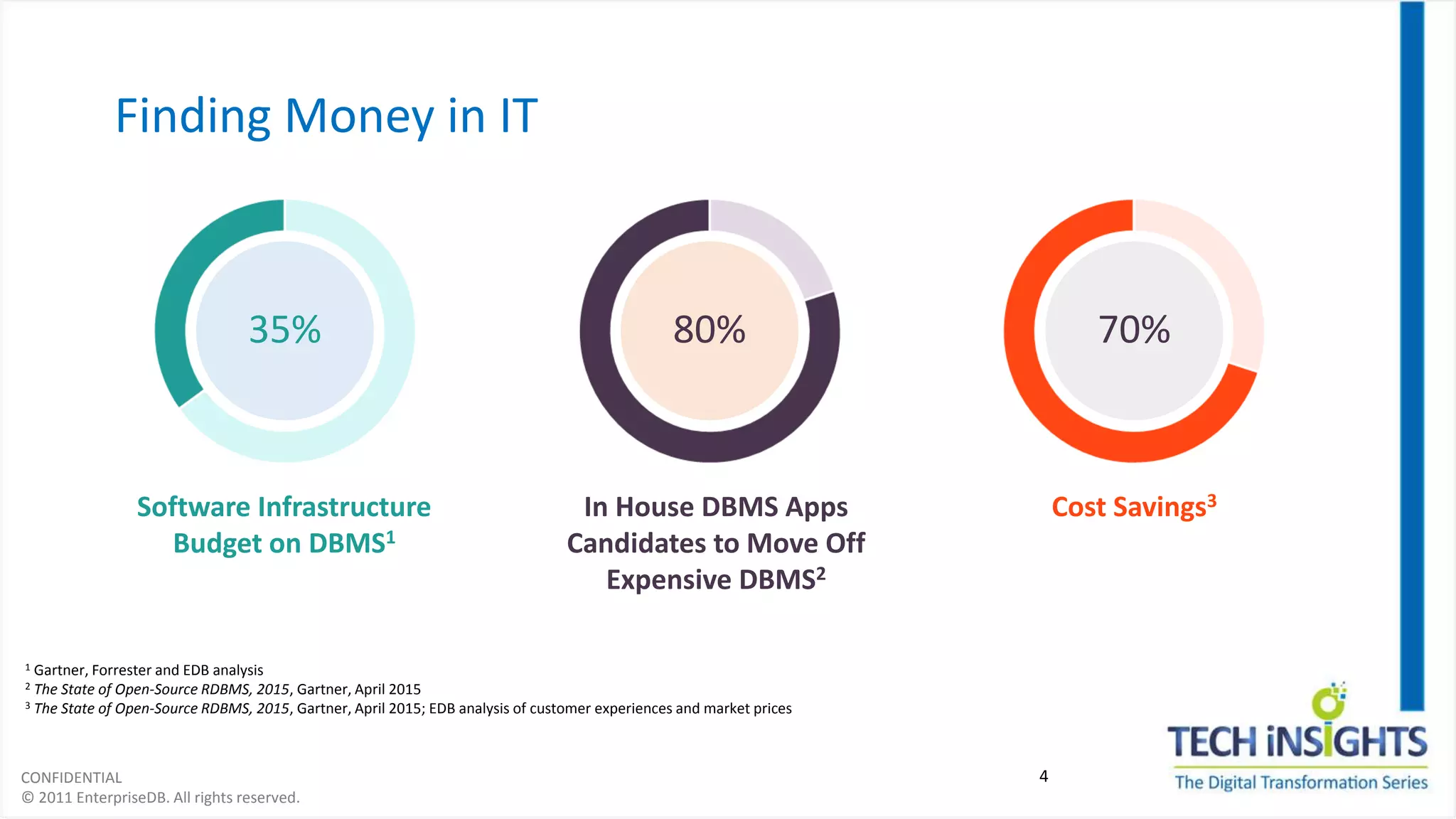
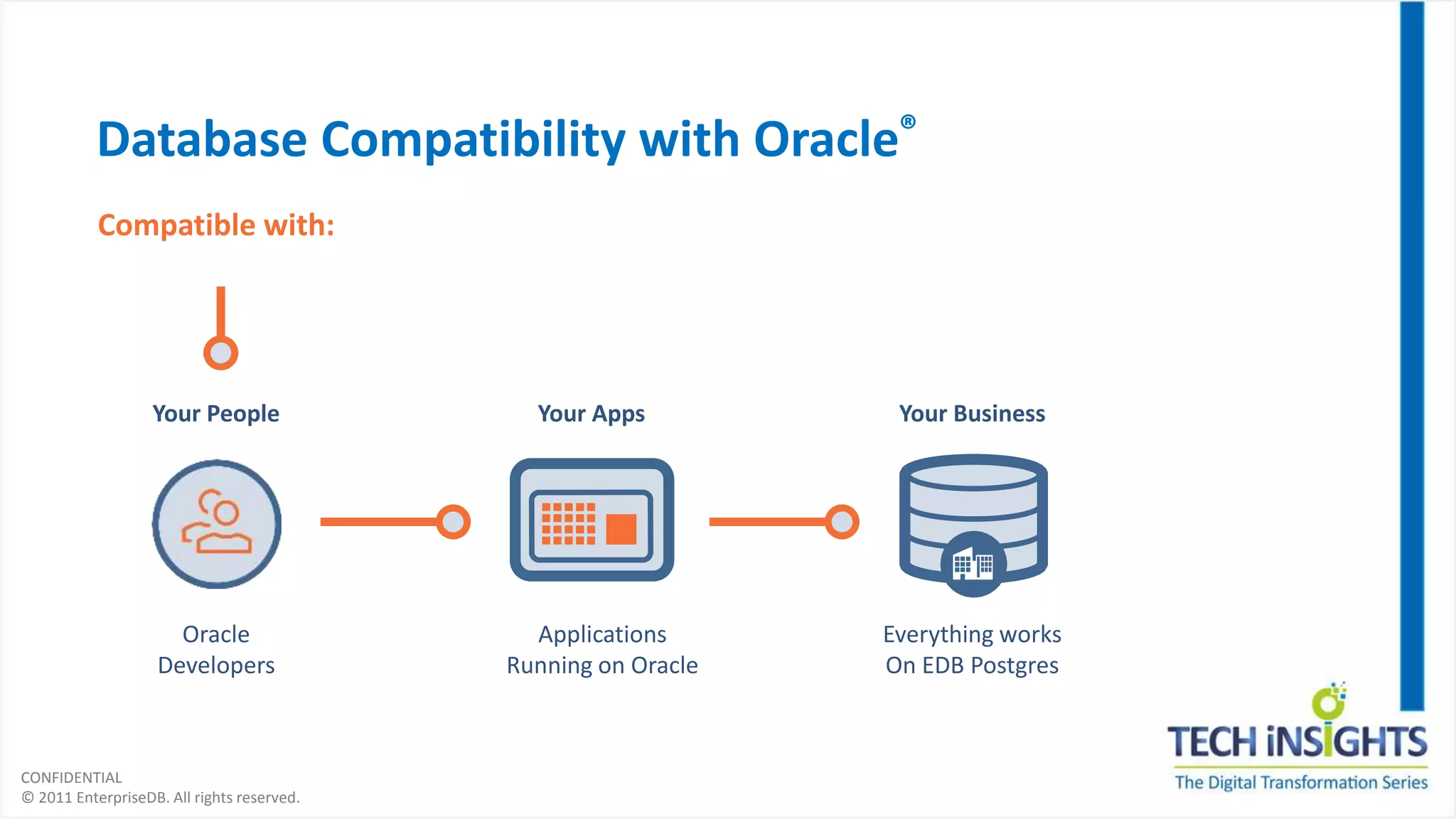
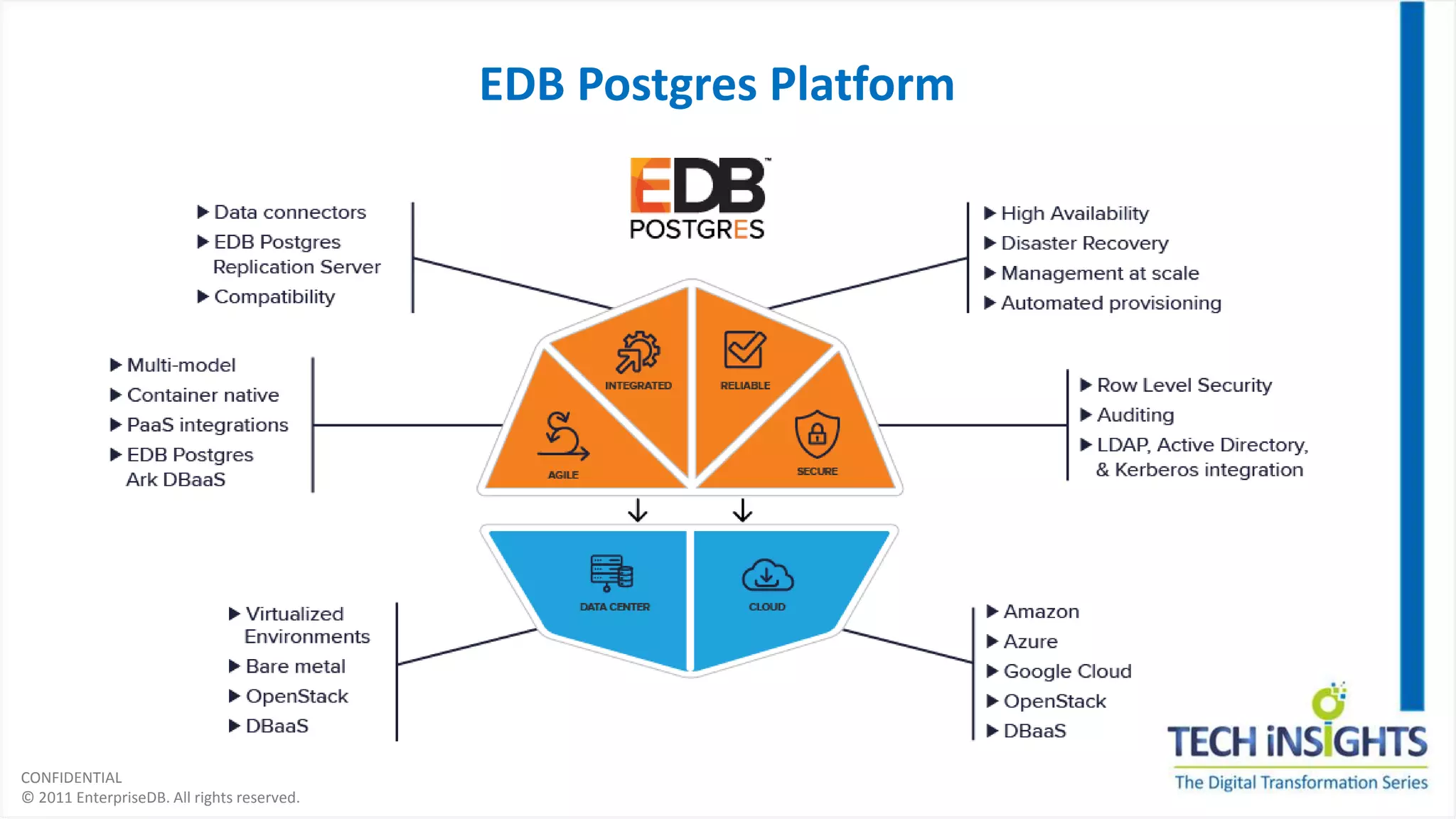
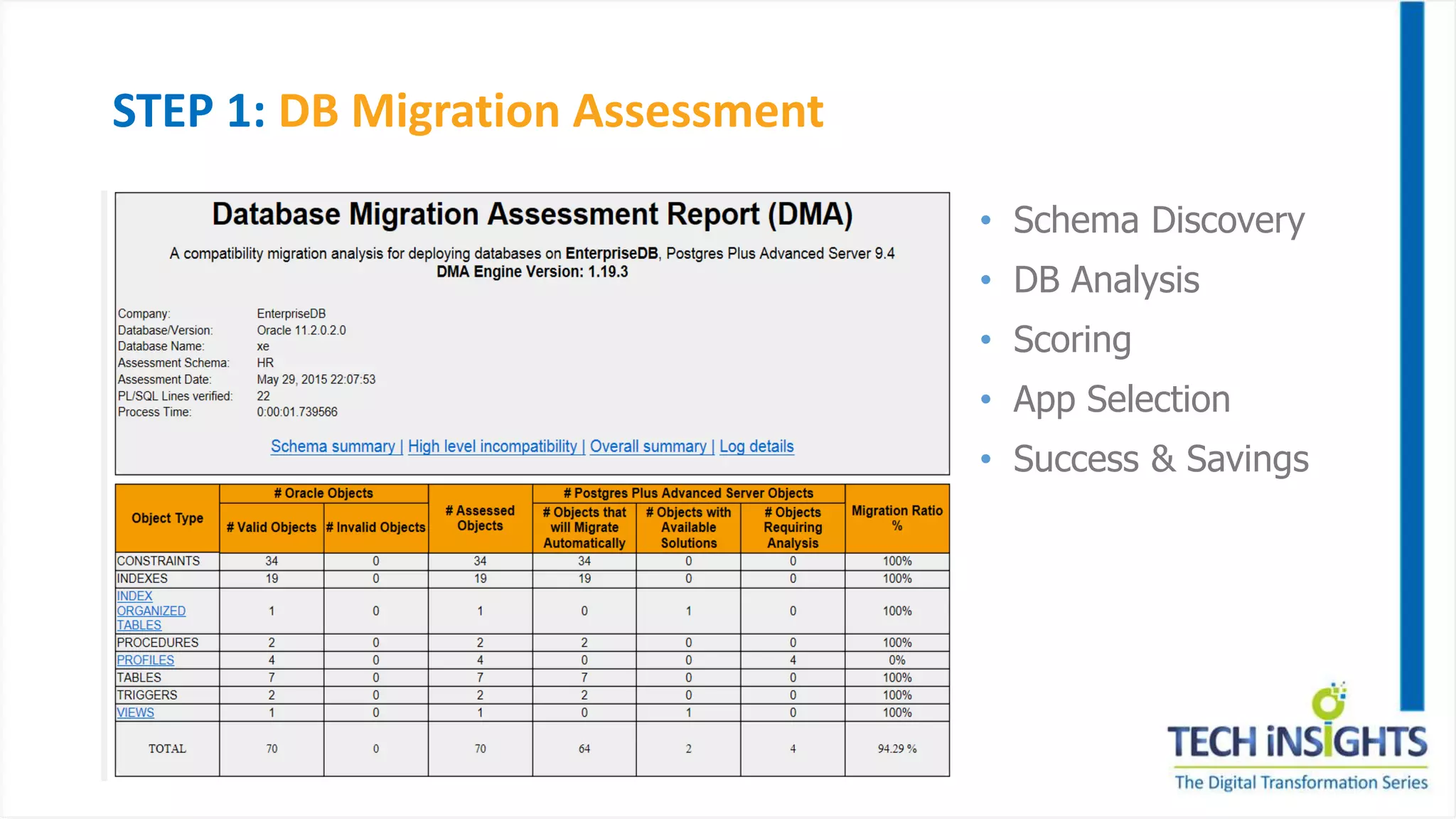
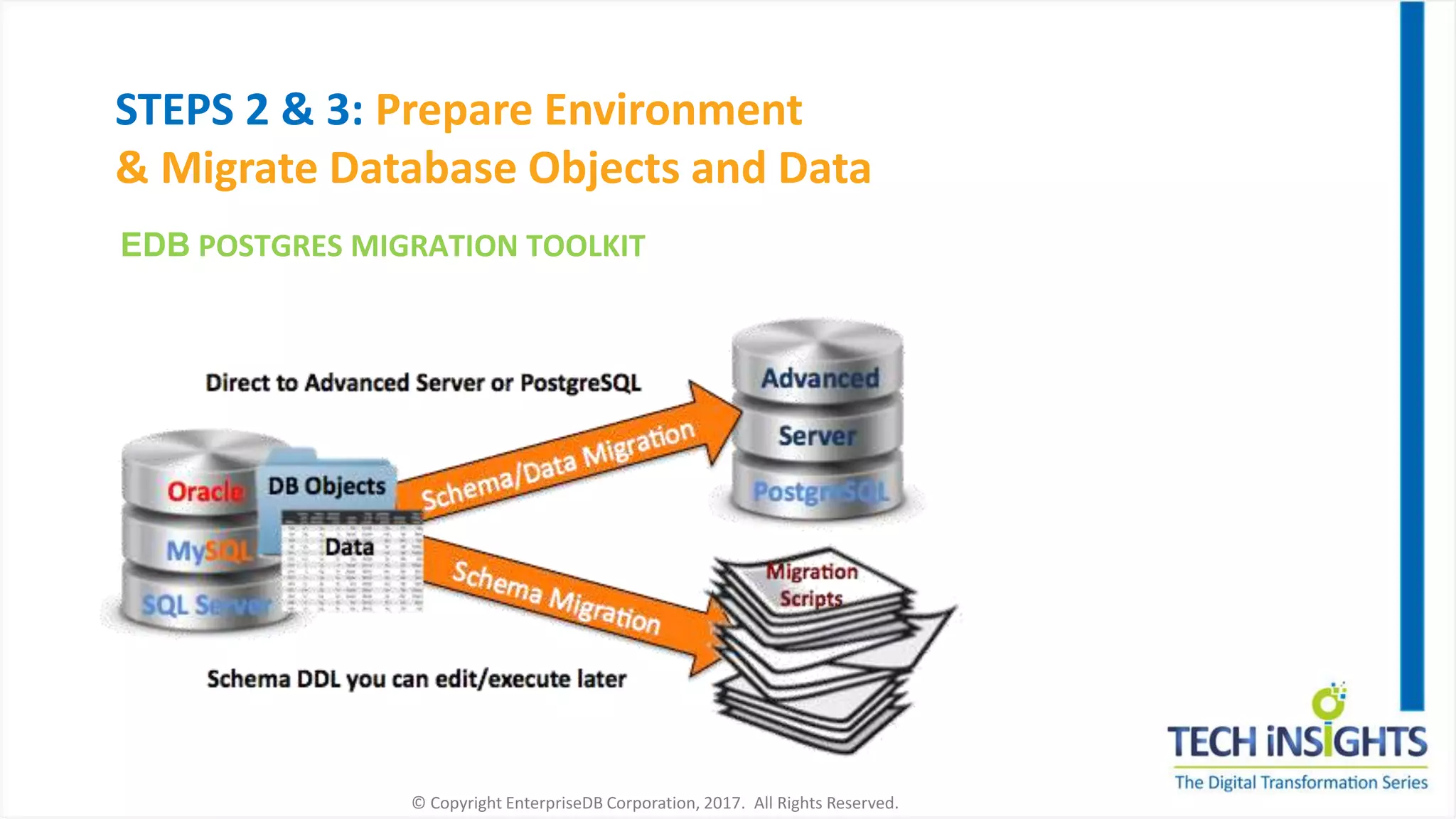
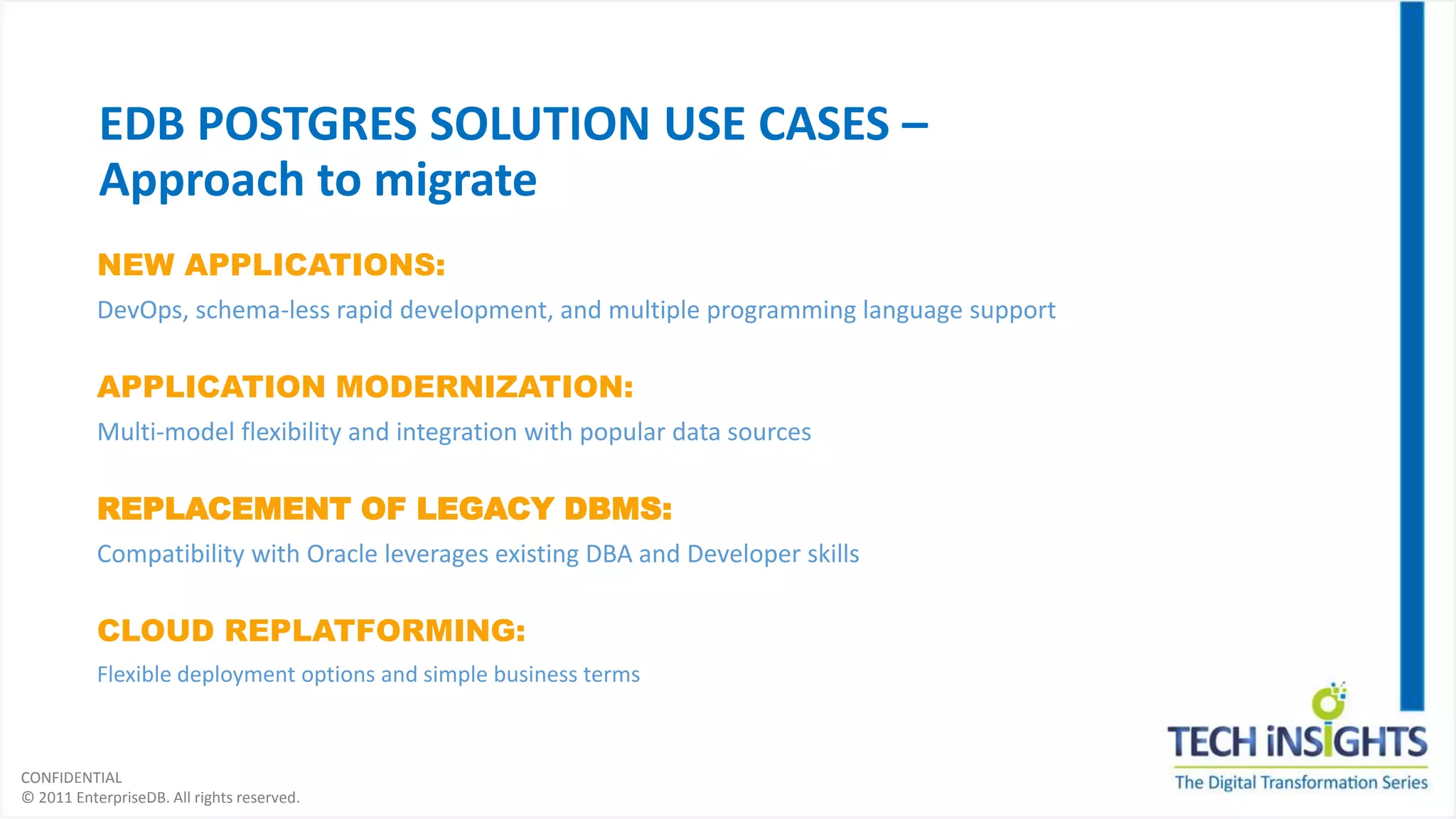
This document discusses migrating from a legacy database to Postgres. It notes that 35% of software budgets are spent on database management systems, 80% of in-house applications are candidates to move off expensive databases, and migrating can result in 70% cost savings. The advantages of Postgres include database compatibility with Oracle, proven performance, enterprise-class support, and being cloud ready. The steps to migrate include assessing the database, preparing the environment, migrating data and objects, porting applications, testing, integrating, and rolling out to production. Migrating allows leveraging existing skills while gaining benefits like agility, cost savings, and flexibility.