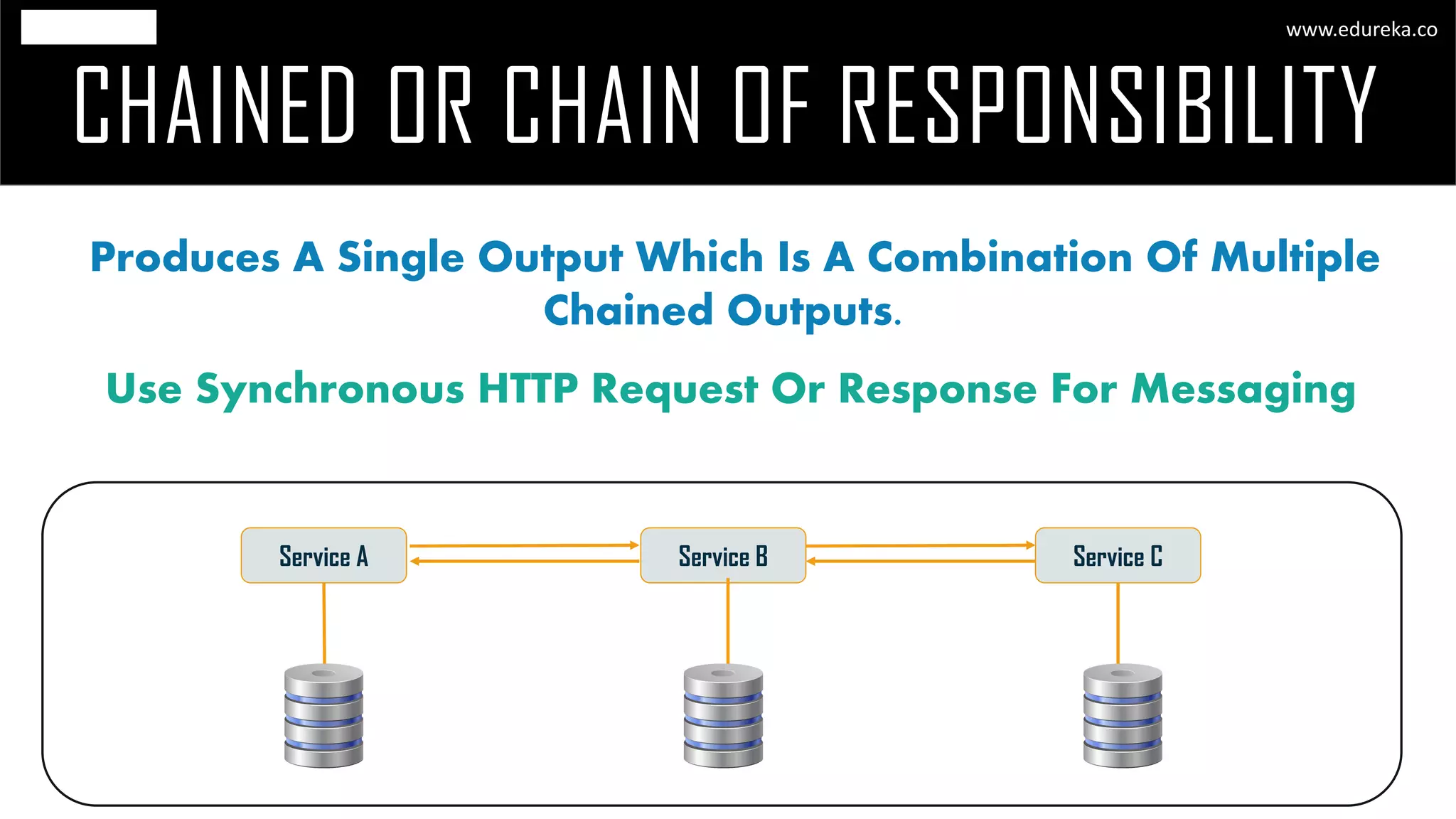
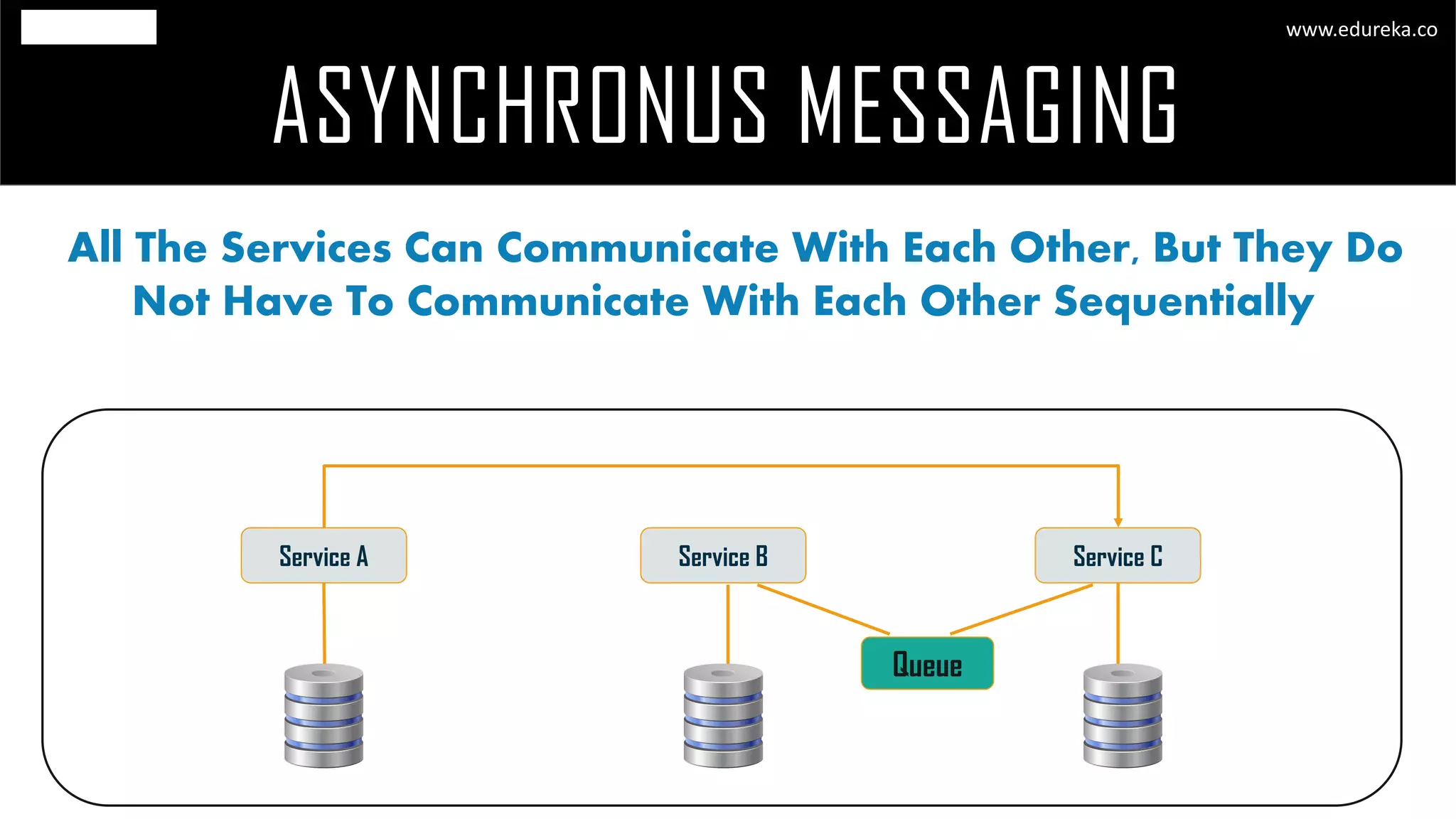
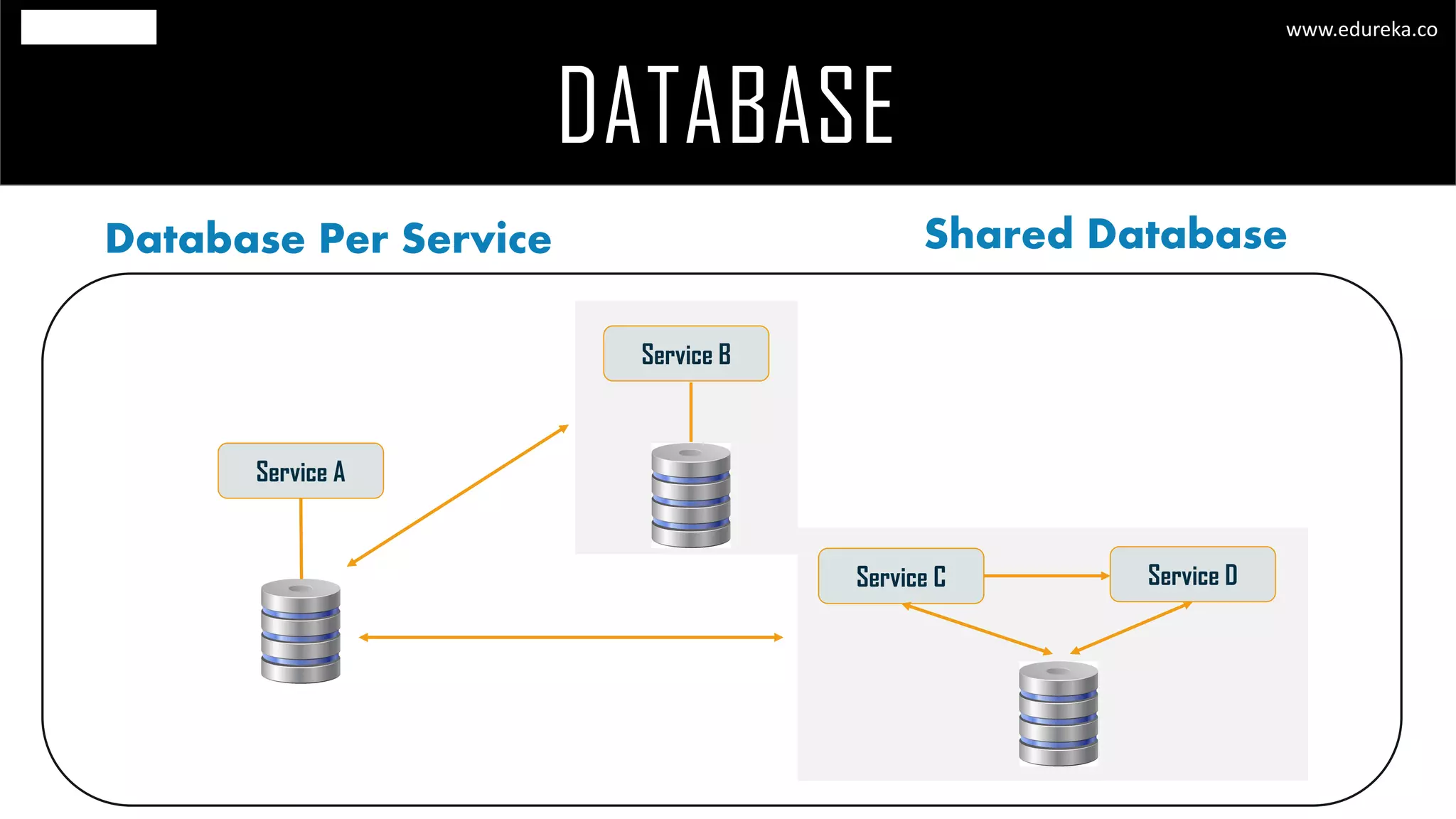
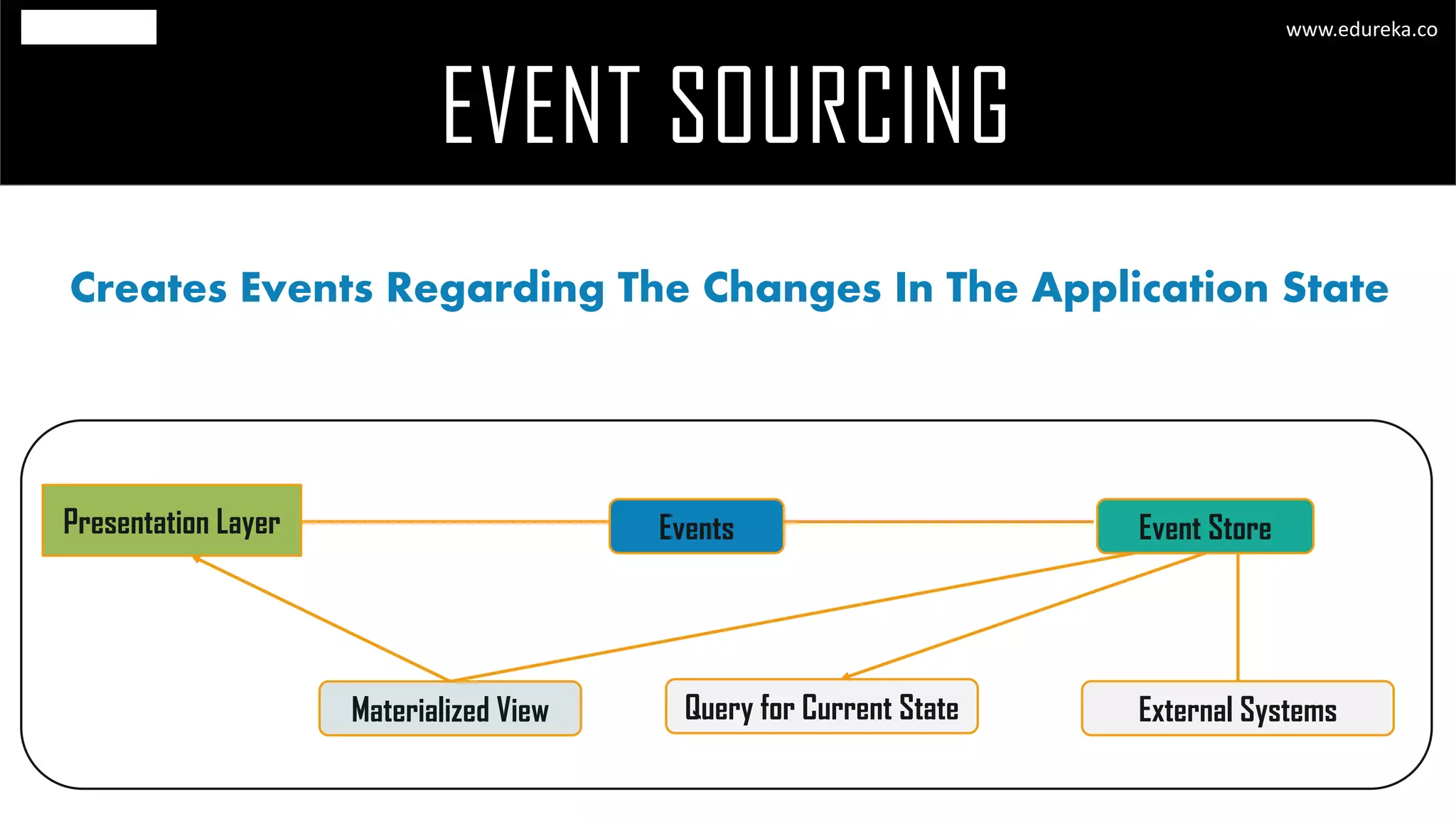
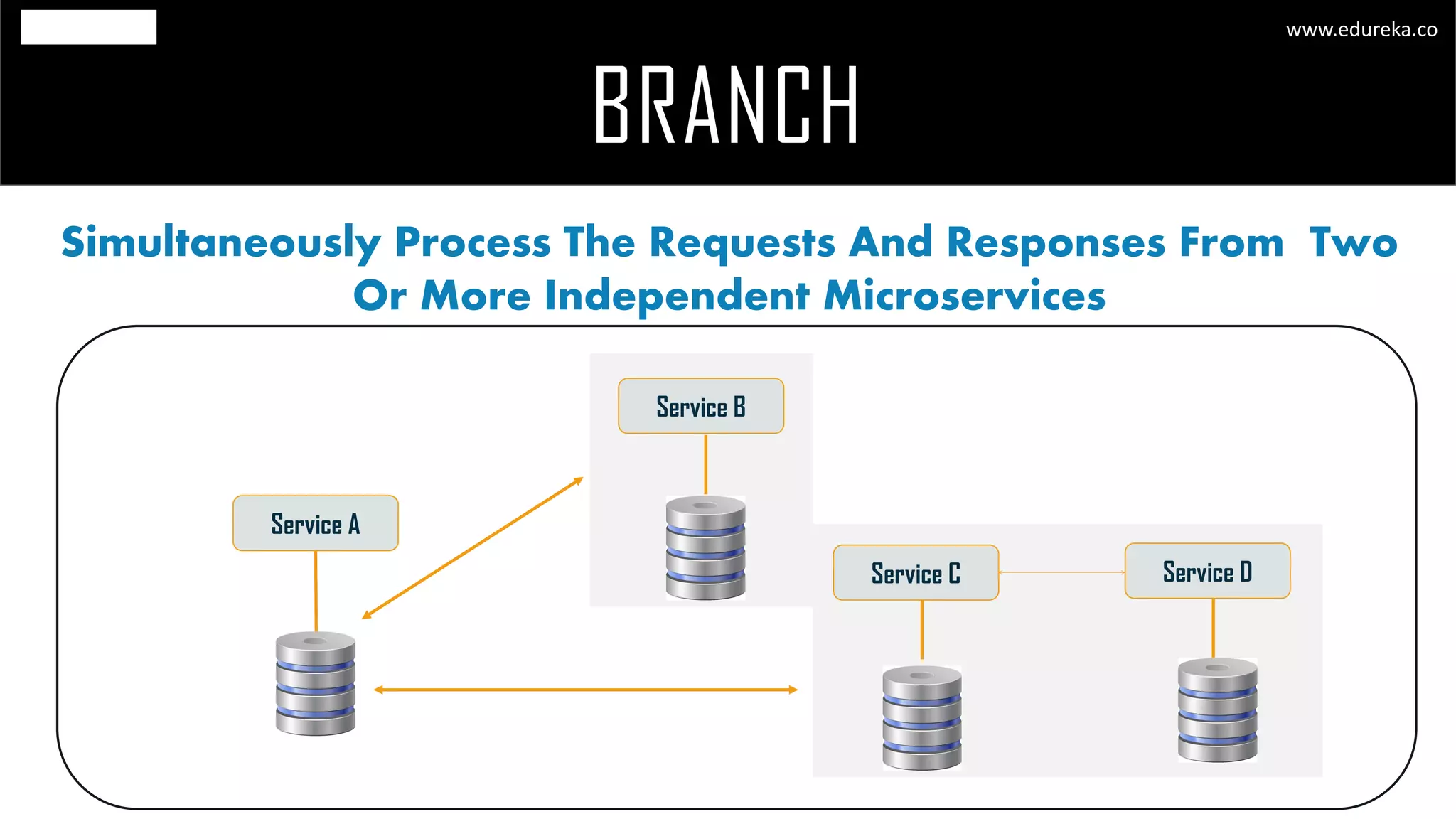
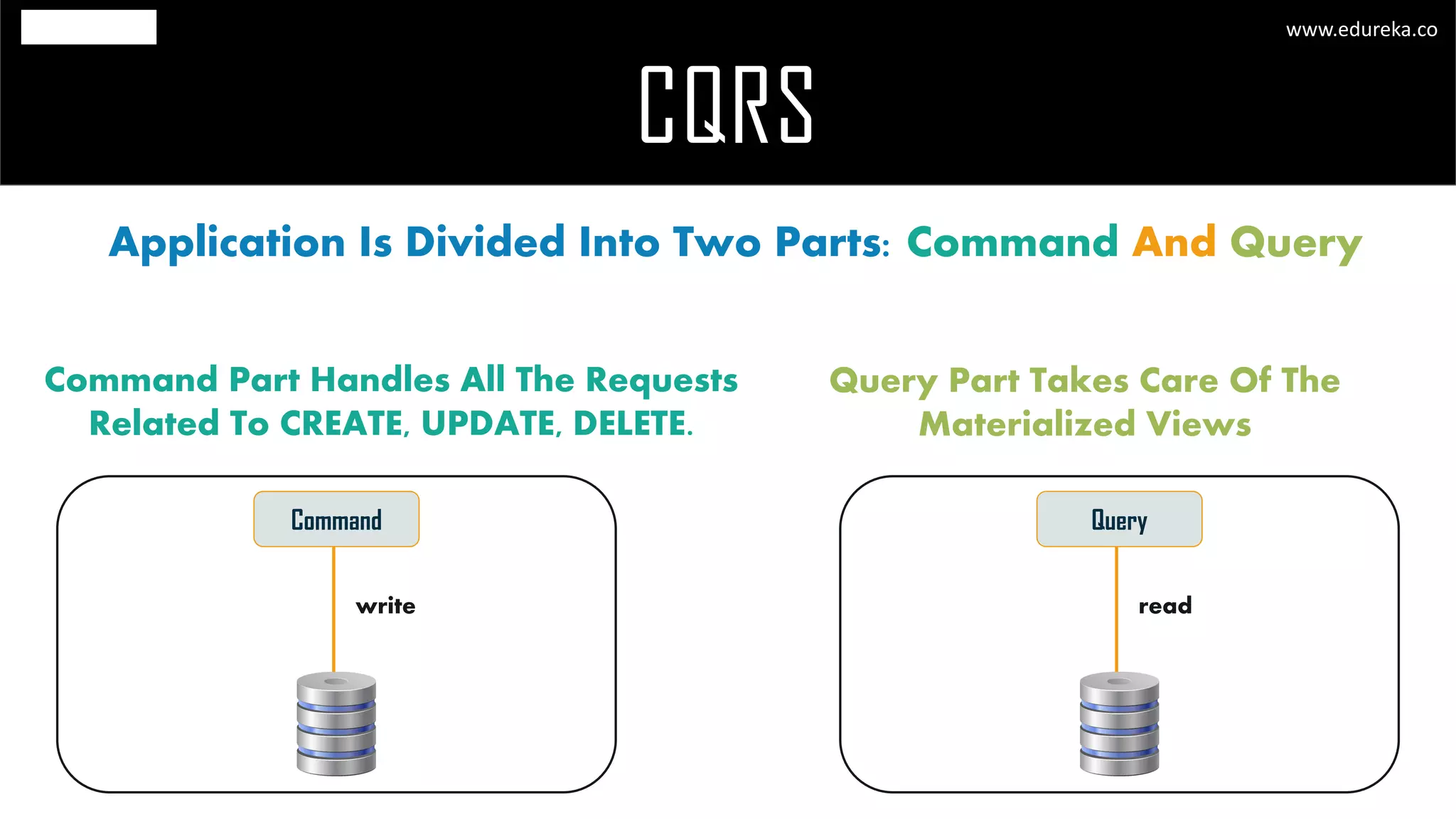
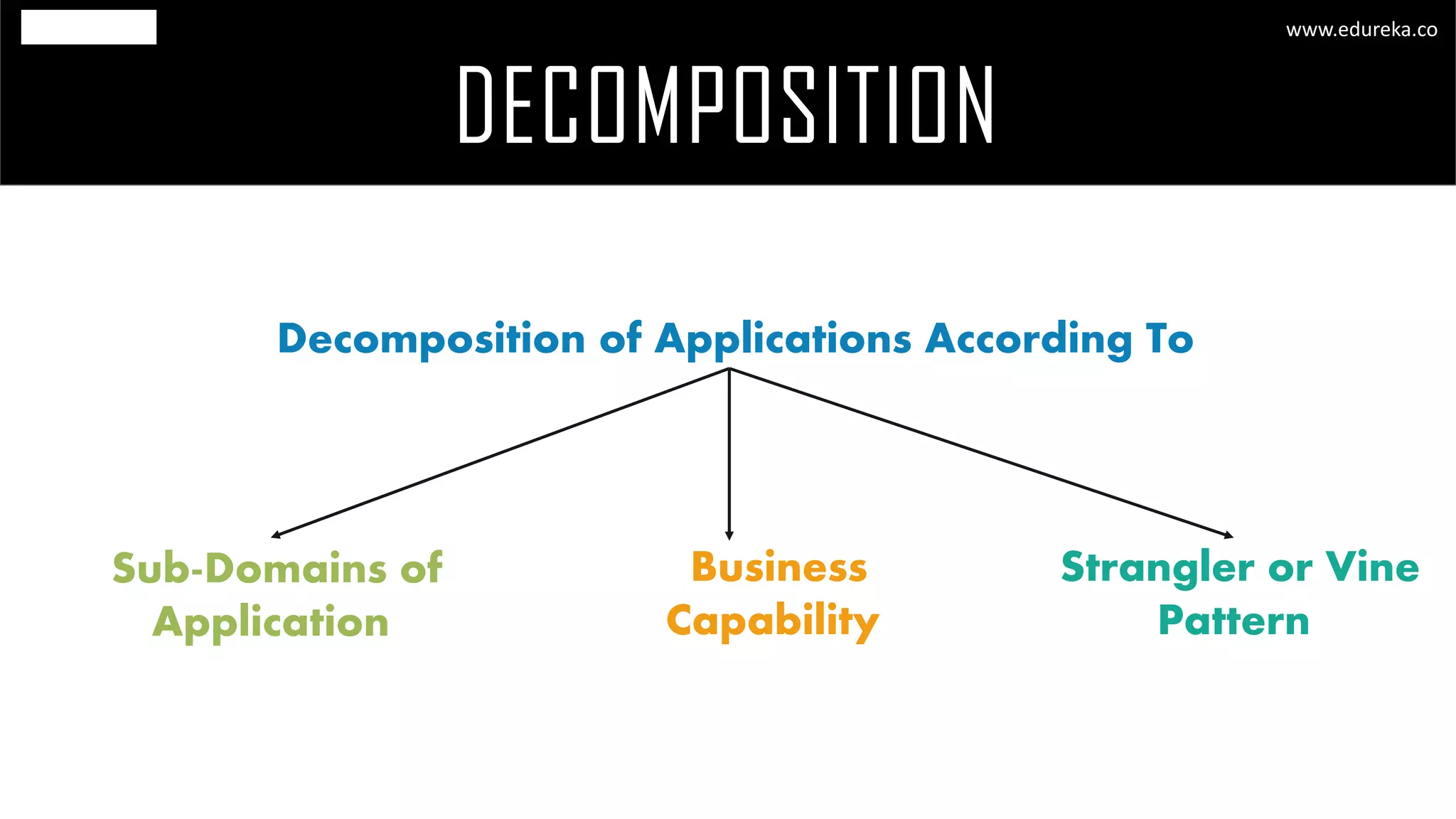
The document discusses the principles and concepts of microservices, defining them as an architectural style that uses small, autonomous services focused on business capabilities. It outlines the importance of design patterns in microservices, presenting various patterns such as aggregator, API gateway, and circuit breaker, which help in structuring and managing these services effectively. Additionally, it highlights key principles such as decentralization, scalability, and continuous monitoring, which are vital for successful microservice implementations.